ON THIS PAGE
Step 2: Up and Running
Access the Apstra GUI
From the latest web browser version of Google Chrome or Mozilla FireFox, enter the URL
https://<apstra_server_ip>where<apstra_server_ip>is the IP address of the Apstra server (or a DNS name that resolves to the IP address of the Apstra server).If a security warning appears, click Advanced and Proceed to the site. The warning occurs because the SSL certificate that was generated during installation is self-signed. We recommend that you replace the SSL certificate with a signed one.
- From the log in page, enter the username and password. The username is admin and the password is the secure password that you created when configuring the Apstra server. The main Apstra GUI screen appears.
Design Your Network
The Apstra design process is highly intuitive because you base your design on physical building blocks such as ports, devices, and racks. When you create these building blocks and specify what ports are used, Apstra has all the information it needs to come up with a reference design for your fabric. Once your design elements, devices and resources are ready, you can start staging your network in a blueprint.
- Apstra Design Elements
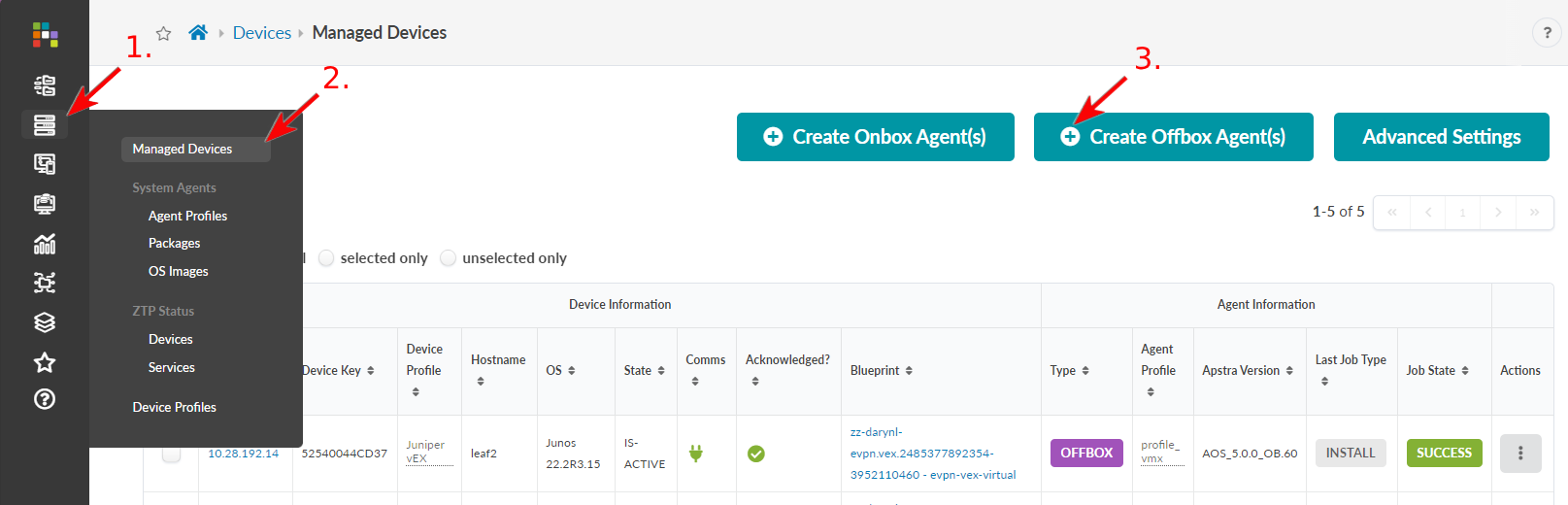
- Install Device System Agents
- Create Resource Pools
- Build Your Network
- Deploy the Network
Apstra Design Elements
At first, you design your fabric using generic building blocks that don't have site-specific details or site-specific hardware. The output becomes a template that you later use in the build stage to create blueprints for all your data center locations. You'll use different design elements to build your network in a blueprint. Keep reading to learn about these elements.
Logical Devices
Logical devices are abstractions of physical devices. Logical devices allow you to create a mapping of the ports you want to use, their speed, and their roles. Vendor-specific information is not included; this lets you plan your network based on device capabilities alone before selecting hardware vendors and models. Logical devices are used in interface maps, rack types and rack-based templates.
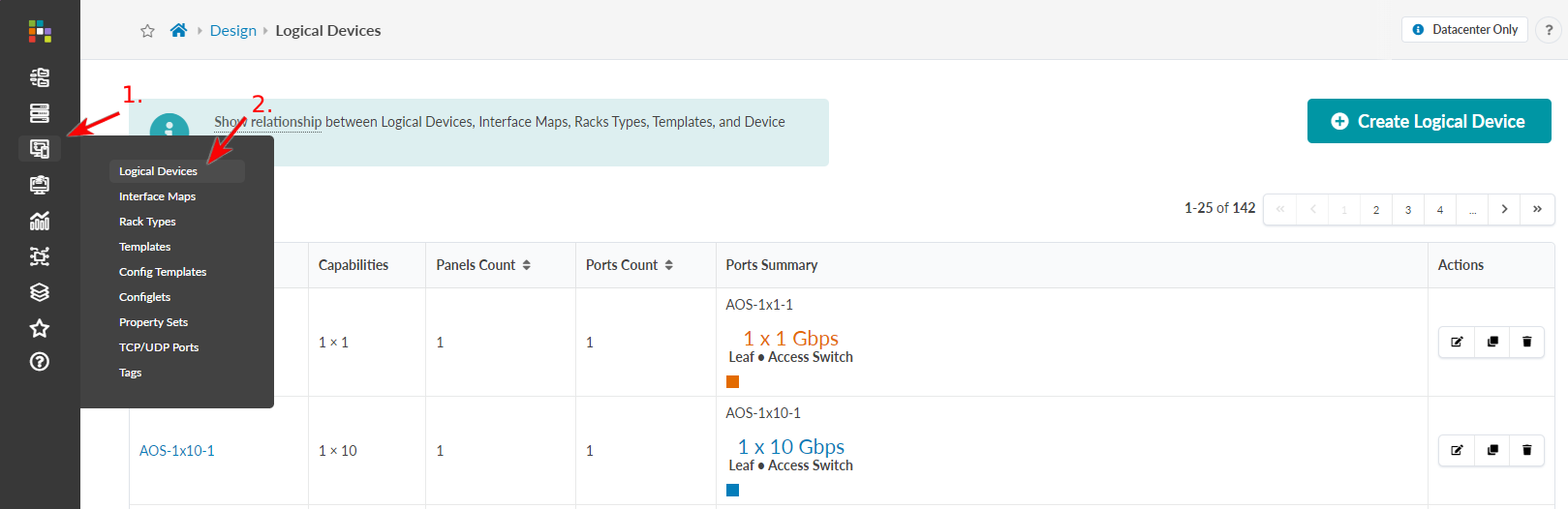
Interface Maps
Interface maps link logical devices to device profiles. Device profiles specify hardware model characteristics. By the time you check the design (global) catalog for interface maps, you'll need to know which models you'll be using. You assign interface maps when you build your network in the blueprint.
Rack Types
Rack types are logical representations of physical racks. They define the type and number of leafs, access switches and/or generic systems (unmanaged systems) in racks. Rack types don't specify vendors, so you can design your racks before selecting hardware.
Templates
Templates specify a network's policy and structure. Policies can include ASN allocation schemes for spines, overlay control protocol, spine-to-leaf link underlay type and other details. The structure includes rack types, spine details and more.
Install Device System Agents
Create Resource Pools
-
From the left navigation menu, navigate to Resources > IP
Pools and click Create IP Pool.
- Enter a name and valid subnet. To add another subnet, click Add a Subnet and enter the subnet.
- Click Create to create the resource pool and return to the summary view.
Build Your Network
When you've got your design elements, devices and resources ready, you can start staging your network in a blueprint. Let's create one now.
Create a Blueprint
-
From the left navigation menu, click
Blueprints, then click Create
Blueprint.

- Type a name for the blueprint.
- Select Datacenter reference design.
- Select a template type (all, rack-based, pod-based, collapsed).
- Select a template from the Template drop-down list. A preview shows template parameters, a topology preview, network structure, external connectivity, and policies.
-
Click Create to create the blueprint and
return to the blueprint summary view. The summary view shows the
overall status and health of your network. When you meet all the
requirements for building the network, the build errors are resolved
and you can deploy the network. We'll start by assigning
resources.
Assign Resources
- From the blueprint summary view, click the blueprint name to go to the blueprint dashboard. After you deploy your blueprint, this dashboard will show details about the status and health of your networks.
- From the top navigation menu of the blueprint, click Staged. This is where you'll build your network. The Physical view appears by default, and the Resources tab in the Build panel is selected. Red status indicators mean that you need to assign resources.
-
Click one of the red status indicators, then click the
Update assignments button.
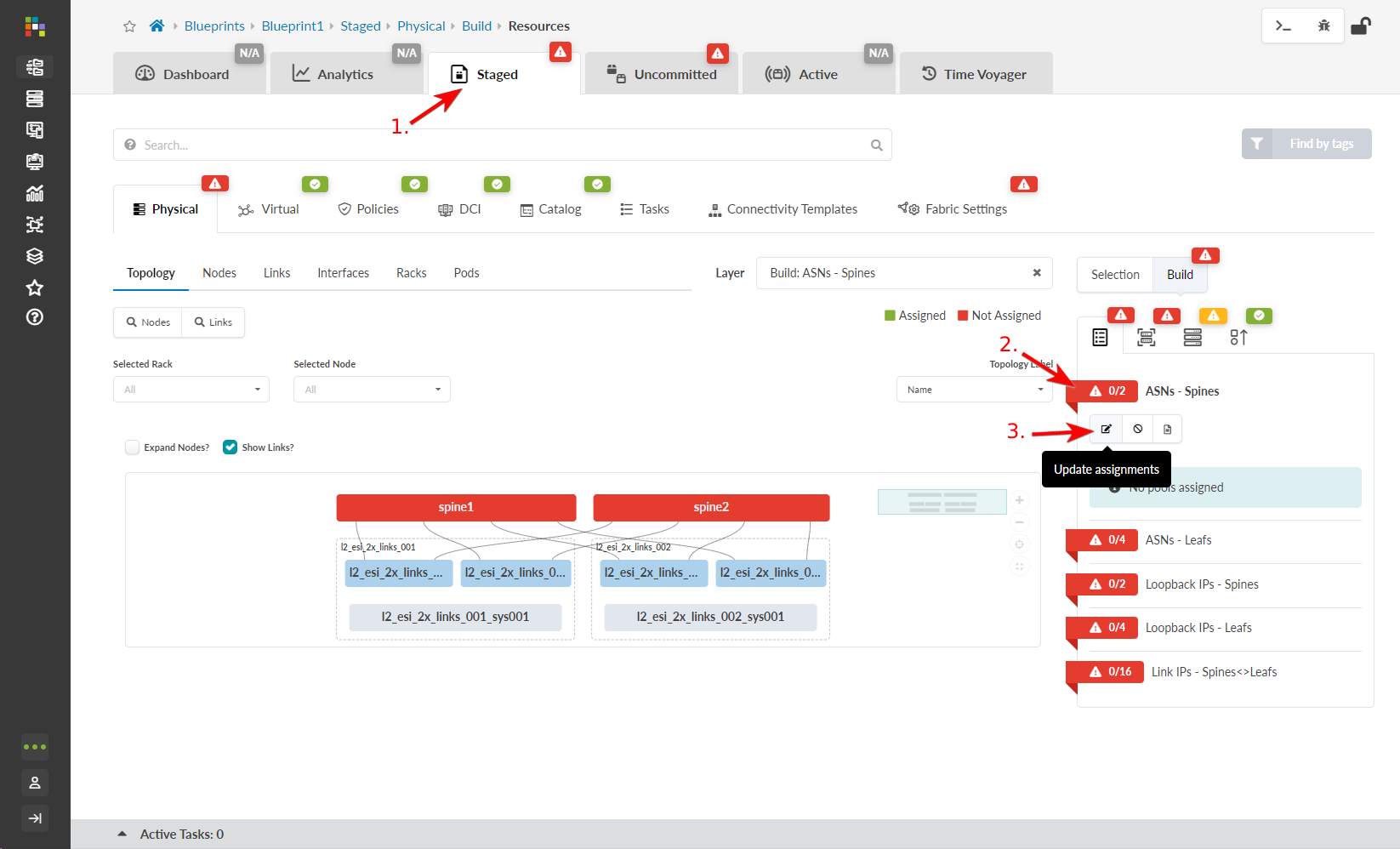
- Select a resource pool (that you created earlier), then click the Save button. The required number of resources are automatically assigned to the resource group from the selected pool. When the red status indicator turns green, the resources are assigned. Changes to the staged blueprint aren't pushed to the fabric until you commit your changes. We'll do that when we're done building the network.
- Continue assigning resources until all status indicators are green.
Assign Interface Maps
-
In the Build panel, click the
Device Profiles tab.
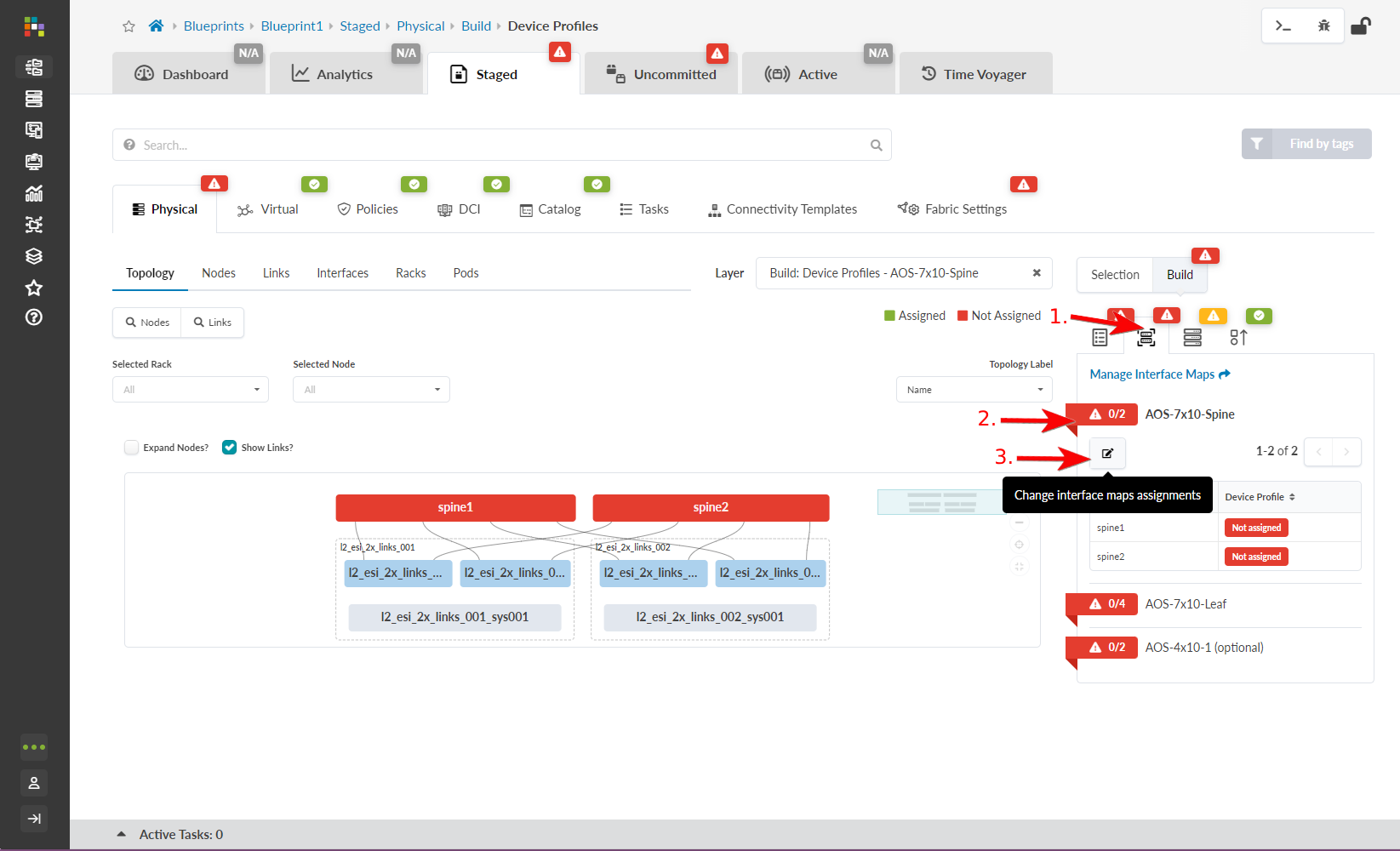
- Click a red status indicator, then click the Change interface maps assignments button (looks like an edit button).
- Select the appropriate interface map for each node from the drop-down list, then click Update Assignments. When the red status indicator turns green, the interface maps have been assigned.
- Continue assigning interface maps until all the required status indicators are green.
Assign Devices
-
In the Build panel, click the
Devices tab.
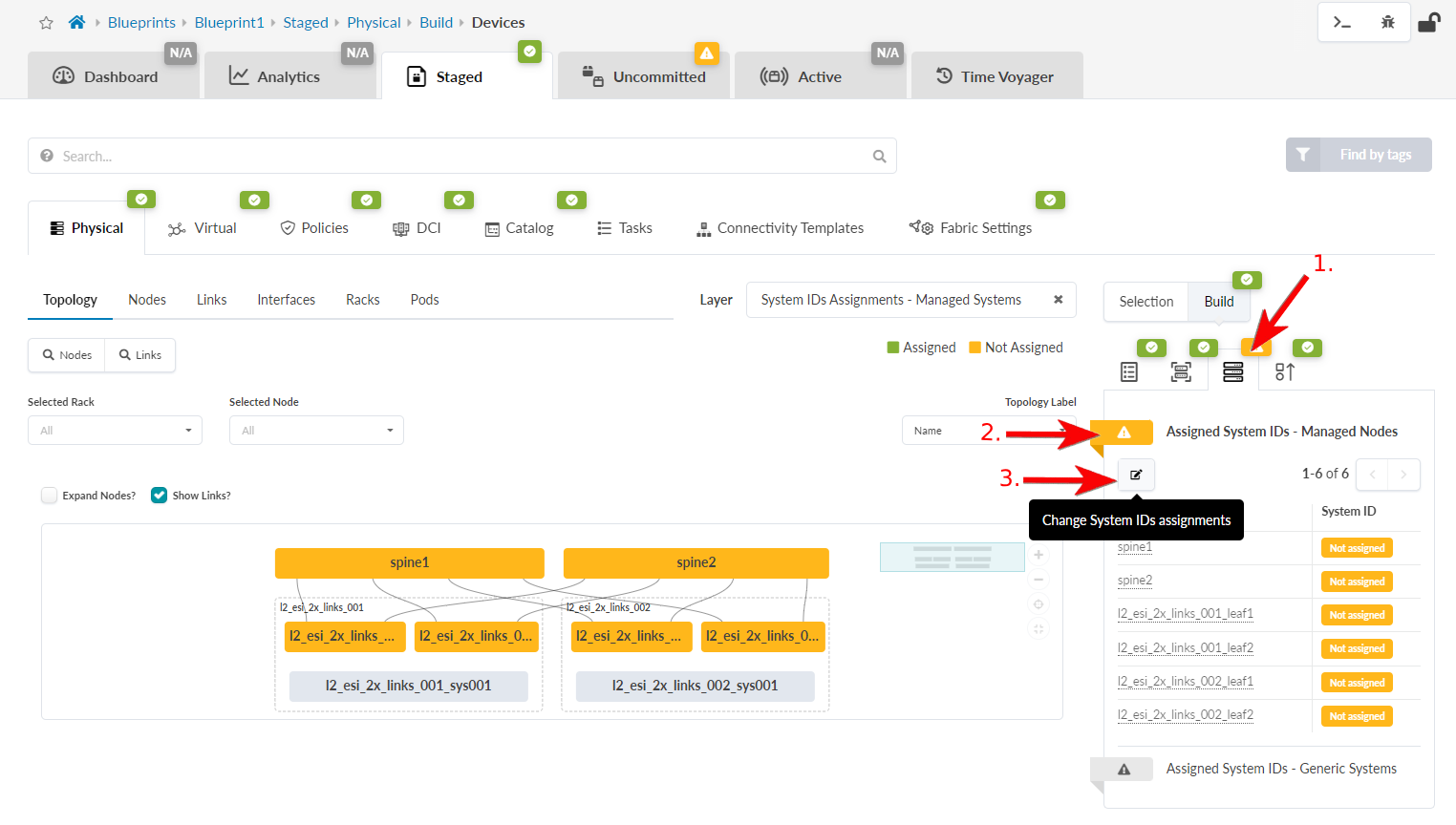
- Click the status indicator for Assigned System IDs (if the nodes list is not already displayed). Unassigned devices are indicated in yellow.
- Click the Change System IDs assignments button (below Assigned System IDs) and, for each node, select system IDs (serial numbers) from the drop-down list.
- Click Update Assignments. When the red status indicator turns green, system IDs have been assigned.
Cable Up Devices
-
Click Links (towards the left of the screen)
to go to the cabling map.
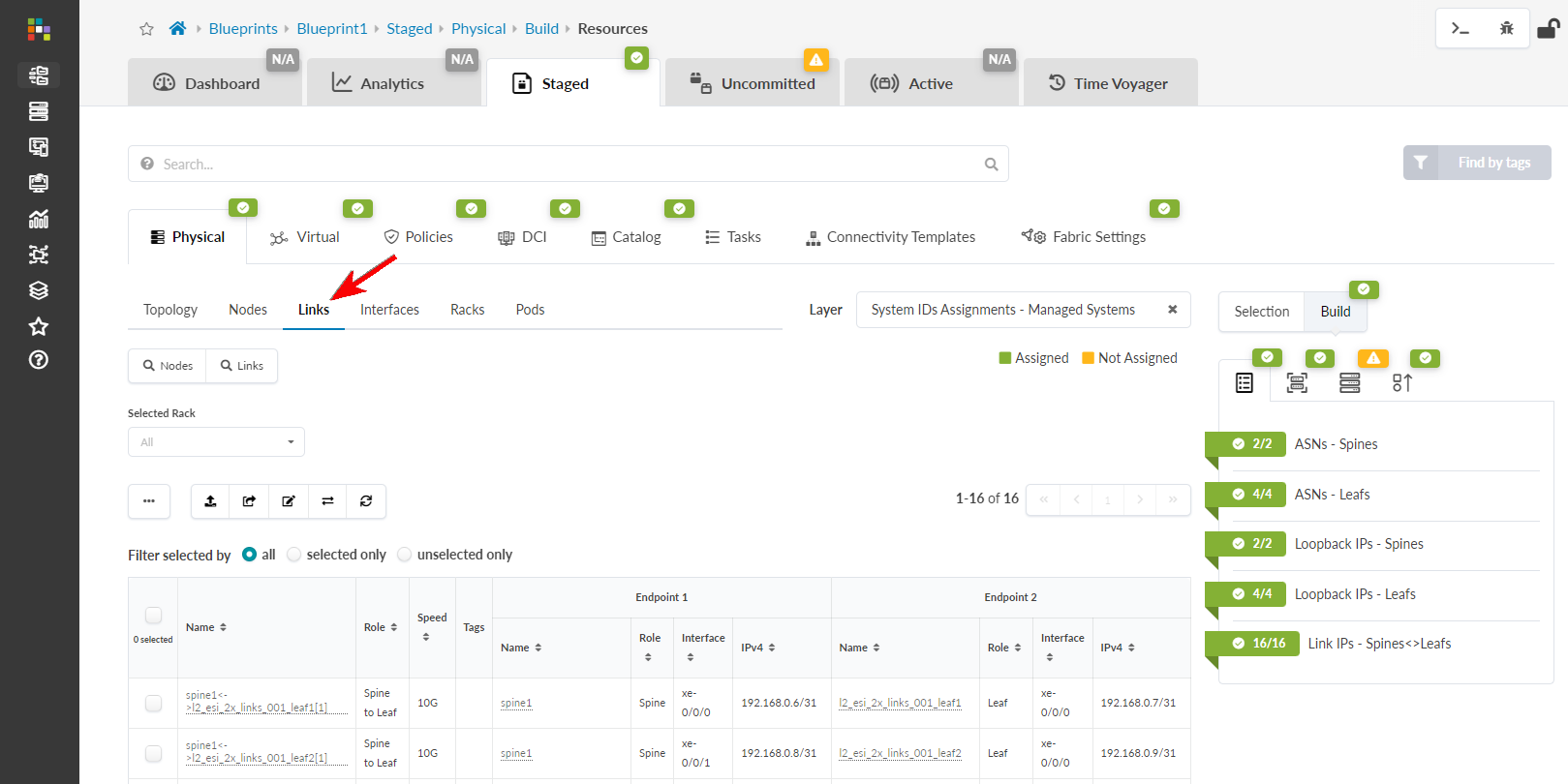
- Review the calculated cabling map and cable up the physical devices according to the map. If you have a set of pre-cabled switches, ensure that you have configured interface maps according to the actual cabling so that calculated cabling matches the actual cabling.
Deploy the Network
-
From the top navigation menu, click Uncommitted
to review staged changes. To see details of changes, click one of the
names in the table.
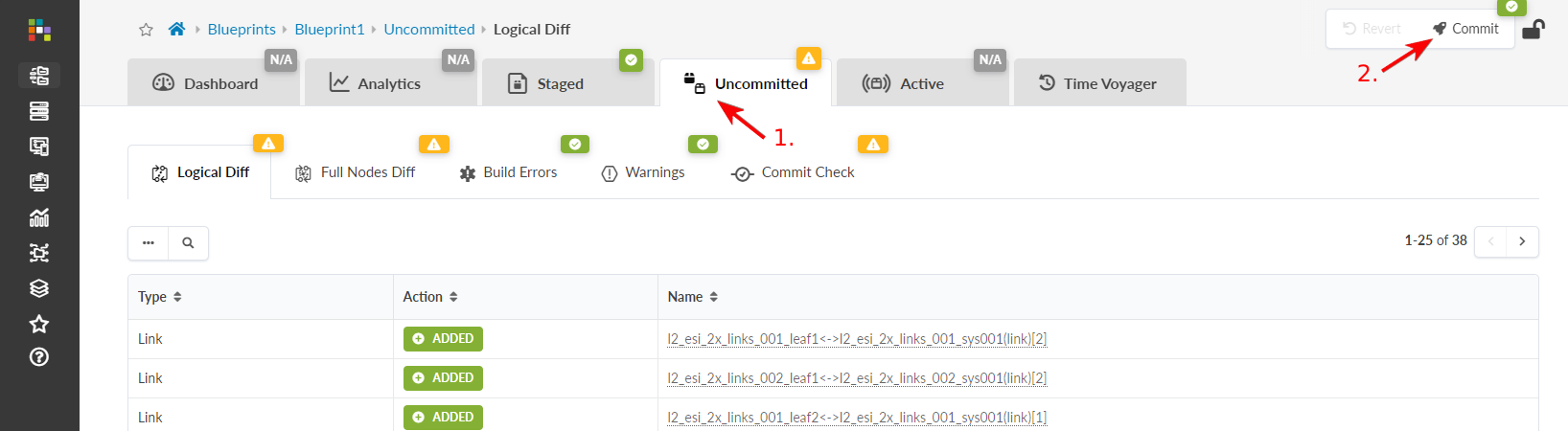
- Click Commit to go to the dialog where you can add a description and commit changes.
- Add a description. When you need to roll back a blueprint to a previous revision, this description is the only information available regarding what has changed.
- Click Commit to push the staged changes to the active blueprint and create a revision.