CTP2000 Clock Interface Modules
Clock interface modules provide clock distribution between modules when the backplane is in use by voice applications.
The clock rear transition module (RTM) is used to input a reference clock into the CTP2000 platform. The clock RTM is installed in the rear of the chassis behind the first interface module as follows:
On CTP2008 devices, the first slot above the processor RTM.
On the CTP2024 and CTP2056 devices, the first slot below the processor RTM.
Clock distribution is accomplished through a “hub-and-spoke” configuration composed of a main module and a spoke module. Clock main modules (Figure 1) and clock spoke modules (Figure 2) allow more clock input types in the CTP2000 chassis and provide the capability for clock distribution when both serial or T1/E1 interface modules and voice modules are installed in the same CTP2000 chassis.

The clock main module accepts an external clock reference and distributes it to the spoke module using a twisted pair cable. Each nonvoice card receives the clock on the first RJ-45 and sends it to the front module.
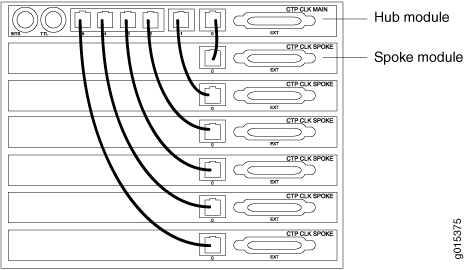
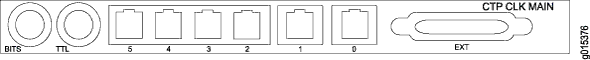
The main clock module has two BNC inputs (BITS and TTL), six RJ-45 ports, and one DB-25 port. Each RJ-45 port can be connected to one spoke module. The spoke module has one ingress RJ-45 port and one DB-25 interface. (See Figure 1, Figure 2, and Figure 3.)
The latest version of the clock main module does not have the BITS connector and no longer supports a BITS BNC input. If you need a BITS timing reference to or from a CTP2000 node, you can use any of ports te-0/0 through te-0/3 if you have a T1/E1 interface module in the first slot.
BITS input is a T1/E1 line interface unit (LIU), with AMI (alternate mark inversion) encoding enabled and B8ZS/HDB3 (Zero Suppression) disabled. The equalization is set for a 0-133 feet cable. An internal 100 ohm termination is present, although it might need to be externally augmented based on the type of cabling used. Any valid AMI signal works properly and it is not restricted to only the "all 1" BITS signal but the ones density must be sufficient to prevent LOS (according to the ITU G.775 recommendation). The TTL input has a slice point of 3.3V/2 = 1.65V relative to chassis ground (GND). Therefore, any signal on the coaxial center conductor that transitions through that voltage registers a transition. There are many signals, besides TTL, that satisfy this criteria. An external termination must be provided that matches the impedance of the cable that goes to the BNC connector.
If you can configure the rate in CTP menu, then the TTL supports a frequency of 2048 KHz for the TTL clock input, provided the signal is good and noise-free (terminated properly). TTL is rate-agile, while BITS is restricted to T1/E1 frequencies.
The TTL input is high-impedance (no on-board termination provided) because a variety of cable types might exist that you can use to drive signal to this connector, such as RG-58 coax (50 ohm), RG-59 coax (75 ohm), or twisted pair (100-120 ohm). Instead of applying a particular impedance termination on the board and have it incorrectly done, we recommend that you configure the impedance termination based on your network environment. For example, a 50 ohm termination is needed if you are using RG-58/U coax cable, which has 50 ohm impedance.
External Reference Clock
The CTP2000 device can receive the external reference clock from any of the following inputs on the clock main module:
The DB-25 connector. The clock input is provided on pins 24 and 11.
The T1/E1 BITS inputs
Note:The latest version of the clock main module does not have the BITS connector and no longer supports a BITS input. If you need a BITS timing reference to or from a CTP2000 node, you can use any of ports te-0/0 through te-0/3 if you have a T1/E1 interface module in the first slot.
The T1/E1 TTL input
Installation Notes for Clock Interface Modules
Main modules and spoke modules are not hot-swappable.
Nonvoice modules and voice modules can be installed in any slot.
Main clock RTMs must be installed in slot 0 behind either a serial module or a T1/E1 module.
Spoke RTMs must be installed behind serial modules and the lowest-numbered T1/E1 slot.
If a T1/E1 module is installed in the slot that is closest to the processor, a spoke RTM is not needed behind any T1/E1 modules. They will synchronize to the H.100 clock.
For platforms with only nonvoice boards (serial or T1/E1 module), only a main RTM is needed for external clock reference input.
The clock RTM is installed in the rear of slot 0 next to the CPU slot. When you upgrade from an older processor to a PP833/PPF84 processor, you can leave the CPU RTM in the chassis. Leaving the CPU RTM in the chassis will not adversely affect the functioning of the PP833/PPF84 processor. Leaving the RTM installed will provide proper airflow within the CTP node.
