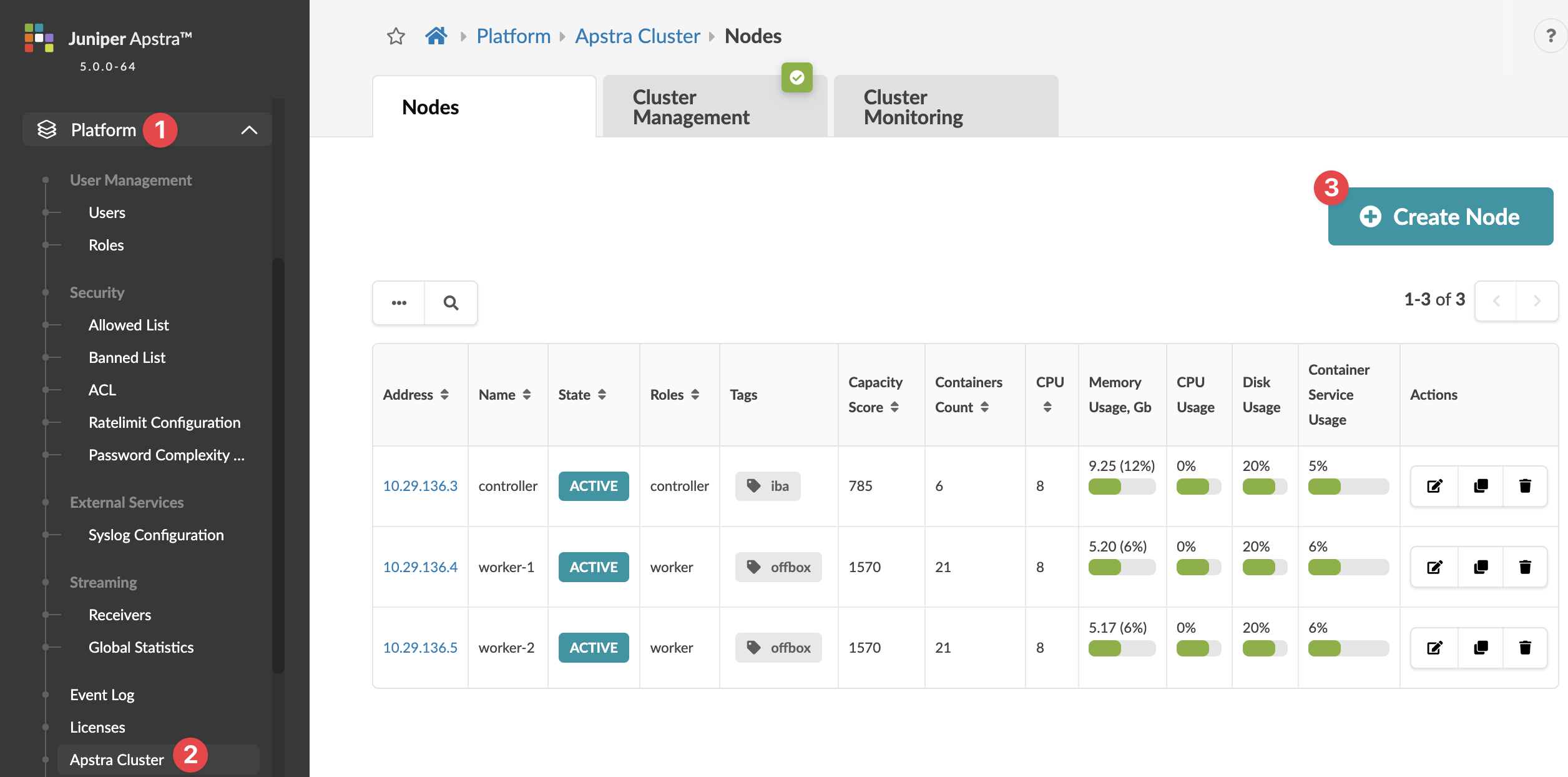
Apstra Cluster Nodes
Nodes Overview
The Apstra controller acts as the cluster manager. When you add a worker VM to the main Apstra controller VM, it registers with the Apstra server VM through sysDB. It collects facts about the VM (such as core/memory/disk configuration and usage), and launches a local VM container. The Apstra controller VM reacts to REST API requests, configures the worker VM for joining or leaving the cluster, and keeps track of cluster-wide runtime information. It also reacts to container configuration entities and schedules them to the worker VM.
Apstra VM nodes include the following details:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Address | IP address or Fully-Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) of the VM |
| Name | Apstra VM name, such as controller (the main Apstra controller node) or worker - iba (a worker node) |
| State | ACTIVE, MISSING, or FAILED |
| Roles | Controller or worker |
| Tags | The controller node and any worker nodes that you add are tagged
with iba and offbox, by default.
If you delete one or both of these tags or delete a worker node with
one or both of these tags, any IBA and/or offbox containers in that
node automatically move to a VM with those tags. Make sure there is
another node with the tag(s) you’re deleting or the containers will
be deleted when you delete the tag or node. |
| Capacity Score |
Apstra uses the capacity score for load balancing new containers across the cluster of available nodes. It's calculated in relation to the configured application weight of each container based on allocated memory. Example calculation - 64GB of memory allocated for the VM and an application weight of 500MB configured for offbox agents:
The capacity score changes only if the memory allocated to the VM is changed, or if the application weight is changed. |
| Containers Count | Number of containers |
| CPU | Number of CPUs |
| Errors | As applicable. An example of an error is when an agent process has restarted because an agent has crashed. |
| Usage* |
|
| Containers | The containers running on the node and the resources that each container uses |
| Username/Password | Apstra Server VM SSH username/password login credentials |
* If memory utilization exceeds 80%, a warning message appears at the top of all GUI pages. This lets you know that you need to free up or add disk space and/or memory soon, to avoid a critical resource shortage.
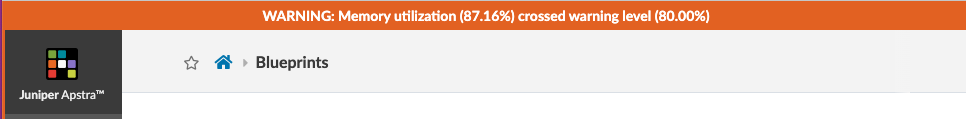
If memory utilization exceeds 90%, a critical message appears at the top of all GUI pages. Before you can make any more changes to the fabric, you must address the shortage by adding disk space to the problematic filesystem(s) or by adding memory, as needed. You can click the link to go to Apstra Cluster Management for more information.
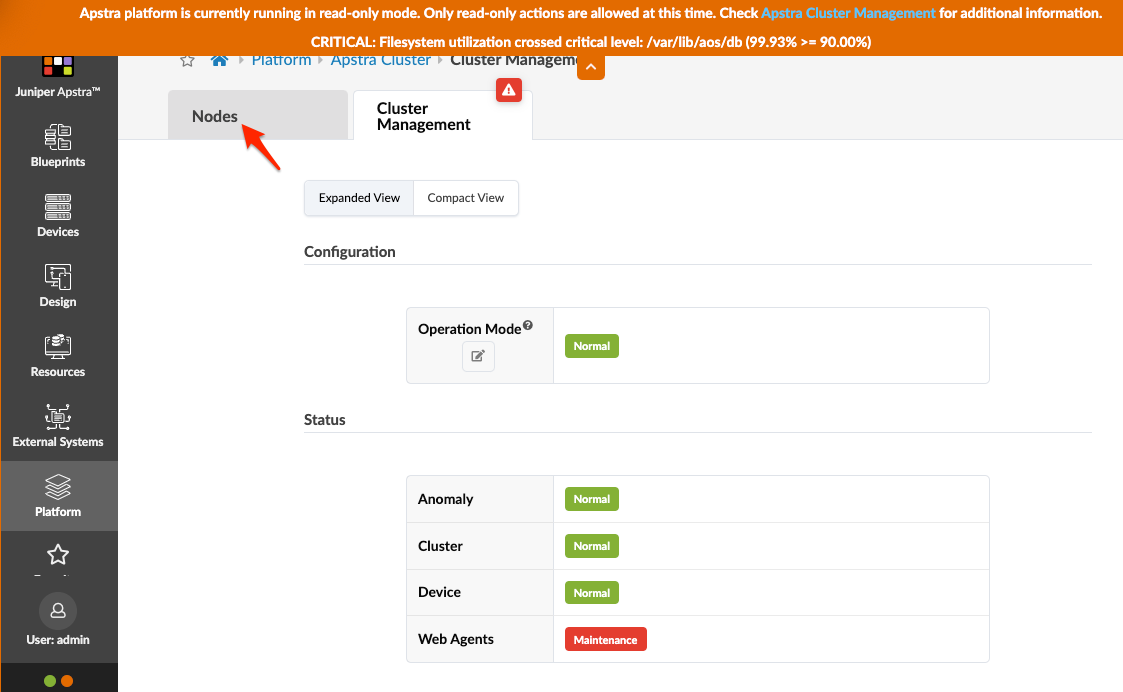
Click the Nodes tab, then click the IP address of the controller for details.
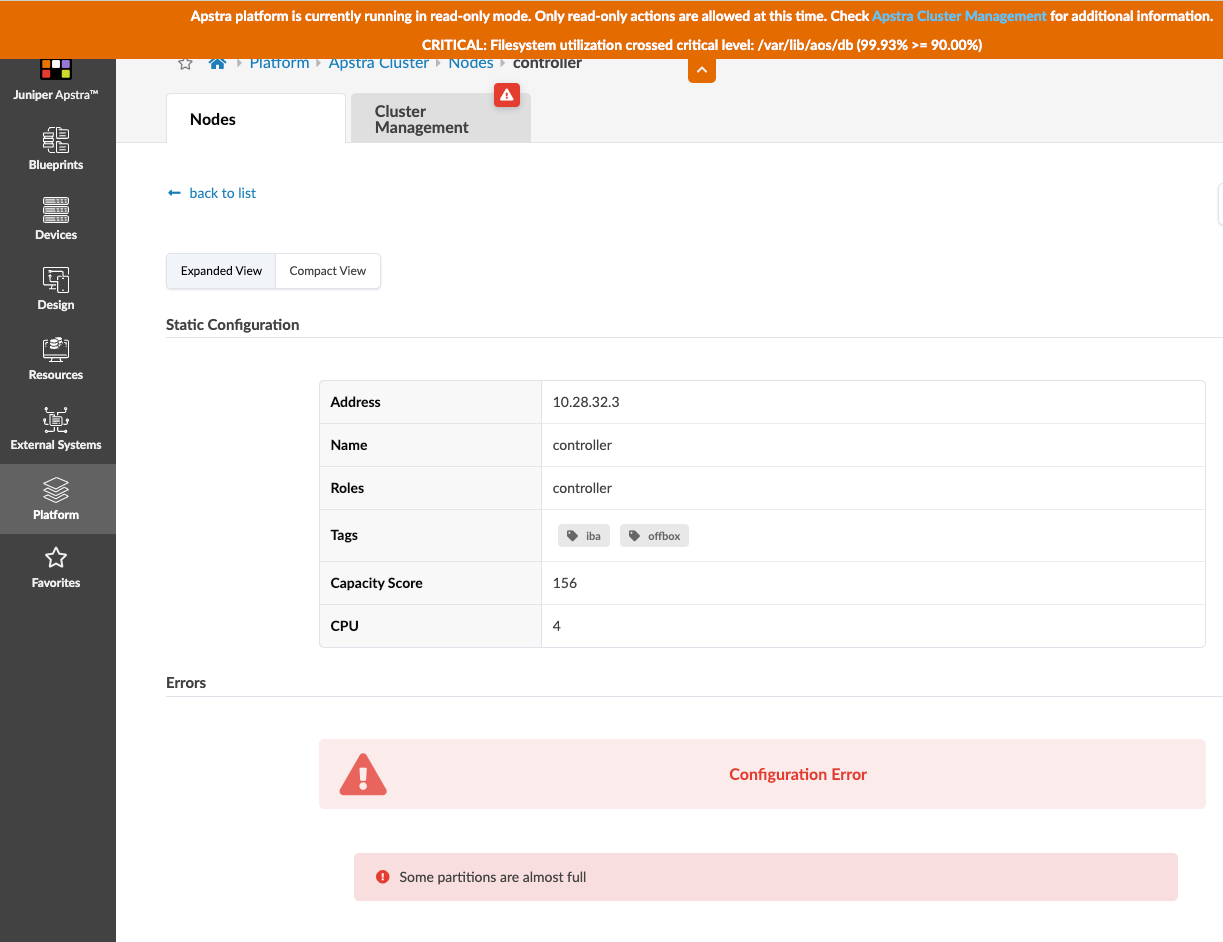
Scroll down to see usage.
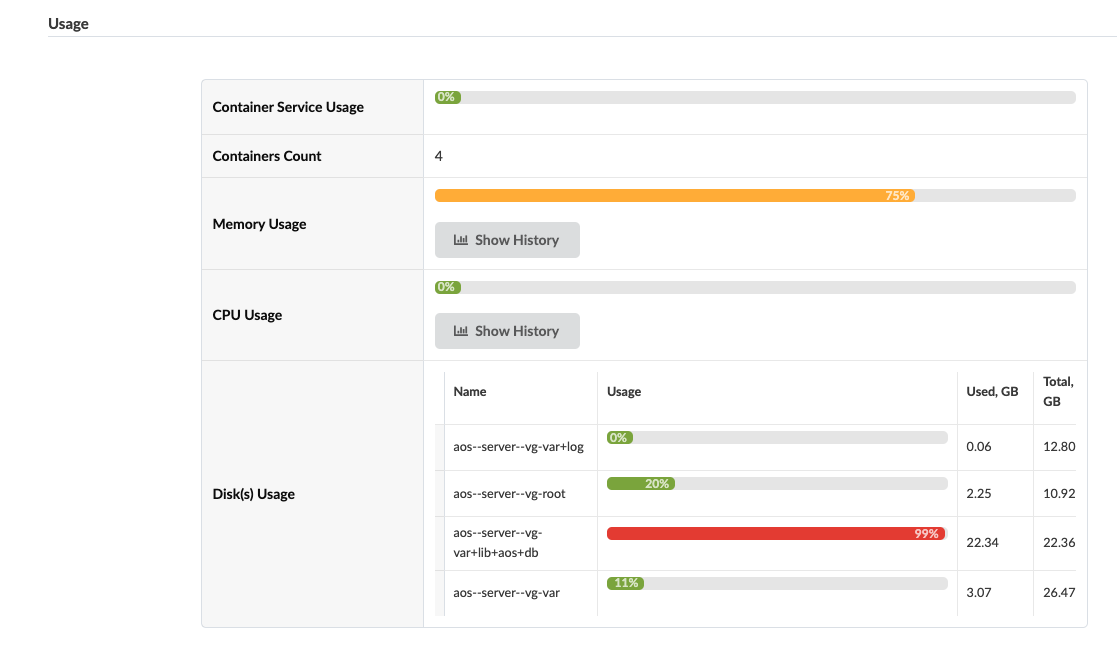
Some suggestions for recovering resources are as follows:
-
Remove the iba tag from the controller VM so that IBA units are rescheduled to worker nodes, thus reducing both memory and disk space usage.
-
Create worker nodes to spread out the load for IBA units and/or offbox device agents.
You can change the default thresholds that trigger warnings and critical messages. In
the Apstra server
configuration file (/etc/aos/aos.conf) change the
options for system_operation_filesystem_thresholds and/or
system_operation_memory_thresholds. Then, send SIGHUP to the
ClusterManager Agent. You can set disk space utilization thresholds on a
per-filesystem basis. For example, you might want to be more conservative with
/var/lib/aos/db which contains MainSysdb's persistence files
and Time Voyager revisions, so crossing a lower usage threshold (such as 85%)
triggers the read-only mode.
To access Apstra VMs, from the left navigation menu, navigate to Platform
> Apstra Cluster. Click a node address to see its details. You
can create, clone, edit and delete Apstra nodes. 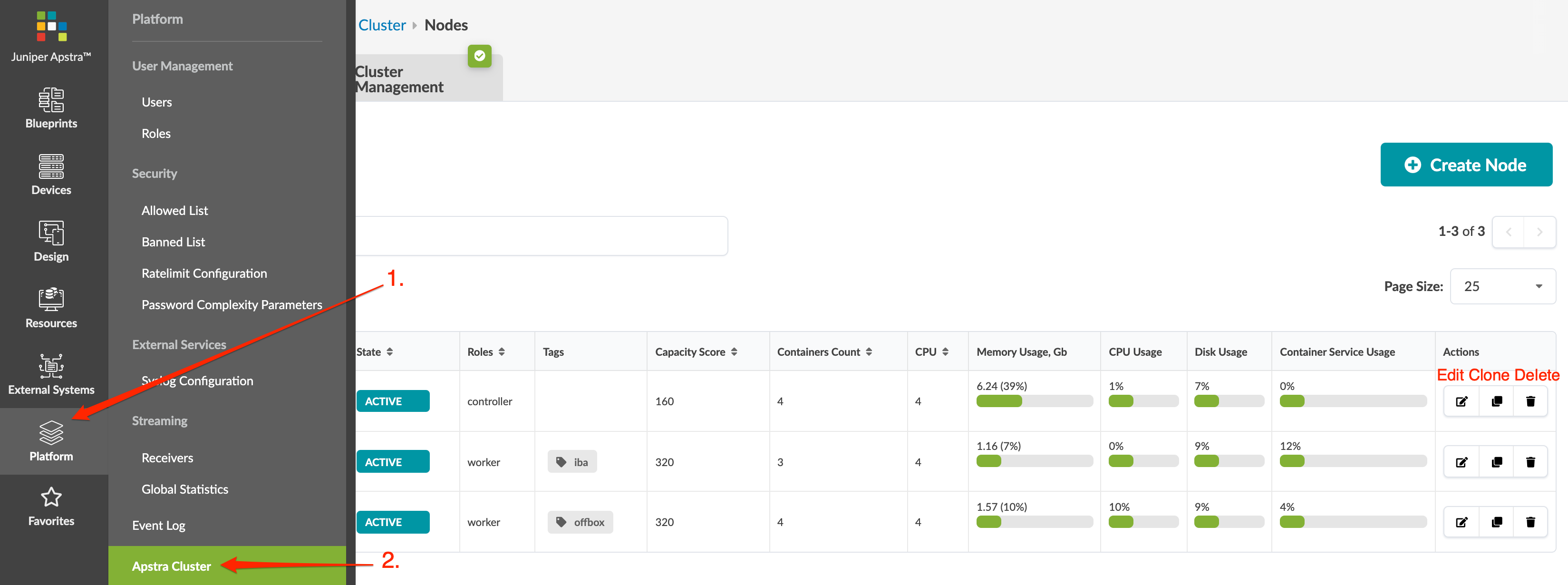
At the bottom left section of every page, you have continuous visibility of platform
health. Green indicates the active state. Red indicates an issue, such as missing
agent, the disk being in read only mode, or an agent rebooting (after the agent has
rebooted, the status returns to active). If IBA Services or
Offbox Agents is green, all containers are launched. If
one of them is red, at least one container has failed. From any page, click one of
the dots, then click a section for details. Clicking
Controller, IBA Services, and
Offbox Agents all take you to
Nodes details.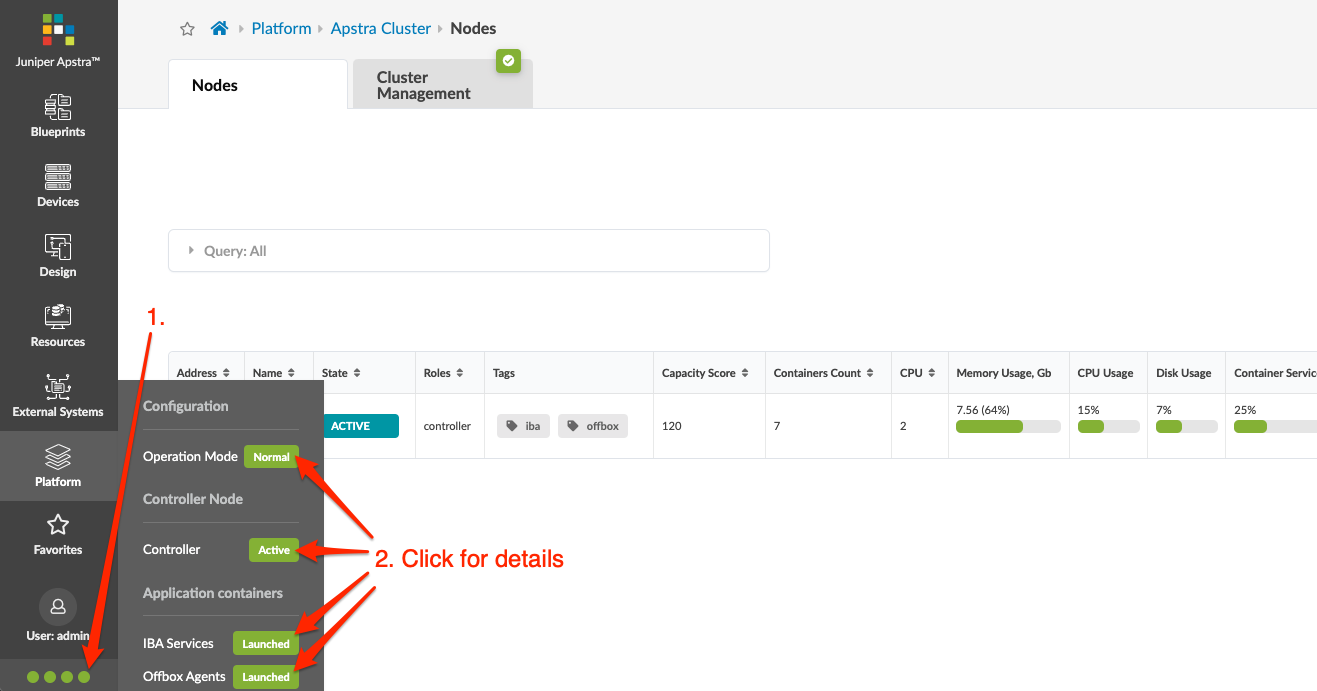
Create Apstra Node
Edit Apstra Node
Delete Apstra Node
When you delete a node that includes iba and/or
offbox tags, the IBA and/or offbox containers (as
applicable) are moved to another node with those tags. Make sure the cluster has
another node with those tags, or the containers will be deleted instead of
moved.
To prevent containers from being deleted, don’t delete nodes with
iba and/or offbox tags unless another
node in the cluster has the same tags.
- Either from the table view (Platform > Apstra Cluster) or the details view, click the Delete button for the Apstra VM to delete.
- Click Delete to delete the Apstra VM.