Deploying Red Hat Openstack with Contrail Control Plane Managed by Tungsten Fabric Operator
This document provides steps needed to use the Operator Framework for Contrail Networking deployment that is using Red Hat Openstack version 16.1 (RHOSP16.1) as it’s orchestration platform.
Figure 1 shows the difference between the classic deployment of RHOSP16.1 and the Tungsten Fabric (TF) Operator based deployment.
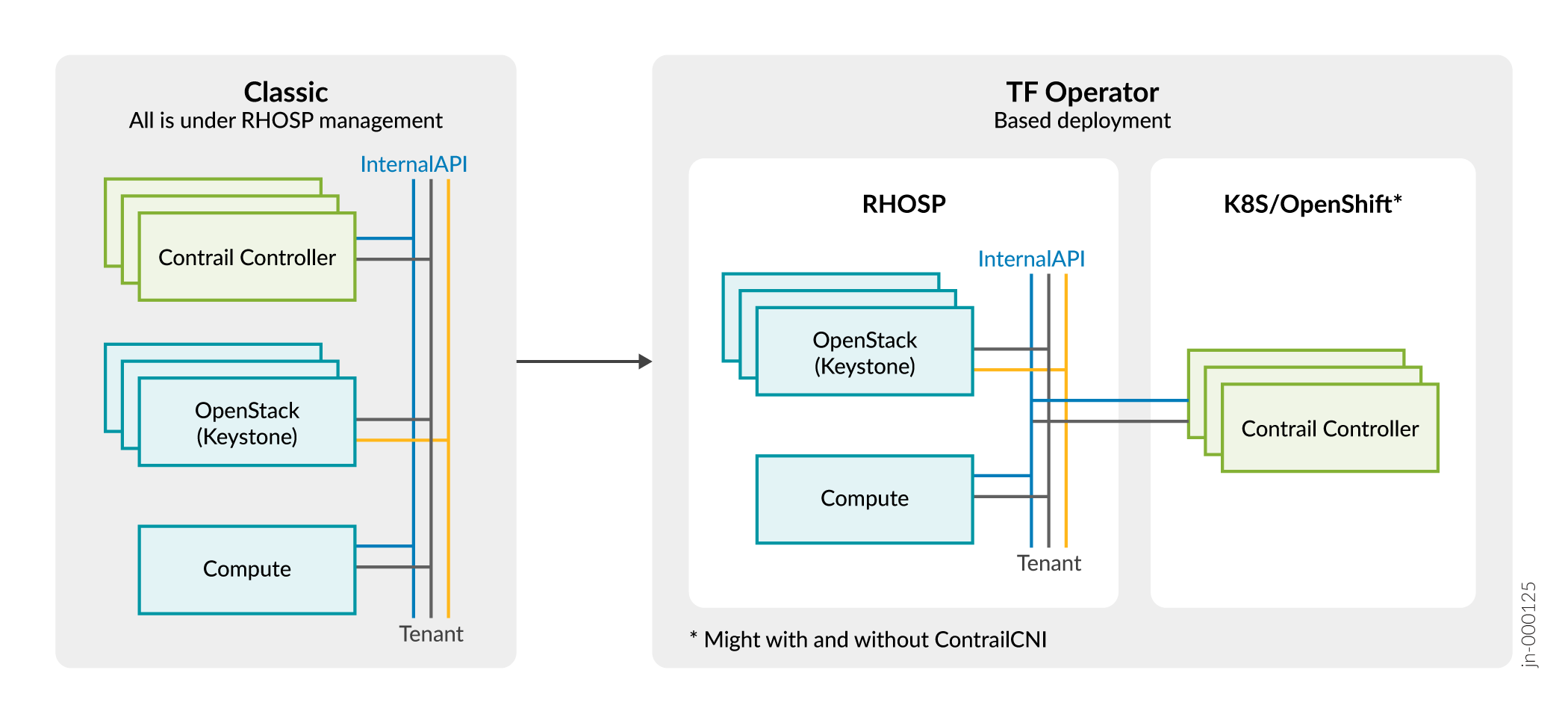
RHOSP does not deploy ContrailController, ContrailAnalytics, and ContrailAnalyticsDatabase Overcloud roles.
Compute nodes are deployed and managed by RHOSP.
Contrail Control plane is deployed separately on top of Kubernetes or OpenShift cluster.
Contrail Control plane nodes require access to RHOSP networks such as Internal API and Tenant. Administrator must configure the Internal API and Tenant, if Kubernetes or OpenShift cluster is deployed outside of the RHOSP networks.
To deploy RHOSP based on TF-Operator:
