Access Gateway Function
Access Gateway Function
The Access Gateway Function (AGF) on Junos OS provides a solution that enables interworking of wireline-connected devices and the 5G core (5GC). In adaptive mode, the AGF manages the access connections between the residential gateway (RG) and the 5GC by providing the 5G signaling that is used in the 5GC network.
-
IP connectivity
-
AAA services
-
QoS to subscribers on the RG
-
Connection between the 5GC and the existing FN-RG, which uses Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), DHCPv6, or Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE)
Figure 1 shows the legacy wireline control protocol stack used by the FN-RG, wireline AGF, and Access and Mobility Management Function (AMF). The wireline AGF acts as an N1 termination point for the FN-RG. N1 signaling is defined in the Non-Access Stratum (NAS) protocol. N2 signaling is defined in the Next Generation Application Protocol (NGAP).

Benefits of Access Gateway Function
-
Offers ease of migration for a subscriber with existing customer premise equipment (CPE), such as an FN-RG, to the 5G core (5GC)
-
Provides a solution that enables interworking between wireline devices and the 5GC
-
Supports existing FN-RG and existing hardware, such as the MX series routers.
-
Optimizes data plane traffic with the User Plane Function (UPF), resulting in improved performance
-
Eases deployment with by enabling the collocation of broadband network gateway (BNG), AGF, and UPF on the same platform
Figure 2 shows the topology that subscribers use to access their broadband service provider. Subscribers can access services through the traditional broadband network gateway (BNG) or through the AGF.
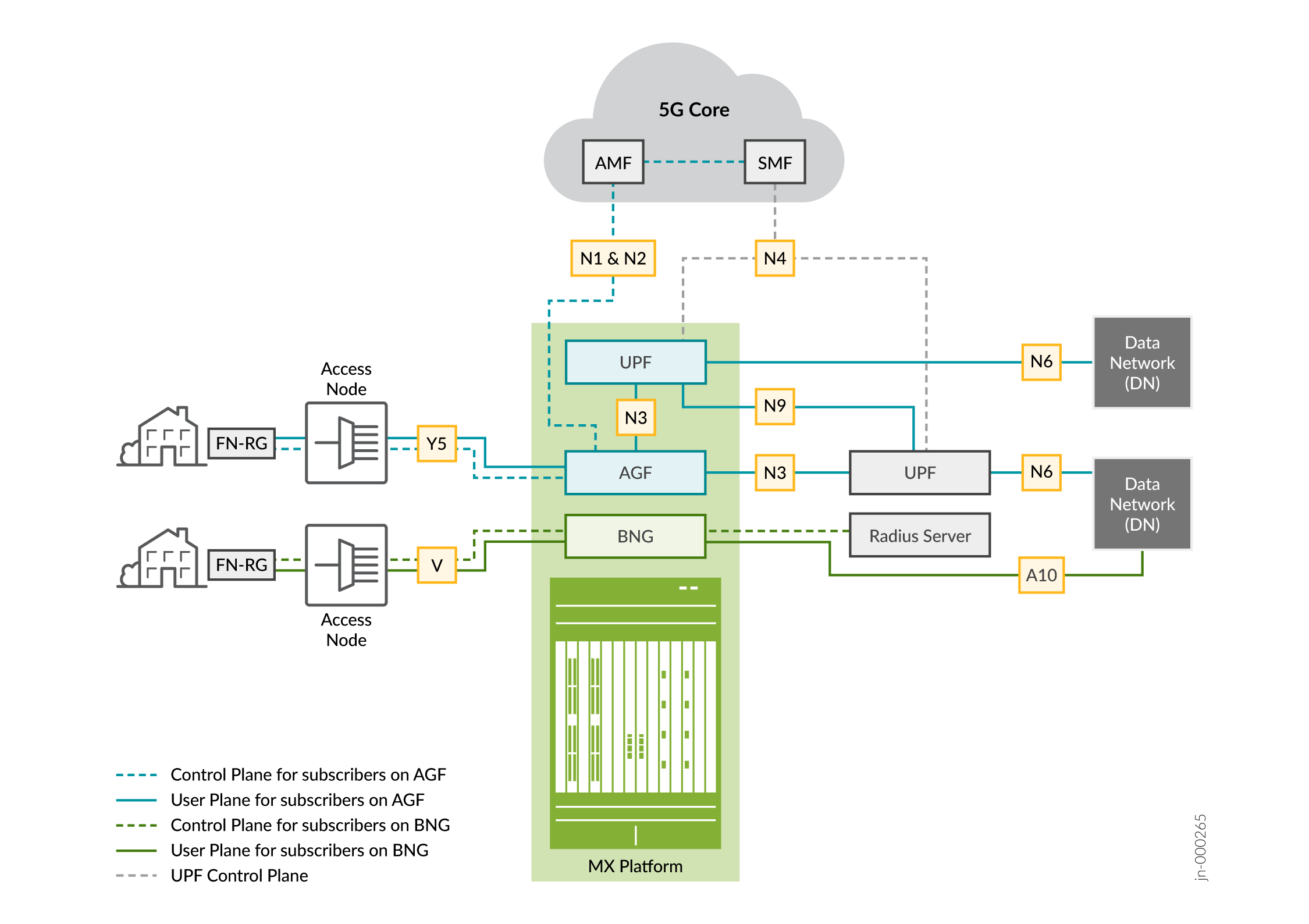
The BNG connects to the FN-RG through an access node that aggregates traffic for the service provider. The BNG routes the aggregated traffic to the service provider's network. The access node can be a DSL access multiplier (DSLAM) or an optical line termination (OLT). The BNG interacts with the FN-RG across the V interface and connects with the data network across the A10 interface.
The AGF connects to the FN-RG through the V interface. The AGF interacts with the wireline network to connect to the 5GC. From the 5GC point of view, the AGF is the equivalent of a 5G base station (gNodeB). In adaptive mode, the AGF provides the N1, N2, and N3 signaling on behalf of FN-RGs when the residential gateways (RGs) connect to the 5GC. The AGF provides the following services:
-
Exchanges control plane data with the Access and Mobility Management functions and Session Management Functions (SMFs) through the N1 and N2 interfaces (The AGF uses N1 and N2 signaling to authenticate, authorize, and manage sessions).
-
Registers the FN-RG as user equipment (UE) when the AGF establishes a connection with the AMF in the 5GC
-
Passes the allocated IP address from the SMF to the FN-RG
-
Passes the PDU session setup information (gateways, DNS, and so on) that is received from the 5GC for the FN-RG
-
Enforces UE-level QoS and policy that it receives from the 5GC
-
Sends and receives user plane data from the User Plane Function (UPF) through the N3 interface
The MX series routers support colocated BNG, AGF, and UPF services. AGF is an integral part of the Junos Multi-Access User Plane solution. See Junos Multi-Access User Plane.
