Overview
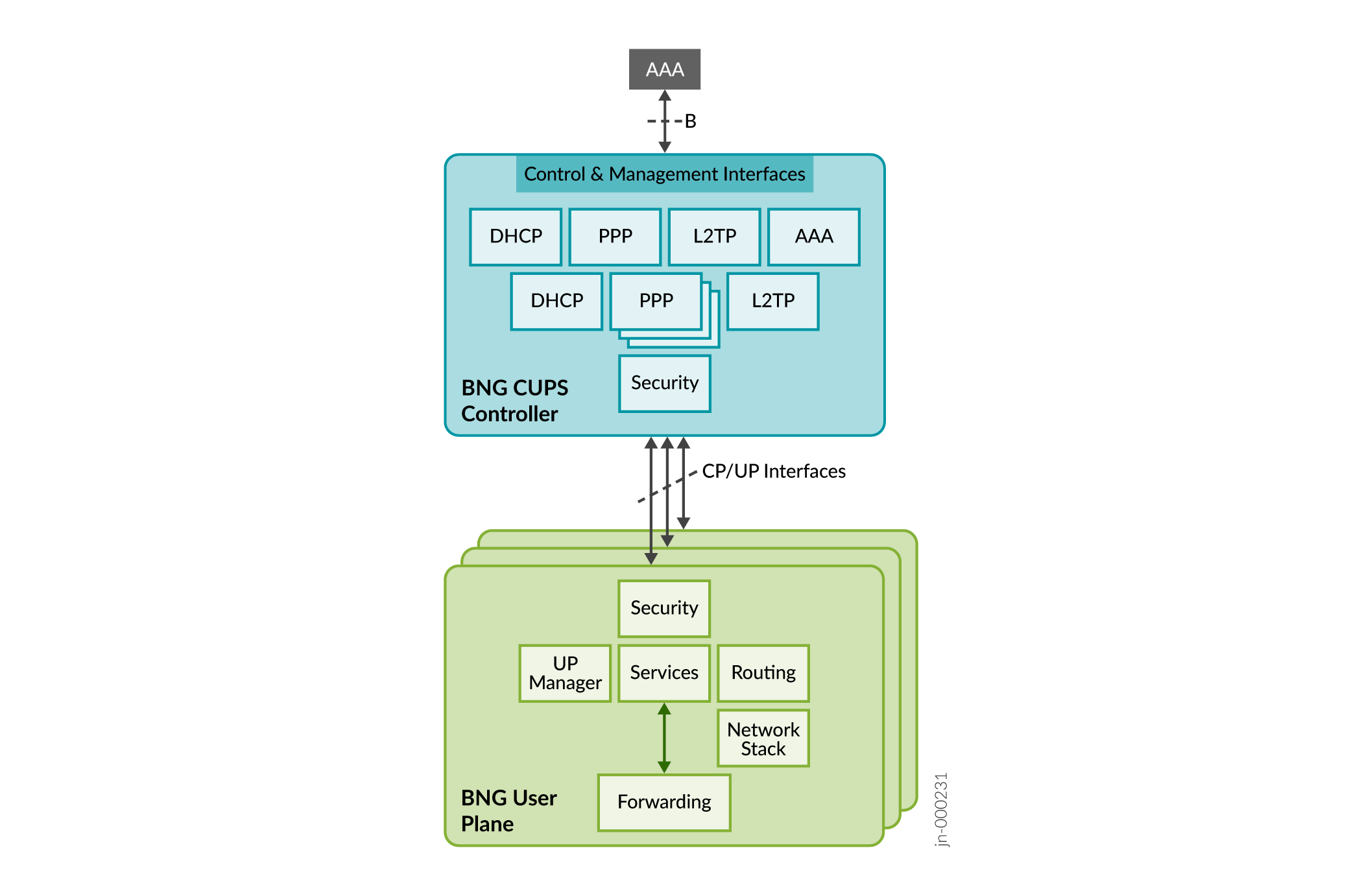
Juniper BNG CUPS architecture separates the broadband network gateway (BNG) stack running in the native Junos OS into a cloud-native application, where the BNG control plane functionality runs on the cloud application and the BNG user plane functionality runs in Junos OS. The cloud environment enables a single control plane to connect with multiple user planes.
In Juniper BNG CUPS, the BNG functions are split into the control plane (Juniper BNG CUPS Controller) functions and the user plane (Juniper BNG User Plane) functions. The management, state, and control packet interfaces operate between the Juniper BNG CUPS Controller (BNG CUPS Controller) and the Juniper BNG User Plane (BNG User Plane).
The BNG CUPS Controller serves as the location for completing subscriber termination, such as control protocol endpoint, authentication, and address assignment. Also, it sets up the proper forwarding states for all its connected BNG User Planes.
The following figure shows how Juniper BNG CUPS functions.

Three types of interfaces exist between the BNG CUPS Controller and the BNG User Planes:
-
Management Interface. Use this interface to:
-
Configure BNG User Planes.
-
Retrieve BNG User Plane information.
-
-
Control Packet Redirect Interface. Use this interface for BNG CUPS Control traffic.
-
State Control Interface. Use this interface to:
-
Identify and form BNG User Plane associations.
-
Program subscriber states from the BNG CUPS Controller to BNG User Planes.
-
Collect subscriber statistics from BNG User Planes.
-
Benefits of Juniper BNG CUPS
A centralized BNG CUPS Controller enables you to use network resources more efficiently through:
-
Address allocation.
-
Load balancing.
-
Management and control.
-
Increased scale. The cloud environment that Juniper BNG CUPS utilizes enables you to increase the number of subscribers supported.
-
Locational independence and separate life-cycle management and maintenance.
-
Throughput and latency optimization, because the BNG User Planes are closer to the subscribers.
Juniper BNG CUPS Feature Support
Juniper BNG CUPS supports the following features:
Client
-
DHCPv4 and DHCPv6 single and dual stack subscribers
-
PPP/PPPoE v4/v6 and dual stack subscribers
-
DHCP PD over PPPv6
-
RADIUS based authentication
-
Interface combinations: Ethernet, aggregated Ethernet, Pseudowire, and Redundant Pseudowire
-
Access to internal routes and multiple framed routes
Class of Service (CoS)
-
You can use dynamically created scheduler maps, schedulers, and traffic control profiles.
-
You can add the following services to dynamic flows:
-
Classifiers
-
Rewrite-rules
-
Output traffic control profiles with scheduler maps
-
-
You can apply CoS at either the subscriber level or at the DVLAN level, but not both.
-
The following service objects are preconfigured for dynamic profiles to use:
-
tcp-0 through tcp-7
-
clacl-dscp-1
-
clacl-dscp-2
-
clacl-dscp-ipv6-1
-
clacl-dscp-ipv6-2
-
clacl-802.1p-1
-
clacl-802.1p-2
-
clacl-inet-1
-
clacl-inet-2
-
rewrite-dscp-1
-
rewrite-dscp-2
-
rewrite-dscp-ipv6-1
-
rewrite-dscp-ipv6-2
-
rewrite-802.1p-1
-
rewrite-802.1p-2
-
rewrite-inet-1
-
rewrite-inet-2
-
Firewall Services
-
Parameterized filters and policers
-
Static filters and policers
L2TP Client
- Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) network server (LNS) subscribers
- L2TP client (LAC) subscribers
- L2TP with dual-stack subscribers
- DHCPv6 over L2TP
- LAC and L2TP tunnel switch (LTS) using RADIUS attributes
- L2TP ERA and performance
-
LNS with non-default LSRI (tunnel and session)
Lawful Intercept
-
Activation and deactivation of RADIUS-based lawful intercept for a flow-based subscriber during login and logout, on both the BNG CUPS Controller and the BNG User Plane
-
Activation and deactivation of RADIUS-based lawful intercept for a flow-based subscriber using RADIUS change of authorization (CoA), on both the BNG CUPS Controller and the BNG User Plane
-
Activation and deactivation of Dynamic Tasking Control Protocol (DTCP) based lawful intercept for a flow-based subscriber, on both the BNG CUPS Controller and the BNG User Plane
-
Attaching of lawful intercept drop policy for a flow-based subscriber, on both the BNG CUPS Controller and the BNG User Plane
-
Reporting of intercept-related events using SNMP traps to a mediation device on the BNG CUPS Controller
Accounting
-
Subscriber interim accounting
-
Subscriber finals accounting
-
Subscriber idle timeout
-
Subscriber IP family flap
-
Subscriber baseline accounting
-
Subscriber residual accounting
Management of Multiple BNG User Planes
-
A BNG CUPS Controller can manage multiple BNG User Planes. The multiple BNG User Plane architecture defines a BNG User Plane instance per BNG User Plane to encapsulate data and work within a BNG User Plane. You can associate a BNG User Plane with only one BNG User Plane instance.
-
The BNG CUPS Controller activates a BNG User Plane instance when the Controller detects an initial connection with a BNG User Plane. You can connect up to sixteen BNG User Planes to one BNG CUPS Controller.
Figure 1shows a multiple BNG User Plane topology.
Subscriber Steering
-
Places subscribers in the desired BNG User Plane based on a RADIUS service group vendor-specific attribute (VSA).
-
Terminates subscribers locally on the default BNG User Plane based on a RADIUS service group VSA.
-
Communicates with the User Plane Selection Function to implement traffic steering by the access node to the desired BNG User Plane.
Additional Information
Forwarding Class Handling
The forwarding-class configuration is a special case. You must
configure the forwarding class names on the BNG User Planes that you configure on
the BNG CUPS Controller.
These matching configurations are required because the number of forwarding classes is limited. Also, other entities in the BNG User Plane use the forwarding class. Thus, the BNG CUPS Controller's forwarding classes must be consistent with the BNG User Plane’s forwarding classes.
You can define additional forwarding classes on the BNG User Plane. You do not need to configure these additional forwarding classes on the BNG CUPS Controller.
Sample and Port Mirroring Handling
If a filter uses the sampling or port-mirroring
options, the related BNG User Plane must also have the corresponding
forwarding-options sampling or forwarding-options
port-mirroring configured. This BNG User Plane configuration determines
how to treat sampled or mirrored packets.
Policy-options prefix-list apply-path limitations
The policy-option prefix-list apply-path command refers only to
other BNG CUPS Controller configuration items.
The apply-path command does not include servers that you configured
on a BNG User Plane in a BNG CUPS Controller prefix list. You add server addresses
to the prefix list as regular addresses.
