What are Routing Policies
Routing policies enable you to control (filter) which routes a routing protocol imports into the routing table and which routes a routing protocol exports from the routing table. Routing policies in Apstra include the following details:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Name |
18 characters or fewer. Alphanumeric, _ and - only. |
| Import Policy |
Specify the Import policies to import, either default route only, all routes, or extra routes only.
|
| Extra Import Routes (user-defined) |
User-defined import routes. If you want the default route to be included, make sure you've selected Default for Import Policy (above). If you want only the extra import routes to apply, make sure you've selected Extra Only for Import Policy.
|
| Export Policy |
|
| Extra Export Routes (user-defined) |
User-defined export routes. If you want other export routes to be included, make sure you've selected them under Export Policy (above). If you want only the extra export routes to apply, make sure none of the export policies are selected under Export Policy. Note:
To enable default route for EVPN host routes, go to Staged > Fabric Settings > Fabric Policy. Then, in the Route Options section, enable the Generate EVPN host routes from ARP/IPv6 ND ARP option.
|
| Aggregate Prefixes |
If you have routing zones associated with your routing policy, and aggregate prefixes are supported on the platform (see the feature matrix) you can specify aggregate prefixes. These are the BGP aggregate routes to be imported into the routing zone (VRF) on all border switches. The aggregated routes are sent to all generic system peers in a routing zone (VRF). CAUTION: Routing policies with aggregate prefixes are applied to the entire routing zone. You cannot configure them individually for BGP sessions (per connectivity point). If you do attempt to apply them via a connectivity template (CT), you could receive the error “Protocol endpoint routing policy aggregate prefixes should be empty”. |
| Expect Default IPv4 Route | To add the expectation that the default route is used in the default routing zone, select this check box when you create the policy. (This field applies to the default route in the default routing zone only.) Checking this box does not change any configuration; it generates the expectation and raises an anomaly when the default route is not present. |
| Expect Default IPv6 Route | To add the expectation that the default route is used in the default routing zone, select this check box when you create the policy. (This field applies to the default route in the default routing zone only.) Checking this box does not change any configuration; it generates the expectation and raises an anomaly when the default route is not present. |
| Associated Routing Zones |
Lists any routing zones that are associated with the routing policy. |
| Associated Protocol Endpoints |
Lists any protocol endpoints that are associated with the routing policy. |
From the blueprint, navigate to Staged > Policies > Routing Policies to go to routing policies in the blueprint.
The default routing policy (not shown in table) is associated with the default routing zone. To see details of a routing policy, click its name.
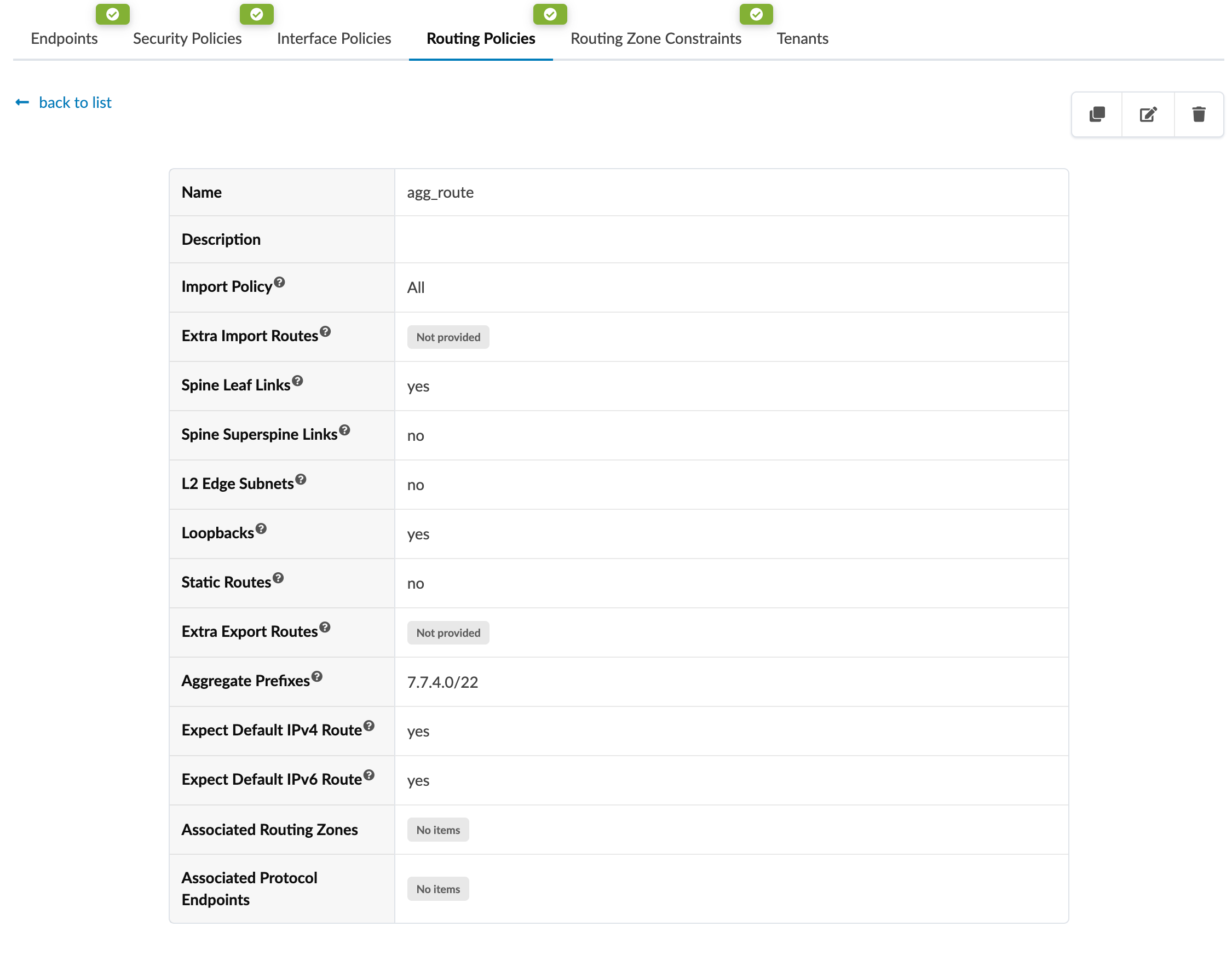
You can't change the default routing policy, but you can create, clone, edit, and delete other routing policies as described in subsequent pages.
