IBMi
The JSA DSM for IBM i, formerly known as AS/400 iSeries, collects audit records and event information from IBM i systems.
The following table identifies the specifications for the IBM i DSM:
Specification |
Value |
|---|---|
Manufacturer |
IBM |
DSM name |
IBM i |
Supported versions |
5R4 |
RPM file name |
DSM-IBMi-JSA_version-build_number.noarch.rpm |
Protocol |
Log File Protocol Syslog |
Event Format |
Common Event Format (CEF). CEF:0 is supported. |
Recorded event types |
Audit records and events |
Automatically discovered? |
No |
Includes identity? |
Yes |
Includes custom properties? |
No |
More information |
To collect events from IBM i systems, complete the following steps:
If automatic updates are not enabled, download and install the most recent version of the IBM i DSM RPM from the Juniper Downloads onto your JSA console.
Configure your IBM i system to communicate with JSA.
Add an IBM i log source on the JSA Console by using the following table to configure the parameters that are required to collect IBM i events:
Table 2: IBM i Log Source Parameters Parameter
Value
Log Source Type
IBM i
Protocol Configuration
Log File
If you are using the PowerTech Interact or LogAgent for System i software to collect CEF formatted syslog messages, you must select the Syslog option
Service Type
Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP)
Configuring IBM i to Integrate with JSA
You can integrate IBM i with JSA.
From https://support.juniper.net/support/downloads/, download the following file:
AJLIB.SAVF
Copy the AJLIB.SAVF file to a computer or terminal that has FTP access to IBM i.
Create a generic online SAVF file on the IBM i by typing the following command:
CRTSAVF QGPL/SAVF
Use FTP on the computer or terminal to replace the IBM i generic SAVF file with the AJLIB.SAVF file that you downloaded.
Type the following commands:
bincd qgpllcd c:\put ajlib.savf AJLIBquitIf you are transferring your SAVF file from another IBM i system, send the file by placing the FTP sub-command mode BINARY before the GET or PUT statement.
Restore the AJLIB file on IBM i by typing the following command:
RSTLIB SAVLIB(AJLIB) DEV(*SAVF) SAVF(QGPL/AJLIB)
AJLIB provides the mapping and data transfer support that is needed to send IBM i audit journal entries to JSA.
Run AJLIB/SETUP
The setup screen is used to configure AJLIB for FTP, SFTP, or a local path to receive the processed entries.
The server user ID is required for FTP or SFTP, and a password is required for FTP. While FTP handles line delimiter conversions, you set the line feed to the expected value for the type of system that receives the SFTP transfers.
If you want to use SFTP, run AJLIB/GENKEY.
This command generates the SSH key pair that is required for SFTP authentication. If the key pair exists, it is not replaced. If you want to generate a new key pair, before you run this command, remove the existing key files from the /ajlib/.ssh directory.
After you generate a key pair, use the following steps to enable the use of the key pair on the server:
Copy the id_rsa.pub file from the /ajlib directory to the SSH server, and then install it in the appropriate folder.
Ensure that the SSH server is added to the known_hosts file of the user profile that runs the AJLIB/AUDITJRN command.
Use the appropriate user profile to do the following steps:
Start a PASE (Portable Application Solutions Environment) shell by typing the following command:
call qp2term
Start a session with the SSH server by typing the following command:
ssh -T <user>@<serveraddress>
If prompted, accept the system key, and enter a password.
Type exit, to close the SSH session.
If you want to run these steps under a different IBM i profile than the one that runs the AJLIB/AUDITRN command, copy the .ssh directory and known_hosts file to the home directory of the profile that is used to run this command.
To configure the filtering of specific entry types, use the AJLIB/SETENTTYP command.
Set up the data collection start date and time for the audit journal library (AJLIB) by typing the following command:
AJLIB/DATETIME
If you start the audit journal collector, a failure message is sent to QSYSOPR.
The setup function sets a default start date and time for data collection from the audit journal to 08:00:00 of the current day.
To preserve your previous start date and time information from a previous installation, you must run AJLIB/DATETIME. Record the previous start date and time and type those values when you run AJLIB/SETUP. The start date and time must contain a valid date and time in the six character system date and system time format. The end date and time must be a valid date and time or left blank.
Run AJLIB/AUDITJRN.
The audit journal collection program starts and sends the records to your remote FTP server: If the transfer to the FTP server fails, a message is sent to QSYSOPR. The process for starting AJLIB/AUDITJRN is typically automated by an IBM i job Scheduler, which collects records periodically.
If the FTP transfer is successful, the current date and time information is written into the start time for AJLIB/DATETIME to update the gather time, and the end time is set to blank. If the FTP transfer fails, the export file is erased and no updates are made to the gather date or time.
Manually Extracting Journal Entries for IBM i
You can run the DSPJRN command to extract journal entries for IBM i when an audit journal receiver chain is broken.
Run the ALJIB/DATETIME command to set the Start Date to *OUTF. This command forces the processing program to use the pre-built QTEMP/AUDITJRN outfile for parsing, instead of using the date time to extract journal entries. After you run the parsing program command AJLIB/AUDITJRN, the DATETIME is set to the new processing date.
Log in to your IBM i system command-line interface (CLI).
Run DSPJRN.
The only changeable parameters in the following example are RCVRNG and ENTTYP. Do not change any other command parameters. Ensure that ENTTP matches the AJLIB/SETENTTYP command settings.
DSPJRN JRN(QSYS/QAUDJRN) RCVRNG(AUDRCV0001 AUDRCV0003) JRNCDE((T)) ENTTYP(*ALL) OUTPUT(*OUTFILE) OUTFILFMT(*TYPE5) OUTFILE(QTEMP/AUDITJRN) ENTDTALEN(*VARLEN 16000 100)
To set the Date Time to use outfile *OUTF support, run the AJLIB/DATETIME command.
Figure 1: DSPJRN Start and End Times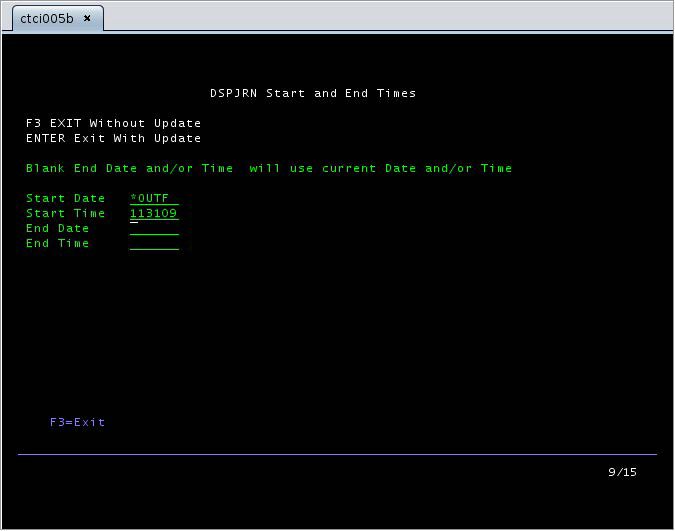
Run AJLIB/AUDITJRN.
The DATETIME is set to the next start date.
Pulling Data when you use the Log File Protocol
You can configure IBM i as the log source, and to use the log file protocol in JSA:
To configure JSA to receive events from an IBM i system, you must select the IBM i option from the Log Source Type list when you add a log source in JSA.
To configure the log file protocol for the IBM i DSM, you must select the Log File option from the Protocol Configuration list and define the location of your FTP server connection settings.
Note:If you are using the PowerTech Interact or LogAgent for System i software to collect CEF formatted syslog messages, you must select the Syslog option from the Protocol Configuration list.
Use the log file protocol option that you select a secure protocol for transferring files, such as Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP).
For a complete list of Log File protocol parameter options, see Log File protocol configuration options in Protocol Configuration Options.
Configuring Townsend Security Alliance LogAgent to Integrate with JSA
You can collect all audit logs and system events from Townsend Security Alliance LogAgent. You must configure Alliance LogAgent for the JSA LEEF and configure a destination that specifies JSA as the syslog server.
Log in to your Townsend Security Alliance LogAgent appliance.
Add the ALLSYL100 to your library list by typing the following command::
addlible allsy1100
To display the main menu select go symain.
Select the option for Configuration
Select Configure Alliance LogAgent and configure the following parameters.
Parameter
Description
Interface version
4=IBM JSA LEEF
Transmit
1=Yes
Data queue control
1=Yes
Format
4=IBM JSA LEEF
From the configuration menu, select Work With TCP Clients.
Select option 2 to change the SYSLOGD client and configure the following parameters.
Parameter
Description
Status
1=Active
Autostart client
1=Yes
Remote IP address
IP address of JSA
Remote port number
514
From the Configuration menu, select Start LogAgent Subsystem. Events flow to JSA.
After TCP services start, consider automatically starting the Alliance LogAgent subsystem by modifying your IPL QSTRUP program to include the following statements:
/* START ALLIANCE LOGAGENT */ QSYS/STRSBS ALLSYL100/ALLSYL100 MONMSG MSGID(CPF0000)
For more information about installing and configuring for Independent Auxiliary Storage Pool operation, and more filter options for events, see your vendor documentation.
IBM i Sample Event Message
Use this sample event message to verify a successful integration with JSA.
Due to formatting issues, paste the message format into a text editor and then remove any carriage returns or line feed characters.
IBM i sample message when you use the Syslog protocol
The following sample event message shows that DRDA Distributed Relational DB access is allowed.
The logs that you send to JSA must be tab-delimited. If you cut and paste the code from this sample, make sure that you press the tab key where indicated by the <tab> variables, then remove the variables.
<176>Apr 24 15:31:58 ibm.i.test LEEF:1.0|Raz-Lee iSecurity|Firewall|1.0|GRE7860| usrName=USERNAME<tab>devTime=2019-04-24-15.31.58.000<tab>devTimeFormat=yyyy-MM-dd- HH.mm.ss.SSS<tab>source=172.16.1.1<tab>sev=10<tab>jobName=948290/QUSER/ QRWTSRVR<tab>pgmName=*NONE<tab>pgmLib=*NONE<tab>entryType=36/A<tab>entryDesc=DRDA Distributed Relational DB access<tab>Action_allowed=1<tab>Src_user_before_Prechk= USERNAME<tab>Source_system=SYSTEM1<tab>Decision_level=USSRV<tab>Authority_set_to_user=USERNA ME<tab>Server_Id=36
|
JSA field name |
Highlighted values in the event payload |
|---|---|
|
Event ID |
GRE7860 |
|
Username |
USERNAME |
|
Severity |
10 |
