MOD_VPN
SUMMARY This section describes how the MOD_VPN works.
MOD_VPN Overview
The MOD_VPN describes the security requirements for a VPN Gateway. This is defined to be a device at the edge of a private network that terminates an IPsec tunnel (support IPsec on tunnel mode), which provides device authentication, confidentiality, and integrity of information traversing a public or untrusted network. This mode is intended to provide a minimal, baseline set of requirements that are targeted at mitigating well defined and described threats to VPN Gateway technology. This introduction describes the features of a compliant Target of Evaluation (TOE), and also discusses how to use the MOD_VPN in conjunction with the NDcPPv2.
For IPsec connection be unintentionally broken, clear the IPsec session with following commands. It re-initiates and establishes the IPsec session.
user@host# run clear security ipsec security-associations user@host# run clear security ike security-associations
Supported IPsec-IKE Algorithms
Your device supports the following IPsec-IKE algorithms:
- Supported encryption algorithms for IPsec
- Supported encryption algorithms for IKE
- Supported IKE DH groups
- Supported IPsec authentication algorithm
- Supported IKE authentication algorithms
- Supported authentication methods
Supported encryption algorithms for IPsec
aes-128-cbc AES-CBC 128-bit encryption algorithm aes-128-gcm AES-GCM 128-bit encryption algorithm aes-192-cbc AES-CBC 192-bit encryption algorithm aes-192-gcm AES-GCM 192-bit encryption algorithm aes-256-cbc AES-CBC 256-bit encryption algorithm aes-256-gcm AES-GCM 256-bit encryption algorithm
[edit] user@host# set security ipsec proposal ipsec-proposal1 encryption-algorithm aes-128-cbc user@host# set security ipsec proposal ipsec-proposal1 encryption-algorithm aes-128-gcm user@host# set security ipsec proposal ipsec-proposal1 encryption-algorithm aes-192-cbc user@host# set security ipsec proposal ipsec-proposal1 encryption-algorithm aes-192-gcm user@host# set security ipsec proposal ipsec-proposal1 encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc user@host# set security ipsec proposal ipsec-proposal1 encryption-algorithm aes-256-gcm
Supported encryption algorithms for IKE
aes-128-cbc AES-CBC 128-bit encryption algorithm aes-128-gcm AES-GCM 128-bit encryption algorithm aes-192-cbc AES-CBC 192-bit encryption algorithm aes-256-cbc AES-CBC 256-bit encryption algorithm aes-256-gcm AES-GCM 256-bit encryption algorithm
[edit] user@host# set security ike proposal ipsec-proposal1 encryption-algorithm aes-128-cbc user@host# set security ike proposal ipsec-proposal1 encryption-algorithm aes-128-gcm user@host# set security ike proposal ipsec-proposal1 encryption-algorithm aes-192-cbc user@host# set security ike proposal ipsec-proposal1 encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc user@host# set security ike proposal ipsec-proposal1 encryption-algorithm aes-256-gcm
Supported IKE DH groups
group14 Diffie-Hellman Group 14 group15 Diffie-Hellman Group 15 group16 Diffie-Hellman Group 16 group19 Diffie-Hellman Group 19 group20 Diffie-Hellman Group 20 group21 Diffie-Hellman Group 21 group24 Diffie-Hellman Group 24
[edit] user@host# set security ike proposal ipsec-proposal1 dh-group group14 user@host# set security ike proposal ipsec-proposal1 dh-group group15 user@host# set security ike proposal ipsec-proposal1 dh-group group16 user@host# set security ike proposal ipsec-proposal1 dh-group group19 user@host# set security ike proposal ipsec-proposal1 dh-group group20 user@host# set security ike proposal ipsec-proposal1 dh-group group21 user@host# set security ike proposal ipsec-proposal1 dh-group group24
Supported IPsec authentication algorithm
hmac-sha-256-128 HMAC-SHA-256-128 authentication algorithm hmac-sha-384 HMAC-SHA-384 authentication algorithm hmac-sha-512 HMAC-SHA-512 authentication algorithm
[edit] user@host# set security ipsec proposal ipsec-proposal1 authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-256-128 user@host# set security ipsec proposal ipsec-proposal1 authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-384 user@host# set security ipsec proposal ipsec-proposal1 authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-512
Supported IKE authentication algorithms
sha-256 SHA 256-bit authentication algorithm sha-384 SHA 384-bit authentication algorithm sha-512 SHA 512-bit authentication algorithm
[edit] user@host# set security ike proposal ipsec-proposal1 authentication-algorithm sha-256 user@host# set security ike proposal ipsec-proposal1 authentication-algorithm sha-384 user@host# set security ike proposal ipsec-proposal1 authentication-algorithm sha-512
Supported authentication methods
certificates Allows ECDSA, RSA and DSA certificates, requires IKEv2 ecdsa-signatures-256 ECDSA signatures (256 bit modulus) ecdsa-signatures-384 ECDSA signatures (384 bit modulus) ecdsa-signatures-521 ECDSA signatures (521 bit modulus) pre-shared-keys Preshared keys rsa-signatures RSA signatures
[edit] user@host# set security ike proposal ipsec-proposal1 authentication-method certificates user@host# set security ike proposal ipsec-proposal1 authentication-method ecdsa-signatures-256 user@host# set security ike proposal ipsec-proposal1 authentication-method ecdsa-signatures-384 user@host# set security ike proposal ipsec-proposal1 authentication-method ecdsa-signatures-521 user@host# set security ike proposal ipsec-proposal1 authentication-method pre-shared-keys user@host# set security ike proposal ipsec-proposal1 authentication-method rsa-signatures
Configure VPN on a Device Running Junos OS
This section describes a sample configurations of an IPsec VPN on a Junos OS device using the following IKE authentication methods:
-
Configuring an IPsec VPN with a Preshared Key for IKE Authentication
-
Configuring an IPsec VPN with an RSA Signature for IKE Authentication
-
Configuring an IPsec VPN with an ECDSA Signature for IKE Authentication
Figure 1 illustrates the VPN topology used in all the examples described in this section. Here, H0 and H1 are the host, and R0 and R1 are the two endpoints of the IPsec VPN tunnel.
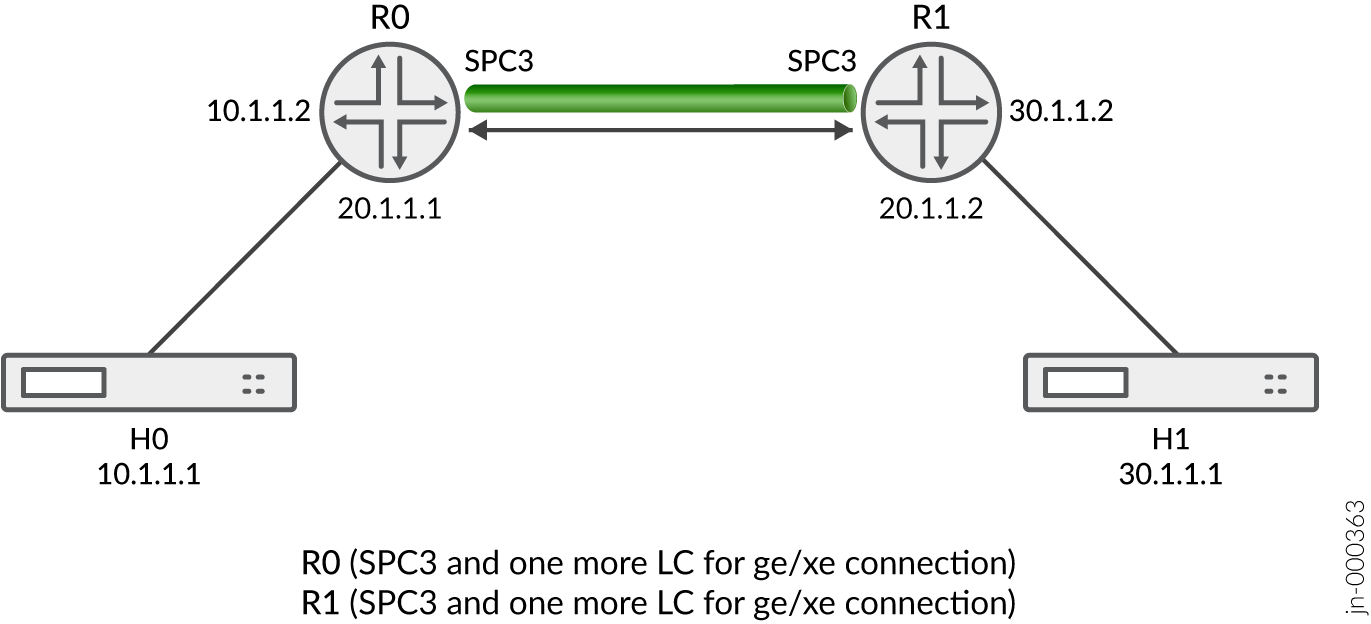
Table 1 provides a complete list of the supported IKE protocols, tunnel modes, Phase 1 negotiation mode, authentication method or algorithm, encryption algorithm, DH groups supported for the IKE authentication and encryption (Phase1, IKE Proposal), and for IPsec authentication and encryption (Phase2, IPsec Proposal). The listed protocols, modes, and algorithms are supported and required for 21.2R2 Common Criteria.
|
IKE Protocol |
Tunnel Mode |
Phase1 Negotiation Mode |
Phase 1 Proposal (P1, IKE) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Authentication Method |
Authentication Algorithm |
DH Group |
Encryption Algorithm |
|||
|
IKEv1 |
Main |
Route |
pre-shared-keys |
sha-256 |
group14 |
aes-128-cbc |
|
IKEv2 |
rsa-signatures-2048 |
sha-384 |
group15 |
aes-128-gcm |
||
|
ecdsa-signatures-256 |
sha-512 |
group16 |
aes-192-cbc |
|||
|
ecdsa-signatures-384 |
group19 |
aes-256-cbc |
||||
|
ecdsa-signatures-521 |
group20 |
aes-256-gcm |
||||
|
group21 |
||||||
|
group24 |
||||||
|
IKE Protocol |
Tunnel Mode |
Phase1 Negotiation Mode |
Phase 2 Proposal (P2, IPsec) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Authentication Algorithm |
DH Group (PFS) |
Encryption Method |
Encryption Algorithm |
|||
|
IKEv1 |
Main |
Route |
hmac-sha-256-128 |
group14 |
ESP |
aes-128-cbc |
|
IKEv2 |
hmac-sha-384 |
group15 |
aes-128-gcm |
|||
|
hmac-sha-512 |
group16 |
aes-192-cbc |
||||
|
group19 |
aes-192-gcm |
|||||
|
group20 |
aes-256-cbc |
|||||
|
group21 |
aes-256-gcm |
|||||
|
group24 |
||||||
The following sections provide sample configurations of IKEv1 IPsec VPN examples
for selected algorithms. Authentication algorithms can be replaced in the
configurations to accomplish the user’s desired configurations. Use set
security ike gateway gw-name version v2-only
command for IKEv2 IPsec VPN.
- Configuring an IPsec VPN with a Preshared Key for IKE Authentication
- Configuring an IPsec VPN with an RSA Signature for IKE Authentication
- Configuring an IPsec VPN with an ECDSA Signature for IKE Authentication
Configuring an IPsec VPN with a Preshared Key for IKE Authentication
In this section, you configure devices running Junos OS for IPsec VPN using a preshared key as the IKE authentication method. The algorithms used in IKE or IPsec authentication, or encryption is shown in Table 2
|
IKE Protocol |
Tunnel Mode |
Phase1 Negotiation Mode |
Phase 1 Proposal (P1, IKE) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Authentication Method |
Authentication Algorithm |
DH Group |
Encryption Algorithm |
|||
|
IKEv1 |
Main |
Route |
pre-shared-keys |
sha-256 |
group14 |
aes-256-cbc |
|
IKE Protocol |
Tunnel Mode |
Phase1 Negotiation Mode |
Phase 2 Proposal (P2, IPsec) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Authentication Algorithm |
DH Group (PFS) |
Encryption Method |
Encryption Algorithm |
|||
|
IKEv1 |
Main |
Route |
hmac-sha-256-128 |
group14 |
ESP |
aes-256-cbc |
A device running Junos OS uses certificate-based authentication or preshared keys for IPsec. TOE accepts ASCII preshared or bit-based keys up to 255 characters (and their binary equivalents) that contain uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters such as !, @, #, $, %, ^, &, *, (, and ). The device accepts the preshared text keys and converts the text string into an authentication value as per RFC 2409 for IKEv1 or RFC 4306 for IKEv2, using the PRF that is configured as the hash algorithm for the IKE exchanges. The Junos OS does not impose minimum complexity requirements for preshared keys. Hence, users are advised to carefully choose long preshared keys of sufficient complexity.
- Configuring IPsec VPN with Preshared Key as IKE Authentication on the Initiator
- Configuring IPsec VPN with Preshared Key as IKE Authentication on the Responder
Configuring IPsec VPN with Preshared Key as IKE Authentication on the Initiator
- Configure the IKE proposal:
[edit] user@host# set security ike proposal ike-proposal1 authentication-method pre-shared-keys user@host# set set security ike proposal ike-proposal1 dh-group group14 user@host# set security ike proposal ike-proposal1 authentication-algorithm sha256 user@host# set security ike proposal ike-proposal1 encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc
Note:Here,
ike-proposal1is the IKE proposal name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure the IKE policy:
[edit] user@host# set security ike policy ike-policy1 mode main user@host# set security ike policy ike-policy1 proposals ike-proposal1
Note:Here,
ike-policy1is the IKE policy name andike-proposal1is the IKE proposal name given by the authorized administrator.user@host# prompt security ike policy ike-policy1 pre-shared-key ascii-text New ascii-text (secret): Retype new ascii-text (secret):
Note:You must enter and reenter the preshared key when prompted. For example, the preshared key can be
Modvpn@jnpr1234.Note:The preshared key can alternatively be entered in hexadecimal format. For example:
[edit] root@host# prompt security ike policy ike-policy1 pre-shared-key hexadecimal
New hexadecimal (secret):Retype new hexadecimal (secret):Enter the hexadecimal preshared key value.
-
Configure the IPsec proposal:
[edit] user@host# set security ipsec security proposal ipsec-proposal1 protocol esp user@host# set security ipsec security proposal ipsec-proposal1 authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-256-128 user@host# set security ipsec proposal ipsec-proposal1 encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc
Note:Here,
ipsec-proposal1is the IPsec proposal name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure the IPsec policy:
[edit] user@host# set security ipsec policy ipsec-policy1 perfect-forward-secrecy keys group14 user@host# set security ipsec policy ipsec-policy1 proposals ipsec-proposal1
Note:Here,
ipsec-policy1is the IPsec policy name andipsec-proposal1is the IPsec proposal name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure the IKE:
[edit] user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 ike-policy ike-policy1 user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 address 20.1.1.2 user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 local-identity inet 20.1.1.1 user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 external-interface xe-0/0/2 user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 version v2-only
Note:Here,
gw1is an IKE gateway name,20.1.1.2is the peer VPN endpoint IP,20.1.1.1is the local VPN endpoint IP, andxe-0/0/2is a local outbound interface as the VPN endpoint. The following additional configuration is also needed in the case of IKEv2. -
Configure the VPN:
[edit] user@host# set security ipsec vpn vpn1 ike gateway gw1 user@host# set security ipsec vpn vpn1 ike ipsec-policy ipsec-policy1 user@host# set security ipsec vpn vpn1 bind-interface st0.0 user@host# set security ipsec vpn vpn1 establish-tunnels immediately
Note:Here,
vpn1is the VPN tunnel name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure service-set:
[edit] user@host# set services service-set IPSEC_SS_SPC3 next-hop-service inside-service-interface vms-5/0/0.1 user@host# set services service-set IPSEC_SS_SPC3 next-hop-service outside-service-interface vms-5/0/0.2 user@host# set services service-set IPSEC_SS_SPC3 ipsec-vpn vpn1
-
Configure interfaces and routing-option:
[edit] user@host# set interfaces xe-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet address 20.1.1.1/24 user@host# set interfaces vms-5/0/0 unit 0 family inet user@host# set interfaces vms-5/0/0 unit 1 family inet user@host# set interfaces vms-5/0/0 unit 1 family inet6 user@host# set interfaces vms-5/0/0 unit 1 service-domain inside user@host# set interfaces vms-5/0/0 unit 2 family inet user@host# set interfaces vms-5/0/0 unit 2 family inet6 user@host# set interfaces vms-5/0/0 unit 2 service-domain outside user@host# set interfaces st0 unit 1 family inet user@host# set interfaces st0 unit 1 family inet6 user@host# set interfaces st0 unit 2 family inet user@host# set interfaces st0 unit 2 family inet6 user@host# set routing-options static route 30.1.1.0/24 next-hop st0.0
Configuring IPsec VPN with Preshared Key as IKE Authentication on the Responder
-
Configure the IKE proposal:
[edit] user@host# set security ike proposal ike-proposal1 authentication-method pre-shared-keys user@host# set security ike proposal ike-proposal1 dh-group group14 user@host# set security ike proposal ike-proposal1 authentication-algorithm sha256 user@host# set security ike proposal ike-proposal1 encryption-algorithm aes-128-cbc
Note:Here,
ike-proposal1is the IKE proposal name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure the IKE policy:
[edit] user@host# set security ike policy ike-policy1 mode main user@host# set security ike policy ike-policy1 proposals ike-proposal1
Note:Here,
ike-policy1is the IKE policy name and ike-proposal1 is the IKE proposal name given by the authorized administrator.user@host# prompt security ike policy ike-policy1 pre-shared-key ascii-text New ascii-text (secret): Retype new ascii-text (secret):
Note:You must enter and reenter the preshared key when prompted. For example, the preshared key can be
Modvpn@jnpr1234.Note:The pre-share key could alternatively be entered in hexadecimal format. For example,
user@host# prompt security ike policy ike-policy1 pre-shared-key hexadecimal
New hexadecimal (secret):Retype new hexadecimal (secret):Here, the hexadecimal preshared key can be
cc2014bae9876543. -
Configure the IPsec proposal:
[edit] user@host# set security ipsec proposal ipsec-proposal1 protocol esp user@host# set security ipsec proposal ipsec-proposal1 authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-256-128 user@host# set security ipsec proposal ipsec-proposal1 encryption-algorithm 3des-cbcaes-128-cbc
Note:Here,
ipsec-proposal1is the IPsec proposal name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure the IPsec policy:
[edit] user@host# set security ipsec policy ipsec-policy1 perfect-forward-secrecy keys group14 user@host# set security ipsec policy ipsec-policy1 proposals ipsec-proposal1
Note:Here,
ipsec-policy1is the IPsec policy name andipsec-proposal1is the IPsec proposal name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure the IKE.
[edit] user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 ike-policy ike-policy1 user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 address 20.1.1.1 user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 local-identity inet 20.1.1.2 user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 external-interface xe-0/0/3 user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 version v2-only
Note:Here,
gw1is an IKE gateway name,20.1.1.1is the peer VPN endpoint IP,20.1.1.2is the local VPN endpoint IP, andxe-0/0/3is a local outbound interface as the VPN endpoint. The following additional configuration is also needed in the case of IKEv2. -
Configure the VPN:
[edit] user@host# set security ipsec vpn vpn1 ike gateway gw1 user@host# set security ipsec vpn vpn1 ike ipsec-policy ipsec-policy1 user@host# set security ipsec vpn vpn1 bind-interface st0.0 user@host# set security ipsec vpn vpn1 establish-tunnels immediately
Note:Here,
vpn1is the VPN tunnel name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure service-set:
[edit] user@host# set services service-set IPSEC_SS_SPC3 next-hop-service inside-service-interface vms-4/0/0.1 user@host# set services service-set IPSEC_SS_SPC3 next-hop-service outside-service-interface vms-4/0/0.2 user@host# set services service-set IPSEC_SS_SPC3 ipsec-vpn vpn1
-
Configure Interfaces and routing-option:
[edit] user@host# set interfaces xe-0/0/3 unit 0 family inet address 20.1.1.2/24 user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 0 family inet user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 1 family inet user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 1 family inet6 user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 1 service-domain inside user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 2 family inet user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 2 family inet6 user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 2 service-domain outside user@host# set interfaces st0 unit 1 family inet user@host# set interfaces st0 unit 1 family inet6 user@host# set interfaces st0 unit 2 family inet user@host# set interfaces st0 unit 2 family inet6 user@host# set routing-options static route 10.1.1.0/24 next-hop st0.0
Configuring an IPsec VPN with an RSA Signature for IKE Authentication
The following section provides an example to configure Junos OS devices for IPsec VPN using RSA Signature as IKE Authentication method, whereas the algorithms used in IKE/IPsec authentication/encryption is as shown in the following table. In this section, you configure devices running Junos OS forIPsec VPN using an RSA signature as the IKE authentication method. The algorithms used in IKE or IPsec authentication or encryption is shown in Table 3
|
IKE Protocol |
Tunnel Mode |
Phase1 Negotiation Mode |
Phase 1 Proposal (P1, IKE) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Authentication Method |
Authentication Algorithm |
DH Group |
Encryption Algorithm |
|||
|
IKEv1 |
Main |
Route |
rsa-signatures-2048 |
sha-256 |
group19 |
aes-128-cbc |
|
IKE Protocol |
Tunnel Mode |
Phase1 Negotiation Mode |
Phase 2 Proposal (P2, IPsec) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Authentication Algorithm |
DH Group (PFS) |
Encryption Method |
Encryption Algorithm |
|||
|
IKEv1 |
Main |
Route |
hmac-sha-256-128 |
group19 |
ESP |
aes-128-cbc |
- Configuring IPsec VPN with RSA Signature as IKE Authentication on the Initiator
- Configuring IPsec VPN with RSA Signature as IKE Authentication on the Responder
Configuring IPsec VPN with RSA Signature as IKE Authentication on the Initiator
-
Configure the PKI. See Example: Configuring PKI.
-
Generate the RSA key pair. See Example: Generating a Public-Private Key Pair.
-
Generate and load the CA certificate. See Example: Loading CA and Local Certificates Manually.
-
Load the CRL. See Example: Manually Loading a CRL onto the Device .
-
Generate and load a local certificate. See Example: Loading CA and Local Certificates Manually.
-
Configure the IKE proposal:
[edit] user@host# set security ike proposal ike-proposal1 authentication-method rsa-signatures user@host# set security ike proposal ike-proposal1 dh-group group19 user@host# set security ike proposal ike-proposal1 authentication-algorithm sha-256 user@host# set security ike proposal ike-proposal1 encryption-algorithm aes-128-cbc
Note:Here,
ike-proposal1is the name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure the IKE policy:
[edit] user@host# set security ike policy ike-policy1 mode main user@host# set security ike policy ike-policy1 proposals ike-proposal1 user@host# set security ike policy ike-policy1 certificate local-certificate cert1
Note:Here,
ike-policy1IKE policy name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure the IPsec proposal:
[edit] user@host# set security ipsec proposal ipsec-proposal1 protocol esp user@host# set security ipsec proposal ipsec-proposal1 authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-256-128 user@host# set security ipsec proposal ipsec-proposal1 encryption-algorithm aes-128-cbc
Note:Here,
ipsec-proposal1is the name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure the IPsec policy:
[edit] user@host# set security ipsec policy ipsec-policy1 perfect-forward-secrecy keys group19 user@host# set security ipsec policy ipsec-policy1 proposals ipsec-proposal1
Note:Here,
ipsec-policy1is the name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure the IKE:
[edit] user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 ike-policy ike-policy1 user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 address 20.1.1.2 user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 local-identity inet 20.1.1.1 user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 external-interface xe-0/0/3 user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 version v2-only
Note:Here,
20.1.1.2is the peer VPN endpoint IP,20.1.1.1is the local VPN endpoint IP, andxe-0/0/3is the local outbound interface as VPN endpoint. The following configuration is also needed for IKEv2. -
Configure VPN:
[edit] user@host# set security ipsec vpn vpn1 ike gateway gw1 user@host# set security ipsec vpn vpn1 ike ipsec-policy ipsec-policy1 user@host# set security ipsec vpn vpn1 bind-interface st0.0 user@host# set security ipsec vpn vpn1 establish-tunnels immediately
Note:Here,
vpn1is the VPN tunnel name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure service-set:
[edit] user@host# set services service-set IPSEC_SS_SPC3 next-hop-service inside-service-interface vms-4/0/0.1 user@host# set services service-set IPSEC_SS_SPC3 next-hop-service outside-service-interface vms-4/0/0.2 user@host# set services service-set IPSEC_SS_SPC3 ipsec-vpn vpn1
-
Configure interfaces and routing-option:
[edit] user@host# set interfaces xe-0/0/3 unit 0 family inet address 20.1.1.1/24 user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 0 family inet user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 1 family inet user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 1 family inet6 user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 1 service-domain inside user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 2 family inet user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 2 family inet6 user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 2 service-domain outside user@host# set interfaces st0 unit 1 family inet user@host# set interfaces st0 unit 1 family inet6 user@host# set interfaces st0 unit 2 family inet user@host# set interfaces st0 unit 2 family inet6 user@host# set routing-options static route 10.1.1.0/24 next-hop st0.0
Configuring IPsec VPN with RSA Signature as IKE Authentication on the Responder
-
Configure the PKI. See Example: Configuring PKI.
-
Generate the RSA key pair. See Example: Generating a Public-Private Key Pair.
-
Generate and load the CA certificate. See Example: Loading CA and Local Certificates Manually.
-
Load the CRL. See Example: Manually Loading a CRL onto the Device .
-
Generate and load a local certificate. See Example: Loading CA and Local Certificates Manually.
-
Configure the IKE proposal:
[edit] user@host# set security ike proposal ike-proposal1 authentication-method rsa-signatures user@host# set security ike proposal ike-proposal1 dh-group group19 user@host# set security ike proposal ike-proposal1 authentication-algorithm sha-256 user@host# set security ike proposal ike-proposal1 encryption-algorithm aes-128-cbc
Note:Here,
ike-proposal1is the name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure the IKE policy:
[edit] user@host# set security ike policy ike-policy1 mode main user@host# set security ike policy ike-policy1 proposals ike-proposal1 user@host# set security ike policy ike-policy1 certificate local-certificate cert1
Note:Here,
ike-policy1IKE policy name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure the IPsec proposal:
[edit] user@host# set security ipsec proposal ipsec-proposal1 protocol esp user@host# set security ipsec proposal ipsec-proposal1 authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-256-128 user@host# set security ipsec proposal ipsec-proposal1 encryption-algorithm aes-128-cbc
Note:Here,
ipsec-proposal1is the name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure the IPsec policy:
[edit] user@host# set security ipsec policy ipsec-policy1 perfect-forward-secrecy keys group19 user@host# set security ipsec policy ipsec-policy1 proposals ipsec-proposal1
Note:Here,
ipsec-policy1is the name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure the IKE:
[edit] user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 ike-policy ike-policy1 user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 address 20.1.1.1 user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 local-identity inet 20.1.1.2 user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 external-interface xe-0/0/4 user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 version v2-only
Note:Here,
20.1.1.1is the peer VPN endpoint IP,20.1.1.2is the local VPN endpoint IP, andxe-0/0/4is the local outbound interface as VPN endpoint. The following configuration is also needed for IKEv2. -
Configure VPN:
[edit] user@host# set security ipsec vpn vpn1 ike gateway gw1 user@host# set security ipsec vpn vpn1 ike ipsec-policy ipsec-policy1 user@host# set security ipsec vpn vpn1 bind-interface st0.0 user@host# set security ipsec vpn vpn1 establish-tunnels immediately
Note:Here,
vpn1is the VPN tunnel name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure service-set:
[edit] user@host# set services service-set IPSEC_SS_SPC3 next-hop-service inside-service-interface vms-4/0/0.1 user@host# set services service-set IPSEC_SS_SPC3 next-hop-service outside-service-interface vms-4/0/0.2 user@host# set services service-set IPSEC_SS_SPC3 ipsec-vpn vpn1 -
Configure Interfaces and routing-option:
[edit] user@host# set interfaces xe-0/0/4 unit 0 family inet address 20.1.1.2/24 user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 0 family inet user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 1 family inet user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 1 family inet6 user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 1 service-domain inside user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 2 family inet user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 2 family inet6 user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 2 service-domain outside user@host# set interfaces st0 unit 1 family inet user@host# set interfaces st0 unit 1 family inet6 user@host# set interfaces st0 unit 2 family inet user@host# set interfaces st0 unit 2 family inet6 user@host# set routing-options static route 30.1.1.0/24 next-hop st0.0
Configuring an IPsec VPN with an ECDSA Signature for IKE Authentication
In this section, you configure devices running Junos OS for IPsec VPN using an ECDSA signature as the IKE authentication method. The algorithms used in IKE or IPsec authentication or encryption are shown in Table 4.
|
IKE Protocol |
Tunnel Mode |
Phase1 Negotiation Mode |
Phase 1 Proposal (P1, IKE) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Authentication Method |
Authentication Algorithm |
DH Group |
Encryption Algorithm |
|||
|
IKEv1 |
Main |
Route |
ecdsa-signatures-256 |
sha-384 |
group14 |
aes-256-cbc |
|
IKE Protocol |
Tunnel Mode |
Phase1 Negotiation Mode |
Phase 2 Proposal (P2, IPsec) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Authentication Algorithm |
DH Group (PFS) |
Encryption Method |
Encryption Algorithm |
|||
|
IKEv1 |
Main |
Route |
No Algorithm |
group14 |
ESP |
aes-256-gcm |
- Configuring IPsec VPN with ECDSA signature IKE authentication on the Initiator
- Configuring IPsec VPN with ECDSA signature IKE authentication on the Responder
Configuring IPsec VPN with ECDSA signature IKE authentication on the Initiator
-
Configure the PKI. See, Example: Configuring PKI.
-
Generate the ECDSA key pair. See Example: Generating a Public-Private Key Pair.
-
Generate and load CA certificate. See Example: Loading CA and Local Certificates Manually.
-
Load CRL. See Example: Manually Loading a CRL onto the Device .
-
Generate and load a local certificate. See Example: Loading CA and Local Certificates Manually.
-
Configure the IKE proposal:
[edit] user@host# set security ike proposal ike-proposal1 authentication-method ecdsa-signatures-256 user@host# set security ike proposal ike-proposal1 dh-group group14 user@host# set security ike proposal ike-proposal1 authentication-algorithm sha-384 user@host# set security ike proposal ike-proposal1 encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc
Note:Here,
ike-proposal1is the IKE proposal name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure the IKE policy:
[edit] user@host# set security ike policy ike-policy1 mode main user@host# set security ike policy ike-policy1 proposals ike-proposal1 user@host# set security ike policy ike-policy1 certificate local-certificate cert1
-
Configure the IPsec proposal:
[edit] user@host# set security ipsec proposal ipsec-proposal1 protocol esp user@host# set security ipsec proposal ipsec-proposal1 encryption-algorithm aes-256-gcm
Note:Here,
ipsec-proposal1is the IPsec proposal name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure the IPsec policy:
[edit] user@host# set security ipsec policy ipsec-policy1 perfect-forward-secrecy keys group14 user@host# set security ipsec policy ipsec-policy1 proposals ipsec-proposal1
Note:Here,
ipsec-policy1is the IPsec policy name andipsec-proposal1is the IPsec proposal name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure IKE:
[edit] user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 ike-policy ike-policy1 user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 address 20.1.1.2 user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 local-identity inet 20.1.1.1 user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 external-interface xe-0/0/3 user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 version v2-only
Note:Here,
gw1is an IKE gateway name,20.1.1.2is the peer VPN endpoint IP,20.1.1.1is the local VPN endpoint IP, andxe-0/0/3is a local outbound interface as the VPN endpoint. The following configuration is also needed for IKEv2. -
Configure the VPN:
[edit] user@host# set security ipsec vpn vpn1 ike gateway gw1 user@host# set security ipsec vpn vpn1 ike ipsec-policy ipsec-policy1 user@host# set security ipsec vpn vpn1 bind-interface st0.0 user@host# set security ipsec vpn vpn1 establish-tunnels immediately
Note:Here,
vpn1is the VPN tunnel name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure service-set:
[edit] user@host# set services service-set IPSEC_SS_SPC3 next-hop-service inside-service-interface vms-4/0/0.1 user@host# set services service-set IPSEC_SS_SPC3 next-hop-service outside-service-interface vms-4/0/0.2 user@host# set services service-set IPSEC_SS_SPC3 ipsec-vpn vpn1
-
Configure Interfaces and routing-option:
[edit] user@host# set interfaces xe-0/0/3 unit 0 family inet address 20.1.1.1/24 user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 0 family inet user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 1 family inet user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 1 family inet6 user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 1 service-domain inside user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 2 family inet user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 2 family inet6 user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 2 service-domain outside user@host# set interfaces st0 unit 1 family inet user@host# set interfaces st0 unit 1 family inet6 user@host# set interfaces st0 unit 2 family inet user@host# set interfaces st0 unit 2 family inet6 user@host# set routing-options static route 10.1.1.0/24 next-hop st0.0
Configuring IPsec VPN with ECDSA signature IKE authentication on the Responder
-
Configure the PKI. See, Example: Configuring PKI.
-
Generate the ECDSA key pair. See Example: Generating a Public-Private Key Pair.
-
Load the CRL. See Example: Manually Loading a CRL onto the Device .
-
Generate and load CA certificate. See Example: Loading CA and Local Certificates Manually.
-
Configure the IKE proposal:
[edit] user@host# set security ike proposal ike-proposal1 authentication-method ecdsa-signatures-256 user@host# set security ike proposal ike-proposal1 dh-group group14 user@host# set security ike proposal ike-proposal1 authentication-algorithm sha-384 user@host# set security ike proposal ike-proposal1 encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc
Note:Here,
ike-proposal1is the IKE proposal name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure the IKE policy:
[edit] user@host# set security ike policy ike-policy1 mode main user@host# set security ike policy ike-policy1 proposals ike-proposal1 user@host# set security ike policy ike-policy1 certificate local-certificate cert1
-
Configure the IPsec proposal:
[edit] user@host# set security ipsec proposal ipsec-proposal1 protocol esp user@host# set security ipsec proposal ipsec-proposal1 encryption-algorithm aes-256-gcm
Note:Here,
ipsec-proposal1is the IPsec proposal name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure the IPsec policy:
[edit] user@host# set security ipsec policy ipsec-policy1 perfect-forward-secrecy keys group14 user@host# set security ipsec policy ipsec-policy1 proposals ipsec-proposal1
Note:Here,
ipsec-policy1is the IPsec policy name andipsec-proposal1is the IPsec proposal name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure the IKE:
[edit] user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 ike-policy ike-policy1 user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 address 20.1.1.1 user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 local-identity inet 20.1.1.2 user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 external-interface xe-0/0/4 user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 version v2-only
Note:Here,
gw1is an IKE gateway name,20.1.1.1is the peer VPN endpoint IP,20.1.1.2is the local VPN endpoint IP, andxe-0/0/4is a local outbound interface as the VPN endpoint. The following configuration is also needed for IKEv2. -
Configure the VPN:
[edit] user@host# set security ipsec vpn vpn1 ike gateway gw1 user@host# set security ipsec vpn vpn1 ike ipsec-policy ipsec-policy1 user@host# set security ipsec vpn vpn1 bind-interface st0.0 user@host# set security ipsec vpn vpn1 establish-tunnels immediately
Note:Here,
vpn1is the VPN tunnel name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure service-set:
[edit] user@host# set services service-set IPSEC_SS_SPC3 next-hop-service inside-service-interface vms-4/0/0.1 user@host# set services service-set IPSEC_SS_SPC3 next-hop-service outside-service-interface vms-4/0/0.2 user@host# set services service-set IPSEC_SS_SPC3 ipsec-vpn vpn1
-
Configure Interfaces and routing-option:
[edit] user@host# set interfaces xe-0/0/3 unit 0 family inet address 20.1.1.2/24 user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 0 family inet user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 1 family inet user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 1 family inet6 user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 1 service-domain inside user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 2 family inet user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 2 family inet6 user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 2 service-domain outside user@host# set interfaces st0 unit 1 family inet user@host# set interfaces st0 unit 1 family inet6 user@host# set interfaces st0 unit 2 family inet user@host# set interfaces st0 unit 2 family inet6 user@host# set routing-options static route 30.1.1.0/24 next-hop st0.0
Configuring Firewall Rules
MX devices allow configuring firewall filter to allow or reject specific traffic.
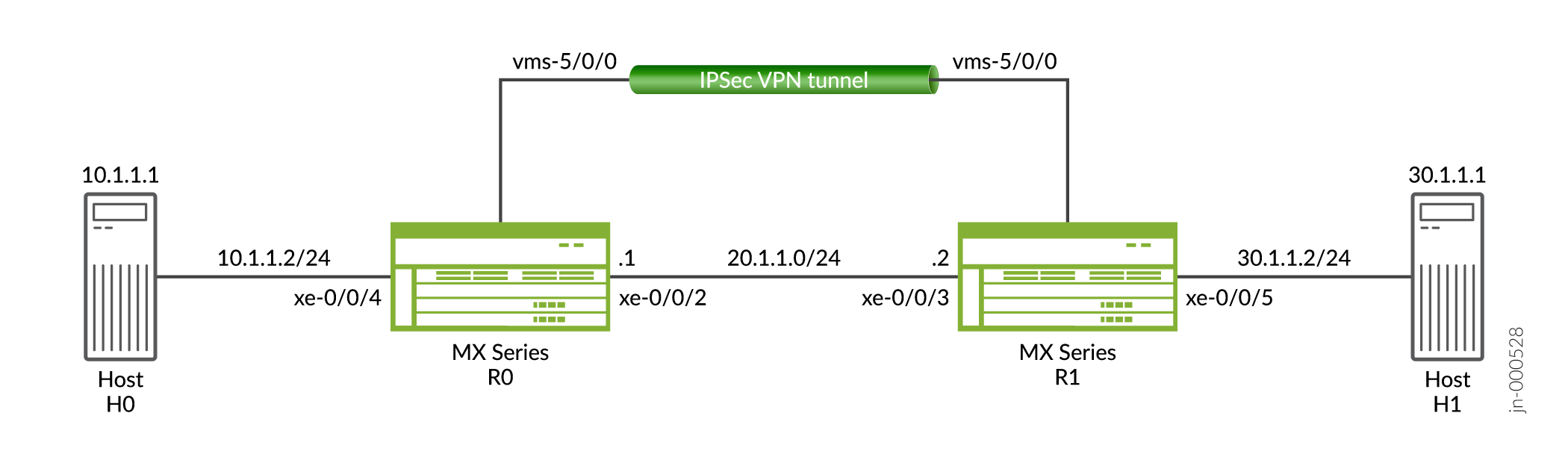
The following procedures explain how to configure IPSec VPN and firewall rules.
For Firewall Filters configuration guide see, Firewall Filters Overview, Chapter 2.
- Configuring IPsec VPN with Firewall Filters on the Initiator
- Configuring IPsec VPN with Firewall Filters on the Responder
- Sample IPsec VPN Log
- Sample Firewall Filters log
Configuring IPsec VPN with Firewall Filters on the Initiator
-
Configure the IKE proposal:
[edit] user@host# set security ike proposal ike-proposal1 authentication-method pre-shared-keys user@host# set security ike proposal ike-proposal1 dh-group group14 user@host# set security ike proposal ike-proposal1 authentication-algorithm sha256 user@host# set security ike proposal ike-proposal1 encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc
Note:Here,
ike-proposal1is the IKE proposal name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure the IKE policy:
[edit] user@host# set security ike policy ike-policy1 mode main user@host# set security ike policy ike-policy1 proposals ike-proposal1
Note:Here,
ike-policy1is the IKE policy name and ike-proposal1 is the IKE proposal namegiven by the authorized administrator.
user@host# prompt security ike policy ike-policy1 pre-shared-key ascii-text New ascii-text (secret): Retype new ascii-text (secret):
Note:You must enter and reenter the preshared key when prompted. For example, the preshared key can be
Modvpn@jnpr1234.Note:The preshared key can alternatively be entered in hexadecimal format. For example:
[edit] root@host# prompt security ike policy ike-policy1 pre-shared-key hexadecimal New hexadecimal (secret): Retype new hexadecimal (secret):
Enter the hexadecimal preshared key value.
-
Configure the IPsec proposal:
[edit] user@host# set security ipsec proposal ipsec-proposal1 protocol esp user@host# set security ipsec proposal ipsec-proposal1 authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-256-128 user@host# set security ipsec proposal ipsec-proposal1 encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc
Note:Here,
ipsec-proposal1is the IPsec proposal name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure the IPsec policy:
[edit] user@host# set security ipsec policy ipsec-policy1 perfect-forward-secrecy keys group14 user@host# set security ipsec policy ipsec-policy1 proposals ipsec-proposal1
Note:Here,
ipsec-policy1is the IPsec policy name andipsec-proposal1is the IPsec proposal name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure the IKE:
[edit] user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 ike-policy ike-policy1 user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 address 20.1.1.2 user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 local-identity inet 20.1.1.1 user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 external-interface xe-0/0/2 user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 version v2-only
Note:Here,
gw1is an IKE gateway name,20.1.1.2is the peer VPN endpoint IP,20.1.1.1is the local VPN endpoint IP, andxe-0/0/2is a local outbound interface as the VPN endpoint. The following additional configuration is also needed in the case of IKEv2. -
Configure the VPN:
[edit] user@host# set security ipsec vpn vpn1 ike gateway gw1 user@host# set security ipsec vpn vpn1 ike ipsec-policy ipsec-policy1 user@host# set security ipsec vpn vpn1 bind-interface st0.0 user@host# set security ipsec vpn vpn1 establish-tunnels immediately
Note:Here,
vpn1is the VPN tunnel name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure service-set:
[edit] user@host# set services service-set IPSEC_SS_SPC3 next-hop-service inside-service-interface vms-5/0/0.1 user@host# set services service-set IPSEC_SS_SPC3 next-hop-service outside-service-interface vms-5/0/0.2 user@host# set services service-set IPSEC_SS_SPC3 ipsec-vpn vpn1
-
Configure interfaces and routing-option:
[edit] user@host# set interfaces xe-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet address 20.1.1.1/24 user@host# set interfaces vms-5/0/0 unit 0 family inet user@host# set interfaces vms-5/0/0 unit 1 family inet user@host# set interfaces vms-5/0/0 unit 1 family inet6 user@host# set interfaces vms-5/0/0 unit 1 service-domain inside user@host# set interfaces vms-5/0/0 unit 2 family inet user@host# set interfaces vms-5/0/0 unit 2 family inet6 user@host# set interfaces vms-5/0/0 unit 2 service-domain outside user@host# set interfaces st0 unit 1 family inet user@host# set interfaces st0 unit 1 family inet6 user@host# set interfaces st0 unit 2 family inet user@host# set interfaces st0 unit 2 family inet6 user@host# set routing-options static route 30.1.1.0/24 next-hop st0.0
-
Configuring Firewall Filters:
[edit] user@host# set interfaces xe-0/0/4 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.1.2/24 user@host# set firewall family inet filter fw_filter1 term 1 from source-address 30.1.1.1/32 user@host# set firewall family inet filter fw_filter1 term 1 from destination-address 10.1.1.1/32 user@host# set firewall family inet filter fw_filter1 term 1 then count inc1 user@host# set firewall family inet filter fw_filter1 term 1 then log user@host# set firewall family inet filter fw_filter1 term 1 then accept user@host# set firewall family inet filter fw_filter1 term 2 then count inc2 user@host# set firewall family inet filter fw_filter1 term 2 then log user@host# set firewall family inet filter fw_filter1 term 2 then reject
Configuring IPsec VPN with Firewall Filters on the Responder
-
Configure the IKE proposal:
[edit] user@host# set security ike proposal ike-proposal1 authentication-method pre-shared-keys user@host# set set security ike proposal ike-proposal1 dh-group group14 user@host# set security ike proposal ike-proposal1 authentication-algorithm sha256 user@host# set security ike proposal ike-proposal1 encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc
Note:Here,
ike-proposal1is the IKE proposal name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure the IKE policy:
[edit] user@host# set security ike policy ike-policy1 mode main user@host# set security ike policy ike-policy1 proposals ike-proposal1
Note:Here,
ike-policy1is the IKE policy name andike-proposal1is the IKE proposal name given by the authorized administrator.user@host# prompt security ike policy ike-policy1 pre-shared-key ascii-text New ascii-text (secret): Retype new ascii-text (secret):
Note:You must enter and reenter the preshared key when prompted. For example, the preshared key can be
Modvpn@jnpr1234.Note:The preshared key can alternatively be entered in hexadecimal format. For example:
[edit] root@host# prompt security ike policy ike-policy1 pre-shared-key hexadecimal
New hexadecimal (secret):Retype new hexadecimal (secret):ere, the hexadecimal preshared key can be cc2014bae9876543.
-
Configure the IPsec proposal:
[edit] user@host# set security ipsec security proposal ipsec-proposal1 protocol esp user@host# set security ipsec security proposal ipsec-proposal1 authentication-algorithm hmac-sha-256-128 user@host# set security ipsec proposal ipsec-proposal1 encryption-algorithm aes-256-cbc
Note:Here,
ipsec-proposal1is the IPsec proposal name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure the IPsec policy:
[edit] user@host# set security ipsec policy ipsec-policy1 perfect-forward-secrecy keys group14 user@host# set security ipsec policy ipsec-policy1 proposals ipsec-proposal1
Note:Here,
ipsec-policy1is the IPsec policy name andipsec-proposal1is the IPsec proposal name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure the IKE:
[edit] user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 ike-policy ike-policy1 user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 address 20.1.1.1 user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 local-identity inet 20.1.1.2 user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 external-interface xe-0/0/3 user@host# set security ike gateway gw1 version v2-only
Note:Here,
gw1is an IKE gateway name,20.1.1.2is the peer VPN endpoint IP,20.1.1.1is the local VPN endpoint IP, andxe-0/0/3is a local outbound interface as the VPN endpoint. The following additional configuration is also needed in the case of IKEv2. -
Configure the VPN:
[edit] user@host# set security ipsec vpn vpn1 ike gateway gw1 user@host# set security ipsec vpn vpn1 ike ipsec-policy ipsec-policy1 user@host# set security ipsec vpn vpn1 bind-interface st0.0 user@host# set security ipsec vpn vpn1 establish-tunnels immediately
Note:Here,
vpn1is the VPN tunnel name given by the authorized administrator. -
Configure service-set:
[edit] user@host# set services service-set IPSEC_SS_SPC3 next-hop-service inside-service-interface vms-4/0/0.1 user@host# set services service-set IPSEC_SS_SPC3 next-hop-service outside-service-interface vms-4/0/0.2 user@host# set services service-set IPSEC_SS_SPC3 ipsec-vpn vpn1
-
Configure interfaces and routing-option:
[edit] user@host# set interfaces xe-0/0/3 unit 0 family inet address 20.1.1.2/24 user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 0 family inet user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 1 family inet user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 1 family inet6 user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 1 service-domain inside user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 2 family inet user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 2 family inet6 user@host# set interfaces vms-4/0/0 unit 2 service-domain outside user@host# set interfaces st0 unit 1 family inet user@host# set interfaces st0 unit 1 family inet6 user@host# set interfaces st0 unit 2 family inet user@host# set interfaces st0 unit 2 family inet6 user@host# set routing-options static route 10.1.1.0/24 next-hop st0.0
-
Configuring Firewall Filters:
[edit] user@host# set interfaces xe-0/0/5 unit 0 family inet address 30.1.1.2/24 user@host# set firewall family inet filter fw_filter1 term 1 from source-address 10.1.1.1/32 user@host# set firewall family inet filter fw_filter1 term 1 from destination-address 30.1.1.1/32 user@host# set firewall family inet filter fw_filter1 term 1 then count inc1 user@host# set firewall family inet filter fw_filter1 term 1 then log user@host# set firewall family inet filter fw_filter1 term 1 then accept user@host# set firewall family inet filter fw_filter1 term 2 then count inc2 user@host# set firewall family inet filter fw_filter1 term 2 then log user@host# set firewall family inet filter fw_filter1 term 2 then reject
Sample IPsec VPN Log
[edit] root@trinity:fips# run show security ipsec security-associations Total active tunnels: 1 Total IPsec sas: 1 ID Algorithm SPI Life:sec/kb Mon lsys Port Gateway <500011 ESP:aes-cbc-128/sha256 0x739b3a54 6508/ unlim - root 500 20.1.1.2 >500011 ESP:aes-cbc-128/sha256 0x538856ed 6508/ unlim - root 500 20.1.1.2
[edit] root@trinity:fips# run show security ike security-associations Index State Initiator cookie Responder cookie Mode Remote Address 11292 UP be4611adbd316f8c fc4e53edda79c178 IKEv2 20.1.1.2
Sample Firewall Filters log
[edit] root@trinity:fips# run show firewall Filter: __default_bpdu_filter__ Filter: fw_filter1 Counters: Name Bytes Packets inc1 0 0 inc2 840 10 [edit] root@trinity:fips# run show firewall log Log : Time Filter Action Interface Protocol Src Addr Dest Addr 11:05:31 pfe R st0.1 ICMP 30.1.1.1 10.1.1.1 11:05:30 pfe R st0.1 ICMP 30.1.1.1 10.1.1.1 [edit] root@trinity:fips# run show firewall log Log : Time Filter Action Interface Protocol Src Addr Dest Addr 11:19:59 pfe R st0.1 TCP 30.1.1.1 10.1.1.1 [edit] root@trinity:fips# run show firewall log Log : Time Filter Action Interface Protocol Src Addr Dest Addr 13:00:18 pfe A ge-0/0/4.0 ICMP 30.1.1.5 10.1.1.1 13:00:17 pfe A ge-0/0/4.0 ICMP 30.1.1.5 10.1.1.1 [edit] root@trinity:fips# run show firewall log Log : Time Filter Action Interface Protocol Src Addr Dest Addr 13:00:45 pfe A ge-0/0/4.0 TCP 30.1.1.5 10.1.1.1
