NSX-T Edge and Connectivity Templates
Overview
Juniper Apstra supports NSX-T Edge connectivity requirements using connectivity templates. Connectivity templates can be used both where NSX-T Edge is hosted on Bare Metal or when used as a virtual machine.
We support VRF lite enabled Tier-0 edge Gateway using connectivity templates.
The use cases below relate to connectivity templates for NSX-T 3.0 Edge:
Set Up NSX-T Tier-0 Router BGP peering
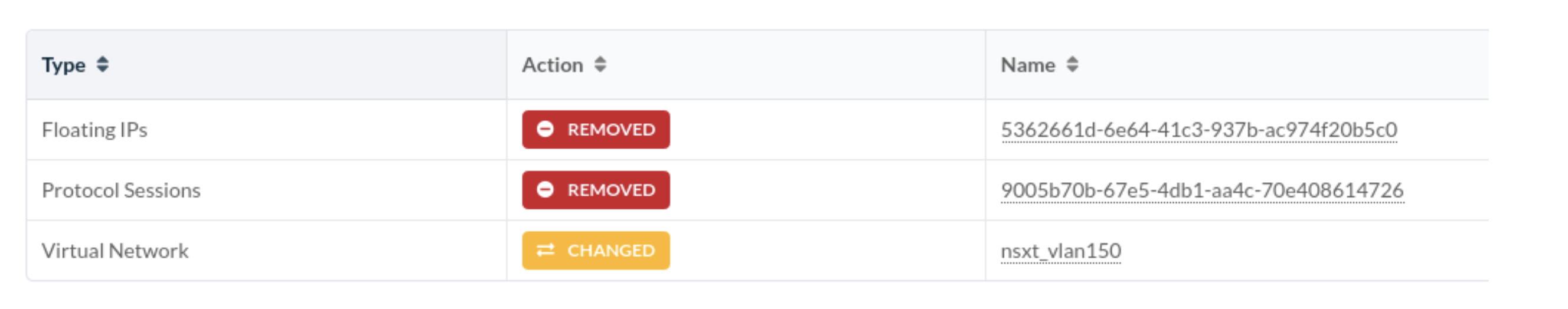
Let's say NSX-T Edge VM uplinks are connected to ToR leaf devices via VLAN Transport
Zone which provides uplink network connectivity to physical infrastructure. Then
Edge VM will also have vmnics as per below screenshot which will help for tunnelling
traffic between Transport Nodes. This is called Overlay Transport Zone. 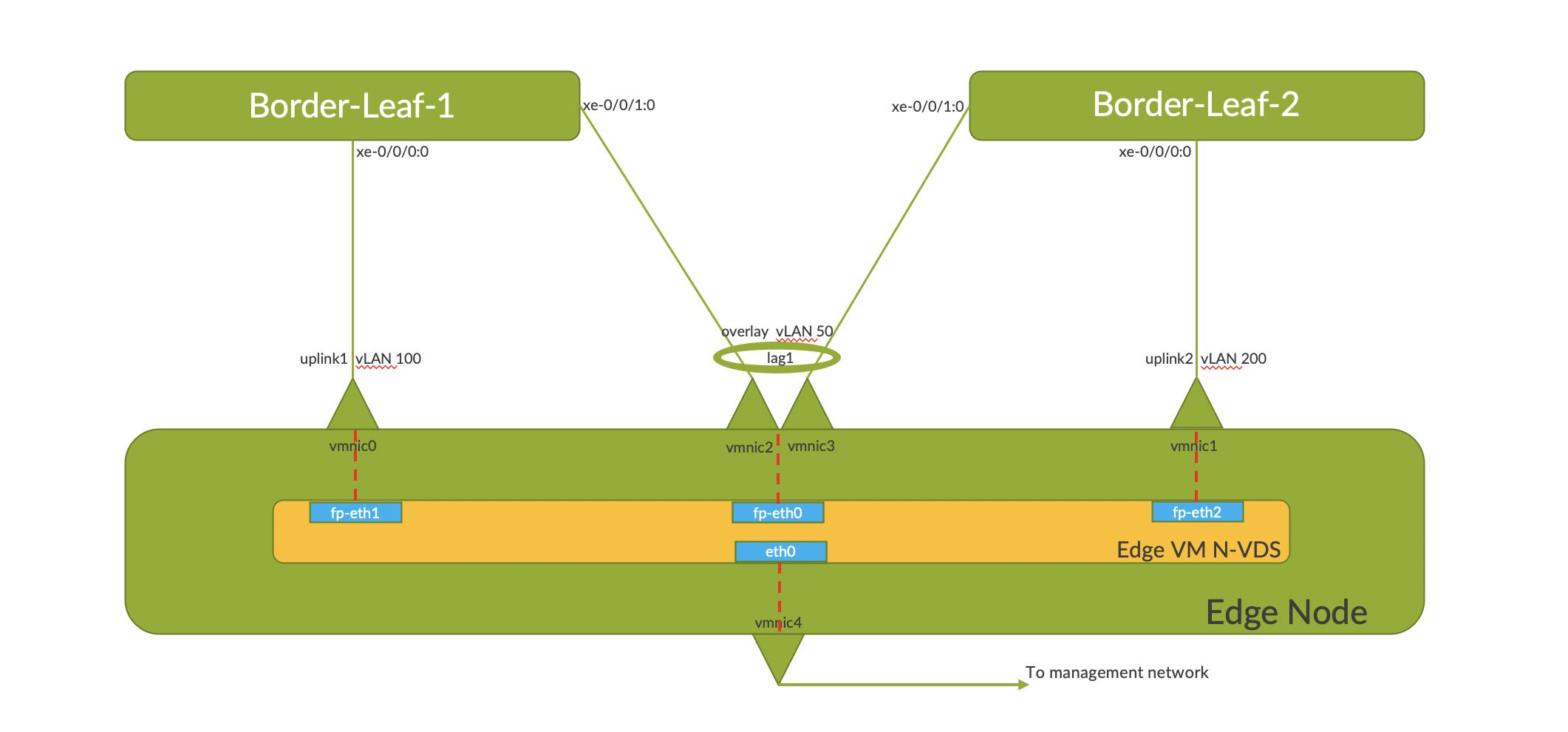
-
Create three Distributed Port Groups for respective vmnics and VLAN Trunking to be enabled on all the Nodes as per the networking depicted in previous screenshot.
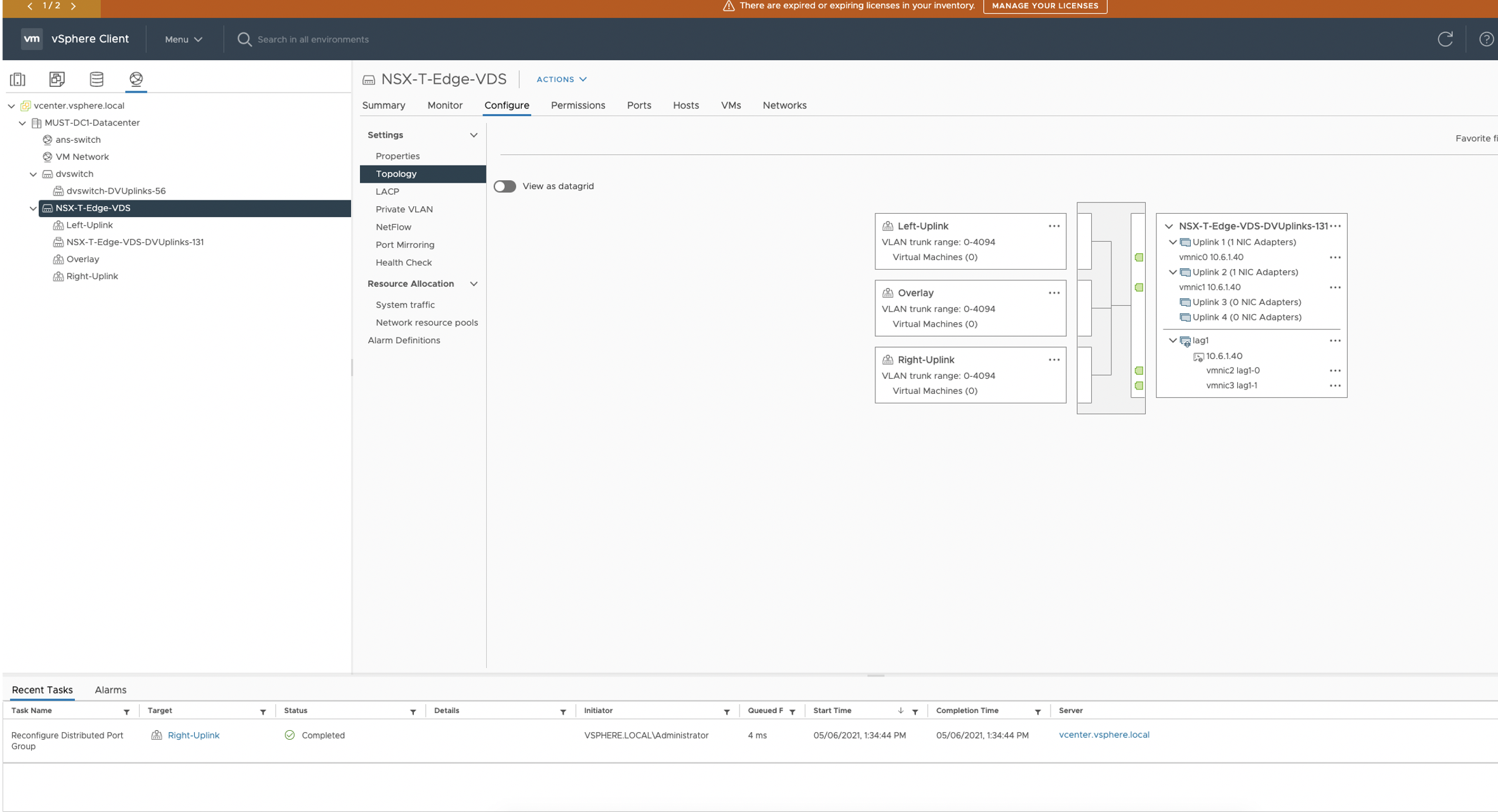
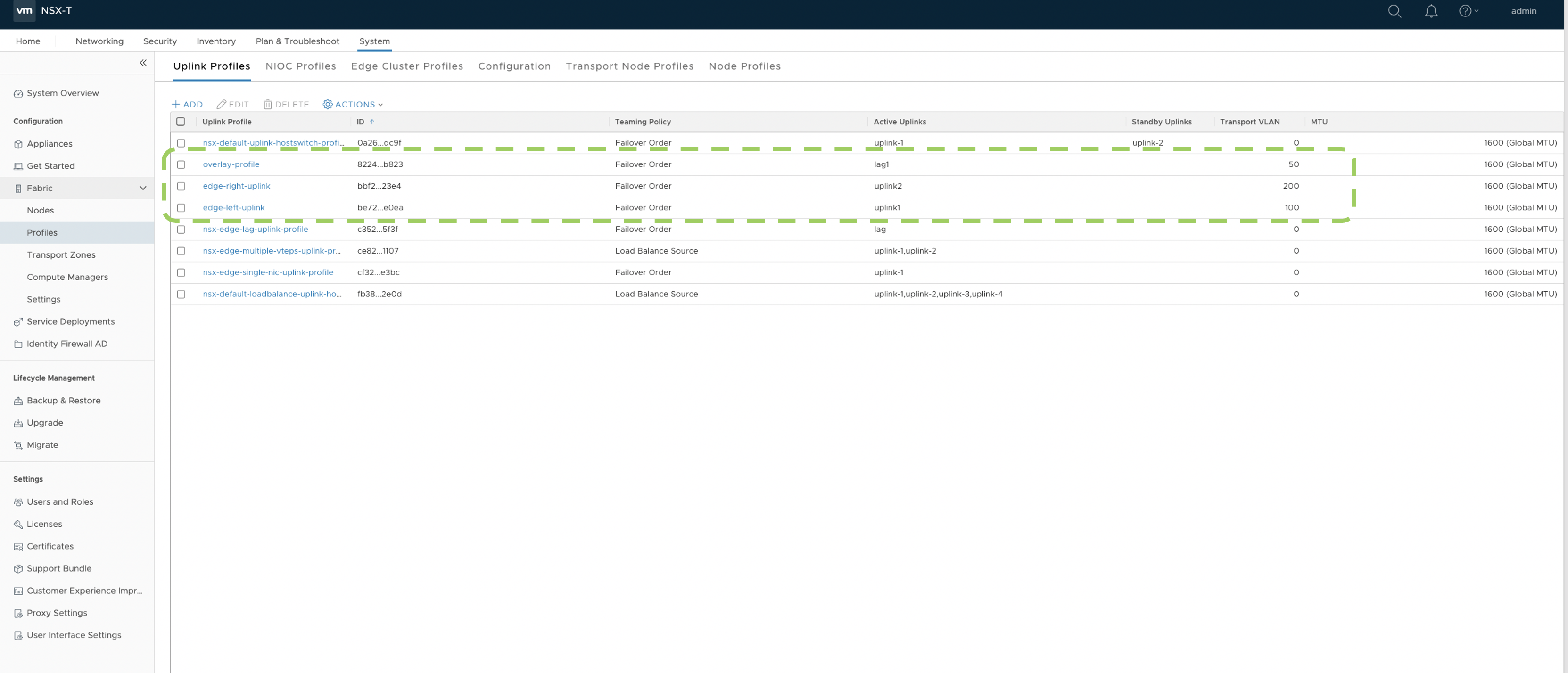
- Create respective Uplink profiles for Overlay and VLAN Transport Zones in NSX
Manager(UI).
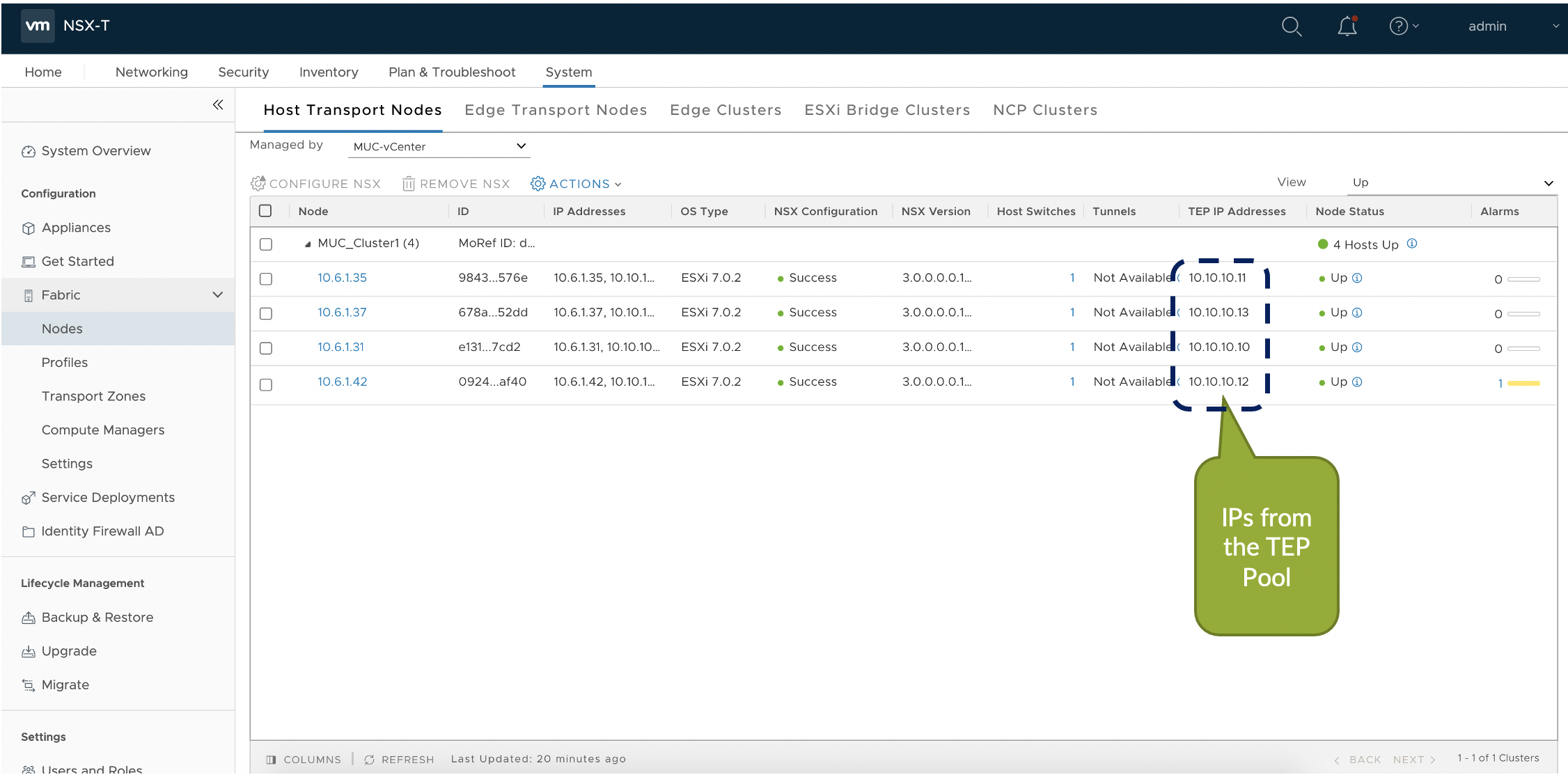
- After NSX-T is configured on the Transport nodes, a Tunnel endpoint(TEP) IP pool
is created in the NSX UI as below:
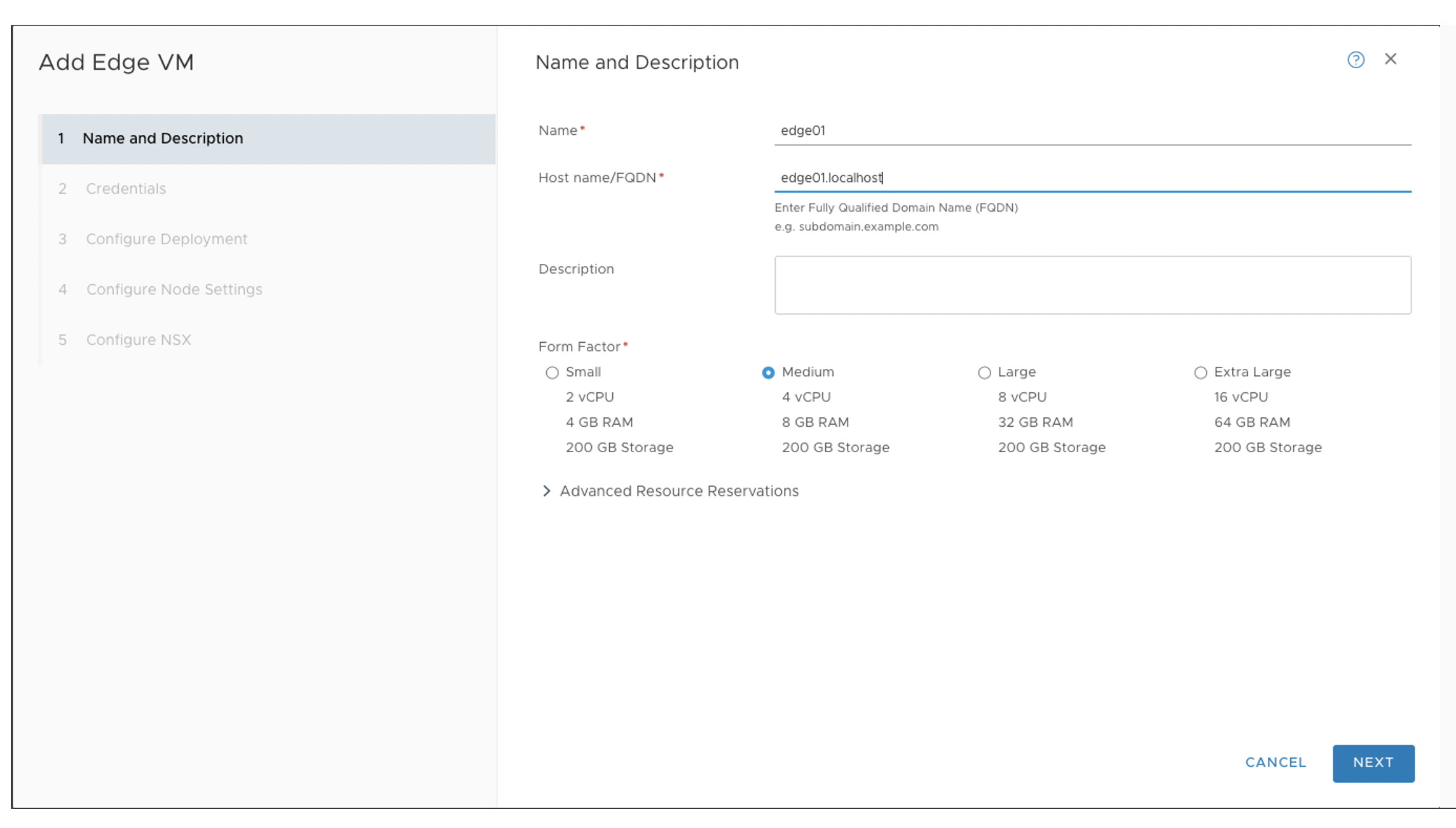
- Now create the NSX-T Edge VM in NSX Manager UI as below. It is used as the
device for north-south communication and BGP peering with Juniper Apstra Fabric.
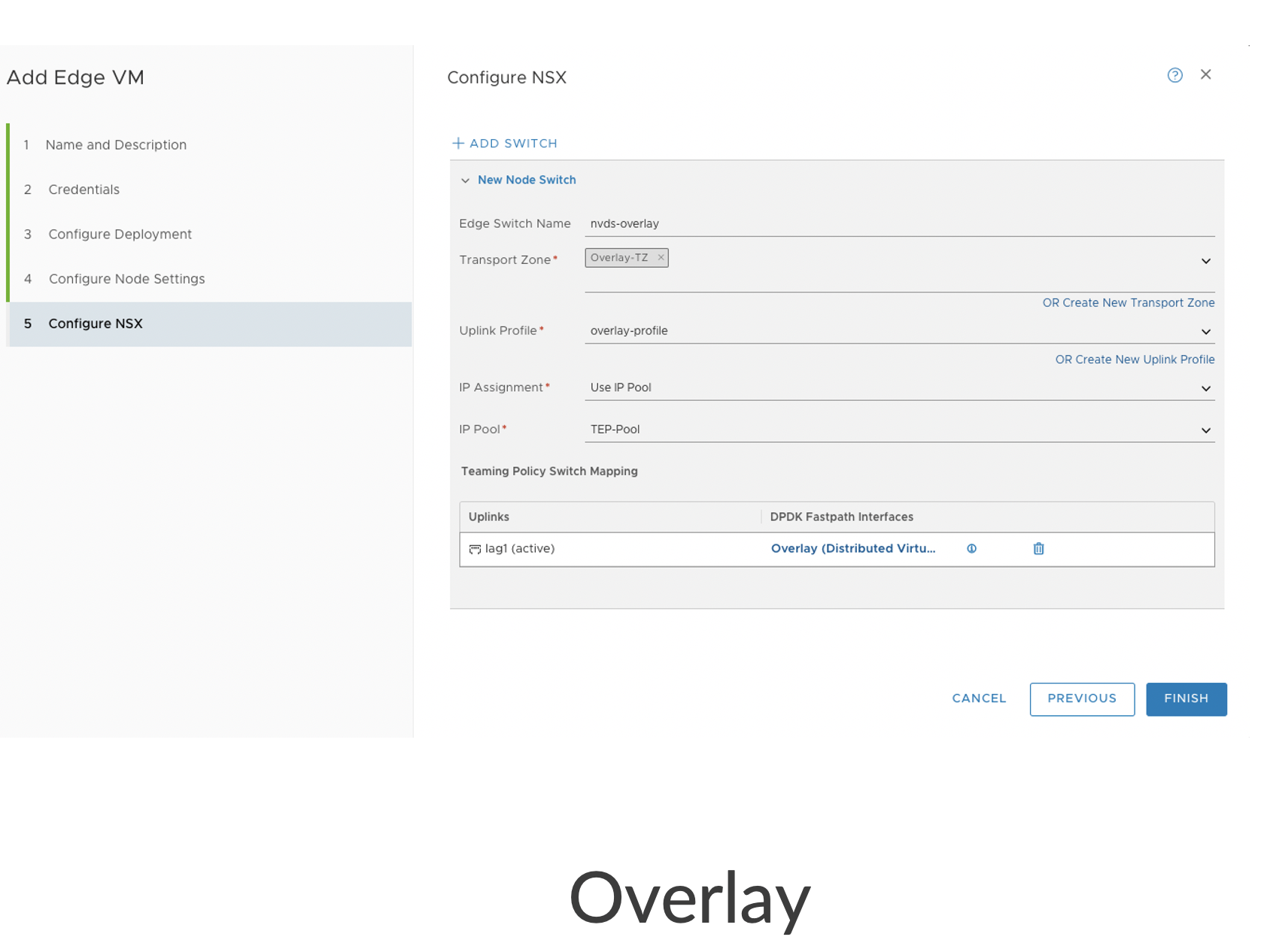
Also configure VDS on the Edge Nodes under NSX Manager(UI) for respective
overlay and Uplink interfaces.
-
Tier-0 Gateway in the NSX-T Edge cluster provides a gateway service between the logical and physical network. In NSX Manager create T0 Gateway which connects to the ToR Leaf via BGP to communicate with the rest of Juniper Apstra Fabric.
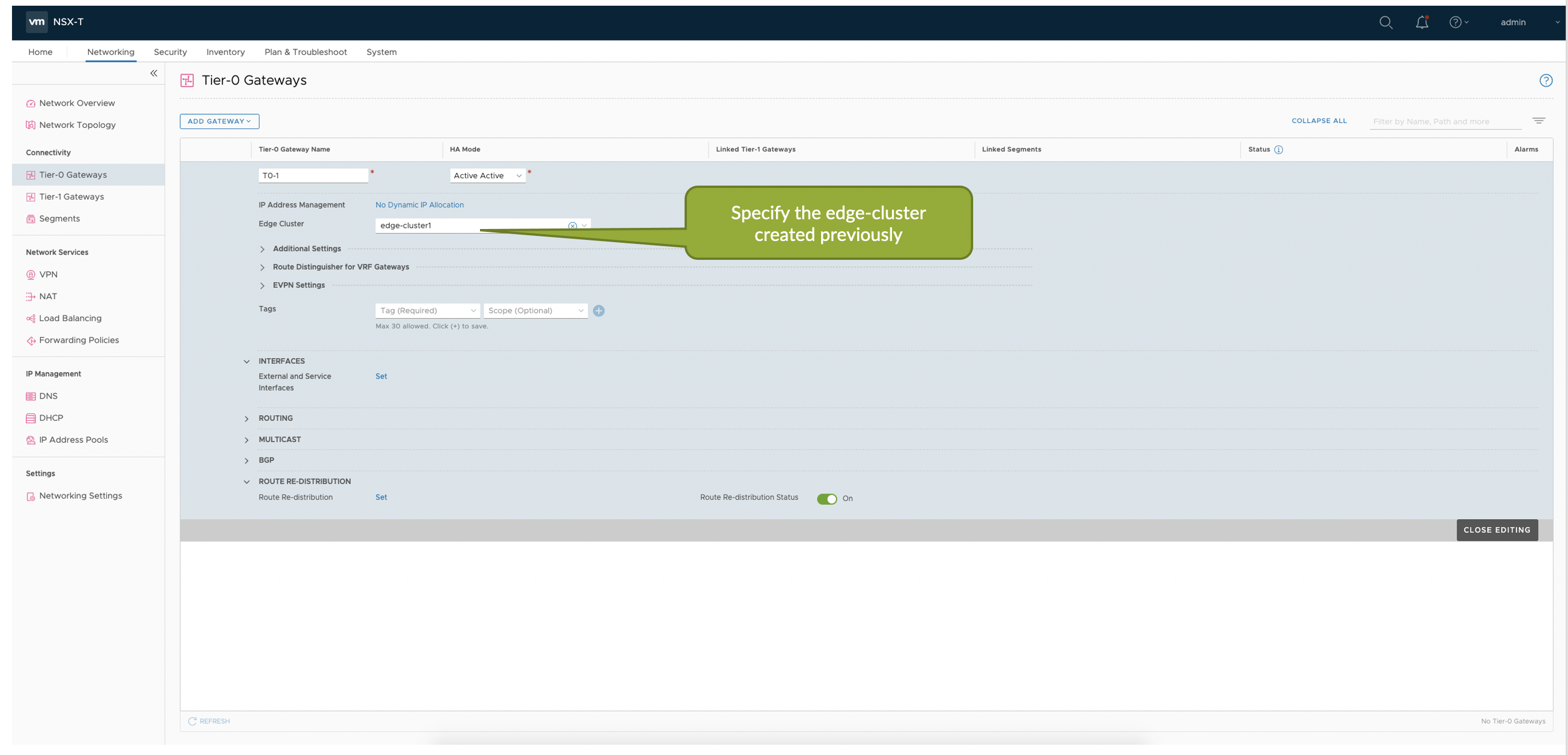
- Add External interfaces to the T0 GW which maps to the Uplink segments
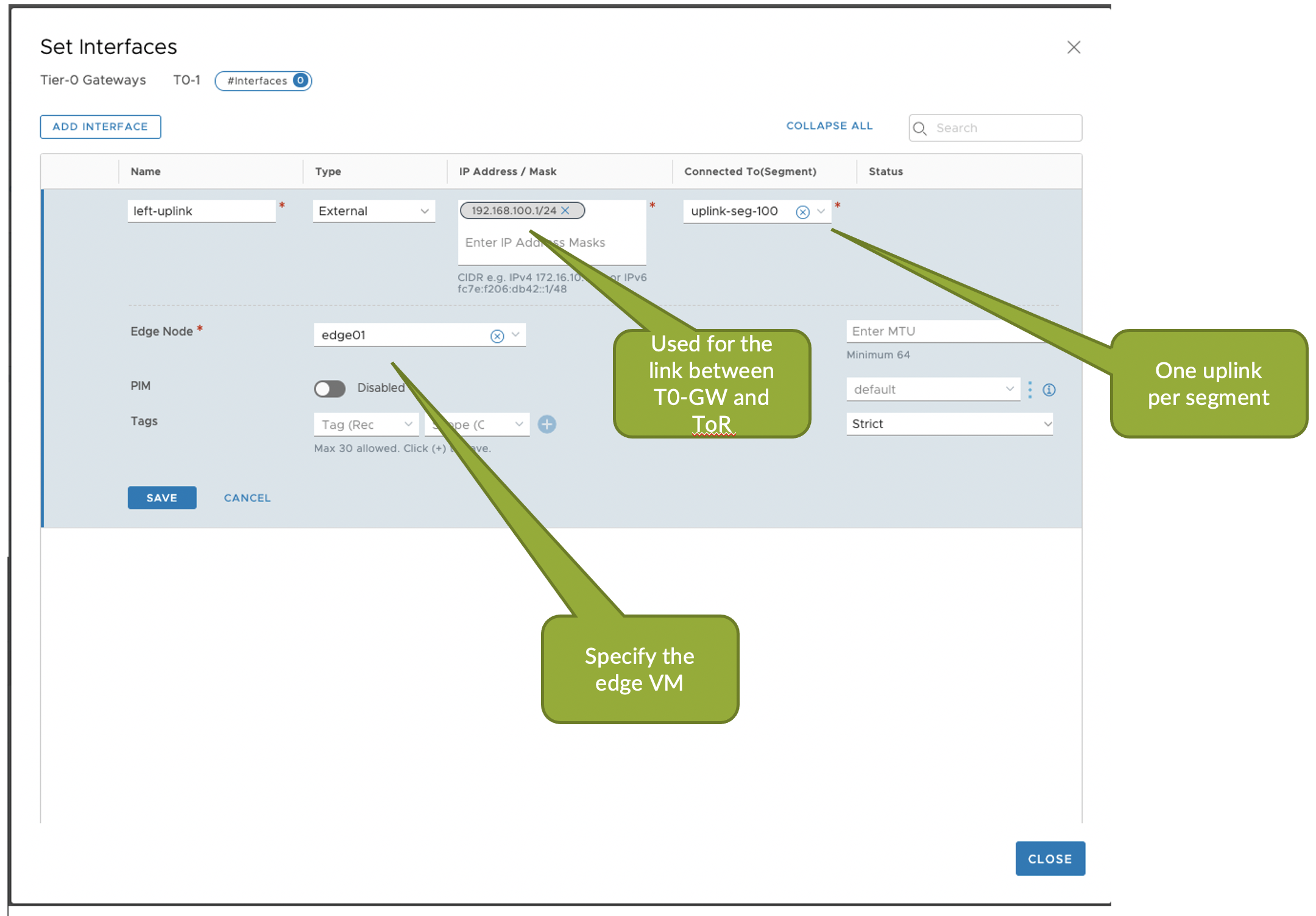
- Configure BGP peering on NSX T0 GW towards Juniper Apstra Fabric in NSX Manager.
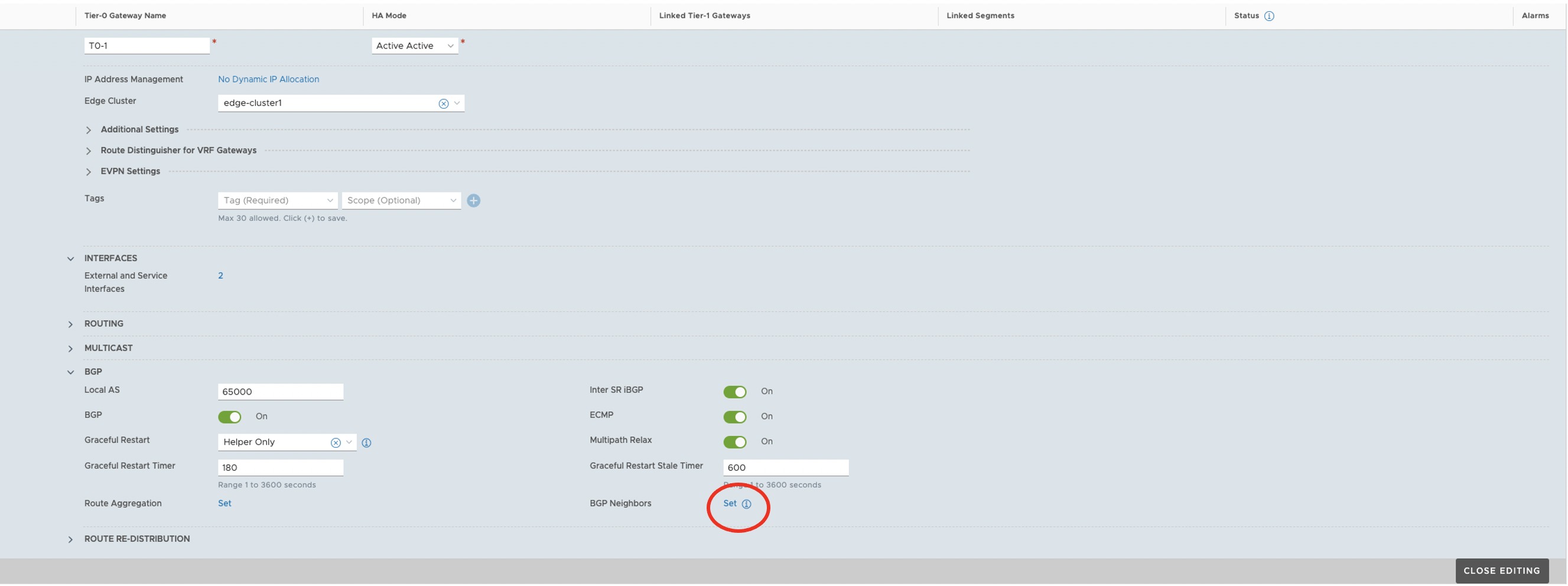
- For NSX-T integration with Juniper Apstra, see NSX-T Integration
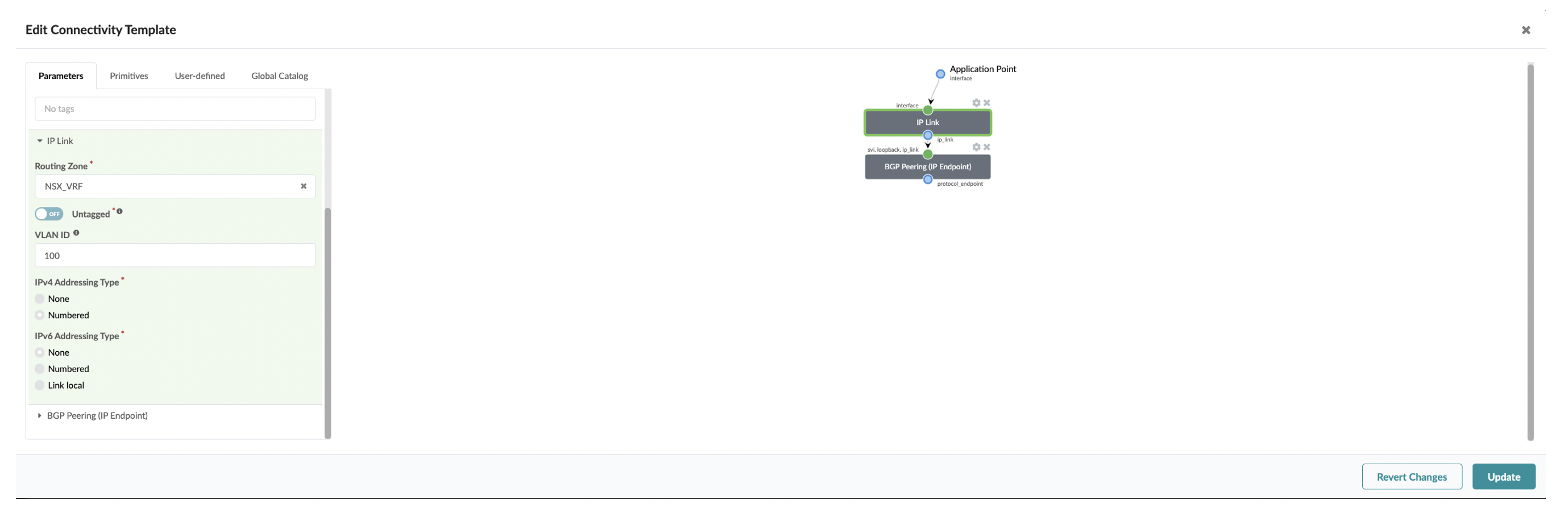
First create a Routing Zone in Juniper Apstra UI which maps to a VRF. Then need to setup IP Link Primitive based connectivity template to establish BGP peering from the NSX-T Edge node to Fabric as below:
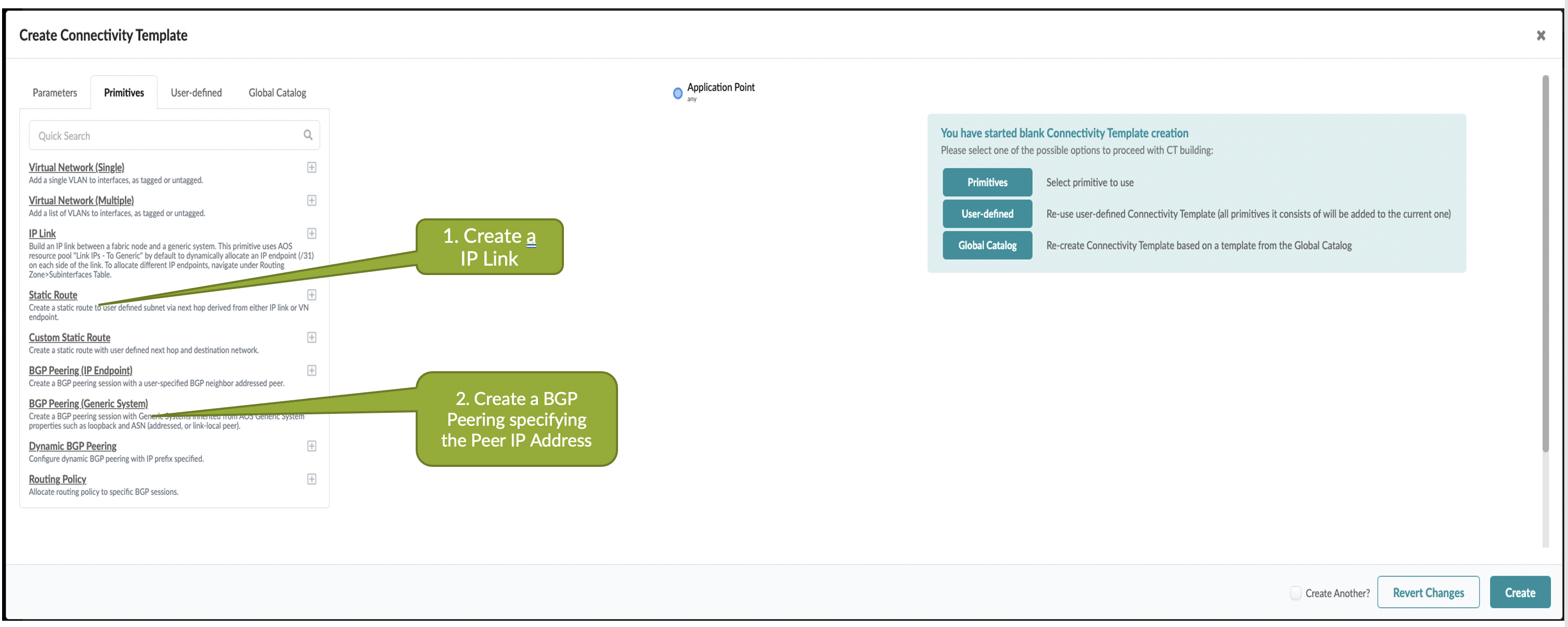
Specify the routing zone on which the IP link will be added and respective VLAN ID.
Set Up NSX-T VRF Lite
With NSX-T VRF Lite we are able to configure per tenant data isolation. Each VLAN can be considered as a separate channel for data plane under VRF gateways.
BGP peering can be built over these VLANs in VRF gateways for route exchange with the upstream Juniper Apstra fabric. Inter-VRF traffic is routed through the physical Juniper Apstra fabric.
- In NSX-T Manager create the VLAN Segments for the Uplink networks for the
tenants.
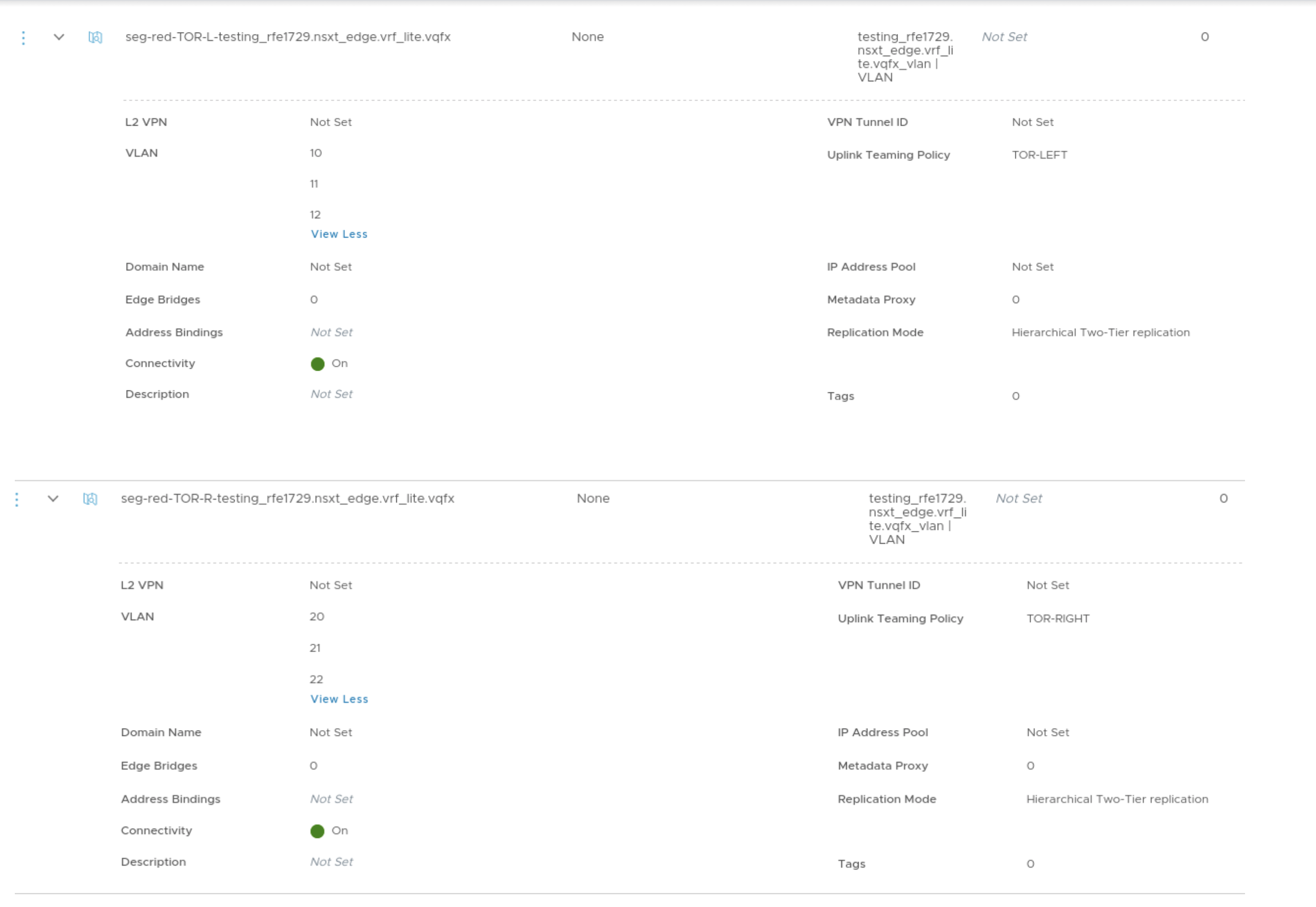
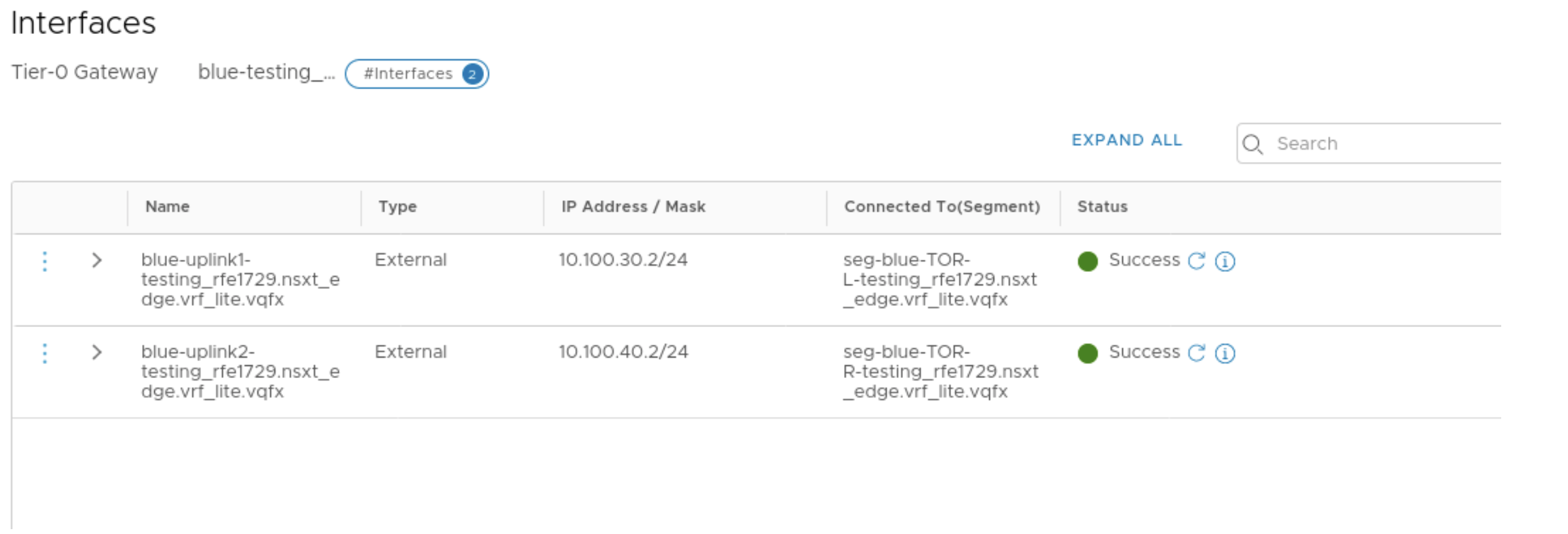
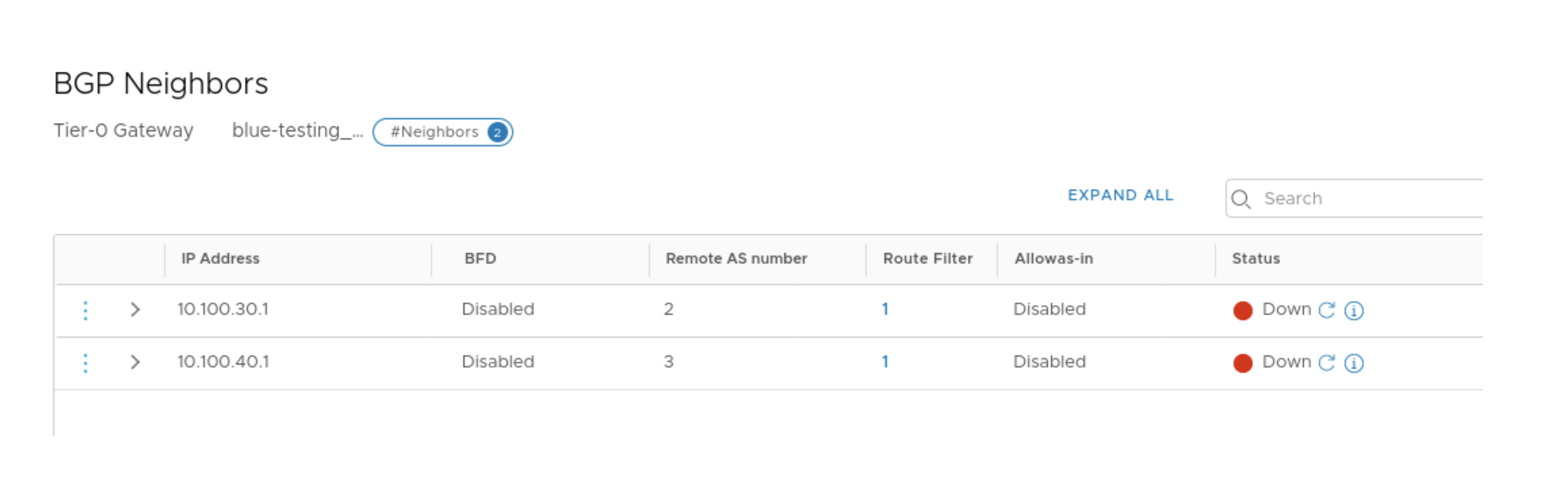
- In NSX-T Manager create the VRF-enabled Tier-0 Gateway for the tenants and add
the uplink interfaces on the VRF enabled Gateways. Thereafter add the BGP
neighbors.
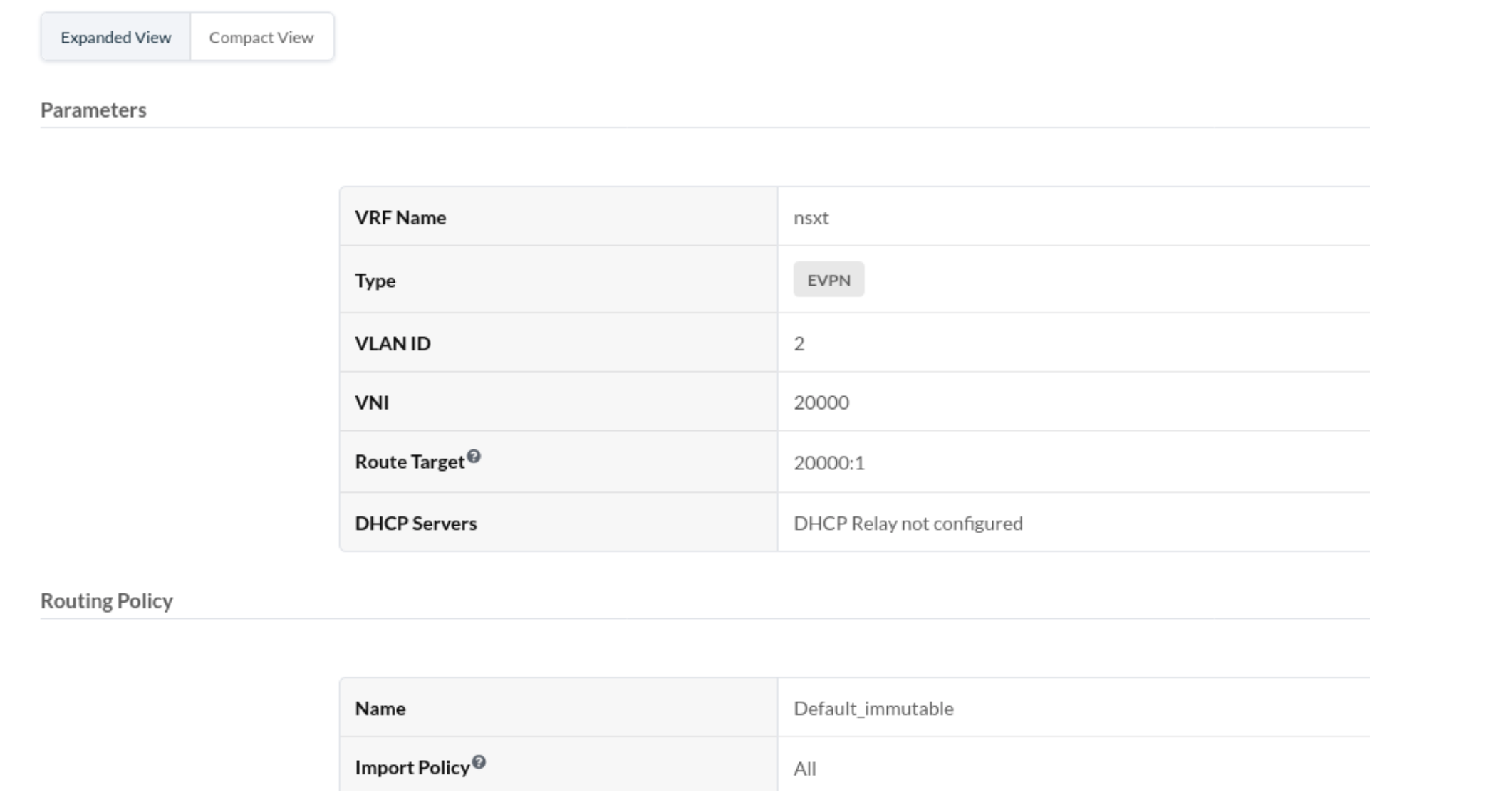
- From the Apstra GUI, setup the Routing Zone and the respective VNs on
which BGP session will be established towards ToR leaf devices as below:
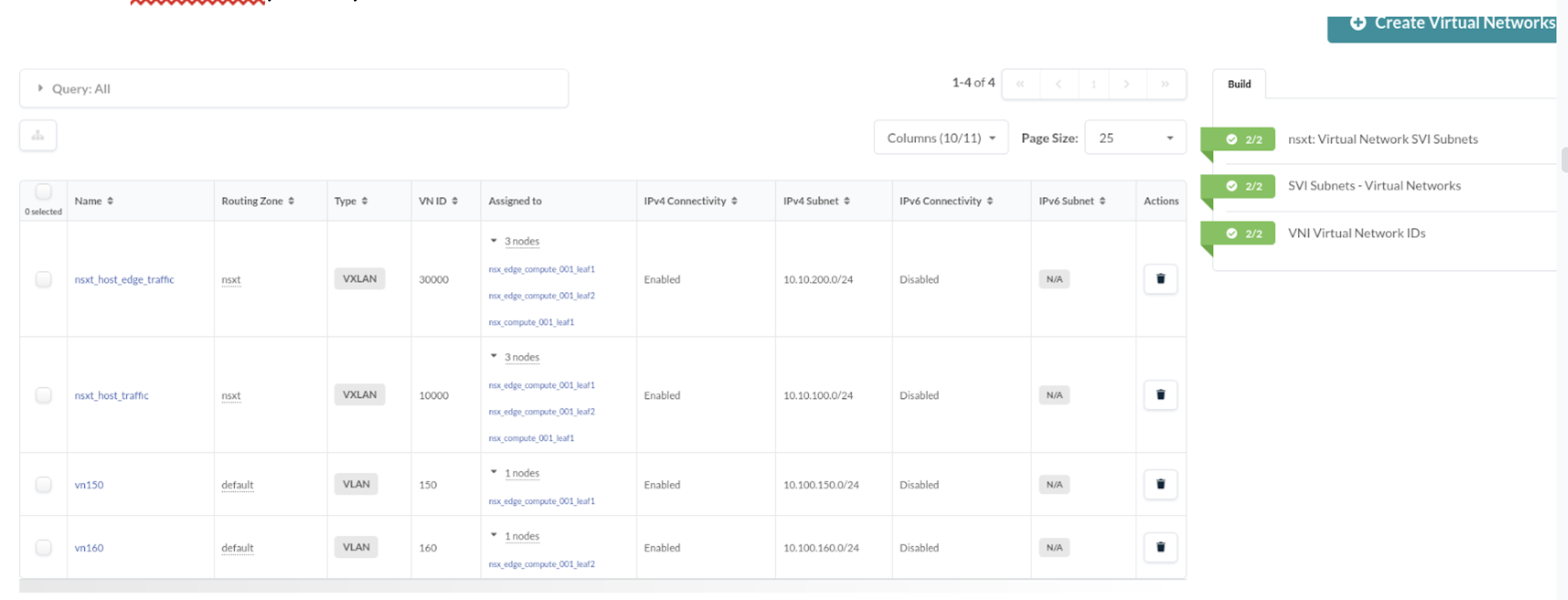
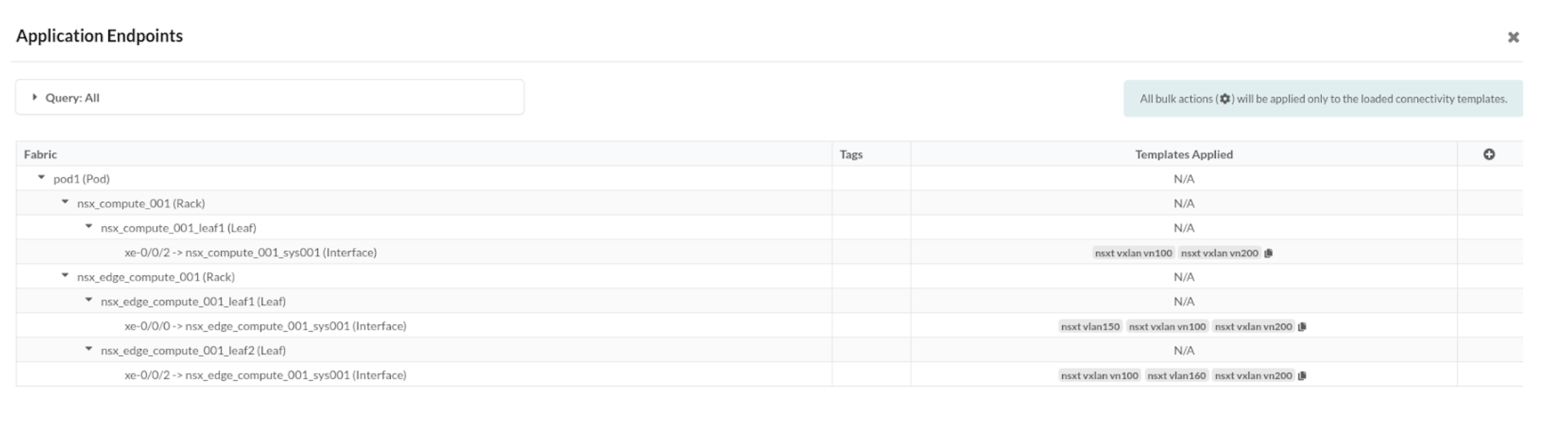
- Create connectivity template under Staged option for the VNs created before and
assign the respective interfaces towards NSX-T Edge VM.
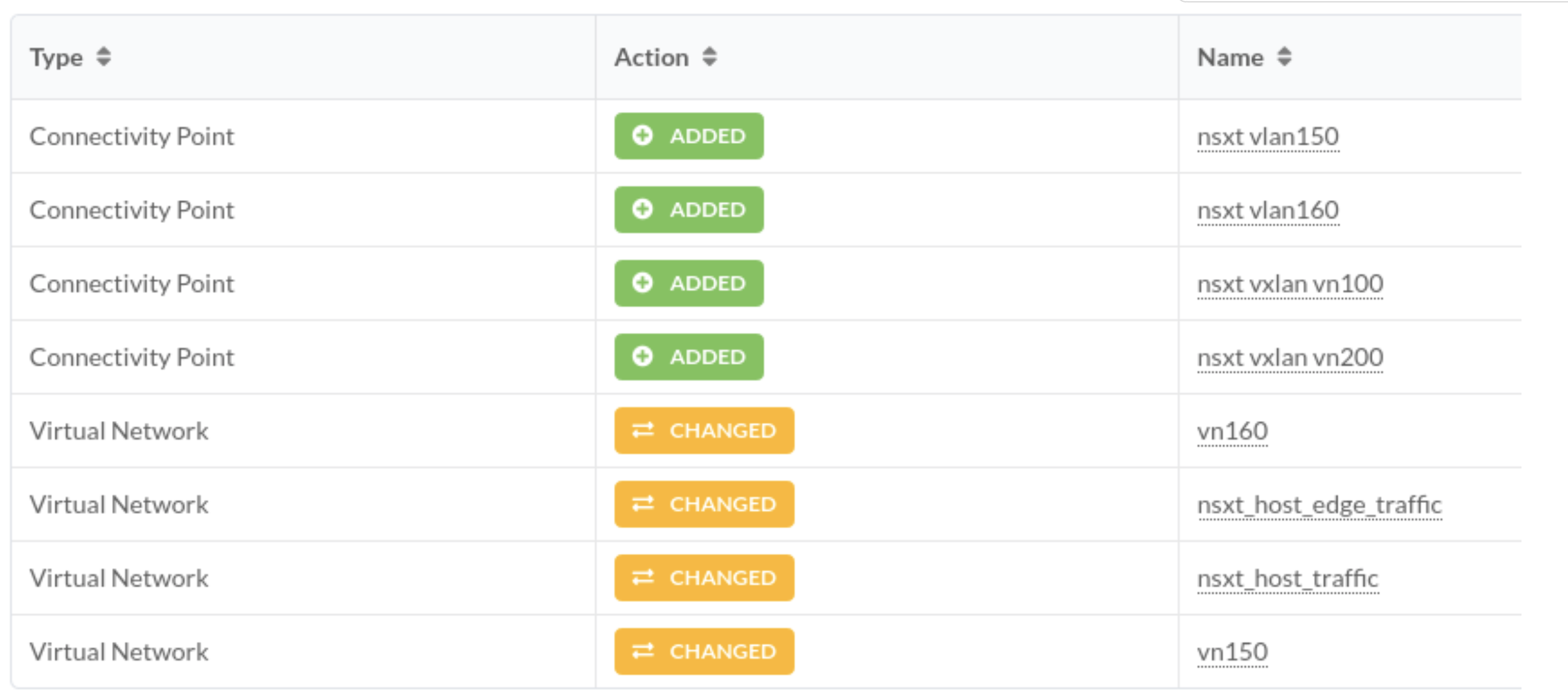
Set Up Default Static Route towards NSX-T Edge
Static default could be required in NSX-T edge setup to provide Internet connectivity. It can be taken care of by adding a default route(0/0) with the next hop pointing towards uplink ToR leaf using a connectivity template.
In the connectivity templates, assign the correct uplink: 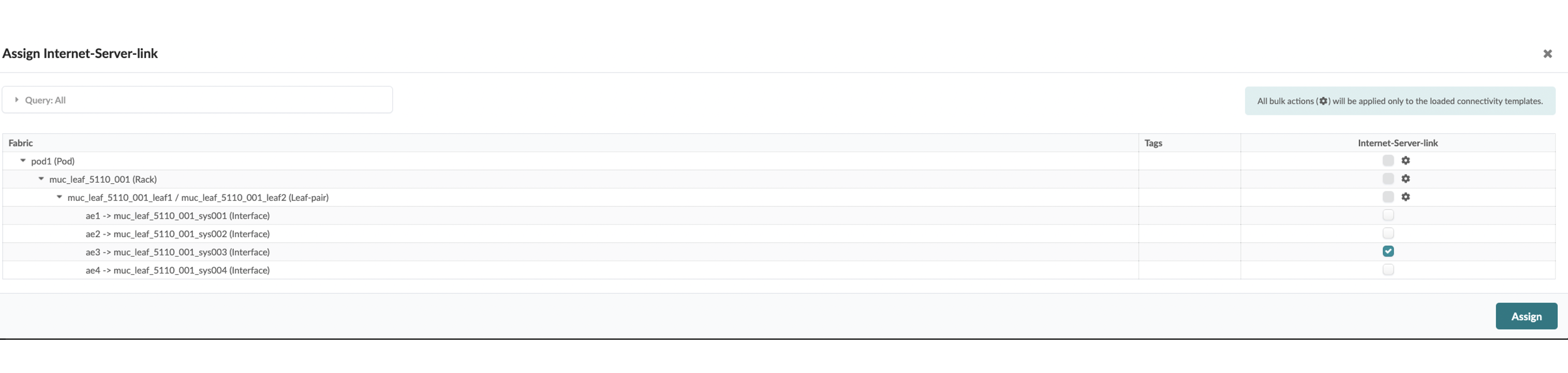
Navigate to Staged > Connectivity Templates > Add Template >
Primitives > Custom Static Route to inject default route: 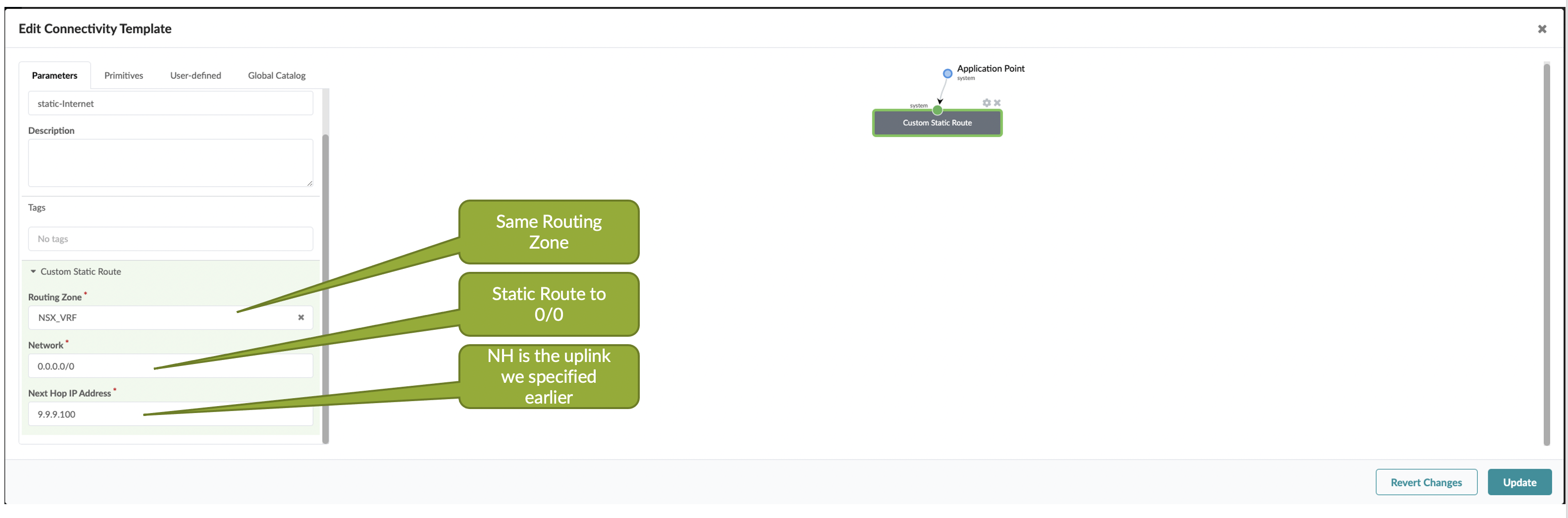
Set Up BGP IPv6 towards NSX-T Edge
We can enable IPv6-based BGP neighborship between T0 Gateway and ToR leaf using connectivity templates.
See "Set up NSX-T VRF Lite" section for details on creating uplink VLAN interfaces on T0 Gateway. This VLAN should be IPv6-enabled.
Create a connectivity template for each of the VXLAN VN and enable BGP towards IPv6
neighbor on NSX-T Edge as below: 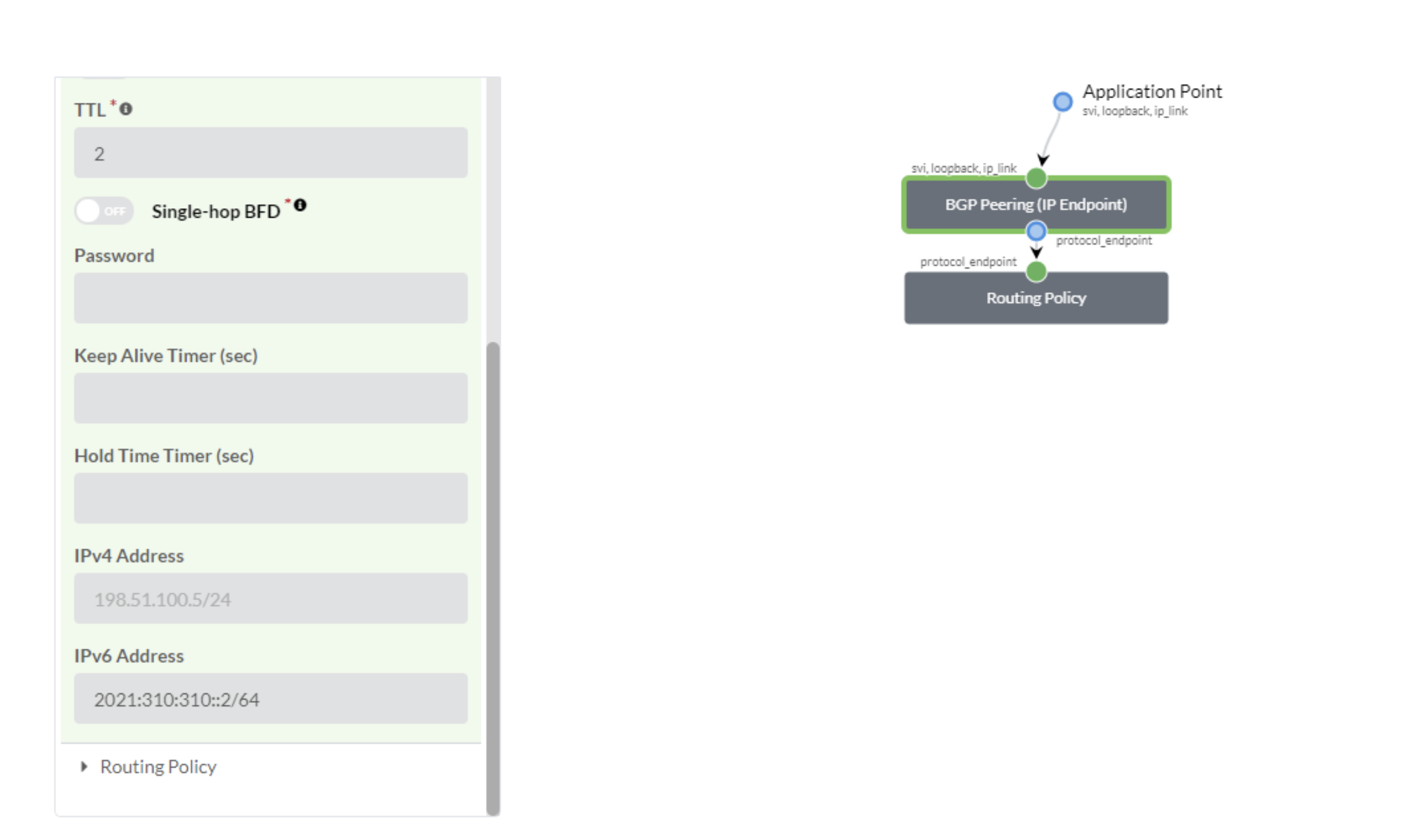
Un-assign BGP on VXLAN VN towards NSX-T Edge
Let's say BGP neighborship from Tier-0 Gateway in NSX-T needs to be torn down towards
ToR Leaf. In this case we need to unassign the interfaces in the Virtual
Network based Connectivity Template used for BGP peering so that it is in
the Ready state, and then delete the connectivity template: