EX9200 Ethernet Switch Datasheet
Download DatasheetProduct Overview
The Juniper Networks EX9200 line of modular Ethernet switches provides a programmable, flexible, and scalable core for delivering mission critical applications in both campus and data center environments, reducing cost and complexity while offering carrier-class reliability. High port densities enable the EX9200 to consolidate and aggregate network layers, dramatically simplifying campus and data center architectures while reducing total cost of ownership (TCO) and lowering power, space and cooling requirements.

Product Description
The EX9200 line of programmable, flexible and scalable modular Ethernet core switches simplifies the deployment of cloud applications, virtualized servers and rich media collaboration tools across campus and data center environments.
The EX9200 is also a key component of Juniper’s AI-Driven Enterprise. The switch decouples the overlay network from the underlay with technologies such as Ethernet VPN (EVPN) and Virtual Extensible LAN (VXLAN), addressing the needs of the modern enterprise network by allowing network administrators to create logical L2 networks over different L3 networks.
The EX9200 is based on Juniper One custom silicon, an ASIC designed by Juniper which provides a programmable Packet Forwarding Engine (PFE) and allows for native support of networking protocols such as virtualization using MPLS over IP and overlay network protocols. ASIC micro code changes delivered through updates to Juniper Networks Junos® operating system provide investment protection by allowing existing hardware to support new or future networking protocols.
The programmability of the EX9200 allows it to support Junos OS-based automation along with the Junos SDK, which enables integration with Puppet and other automation applications. The EX9200’s network programmability also enables integration with leading orchestration applications such as OpenStack.
Three EX9200 chassis options are available, providing full deployment flexibility:
- EX9204 Ethernet Switch, a 4-slot, 5 U chassis that supports up to three line cards
- EX9208 Ethernet Switch, an 8-slot, 8 U chassis that supports up to six line cards
- EX9214 Ethernet Switch, a 14-slot, 16 U chassis that supports up to 12 line cards
All three EX9200 chassis can accommodate any combination of the following EX9200 Ethernet line cards:
- EX9200-15C, a 15-port 100GbE QSFP28 or 40GbE QSFP+ line card
- EX9200-12QS, a multi-rate 12-port 40GbE QSFP+ or 4-port 100GbE QSFP28 line card
- EX9200-40XS, a 40-port 10GbE SFP+ line card that supports MACsec
- EX9200-32XS*, a 32-port 10GbE small form factor pluggable transceiver plus (SFP+) line card
- EX9200-40F*-M, a 40-port 100FX/1000BASE-X line card supporting MACsec
- EX9200-40F*, a 40-port 100FX/1000BASE-X small form-factor pluggable transceiver (SFP) line card
- EX9200-40T*, a 40-port 10/100/1000BASE-T RJ-45 line card
- EX9200-6QS*, a 6-port 40GbE QSFP+ or 24-port 10GbE SFP+ combo line card
- EX9200-2C-8XS*, a 2-port 100GbE C form-factor pluggable (CFP) + 8-port 10GbE SFP+ line card
The EX9200 chassis can also accommodate a flexible Modular Port Concentrator (MPC) line card, the EX9200-MPC, that can accept any combination of three modular interface cards (MICs):
- EX9200-10XS-MIC, a 10-port 10GBASE-X (half-slot) MIC
- EX9200-20F-MIC, a 20-port GBASE-X (half-slot) MIC
- EX9200-40T-MIC, a 40-port 10/100/1000GBASE-T MIC that supports MACsec
Fully configured, a single EX9214 chassis can support up to 480 10GbE ports (all at wire speed), delivering one of the industry’s highest line-rate 10GbE port densities for this class of feature rich and programmable switch. The EX9200 switch fabric is capable of delivering up to 480 Gbps (full duplex) per slot. The pass-through midplane design also supports a future capacity of up to 13.2 Tbps.
* ISSU is only supported on the EX9200-32XS, EX9200-40F, EX9200-40T, EX9200-40F-M, and EX9200-2C-8S, EX9200-6QS, and EX9200-2C-8S | |||
| Feature | EX9204 | EX9208 | EX9214 |
| Architecture | Separate dedicated data, control, and management planes | ||
| Power | Holds up to four power supplies:
Maximum power draw: 2,199 W (DC), 2,421 W (AC) | Holds up to four power supplies:
Maximum power draw: 4,388 W (DC), 4,831 W (AC) | Holds up to four power supplies (two power supplies per power zone; two power zones per system)
Maximum power draw: 9,534 W (DC), 9,318 W (AC) |
| Cooling |
|
|
|
| Weight (fully loaded) | 128.0 lbs (58.1 Kg) | 163.6 lbs (74.2 Kg) | 350.1 lbs (158.8 Kg) |
| Fabric |
|
|
|
| Routing Engine |
| ||
| Operating system | Juniper Networks Junos operating system | ||
| High availability | Hardware designed for continuous operation:
| ||
| Layer 2 features |
| ||
| * Supported in hardware on EX9200-15C and will be enabled on software in a future release | |||
| Feature | EX9204 | EX9208 | EX9214 |
| Layer 3 features |
| ||
| Hardware tunneling |
| ||
| Multicast |
| ||
| Firewall filters | Ingress and egress L2-L4 access control lists (ACLs):
Control plane denial-of-service (DoS) protection | ||
| Quality of service (QoS) |
| ||
| Virtualization |
| ||
| Management |
| ||
Architecture and Key Components
The EX9200 campus and data center core Ethernet switches share a number of architectural elements. The Routing Engines employed by these switches run Junos OS, which processes all Layer 2 and Layer 3 protocols, while the Switch Fabric modules manage the chassis and provide switching functionality for data traffic coming from line cards.
The EX9200 line cards, which are common across all EX9200 platforms, include Packet Forwarding Engines (PFEs) that process network traffic, as well as a line-card processor that provides scalable local control.
In the data center, the EX9200 architecture is designed for very large deployments, with no head-of-line blocking, a single tier low latency switch fabric, efficient multicast replication handling, and deep buffering to ensure performance at scale. The EX9200 chassis midplane distributes the control and management signals over independent paths to the various system components and distributes power throughout the system. Data plane signals pass directly from the EX9200 line cards to the EX9200 Switch Fabric modules via a unique pass-through connector system that provides unparalleled signal quality for future generations of fabric ASICs.
To maintain uninterrupted operation, the EX9200’s fan trays cool the line cards, Routing Engine, and Switch Fabric modules with redundant, variable speed fans. In addition, the EX9200 power supplies convert building power to the internal voltage required by the system.
All EX9200 components are hot-swappable, and all central functions are available in redundant configurations, providing high operational availability by allowing continuous system operation during maintenance or repairs.
EX9200 Campus Deployment Options
The EX9200 is designed primarily for the following two use cases:
- EVPN multihoming* or MC-LAG**: A pair of interconnected EX9200 switches can be deployed to provide EVPN multihoming (ESI-LAG) or multichassis link aggregation (MC-LAG) in a collapsed core/distribution configuration. This eliminates the need for Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) across the campus network by providing multihoming capabilities from the access to the distribution layer, while the distribution to the core layer is an L3 IP fabric. EVPN multihoming also supports horizontal scaling with more than two devices in the distribution layer and can extend EVPN to the core.
- Campus fabric*: The AI-Driven Enterprise architecture decouples the overlay network from the underlay with technologies such as EVPN and VXLAN, addressing the needs of the modern enterprise network by allowing network administrators to create logical L2 networks over different L3 networks. Juniper supports various EVPN-VXLAN-based campus fabric architectures, including:
- Campus fabric core-distribution
- Campus fabric IP Clos
Campus fabric architectures let you manage your campus and data center as a single IP fabric, with over-the-top (OTT) policy and control provided by Juniper. Any number of switches can be connected in a Clos network or IP fabric; EVPN-VLAN extends the fabric and connects multiple enterprise buildings while VXLAN stretches L2 across the network. An IP Clos network between the distribution and core layers can exist in two modes: centrally routed bridging overlay or edge-routed bridging overlay.
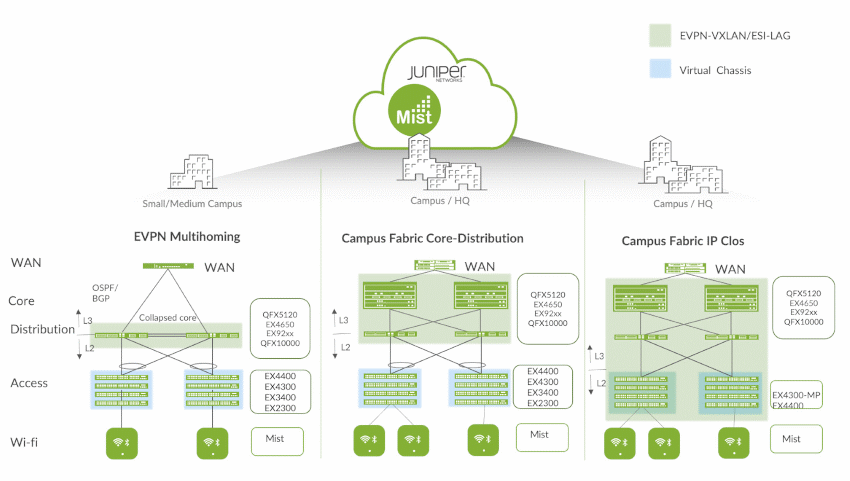
Figure 1: EX9200 EVPN multihoming/MC-LAG and campus fabric deployment options
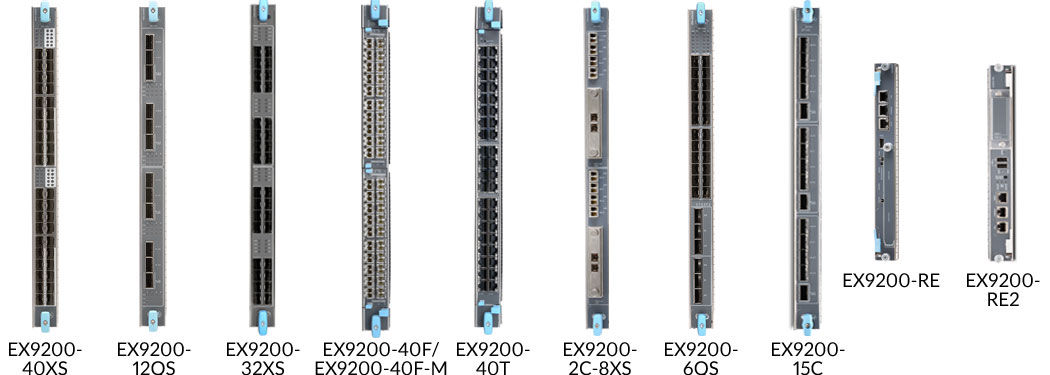
EX9200 Line Cards
The EX9200 line cards support an extensive set of Layer 2 and Layer 3 services that can be deployed in any combination of L2-L3 applications.
Each EX9200 line card is built upon Juniper One custom silicon, which supports a wide range of Layer 2 and Layer 3 Ethernet functionality including 802.1Q VLAN, link aggregation, Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP), L2 to L3 mapping, and port monitoring. Additionally, the line cards support filtering, sampling, load balancing, rate limiting, class of service (CoS), and other key features needed for the deployment of dependable, high-performance Ethernet infrastructure.
EX9200 Routing Engine
The EX9200 switch’s Routing Engine is based on the same field-proven hardware architecture used by Juniper Networks routers, bringing the same carrier-class performance and reliability to the EX9200 that Juniper routers bring to the world’s largest service provider networks. The RE’s central CPU performs all system control functions and maintains hardware forwarding table and routing protocol states for the EX9200. Dedicated hardware on the RE supports chassis management functions such as environmental monitoring. Communication between RE modules and individual line cards takes place over a dedicated internal GbE out-of-band control interface.
There are two EX9200 Routing Engines: the EX9200-RE* and EX9200-RE2. The EX9200-RE* supports control and management plane functionality with an integrated Routing Engine that features a quad-core, 1.73 GHz Intel processor with 16 gigabytes of DRAM and dual front pluggable SSDs, each providing 32 GB of storage for Junos OS images and logs.
The EX9200-RE2 features a six-core, 2 GHz Intel processor with 64 gigabytes of DRAM and dual front-pluggable SSDs, each providing 64 GB of storage for Junos OS images and logs. The 10GbE Routing Engine-to-switch fabric interface will allow running virtualized applications in the future.
Both Routing Engines feature AUX, console, and Ethernet ports on the front panel to support out-of-band system management and monitoring, while an external USB port accommodates a removable media interface for manually installing Junos OS images.
EX9200 Switch Fabric
The EX9200-SF3** and EX9200-SF2 Switch Fabric modules are hot- swappable and serves as the central non-blocking matrix through which all network data passes. The EX9200-SF2 supports 480 Gbps throughput per slot and the EX9200-SF3 supports 1.5 Tbps throughput per slot.
On the EX9204 and EX9208 switches, two EX9200-SF3 or EX9200-SF2 Switch Fabric modules deployed in a redundant configuration deliver up to 1.5 Tbps or 480 Gbps system throughput per slot, respectively. The Switch Fabric module installed first functions as the master, while the second serves as a backup.
On the EX9214, three EX9200-SF3 or EX9200-SF2 Switch Fabric modules deployed in a redundant configuration deliver 1.5 Tbps or 480 Gbps system throughput per slot, respectively. Traffic is load-balanced across the first two Switch Fabric modules installed, which together function as the master switch fabric, while the third serves as a backup.
Switch Fabric modules perform the following key functions:
- Monitoring and controlling system functions
- Interconnecting all line cards
- Clocking and system resets
- Acting as Routing Engine carrier
| EX9204 Typical Power | EX9204 Reserved Power | EX9208 Typical Power | EX9208 Reserved Power | EX9214 Typical Power | EX9214 Reserved Power | |
| Base system | 410 W | 410 W | 560 W | 560 W | 1,290 W | 1,670 W |
| Redundant system | 690 W | 690 W | 800 W | 800 W | 1,530 W | 1,910 W |
Power
Each EX9200 chassis contains four power supply bays to provide complete flexibility for provisioning and redundancy. The power supplies connect to the midplane, which distributes the different output voltages produced by the power supplies to the switch components, depending on their voltage requirements. Each power supply is cooled by its own internal cooling system. All EX9200 chassis support both AC and DC power supplies; however, AC and DC supplies cannot be mixed in the same chassis.
- The AC supplies on the EX9204 chassis accept 100 to 240 V AC input and deliver 2,050 watts of power to the chassis, while the DC power supplies accept -40 to -72 V DC input and deliver 2,400 watts of power to the chassis. The EX9204 can be provisioned with either one or two AC power supplies with high line (200-240 V AC) power inputs, two or four AC power supplies with low line (100-120 V AC) power inputs, or one or two DC power supplies.
- The AC supplies on the EX9208 chassis accept 100 to 240 V AC input and deliver 2,050 W of power to the chassis, while the DC power supplies accept -40 to -72 V DC input and deliver 2,400 W of power to the chassis. The EX9208 can be provisioned with either two or four AC power supplies with high line (200-240 V AC) power inputs, three or four AC power supplies with low line (100-120 VAC) power inputs, or two or four DC power supplies.
- The AC supplies on the EX9214 chassis accept 200 to 240 V AC input and deliver 4,100 W of power to the chassis, while the DC power supplies accept -40 to -72 V DC input and deliver 4,100 W of power to the chassis. Power supplies on the EX9214 chassis are divided into two zones, with adjacent power supplies supporting separate zones. The EX9214 must be provisioned with a minimum of one and a maximum of two AC or DC power supplies per zone.
| Typical Power | Maximum Power | |
| EX9200-40T Line Card | 206 W | 239 W |
| EX9200-40F Line Card | 219 W | 239 W |
| EX9200-32XS Line Card | 550 W | 610 W |
| EX9200-40XS Line Card | 465 W | 545 W |
| EX9200-12QS | 465 W | 545 W |
| EX9200-15C | 700 W | 785 W |
| EX9200-2C-8XS Line Card | 530 W | 610 W |
| EX9200-MPC | 461 W | 534 W |
| EX9200-10XS-MIC | 29.8 W | 29.8 W |
| EX9200-20F-MIC | 37 W | 37 W |
| EX9200-40T-MIC | 41 W | 41 W |
| EX9200 Switch Fabric | 150 W | 150 W |
| EX9200 Switch Fabric-2 | 155 W | 155 W |
| EX9200 Switch Fabric-3 | 385 W | 400 W |
| EX9200 Routing Engine | 90 W | 90 W |
| EX9200 Routing Engine-2 | 90 W | 90 W |
| EX9204 | EX9208 | EX9214 | |
| 100-120V AC Input | 1,167 W | 3,501 W | N/A |
| 200-240 V AC Input | 2,050 W | 4,100 W | 8,200 W |
| -40 to -72 V DC Input | 2,400 W | 4,100 W | 8,200 W |
| EX9204 | EX9208 | EX9214 | |
| * All line cards of the same type; some configurations could be over-subscribed ** EX9200-15C not supported on slots 0,1, 11 | |||
| EX9200-40XS | 3 | 6 | 11 |
| EX9200-15C | 2 | 6 | 7** |
| EX9200-12QS | 3 | 6 | 11 |
| EX9200-32XS | 2 | 4 | 10 |
| EX9200-6QS | 2 | 4 | 10 |
| EX9200-2C-8XS | 3 | 6 | 11 |
| EX9200-40T | 3 | 6 | 11 |
| EX9200-40F | 3 | 6 | 11 |
| EX9200-MPC | 3 | 6 | 11 |
Features and Benefits
Simplified Network Architectures
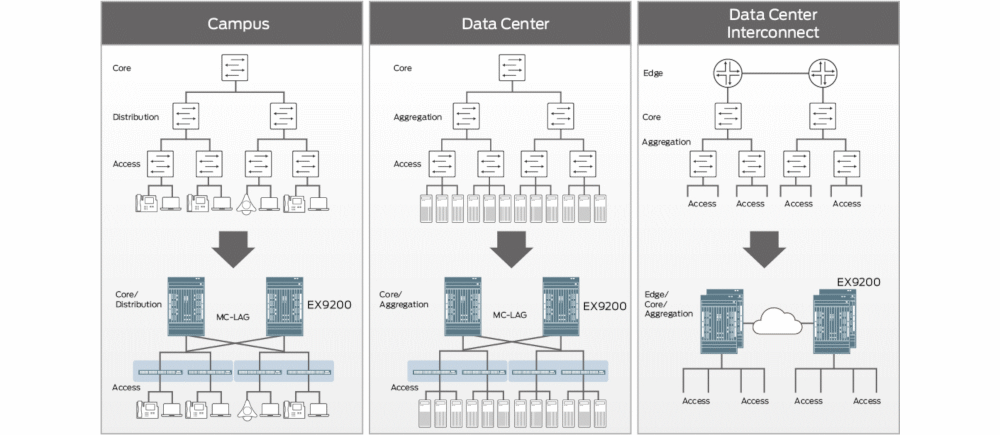
The EX9200 is ideal for simplifying campus, data center, and combined campus and data center network environments by collapsing network layers.
In the campus, the EX9200 collapses the core and distribution layers; when used with Juniper access layer switches deployed in an MC-LAG configuration, (supported only with SF2), the EX9200 helps eliminate Spanning Tree Protocol, dramatically simplifying the network architecture and network operations.
Similarly, in the data center the EX9200 can be used to collapse core and aggregation layers; again, when used with Juniper access switches in an MC-LAG configuration, the EX9200 helps reduce the number of managed devices by more than 50% and eliminates Spanning Tree Protocol from the network.
In combined campus and data center environments, the EX9200 consolidates network layers to simplify the network architecture and operations.
In all scenarios, the EX9200 delivers a simple, secure, virtualized network environment that increases enterprise business agility.
High Availability
EX9200 core switches deliver a number of high availability features that ensure uninterrupted, carrier-class performance. Each EX9200 chassis includes an extra slot to accommodate a redundant Routing Engine module which serves as a backup in hot-standby mode, ready to take over in the event of a master Routing Engine failure. If the master fails, the integrated L2 and L3 graceful Routing Engine switchover (GRES) feature of Junos OS, working in conjunction with the nonstop active routing (NSR) and nonstop bridging (NSB) features, ensures a seamless transfer of control to the backup, maintaining uninterrupted access to applications, services, and IP communications.
Carrier-Class Operating System
The EX9200 line of switches runs the same Junos OS used by all other Juniper Networks EX Series Ethernet Switches, as well as the Juniper Networks routers that power the world’s largest and most complex networks.
By using a common operating system, Juniper delivers a consistent implementation and operation of control plane features across all products. To maintain that consistency, Junos OS adheres to a highly disciplined development process that uses a single source code, follows a single release train, and employs a highly available modular architecture that prevents isolated failures from bringing down an entire system.
These attributes are fundamental to the core value of the software, enabling all Junos OS-powered products to be updated simultaneously with the same software release. All features are fully regression tested, making each new release a true superset of the previous version; customers can deploy the software with complete confidence that all existing capabilities will be maintained and operate in the same way.
Simplified Management and Operations
A range of system management options are available for the EX9200 line of switches as well.
The standard Junos OS CLI provides the same granular management capabilities and scripting parameters found in all Junos OS-powered devices. In addition, integrated Junos XML management protocol tools provide early detection and automatic resolution of potential problems related to the operating system.
Juniper Networks Junos Space software provides system-level management across all EX Series Ethernet Switches, as well as other Juniper products deployed throughout the network—all from a single console.
MACsec
The EX9200-40XS and EX9200-15C line cards support IEEE 802.1ae MACsec with AES-256 bit encryption, providing support for link-layer data confidentiality, data integrity, and data origin authentication. The EX9200-40F-M and EX9200-20F-MIC line cards support AES-128 bit encryption. A single EX9200-SFL license is required for the EX9200 chassis in order to enable MACsec in software.
Defined by IEEE 802.1AE, MACsec provides secure, encrypted communication at the Link Layer that is capable of identifying and preventing threats from denial of service (DoS) and other intrusion attacks, as well as man-in-the-middle, masquerading, passive wiretapping, and playback attacks launched from behind the firewall. When MACsec is deployed on switch ports, all traffic is encrypted on the wire, but traffic inside the switch is not. This allows the switch to apply all network policies such as QoS, deep packet inspection and sFlow to each packet without compromising the security of packets on the wire.
Hop-by-hop encryption enables MACsec to secure communications while maintaining network intelligence. In addition, Ethernet-based WAN networks can use MACsec to provide link security over longhaul connections. MACsec is transparent to Layer 3 and higher-layer protocols and is not limited to IP traffic; it works with any type of wired or wireless traffic carried over Ethernet links.
Scale Licenses
EX9204-ML, EX9208-ML, and EX9214-ML Mega Scale license SKUs enable an EX9200 chassis to support 512K FIB and ARP entries. Only one ML license is required per chassis.

Specifications
| EX9204 | EX9208 | EX9214 | |
| Backplane capacity | Up to 3 Tbps* | Up to 7.5Tbps* | Up to 12 Tbps* |
| Maximum fabric bandwidth/slot | 1.5 Tbps/slot | 1.5 Tbps/slot | 1.5 Tbps/slot |
| Maximum 1GbE wire speed port density (wire speed) | 120 | 240 | 440 |
| Maximum 10GbE wire speed port density (wire speed) | 144 (96) | 288 (240) | 576 (480) |
| Maximum 25GbE wire speed port density (wire speed) | 120** | 360** | 480** |
| Maximum 40GbE wire speed port density (wire speed) | 30 | 90 | 120 |
| Maximum 100GbE wire speed port density (wire speed) | 30 | 90 | 120 |
| * With breakout cables ** No fabric redundancy with EX9200-15C | |||
| EX9204 | EX9208 | EX9214 | |
| Dimensions (W x H x D) | 17.5 x 8.7 x 27.75 in | 17.5 x 14 x 27.75 in | 17.5 x 27.8 x 27.75 in |
| Rack units | 5 U | 8 U | 16 U |
| Weight | |||
Base configuration Redundant configuration Chassis with midplane Fully loaded chassis | 68.3 lbs (31.0 kg) 97.8 lbs (44.4 kg) 52.0 lbs (23.6 kg) 128.0 lbs (58.1 kg) | 88.4 lbs (40.1 kg) 111.2 lbs (50.5 kg) 65.5 lbs (29.7 kg) 163.6 lbs (74.2 kg) | 203.5 lbs (92.3 kg) 225.1 lbs (102.1 kg) 150.0 lbs (68.0 kg) 350.1 lbs (158.8 kg) |
| Total number of slots | 4 | 8 | 14 |
| Slots available for line cards** | 2 with fabric redundancy (3 without)* | 6* | 11 with fabric redundancy (12 without)* |
| Line Cards | EX9204 | EX9208 | EX9214 |
| EX9200-32XS | 773 Mpps | 1.9 Bpps | 3.9 Bpps |
| EX9200-40T | 178 Mpps | 357 Mpps | 654 Mpps |
| EX9200-40F | 178 Mpps | 357 Mpps | 654 Mpps |
| EX9200-2C-8XS | 568 Mpps | 1.42 Bpps | 2.84 Bpps |
| EX9200-40F-M | 178 Mpps | 357 Mpps | 654 Mpps |
| EX9200-MPC | 580 Mpps | 1.16 Bpps | 2.32 Bpps |
| EX9200-40XS | 730 Mpps | 2.42 Bpps | 4.02 Bpps |
| EX9200-12QS | 806 Mpps | 2.42 Bpps | 4.43 Bpps |
| EX9200-15C | 2.3 Bpps | 6.99 Bpps | 8.154 Bpps |
Line Card Specifications
Dimensions (W x H x D)
- 1.25 x 17 x 22 in (3.2 x 43.2 x 55.9 cm)
Weight
- EX9200-40T: 14.0 lbs (6.6 kg)
- EX9200-40F: 14.8 lbs (6.7 kg)
- EX9200-40F-M: 16.2 lbs (7.3 kg)
- EX9200-32XS: 19.2 lbs (8.7 kg)
- EX9200-6QS: 21.4 lbs (9.7 kg)
- EX9200-2C-8XS: 19.4 lbs (8.8 kg)
- EX9200-MPC: 15.96 lb (7.26 kg)
- EX9200-10XWS-MIC: 1.54 lb (0.70 kg)
- EX9200-20F-MIC: 1.2 lb (0.54 kg)
- EX9200-40T-MIC: 1.9 lb (0.9 kg)
- EX9200-40XS: 17 lb (7.7 kg)
- EX9200-12QS: 15.7 lb (7.12kg)
- EX9200-15C: 20.4 lb (9.25 kg)
- EX9200-SF3: 13.6 lb (6.2 kg)
IEEE Compliance
- IEEE 802.1AB: Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP)
- IEEE 802.1D-2004: Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
- IEEE 802.1p: Class-of-service (CoS) prioritization
- IEEE 802.1Q: Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks
- IEEE 802.1s: Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP)
- IEEE 802.1w: Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP)
- IEEE 802.3: 10BASE-T
- IEEE 802.3u: 100BASE-T
- IEEE 802.3ab: 1000BASE-T
- IEEE 802.3z: 1000BASE-X
- IEEE 802.3ae: 10-Gigabit Ethernet
- IEEE 802.3ba: 40-Gigabit/100-Gigabit Ethernet
- IEEE 802.3ah: Operation, Administration, and Maintenance (OAM)
- IEEE 802.3ad: Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
- IEEE 802.1ae: Media Access Control Security
RFC Compliance
- RFC 768: UDP
- RFC 783: Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP)
- RFC 791: IP
- RFC 792: Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
- RFC 793: TCP
- RFC 826: ARP
- RFC 854: Telnet client and server
- RFC 894: IP over Ethernet
- RFC 903: Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP)
- RFC 906: TFTP Bootstrap
- RFC 951, 1542: BootP
- RFC 1027: Proxy ARP
- RFC 1058: RIP v1
- RFC 1112: IGMP v1
- RFC 1122: Host Requirements
- RFC 1195: Use of Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) IS-IS for Routing in TCP/IP and Dual Environments (TCP/IP transport only)
- RFC 1256: IPv4 ICMP Router Discovery Protocol (IRDP)
- RFC 1492: TACACS+
- RFC 1519: Classless Interdomain Routing (CIDR)
- RFC 1587: OSPF NSSA Option
- RFC 1591: Domain Name System (DNS)
- RFC 1745: BGP4/IDRP for IP-OSPF Interaction
- RFC 1765: OSPF Database Overflow
- RFC 1771: Border Gateway Protocol 4
- RFC 1772: Application of the Border Gateway Protocol in the Internet
- RFC 1812: Requirements for IP Version 4 Routers
- RFC 1965: Autonomous System Confederations for BGP
- RFC 1981: Path maximum transmission unit (MTU) Discovery for IPv6
- RFC 1997: BGP Communities Attribute
- RFC 2030: Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP)
- RFC 2068: HTTP server
- RFC 2080: RIPng for IPv6
- RFC 2081: RIPng Protocol Applicability Statement
- RFC 2131: BOOTP/Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) relay agent* and DHCP server*
- RFC 2138: RADIUS Authentication
- RFC 2139: RADIUS Accounting
- RFC 2154: OSPF with Digital Signatures (password, Message Digest 5)
- RFC 2236: IGMP v2
- RFC 2267: Network Ingress Filtering
- RFC 2270: BGP-4 Dedicated autonomous system (AS) for Sites/Single Provider
- RFC 2283: Multiprotocol Extensions for BGP-4
- RFC 2328: OSPF v2 (Edge mode)
- RFC 2338: VRRP*
- RFC 2362: PIM-SM (Edge mode)
- RFC 2370: OSPF Opaque LSA Option
- RFC 2373: IPv6 Addressing Architecture
- RFC 2375: IPv6 Multicast Address Assignments
- RFC 2385: TCP MD5 Authentication for BGPv4
- RFC 2439: BGP Route Flap Damping
- RFC 2453: RIP v2
- RFC 2460: Internet Protocol, v6 (IPv6) specification
- RFC 2461: Neighbor Discovery for IP Version 6 (IPv6)
- RFC 2462: IPv6 Stateless Address Autoconfiguration
- RFC 2463: ICMPv6
- RFC 2464: Transmission of IPv6 Packets over Ethernet Networks
- RFC 2474: DiffServ Precedence, including 8 queues/port
- RFC 2475: DiffServ Core and Edge Router Functions
- RFC 2526: Reserved IPv6 Subnet Anycast Addresses
- RFC 2545: Use of BGP-4 Multiprotocol Extensions for IPv6 Interdomain Routing
- RFC 2547: BGP/MPLS VPNs
- RFC 2597: DiffServ Assured Forwarding (AF)
- RFC 2598: DiffServ Expedited Forwarding (EF)
- RFC 2710: Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) for IPv6
- RFC 2711: IPv6 Router Alert Option
- RFC 2740: OSPF for IPv6
- RFC 2796: BGP Route Reflection (supersedes RFC 1966)
- RFC 2796: Route Reflection
- RFC 2858: Multiprotocol Extensions for BGP-4
- RFC 2893: Transition Mechanisms for IPv6 Hosts and Routers
- RFC 2918: Route Refresh Capability for BGP-4
- RFC 3031: Multiprotocol Label Switching Architecture
- RFC 3032: MPLS Label Stack Encoding
- RFC 3036: LDP Specification
- RFC 3065: Autonomous System Confederations for BGP
- RFC 3176 sFlow
- RFC 3215: LDP State Machine
- RFC 3306: Unicast-Prefix-based IPv6 Multicast Addresses
- RFC 3376: IGMP v3
- RFC 3392: Capabilities Advertisement with BGP-4
- RFC 3446: Anycast Rendevous Point (RP) Mechanism using PIM and MSDP
- RFC 3478: Graceful Restart for Label Distribution Protocol
- RFC 3484: Default Address Selection for IPv6
- RFC 3513: Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) Addressing
- RFC 3569: PIM-SSM PIM Source Specific Multicast
- RFC 3587: IPv6 Global Unicast Address Format
- RFC 3618: Multicast Source Discovery Protocol (MSDP)
- RFC 3623: OSPF Graceful Restart
- RFC 3768: Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP)*
- RFC 3810: Multicast Listener Discovery Version 2 (MLDv2) for IP
- RFC 3973: PIM-Dense Mode
- RFC 4213: Basic Transition Mechanisms for IPv6 Hosts and Routers
- RFC 4291: IPv6 Addressing Architecture
- RFC 4360: BGP Extended Communities Attribute
- RFC 4364: BGP/MPLS IP Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
- RFC 4443: ICMPv6 for the IPv6 specification
- RFC 4486: Sub codes for BGP Cease Notification message
- RFC 4552: Authentication/Confidentiality for OSPFv3
- RFC 4604: Using Internet Group Management Protocol Version 3 (IGMPv3)
- RFC 4724: Graceful Restart Mechanism for BGP
- RFC 4761: Virtual Private LAN Service (VPLS) using BGP for auto-discovery and signaling
- RFC 4798: Connecting IPv6 Islands over IPv4 MPLS Using IPv6 Provider Edge Routers (6PE)
- RFC 4861: Neighbor Discovery for IPv6
- RFC 4862: IPv6 Stateless Address Autoconfiguration
- RFC 5095: Deprecation of Type 0 Routing Headers in IPv6
- RFC 5286, Basic Specification for IP Fast Reroute: Loop-Free Alternates
- RFC 5306: Restart Signaling for IS-IS
- RFC 5308: Routing IPv6 with IS-IS
- RFC 5340: OSPF for IPv6
- Draft-ietf-bfd-base-09.txt: Bidirectional Forwarding Detection
- Draft-ietf-l2vpn-evpn-00.txt: BGP MPLS-based Ethernet VPN
Services and Manageability
- Virtual eXtensible Local Area Network (VXLAN)*
- REST API
- NETCONF sessions over outbound HTTPS
- Juniper Extension Toolkit (JET)
- OpenFlow v1.3
- Junos OS CLI
- Out-of-band management: Serial; 10/100/1000BASE-T Ethernet
- ASCII configuration file
- Rescue configuration
- Configuration rollback
- Image rollback
- SNMP: v1, v2c, v3
- RMON (RFC 2819): Groups 1, 2, 3, 9
- Network Time Protocol (NTP)
- DHCP server*
- DHCP relay with Option 82*
- RADIUS
- TACACS+
- SSHv2
- Secure copy
- DNS resolver
- Syslog logging
- Environment monitoring
- Temperature sensor
- Configuration backup via FTP/secure copy
Network Management—MIB Support
- J-Flow
- RFC 1155: Structure of Management Information (SMI)
- RFC 1157: SNMPv1
- RFC 1212, RFC 1213, RFC 1215: MIB-II, Ethernet-like MIB, and traps
- RFC 1657: BGP-4 MIB
- RFC 1724: RIPv2 MIB
- RFC 1850: OSPFv2 MIB
- RFC 1901: Introduction to Community-based SNMPv2
- RFC 1902: Structure of Management Information for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)
- RFC 1905, RFC 1907: SNMP v2c, SMIv2, and Revised MIB-II
- RFC 2011: SNMPv2 for IP using SMIv2
- RFC 2012: SNMPv2 for transmission control protocol using SMIv2
- RFC 2013: SNMPv2 for user datagram protocol using SMIv2
- RFC 2096: IPv4 Forwarding Table MIB
- RFC 2287: System Application Packages MIB
- RFC 2465: Management Information Base for IP Version 6
- RFC 2570–2575: SNMPv3, user-based security, encryption, and authentication
- RFC 2576: Coexistence between SNMP Version 1, Version 2, and Version 3
- RFC 2578: SNMP Structure of Management Information MIB
- RFC 2579: SNMP Textual Conventions for SMIv2
- RFC 2665: Ethernet-like interface MIB
- RFC 2787: VRRP MIB
- RFC 2819: RMON MIB
- RFC 2863: Interface Group MIB
- RFC 2863: Interface MIB
- RFC 2922: LLDP MIB
- RFC 2925: Ping/Traceroute MIB
- RFC 2932: IPv4 Multicast MIB
- RFC 3413: SNMP Application MIB
- RFC 3826: The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) Cipher Algorithm in the SNMP
- RFC 4188: STP and Extensions MIB
- RFC 4363: Definitions of Managed Objects for Bridges with traffic classes, multicast filtering, and VLAN extensions
- Draft-ietf-idr-bgp4-mibv2-02.txt: Enhanced BGP-4 MIB
- Draft-ietf-isis-wg-mib-07
- Draft-reeder-snmpv3-usm-3desede-00
- Draft-ietf-idmr-igmp-mib-13
- Draft-ietf-idmr-pim-mib-09
- Draft-ietf-bfd-mib-02.txt
Troubleshooting
- Debugging: CLI via console, Telnet, or SSH
- Diagnostics: Show, debug, and statistics commands
- Firewall-based port mirroring
- IP tools: Extended ping and trace
- Juniper Networks commit and rollback
Environmental Ranges
- Operating temperature: 32° to 104° F (0° to 40° C)
- Storage temperature: -40° to 158° F (-40° to 70° C)
- Operating altitude: Up to 10,000 ft (3,048 m)
- Relative humidity operating: 5 to 90% (noncondensing)
- Relative humidity nonoperating: 5 to 95% (noncondensing)
- Seismic: Designed to meet GR-63, Zone 4 earthquake requirements
Maximum Thermal Output
- EX9204 AC power: 8,252 BTU/hour (2,420 W); DC power: 7,495 BTU/hour (2,198 W)
- EX9208 AC power: 16,473 BTU/hour (4,831 W); DC power: 14,963 BTU/hour (4,388 W)
- EX9214 AC power: 31,774 BTU/hour (9,318 W); DC power: 32,510 BTU/hour (9,354 W)
Safety and Compliance
Safety
- CAN/CSA-22.2 No. 60950-00/UL 1950 Third Edition, Safety of Information Technology Equipment
- EN 60825-1 Safety of Laser Products—Part 1: Equipment Classification, Requirements, and User’s Guide
- EN 60950 Safety of Information Technology Equipment
- IEC 60950-1 (2001) Safety of Information Technology Equipment (with country deviations)
- EN 60825-1 +A1+A2 (1994) Safety of Laser Products—Part 1: Equipment Classification
- EN 60825-2 (2000) Safety of Laser Products—Part 2: Safety of Optical Fiber Comm. Systems
- C-UL to CAN/CSA 22.2 No.60950-1 (Second Edition)
- TUV/GS to EN 60950-1, Amendment A1-A4, A11
- CE-IEC60950-1, all country deviations
EMC
- AS/NZS CISPR22:2009
- EN 55022 2006+A1:2007 European Radiated Emissions
- FCC 47CFR , Part 15 Class A (2009) USA Radiated Emissions
- VCCI-V-3/2009.04 and V-4/2009.04 Japanese Radiated Emissions
- BSMI CNS 13438 and NCC C6357 Taiwan Radiated Emissions
- EN 300 386 V1.5.1 Telecom Network Equipment - EMC requirements
- ICES-003 Issue 4, Feb 2004 Canada Radiated Emissions
- CISPR 24:1997/A1:2001/A2:2002 IT Equipment Immunity Characteristics
Immunity
- EN 55024:1998/A1:2001/A2:2003 Information Technology Equipment Immunity Characteristics
- EN-61000-3-2 (2006) Power Line Harmonics
- EN-61000-3-3 +A1 +A2 +A3 (1995) Power Line Voltage Fluctuations
- EN-61000-4-2 +A1 +A2 (1995) Electrostatic Discharge
- EN-61000-4-3 +A1+A2 (2002) Radiated Immunity
- EN-61000-4-4 (2004) Electrical Fast Transients
- EN-61000-4-5 (2006) Surge
- EN-61000-4-6 (2007) Immunity to Conducted Disturbances
- EN-61000-4-11 (2004) Voltage Dips and Sags
Customer-Specific EMC Requirements
- GR-1089-Core Issue 6 (May, 2011) EMC and Electrical Safety for Network Telecommunications Equipment
- AT&T TP-76200 Issue 17 (2012) Network Equipment Power, Grounding, Environmental, and Physical Design Requirements
- Verizon TPR.9305 Issue 5 (2012) Verizon NEBS Compliance: NEBS Compliance Clarification Document
- Deutsche Telekom 1TR9 (2008) EMC Specification
- British Telecom EMC Immunity Requirements (2007)
- IBM C-S 2-0001-005 ESD
- IBM C-S 2-0001-012 Radio Frequency Electromagnetic Susceptibility
- ITU-T K.20 (2011) Resistibility of telecommunication equipment installed in telecom centers to over voltages and over currents
- Juniper Inductive GND (JIG)
ETSI
- ETSI EN-300386-2 Telecommunication Network Equipment Electromagnetic Compatibility Requirements
Network Equipment Building System (NEBS)
- SR-3580 NEBS Criteria Levels (Level 3 Compliance)
- GR-63-Core: NEBS, Physical Protection
Environmental
- Reduction of Hazardous Substances (ROHS) 5/6
Telco
- Common Language Equipment Identifier (CLEI) code
Warranty
For warranty information, please visit https://support.juniper.net/support/warranty/.
Juniper Networks Services and Support
Juniper Networks is the leader in performance-enabling services that are designed to accelerate, extend, and optimize your high-performance network. Our services allow you to maximize operational efficiency while reducing costs and minimizing risk, achieving a faster time to value for your network. Juniper Networks ensures operational excellence by optimizing the network to maintain required levels of performance, reliability, and availability. For more details, please visit https://www.juniper.net/us/en/products.html.
Ordering Information
| Product Number | Description |
| Hardware | |
| EX9204-BASE3B-AC | Base EX9204 system configuration: 4-slot chassis with passive midplane and 1x fan tray, 1x EX9200-RE2 Routing Engine, 1x Switch Fabric-2 module, 2x 2,520 W AC PSUs, and all necessary blank panels. |
| EX9204-RED3B-AC | Redundant EX9204 system configuration: 4-slot chassis with passive midplane and 1x fan tray, 2xEX9200-RE2 Routing Engines, 2x Switch Fabric-2 modules, 4x 2,520 W AC PSUs, and all necessary blank panels. |
| EX9204-RED3B-DC | Redundant EX9204 system configuration: 4-slot chassis with passive midplane and 1x fan tray, 2x EX9200-RE2 Routing Engines, 2x Switch Fabric-2 modules, 4x 2,520W DC PSUs, and all necessary blank panels. |
| EX9208-BASE3B-AC | Base EX9208 system configuration: 8-slot chassis with passive midplane and 1x fan tray, 1x EX9200-RE2 Routing Engine, 1x Switch Fabric-2 modules, 3x 2,520 W AC PSUs, and all necessary blank panels. |
| EX9208-RED3B-AC | Redundant EX9208 system configuration: 8-slot chassis with passive midplane and 1x fan tray, 2x EX9200-RE2 Routing Engines, 2x Switch Fabric-2 modules, 4x 2,520 W AC PSUs, and all necessary blank panels. |
| EX9208-RED3B-DC | Redundant EX9208 system configuration: 8-slot chassis with passive midplane and 1x fan tray, 2x EX9200-RE2 Routing Engines, 2x Switch Fabric-2 modules, 4x 2,520 W DC PSUs, and all necessary blank panels. |
| EX9214-BASE3B-AC | Base EX9214 system configuration: 14-slot chassis with passive midplane and 2x fan trays, 1x EX9200-RE2 Routing Engine, 2x Switch Fabric-2 modules, 3x 4,100 W AC PSUs, and all necessary blank panels. |
| EX9214-RED3B-DC | Redundant EX9214 system configuration: 14-slot chassis with passive midplane and 2x fan trays, 2x EX9200-RE2 Routing Engines, 3x Switch Fabric-2 modules, 4x 4,100W DC PSUs, and all necessary blank panels. |
| EX9204-AC-BND2 | Bundle comprising of EX9204-BASE3B-AC and EX9200-32XS line card , shipped separately as two items |
| EX9204-BASE3B-AC-T | Base EX9204 TAA system configuration: 4-slot chassis with passive midplane and 1x fan tray, 1x EX9200-RE2 Routing Engine, 1x Switch Fabric-2 module, 2x 2,520 W AC PSUs, and all necessary blank panels. |
| EX9204-RED3B-AC-T | Redundant EX9204 TAA system configuration: 4-slot chassis with passive midplane and 1x fan tray, 2x EX9200-RE2 Routing Engines, 2x Switch Fabric-2 modules, 4x 2,520W AC PSUs, and all necessary blank panels. |
| EX9208-BASE3B-AC-T | Base EX9208 TAA system configuration: 8-slot chassis with passive midplane and 1x fan tray, 1x EX9200-RE2 Routing Engine, 1x Switch Fabric-2 modules, 3x 2,520W AC PSUs, and all necessary blank panels. |
| EX9208-RED3B-AC-T | Redundant EX9208 TAA system configuration: 8-slot chassis with passive midplane and 1x fan tray, 2x EX9200-RE2 Routing Engines, 2x Switch Fabric-2 modules, 4x 2,520W AC PSUs, and all necessary blank panels. |
| EX9214-BASE3B-AC-T | Base EX9214 TAA system configuration: 14-slot chassis with passive midplane and 2x fan trays, 1x EX9200-RE2 Routing Engine, 2x Switch Fabric-2 modules, 3x 4,100W AC PSUs, and all necessary blank panels. |
| EX9214-RED3B-AC-T | Redundant EX9214 TAA system configuration: 14-slot chassis with passive midplane and 2x fan trays, 2x EX9200-RE2 Routing Engines, 3x Switch Fabric-2 modules, 4x 4,100W AC PSUs, and all necessary blank panels. |
| EX9214-RED-3B-AC | Redundant EX9214 system configuration: 14-slot chassis with passive midplane and 2x fan trays, 2x EX9200-RE2 Routing Engines, 3x Switch Fabric-2 modules, 4x 4,100W AC PSUs, and all necessary blank panels. |
| EX9204-BASE3C-AC | Base EX9204 system configuration: 4-slot chassis with passive midplane and 1x fan tray, 1x EX9200-RE2 routing engine, 1x EX9200-SF3module, 2x 2520W AC PSUs |
| EX9204-RED3C-AC | Redundant EX9204 system configuration: 4-slot chassis with passive midplane and 1x fan tray, 2xEX9200-RE2 routing engines, 2x EX9200-SF3 modules, 2x 2520W AC PSUs |
| EX9204-RED3C-DC | Redundant EX9204 system configuration: 4-slot chassis with passive midplane and 1x fan tray, 2xEX9200-RE2 routing engines, 2x EX9200-SF3 modules, 2x 2520W DC PSUs |
| EX9208-BASE3C-AC | Base EX9208 system configuration: 8-slot chassis with passive midplane and 1x fan tray, 1x EX9200-RE2 routing engine, 1x EX9200-SF3modules, 2x 2520W AC PSUs |
| EX9208-RED3C-AC | Redundant EX9208 system configuration: 8-slot chassis with passive midplane and 1x fan tray, 2x EX9200-RE2 routing engines, 2x EX9200-SF3 modules, 2x 2520W AC PSUs |
| EX9208-RED3C-DC | Redundant EX9208 system configuration: 8-slot chassis with passive midplane and 1x fan tray, 2x EX9200-RE2 routing engines, 2x EX9200-SF3 modules, 2x 2520W DC PSUs |
| EX9214-BASE3C-AC | Base EX9214 system configuration: 14-slot chassis with passive midplane and 2x fan trays, 1x EX9200-RE2 routing engine, 3x EX9200-SF3 modules, 2x 4100W AC PSUs |
| EX9214-RED3C-AC | Redundant EX9214 system configuration: 14-slot chassis with passive midplane and 2x fan trays, 2x EX9200-RE2 routing engines, 3x EX9200-SF3 modules, 2x 4100W AC PSUs |
| EX9214-RED3C-DC | Redundant EX9214 system configuration: 14-slot chassis with passive midplane and 2x fan trays, 2x EX9200-RE2 routing engines, 3x EX9200-SF3 modules, 2x 4100W DC PSUs |
| EX9200 Line Cards | |
| EX9200-15C | 15x 100GbE/40GbE line card with MACsec AES-256 for EX9200 |
| EX9200-40XS | 40-port 10GbE SFP+ line card supporting MACsec AES-256 (requires SFL software license for activation); requires SFP+ optics sold separately |
| EX9200-12QS | 12-port 40GbE QSFP+ or 4-port 100GbE QSFP28 combo line card; requires optics sold separately |
| EX9200-MPC | EX9200 Modular Port Concentrator (MPC) |
| EX9200-20F-MIC | EX9200 20-port GBASE-X (half-slot) Modular Interface Card (MIC) supporting MACsec AES-128 (requires SFL software license for activation); requires EX9200-MPC (ordered separately) |
| EX9200-10XS-MIC | EX9200 10-port 10GBASE-X (half-slot) Modular Interface Card (MIC); requires EX9200-MPC (ordered separately) |
| EX9200 Pluggable Optics | |
| EX-SFP-1FE-FX | SFP 100BASE-FX Fast Ethernet Optics, 1,310 nm for 2 km transmission on MMF |
| EX-SFP-FE20KT13R15 | SFP 100BASE-BX Fast Ethernet Optics, Tx 1,310 nm/Rx 1,550 nm for 20 km transmission on single strand of SMF |
| EX-SFP-FE20KT15R13 | SFP 100BASE-BX Fast Ethernet Optics, Tx 1,550 nm/Rx 1,310 nm for 20 km transmission on single strand of SMF |
| EX-SFP-1FE-LX40K | SFP 100BASE-LX Fast Ethernet optics, 1310nm for 40km transmission on SMF |
| EX-SFP-1GE-LX40K | SFP 1000BASE-LX Gigabit Ethernet Optics, 1,310 nm for 40 km transmission on single-mode fiber-optic (SMF) |
| EX-SFP-1GE-SX | SFP 1000BASE-SX Gigabit Ethernet Optics, 850 nm for up to 550 m transmission on MMF |
| EX-SFP-GE10KT13R15 | SFP 1000BASE-BX Gigabit Ethernet Optics, Tx 1,310 nm/Rx 1,550 nm for 10 km transmission on single strand of SMF |
| EX-SFP-GE40KT15R13 | SFP 1000BASE-BX Gigabit Ethernet Optics, Tx 1,550 nm/Rx 1,310 nm for 40 km transmission on single strand of SMF |
| EX-SFP-1GE-LH | SFP 1000BASE-LH Gigabit Ethernet Optics, 1,550 nm for 70 km transmission on SMF |
| EX-SFP-GE10KT13R14 | SFP 1000BASE-BX Gigabit Ethernet Optics, Tx 1,310 nm/Rx 1,490 nm for 10 km transmission on single strand of SMF |
| EX-SFP-GE10KT15R13 | SFP 1000BASE-BX Gigabit Ethernet Optics, Tx 1,550 nm/Rx 1,310 nm for 10 km transmission on single strand of SMF |
| EX-SFP-1GE-LX | SFP 1000BASE-LX Gigabit Ethernet Optics, 1,310 nm for 10 km transmission on SMF |
| EX-SFP-GE10KT14R13 | SFP 1000BASE-BX Gigabit Ethernet Optics, Tx 1,490 nm/Rx 1,310 nm for 10 km transmission on single strand of SMF |
| EX-SFP-GE40KT13R15 | SFP 1000BASE-BX Gigabit Ethernet Optics, Tx 1,310 nm/Rx 1,550 nm for 40 km transmission on single strand of SMF |
| EX-SFP-1GE-T | SFP 1000BASE-T 10/100/1000 Copper Transceiver Module for up to 100 m transmission on Cat5 |
| EX-SFP-10GE-SR | SFP+ 10GBASE-SR 10-Gigabit Ethernet Optics, 850 nm for up to 300 m transmission on multimode fiber-optic (MMF) |
| EX-SFP-10GE-ZR | SFP+, 10GBASE-ZR 10-Gigabit Ethernet Optics, 1,550 nm for 80 km transmission on SMF |
| EX-SFP-10GE-LR | SFP+ 10GBASE-LR 10-Gigabit Ethernet Optics, 1,310 nm for 10 km transmission on SMF |
| EX-SFP-10GE-USR | SFP+ 10GBASE-SR; LC connector; 850nm; 100m reach on multicode fiber |
| EX-SFP-10GE-ER | SFP+ 10GBASE-ER 10-Gigabit Ethernet Optics, 1,550 nm for 40 km transmission on SMF |
| EX-SFP-10GE-LRM | SFP+, 10GBASE-LRM, LC connector; 850nm; up to 220m reach on multicode fiber |
| QFX-QSFP-40GE-SR4 | QSFP+ 40GBASE-SR4 40-Gigabit Optics, 850 nm for up to 150 m transmission on MMF |
| JNP-QSFP-40G-LR4 | 40GBASE-LR4 QSFP+ pluggable module |
| JNP-QSFP-40G-LR4 | QSFP+ 40GBASE-LR4 40 gigabit optics for up to 10km transmission on SMF |
| QFX-QSFP-40G-SR4 | QSFP+ 40GBASE-SR4 40 gigabit optics, 850nm for up to 150m transmission on MMF |
| QSFPP-4X10GE-SR | QSFP+ 40GBASE optics, up to 200m transmission onpParallel single mode (4X10GbE SR up to 200m) |
| JNP-QSFP-4X10GE-LR | QSFP+ 40GBASE optics, up to 10km transmission on parallel single mode (4X10GbE LR up to 10km) |
| CFP-100GBASE-SR10 | CFP 100GbE pluggable module, MMF, 850nm for 200M transmission |
| CFP-GEN2-100GBASE-LR4 | CFP 100GBASE-LR4 (second generation) pluggable module, compliant with IEEE 802.3ba |
| CFP-GEN2-CGE-ER4 | CFP 100GBASE-ER4 (second generation) pluggable module compliant with IEEE 802.3ba |
| JNP-QSFP-100G-LR4 | QSFP28 100GBASE-L4 optics for up to 10km transmission over serial SMF |
| JNP-QSFP-100G-SR4 | QSFP28 100GBASE-SR4 optics for up to 100m transmission over parallel MMF |
| EX9200 Software Feature Licenses | |
| EX9204-AFL | EX9204 Advanced Feature License |
| EX9208-AFL | EX9208 Advanced Feature License |
| EX9214-AFL | EX9214 Advanced Feature License |
| EX9200-SFL | Security feature license for EX9200 to enable MACsec on EX9200-20F-MIC |
| EX9204-ML | Mid-scale license to enable 512K FIB and ARP entries on EX9204 chassis (one required per chassis) |
| EX9208-ML | Mid-scale license to enable 512K FIB and ARP entries on EX9208 chassis (one required per chassis) |
| EX9214-ML | Mid-scale license to enable 512K FIB and ARP entries on EX9214 chassis (one required per chassis) |
| EX9200 Power Cords | |
| CBL-M-PWR-RA-AU | AC Power Cord, Australia (SAA/3/15), C19, 15 A/250 V, 2.5 m, Right Angle |
| CBL-M-PWR-RA-CH | AC Power Cord, China (GB 2099.1-1996, Angle), C19, 16 A/250 V, 2.5 m, Right Angle |
| CBL-M-PWR-RA-EU | AC Power Cord, Cont. Europe (VII), C19, 16 A/250 V, 2.5 m, Right Angle |
| CBL-M-PWR-RA-IT | AC Power Cord, Italy (I/3/16), C19, 16 A/250 V, 2.5 m, Right Angle |
| CBL-M-PWR-RA-JP | AC Power Cord, Japan (NEMA LOCKING), C19, 20 A/250 V, 2.5 m, Right Angle |
| CBL-M-PWR-RA-TWLK-US | AC Power Cord, US (NEMA LOCKING), C19, 20 A/250 V, 2.5 m, Right Angle |
| CBL-M-PWR-RA-UK | AC Power Cord, UK (BS89/13), C19, 13 A/250 V, 2.5 m, Right Angle |
| CBL-M-PWR-RA-US | AC Power Cord, USA/Canada (N6/20), C19, 20 A/250 V, 2.5 m, Right Angle |
| CBL-PWR-C19S-162-JP | Power Cord, AC, Japan, NEMA 6-20 to C19, 16 A/250 V, 2.5 m, Straight |
| CBL-PWR-C19S-162-JPL | Power Cord, AC, Japan/US, C19 at 70-80mm, 16 A/250 V, 2.5 m, Straight, Locking Plug |
| CBL-PWR-RA-JP15 | AC Power Cable: JIS 8303 15 A/125 V 2.5 m length for Japan, Right Angle |
| CBL-PWR-RA-TWLK-US15 | AC Power Cable: NEMA L5-15P (twist lock) 15 A/125 V 2.5 m length for U.S., Canada, and Mexico, Right Angle |
| CBL-PWR-RA-US15 | AC Power Cable: NEMA 5-15 15 A/12 5 V 2.5 m length for North America, parts of South America, parts of Central America, parts of Africa, and parts of Asia, Right Angle |
| EX9200 Field Replaceable Units | |
| EX9200-SF2 | EX9200 480 Gbps Switch Fabric-2 module |
| EX9200-DF3 | EX9200 1.5 Tbps Switch Fabric-3 module |
| EX9204-CHAS3-S | EX9200 4-slot chassis 3 with passive midplane |
| EX9208-CHAS3-S | EX9200 8-slot chassis 3 with passive midplane |
| EX9214-CHAS3-S | EX9200 14-slot chassis with passive midplane |
| EX9200-LC-SF-BLANK | EX9200 line card, switch fabric blank cover panel, spare |
| PWR-MX480-2520-AC-S | 2520 W AC Power Supply for EX9208, spare (Note: AC power cords are sold separately) |
| PWR-MX480-2400-DC-S | 2400 W DC Power Supply for EX9208, spare |
| PWR-MX960-4100-AC-S | 4100 W AC Power Supply for EX9214, spare (Note: AC power cords are sold separately) |
| PWR-MX960-4100-DC-S | 4100 W DC Power Supply for EX9214, spare |
| FFANTRAY-MX240-HC-S | High capacity fan tray, spare |
| FFANTRAY-MX480-HC-S | EX9208 fan tray, spare |
| FFANTRAY-MX960-HC-S | EX9216 fan tray (upper or lower), spare |
| FLTR-KIT-MX240-S | EX9204 Air Filter, spare |
| FLTR-KIT-MX480-S | EX9208 Air Filter, spare |
| FLTR-KIT-MX960-S | EX9214 Air Filter, spare |
| EX9200 Support* | |
| SVC-COR-EX9204 | Juniper Care Core Support for EX9204 |
| SVC-COR-EX9204-3A | Juniper Care Core Support for EX9204-BASE3A (also REDUND3A models) |
| SVC-COR-EX9208 | Juniper Care Core Support for EX9208 |
| SVC-COR-EX9208-3A | Juniper Care Core Support for EX9208-BASE3A (also REDUND3A models) |
| SVC-COR-EX9214 | Juniper Care Core Support for EX9214 |
| SVC-COR-EX9214-3A | Juniper Care Core Support for EX9214-BASE3A (also REDUND3A models) |
| SVC-CP-EX9204 | Juniper Care Core Plus Support for EX9204 |
| SVC-CP-EX9204-3A | Juniper Care Core Plus Support for EX9204-BASE3A (also REDUND3A models) |
| SVC-CP-EX9208 | Juniper Care Core Plus Support for EX9208 |
| SVC-CP-EX9208-3A | Juniper Care Core Plus Support for EX9208-BASE3A (also REDUND3A models) |
| SVC-CP-EX9214 | Juniper Care Core Plus Support for EX9214 |
| SVC-CP-EX9214-3A | Juniper Care Core Plus Support for EX9214-BASE3A (also REDUND3A models) |
About Juniper Networks
At Juniper Networks, we are dedicated to dramatically simplifying network operations and driving superior experiences for end users. Our solutions deliver industry-leading insight, automation, security and AI to drive real business results. We believe that powering connections will bring us closer together while empowering us all to solve the world’s greatest challenges of well-being, sustainability and equality.
1000432 - 022 - EN AUG 2022






















