Step 1: Begin
This guide walks you through the simple steps to install Paragon Automation and use Paragon Automation to onboard, manage, and monitor network devices.
Meet Paragon Automation
Paragon Automation provides end-to-end transport network automation and simplifies the adoption of network automation for device, network, and service life cycles from Day 0 to Day 2.
You can onboard ACX7000 Series, PTX Series, and MX Series, in Paragon Automation Supported Hardware to Paragon Automation and manage them.
Install Paragon Automation
Before you install the Paragon Automation application, ensure that your server(s) meet the requirements listed in this section. A Paragon Automation cluster should contain only four nodes [virtual machines (VMs)], with three nodes acting as both primary and worker nodes and one node acting as a worker-only node.
Requirements
Hardware Requirements
Each node VM must have the following minimum hardware resources:
-
16-core vCPU
-
32-GB RAM
-
300-GB SSD
-
These VMs do not need to be in the same server, but the nodes need to be able to communicate over an L2 network.
-
The hardware resources needed for each node VM depend on the size of the network that you want to onboard. To get a scale and size estimate of a production deployment and to discuss detailed dimensioning requirements, contact your Juniper Partner or Juniper Sales Representative.
-
SSDs are mandatory.
Software Requirements
Use VMware ESXi 8.0 to deploy Paragon Automation.
Network Requirements
The four nodes must be able to communicate with each other through SSH. You need to have the following addresses available for the installation, all in the same IP network.
-
Four IP addresses, one for each of the four nodes
-
Network gateway IP address
-
A Virtual IP (VIP) address for generic ingress shared between gNMI, OC-TERM (SSH connections from devices), and the Web UI.
-
A VIP address for Paragon Active Assurance Test Agent gateway (TAGW).
Browser Requirements
Paragon Automation is supported on the latest version of Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Safari.
The recommended browser is Google Chrome.
Create and Configure VMs
A system administrator can install Paragon Automation by downloading an OVA bundle and using the OVA bundle to deploy the node VMs on a VMware ESXi Server. Alternatively, you can also extract the OVF and VMDK files from the OVA bundle and use them to deploy the node VMs. Paragon Automation runs on a Kubernetes cluster with three primary/worker nodes and one worker-only node. The installation is air-gapped but you need Internet access to download the OVA bundle to your computer.
Figure shows the workflow for installing Paragon Automation.
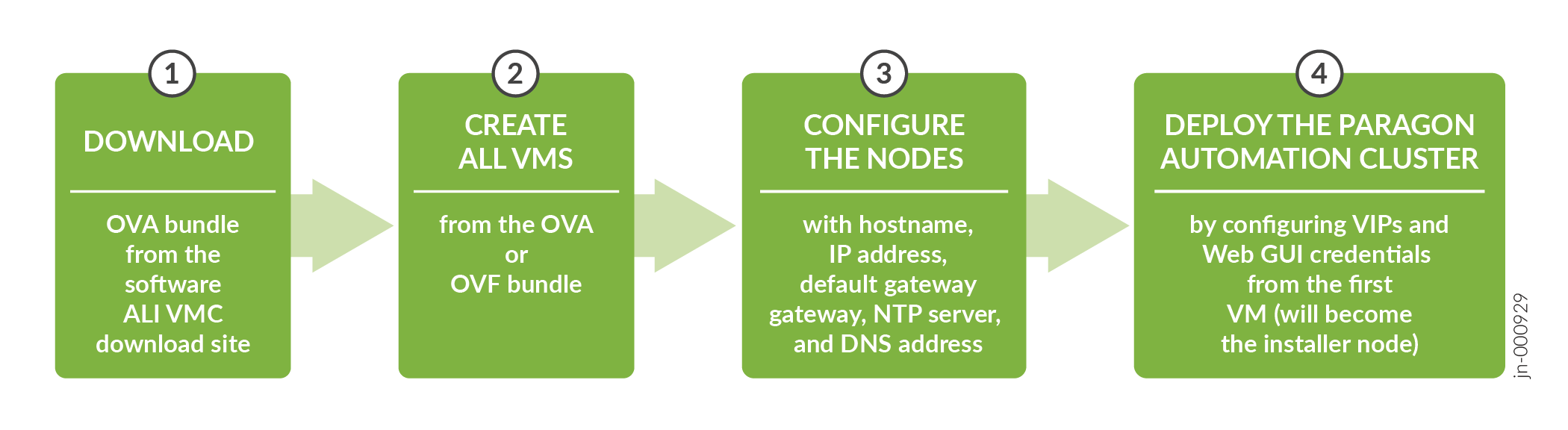
You use the OVA (or OVF and VMDK files) bundle to create your node VMs. The software download files come prepackaged with the OS and all packages required to create the VMs and deploy your Paragon Automation cluster. The VMs have a Linux base OS of Ubuntu 22.04.4 LTS (Jammy Jellyfish).
Once the VMs are created, you must configure each VM in the same way. When all the VMs are configured, you can deploy the Paragon Automation cluster from the first VM.
-
Download the OVA bundle onto your computer.
You can use the OVA as a whole to create the VMs or alternatively, extract and use the OVF and .vmdk files from the OVA to create your VMs. -
Log in to the VMware ESXi 8.0 server to install Paragon Automation.
-
Create the node VMs.
To create the node VMs:
-
Right-click the Host icon and select Create/Register VM.
The New virtual machine wizard appears.
-
On the Select creation type page, select Deploy a virtual machine from an OVF or OVA file and click Next.
-
On the Select OVF and VMDK files page, enter a name for the node VM.
Click to upload or drag and drop the OVA file or the OVF file along with the .vmdk files. Review the list of files to be uploaded and click Next.
-
On the Select storage page, select the datastore that can accommodate 300-GB SSD for the node VM.
Click Next. The extraction of files begins and takes a few minutes.
-
On the Deployment options page:
-
Select the virtual network to which the node VM will be connected.
-
Select the Thick disk provisioning option.
-
Enable the VM to power on automatically.
Click Next.
-
-
On the Ready to complete page, review the VM settings.
Click Finish to create the node VM.
-
Power on the VM.
-
Follow steps 3.a to 3g to create three more nodes. Enter appropriate VM names when prompted.
Alternatively, if you are using VMware vCenter, you can right-click the VM, and click the Clone > Clone to Virtual Machine option to clone the newly created VM. Clone the VM thrice to create the remaining node VMs.
Enter appropriate VM names when prompted.
-
After all the VMs are created, verify that the VMs have the correct specifications and are powered on.
-
-
Configure the Nodes.
To configure the nodes:
-
Connect to the node VM console of the first VM node.
You are logged in to the node as the root user automatically and prompted to change your password.
-
Enter and re-enter the new password.
You are automatically logged out of the VM.
Note:We recommend that you enter the same password for all the VMs.
-
When prompted, log in again as root user with the newly configured password.
-
Configure the hostname and IP address of the VM, gateway, and DNS servers when prompted.
For information, see Install Paragon Automation.
-
When prompted, if you are sure to proceed, review the information displayed, type y, and press Enter.
-
Ping each node from the other three nodes to ensure that the nodes can reach each other.
-
You can now deploy the cluster.
Deploy the Cluster
You can deploy the Paragon Automation cluster either by using Paragon Shell CLI commands or by using the interactive deployment wizard in the Linux root shell.
This section describes deploying the cluster by using the deployment wizard. For information about deploying the cluster by using Paragon shell, see Install Paragon Automation by using Paragon Shell.
To deploy a Paragon Automation cluster by using the deployment wizard from the Linux root shell:
-
Log into the first VM node and log back in as the root user with the newly configured password.
You are in the Paragon Shell operational mode.
In the login message that appears, each node in the cluster is referred to as a controller. This first VM from where you create the cluster is referred to as Controller-1.
-
Exit Paragon Shell by executing the
exitcommand.You are in the Linux root shell now.
-
When prompted whether you want to create a cluster, type y and press Enter.
-
Configure the VIP addresses (general ingress and Test Agent gateway), the IP addresses of Controller-2, Controller-3, and Controller-4 VMs (corresponding to the second, third, and fourth VM created and configured before), the Web admin e-mail address and password, and the NTP server address.
For more information, refer to Deploy the Cluster Using the Deployment Wizard.
-
When prompted whether you want to proceed, type y and press Enter.
-
When prompted, enter the SSH password for the VMs, enter the same password that you configured to log in to the VMs.
The cluster deployment begins. The deployment takes around an hour to complete.
-
Upon successful completion of the deployment, the application cluster is created and you are logged in to Paragon Shell.
The console output displays the four Controller IP addresses, the Paragon Active Assurance Test Agent gateway VIP address, the Web admin user e-mail address, and the Web UI IP address.
Welcome to Juniper Paragon Automation This VM 172.16.154.95 is part of an on-prem system. ========================================================================= Controller IP : 172.16.154.93, 172.16.154.94, 172.16.154.95, 172.16.154.96 PAA Virtual IP : 172.16.154.99 UI : https://172.16.154.97 Web Admin User : user@domain =========================================================================
-
Log out of the node VM and log in again to Paragon Shell to see the updated command prompt.
The CLI command prompt displays your log in user name and the node hostname that you configured previously.
-
(Optional) Configure SMTP-based user management. To configure SMTP, perform the steps described in Configure SMTP Settings in Paragon Shell.
-
(Optional) Upload custom user certificates. To configure Paragon Automation to use custom user certificates, perform the steps described in Upload User Certificates.
You can now log in to the Paragon Automation GUI by using the Web admin user ID and password.
Log in to Paragon Automation
To log in to the Paragon Automation Web GUI:
-
Enter https://web-ui-ip-address in a browser to open the Paragon Automation login page.
-
Enter the Web admin user e-mail address and password that you configured while deploying Paragon Automation.
The New Account page appears. You are now logged into Paragon Automation. You can now create organizations, sites, and users.
Add an Organization, a Site, and Users
Add an Organization
After you log in to the Paragon Automation GUI for the first time after installation, you must create an organization. After you create the organization, you are the superuser for the organization.
You can add only one organization in this release. Adding more than one organization can lead to performance issues and constrain the disk space in the Paragon Automation cluster.
To create an organization:
After you create an organization, you can add sites and users to the organization.
Create a Site
A site represents the location where devices are installed. You must be a superuser to add a site.
Add Users
The superuser can add users and define roles for the users.
To add a user to the organization:
