| Purpose |
Detect hypervisor redundancy.
|
| Source Processors |
| Hypervisor and connected leaf (generic graph) |
output stage: hypervisor_and_leaf (text set) (generated from
graph)
|
| Hypervisor pnic and vnet (generic graph collector) |
output stage: hypervisor_pnic_vnet (text set) (generated from
graph)
|
|
| Additional Processor(s) |
| Hypervisor and leaf count (set count) |
input stage: hypervisor_and_leaf
output stage: hypervisors_leaf_count (number set)
|
| Hypervisor vnet pnic count (set count) |
input stage: hypervisors_pnic_vnet
output stage: hypervisors_vnet_pnic_count (number set)
|
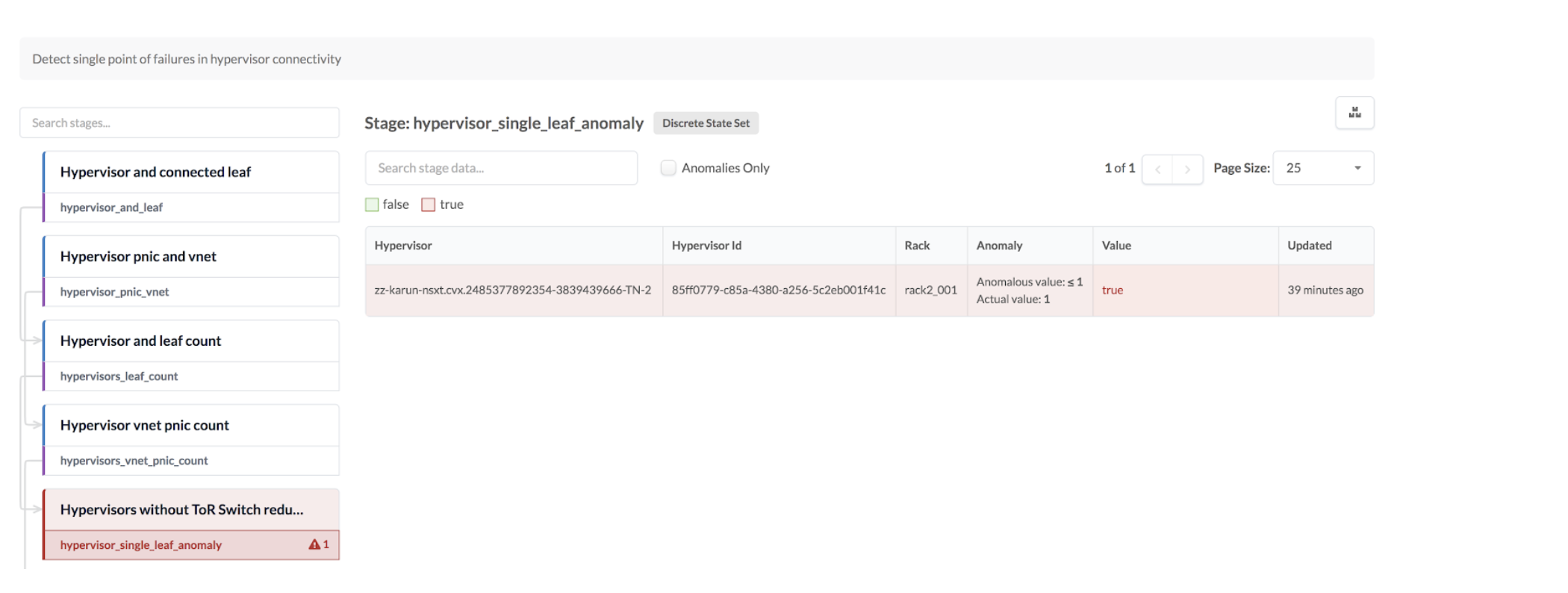
| Hypervisor without ToR Switch redundancy (range) |
input stage: hypervisors_leaf_count
output stage: hypervisor_single_leaf_anomaly (discrete state
set)
|
| Networks without link redundancy (range) |
input stage: hypervisors_vnet_pnic_count
output stage: hypervisor_vnet_single_pnic_anomaly (discrete state
set)
|
|
| Example Usage |
NSX-T Integration - an anomaly is raised in cases without redundancy
or a single point of failure (SPOF) in hypervisor connectivity. Examples
include:
- NSX-T transport nodes with a single non-LAG uplink towards ToR leaf
devices in the fabric can result in a single point of failure (SPOF) for
overlay traffic.
- NSX-T transport nodes with a single LAG uplink with both members going
to a single ToR leaf can result in a single point of failure
(SPOF).
- Lack of redundancy between fabric LAG dual-leaf devices and ESXi
hosts.
 |
For more information about this probe, from the blueprint, navigate to
Analytics > Probes, click Create
Probe, then select Instantiate Predefined Probe
from the drop-down list. Select the probe from the Predefined
Probe drop-down list to see details specific to the probe.

