BGP Peers Summary
To access the BGP Peers section, navigate to Routers > Router Name > Insights page. Then click the BGP tab in the Routing Protocols section.
You can view BGP Peers summary of a router in the BGP Peers section. The BGP peer information table, the Peer Flaps graph and the Routing Table Peer Stats graph provide information about the status of all BGP peers of a router. You can use this information to address peering issues that need immediate attention.
The widgets below the header display the following information about a router's BGP peers:
-
Peers─Number of BGP peers of the router.
-
Down─Number of BGP peers that are down for the router.
Click the Down widget to filter the Peers Information table. The Peers Information table now displays only those peers whose status is down.
-
Peer Groups─Number of peer groups for the router.
The BGP Peers section is updated every three minutes. Click the refresh icon to trigger a manual refresh, if needed.
The data displayed on the graphs in BGP Peers Summary section are different from those displayed in BGP Global Summary section in that the data in BGP Peer Summary section are for the routing table of a specific peer.
Peers Information
The Peers Information table displays information such as peer status and network layer reachability information (NLRI) about a router's BGP peer. You can use this table to get a quick view of the state of the BGP sessions established between a router and all its BGP peers.
You can search and filter the table by using keywords. Click the search icon (magnifying glass), enter the search term in the text box, and press Enter. The search results are updated in the table. You can also sort the columns in the table by header. Click any column header to sort its entries. Table 1 describes the fields in the Peers Information Table.
You can customize both Peers Information table and the Routing Table Summary table, to display only the desired information by selecting the columns that should appear in the table. Click the table setting icon to choose the information you want to view on the table.
The Peers Information table is expandable. Click the down arrow on a row (a peer) to expand the table to display details of all routing tables for that peer. Table 2 describes the fields in the routing tables summary of a peer.
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
State |
Current state of the BGP session:
|
|
Peer |
IP address of the BGP peer. |
|
Description |
Brief description of the peer. |
|
Active Prefixes |
Total number of active prefixes in all peer routing tables. |
|
Peer AS |
AS number of the peer. For internal BGP (IBGP), this number is the same as Local AS. |
|
Local AS |
AS number of the local routing device. |
|
Peer Group |
The BGP group the peer belongs to. |
|
Last Flap Event |
Last activity that occurred in the BGP session:
|
|
Last Error |
Last error that occurred in the BGP session:
|
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Routing Table |
Name of the routing table. |
|
Address Family |
Address family of the routing table. An address family can be IPv4, IPv6, inet-vpn and so on. |
|
Prefix Limit |
Maximum number of prefixes received on a BGP peer session. Range: 1 through 4,294,967,295 (232 – 1) |
|
Active Prefixes |
Number of prefixes received from the peer that are active in the routing table. |
|
Accepted Prefixes |
Number of prefixes that are accepted in a BGP peer session. |
|
Advertised Prefixes |
Number of prefixes advertised to a peer. |
|
Received Prefixes |
Number of prefixes from the peer, both active and inactive, that are present in the routing table. |
BGP Peers Charts
The BGP peers chart section displays Peer Flaps graph and Routing Table Peer Stats graph for routing tables of a specific peer.
Peer Flaps
Flap count is the total number of BGP session flaps from a router. The Peers Flaps graph displays the summary of router flaps for a given peer, in the form of a time series graph. The graph displays flap delta which is the difference between the current flap count and previous flap count, and indicates the stability of the peer.
To view peer flaps data, select a peer from the Peer drop-down list. Then select a routing table of the peer. The peer flaps graph displays data for the selected peer, for the selected routing table.
You can move the slider across the graph. A pop-up on the slider displays the flap count delta for that period. As you move the slider along the graph, you can see the slider of the Router Events graph also move, simultaneously.
Using this feature, you can visually correlate a router event (from the Router Events graph) to a peak in the router flaps delta value. For example, you can analyze a BGP route flapping situation by investigating router events that might have occurred in the same time interval.
Click the expand icon for an enlarged view of the graph.
If the flaps delta is zero, Global Peers Flaps graph will not display any data along the y-axis.
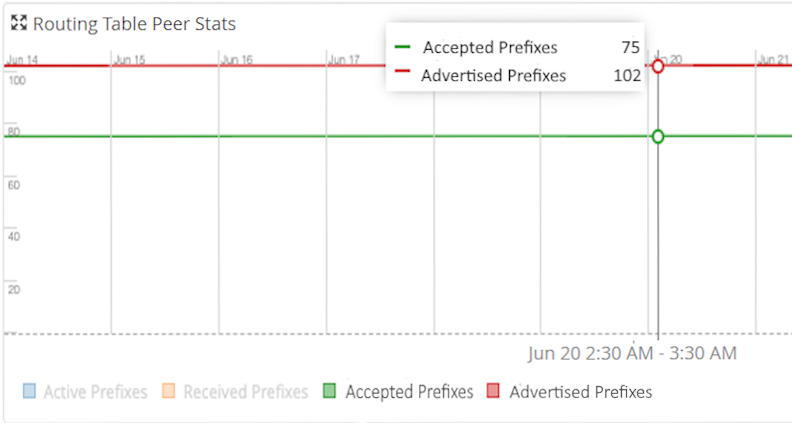
Routing Table Peer Stats
The Routing Table Peer Stats graph displays the NLRI with the count of active prefixes, received prefixes, accepted prefixes, and advertised prefixes.
To view routing table peer statistics:
-
Select a peer from the Peer drop-down list.
-
Then select a routing table of the peer.
The Routing Table Peer Stats graph displays data for the selected peer, for the selected routing table.
-
Active Prefixes─Number of prefixes received from the peer that are active in the routing table.
-
Received Prefixes─Number of prefixes from the peer, both active and inactive, that are in the routing table.
-
Accepted Prefixes─Number of prefixes that are accepted in a BGP peer session.
-
Advertised Prefixes─Number of prefixes advertised to a peer.
You can move the slider across the graph. A pop-up on the slider displays the count of specific prefixes for that period. As you move the slider along the graph, you can see the slider of the Router Events graph also move, simultaneously.
The Routing Table Peer Stats graph enables you to visually correlate a router event (from the Router Events graph) to the number of specific prefixes in each period.
Click the expand icon for an enlarged view of the graph.
You can view the legend below the graph to interpret the plotted lines.
You can filter the prefixes in the Routing Table Peer Stats graph by clicking the legend.
View Past Peer Routes
Juniper Routing Assurance stores the routing table information of BGP peers that were reachable in the past. Using this feature, you can view the BGP peers that were reachable and the RIBs of peers that were available in the past. You can use these RIBs to view the drops in received routes.
To view the previously reachable BGP peers and the previously available routes:
-
Click Show Previous in the BGP Peers section.
-
Select All.
You can see that the Peers Information table is updated with the historic routing table or tables with their last seen timestamp.
-
Select a peer from the Select Peer drop-down list.
-
Then select the routing table from the Select Routing Table drop-down list.
The Peer Flaps and the Routing Table Peer Stats graphs are updated to display the drop in received routes.
The historical peer route information will be stored in the BGP Peers section for seven days.
You can use the historical peer routes to:
-
Track BGP peers that were reachable in the past.
-
View routes through the BGP peers that were available in the past.
Use the Routing Table Peer Stats graph and the Router Events graph to correlate events that occurred before a route or a BGP peer in the routing table became unreachable. For example, a BGP neighbor down event might have caused a route to be unavailable.
The widget Down displays the number of peers that are down and does not include the peers that were down previously. Similarly, Active Prefixes is the total number of all the active prefixes of all routing tables. This count does not include the active prefixes of routes previously present in the table.
When an unreachable BGP peer or an unavailable routing table becomes reachable or available again, it will be listed as an active route and not as a previous route or peer.