Traffic Burst Management on MIC and MPC Interfaces Overview
You can manage the impact of bursts of traffic on your network by configuring a burst-size value with the shaping rate or the guaranteed rate. The value is the maximum bytes of rate credit that can accrue for an idle queue or scheduler node. When a queue or node becomes active, the accrued rate credits enable the queue or node to catch up to the configured rate.
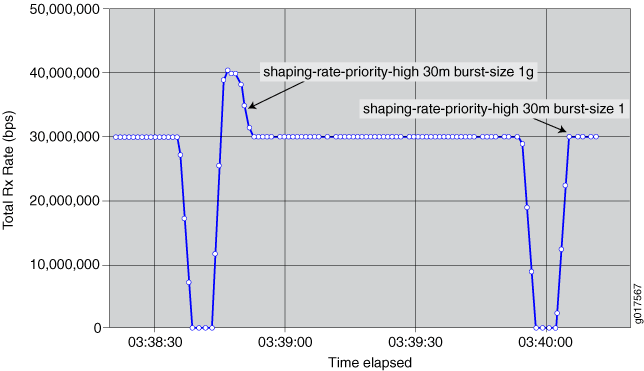
In Figure 1, the network administrator configures a large burst-size value for the shaping rate, then configures a small burst-size value. The larger burst size is subject to a maximum value. The smaller burst size is subject to a minimum value that enables the system to achieve the configured rates.
In both configurations, the scheduler node can burst beyond its shaping rate for a brief interval. The burst of traffic beyond the shaping rate is more noticeable with the larger burst size than the smaller burst size.
Guidelines for Configuring the Burst Size
Typically, the default burst-size (100 ms) for both scheduler nodes and queues on MIC and MPC interfaces is adequate for most networks. However, if you have intermediate equipment in your network that has very limited buffering and is intolerant of bursts of traffic, you might want to configure a lower value for the burst size.
Use caution when selecting a different burst size for your network. A burst size that is too high can overwhelm downstream networking equipment, causing dropped packets and inefficient network operation. Similarly, a burst size that is too low can prevent the network from achieving your configured rate.
When configuring a burst size, keep the following considerations in mind:
The system uses an algorithm to determine the actual burst size that is implemented for a node or queue. For example, to reach a shaping rate of 8 Mbps, you must allocate 1MB of rate credits every second. A shaping rate of 8 Mbps with a burst size of 500,000 bytes of rate-credit per seconds enables the system to transmit at most 500,000 bytes, or 4 Mbps. The system cannot implement a burst size that prevents the rate from being achieved.
For more information, see How the System Calculates the Burst Size.
There are minimum and maximum burst sizes for each platform, and different nodes and queue types have different scaling factors. For example, the system ensures the burst cannot be set lower than 1 Mbps for a shaping rate of 8 Mbps. To smoothly shape traffic, rate credits are sent much faster than once per second. The interval at which rate credits are sent varies depending on the platform, the type of rate, and the scheduler level.
When you have configured adjustments for the shaping rate (either by percentage or through an application such as ANCP or Multicast OIF), the system bases the default and minimum burst-size calculations on the adjusted shaping rate.
When you have configured cell shaping mode to account for ATM cell tax, the system bases the default and minimum burst-size calculations on the post-tax shaping rate.
The guaranteed rate and shaping rate share the value specified for the burst size. If the guaranteed rate has a burst size specified, that burst size is used for the shaping rate; if the shaping rate has a burst size specified, that bursts size is used for the guaranteed rate. If you have specified a burst size for both rates, the system uses the lesser of the two values.
The burst size configured for the guaranteed rate cannot exceed the burst-size configured for the shaping rate. Starting in Junos OS Release 15.1, the CLI no longer generates a commit error when the guaranteed-rate burst size is statically configured to be more than the shaping-rate burst size. This behavior changed with the advent of enhanced subscriber management. The system logs an error when the guaranteed-burst rate is higher, whether it is configured statically, dynamically with predefined variables, or by means of a change of authorization request.
If you have not configured a guaranteed rate, logical interfaces and interface sets receive a default guaranteed rate from the port speed. Queues receive a default guaranteed rate from the parent logical interface or interface set.
Burst-size is not supported with
per-priority-shaping.
How the System Calculates the Burst Size
When calculating the burst size, the system uses an exponent of a power of two. For example:
Shaping-rate in bps * 100 ms / (8 bits/byte * 1000 ms/s)
= 1,875,000 bytes
The system then rounds this value up. For example, the system uses the following calculation to determine the burst size for a scheduler node with a shaping rate of 150 Mbps:
Max (Shaping rate, Guaranteed rate) bps * 100 ms / (8 bits/byte
* 1000 ms/s) = 1,875,000 bytes
Rounded up to the next higher power of two = 2,097,150
(which is 2**21, or 0x200000)
The system assigns a single burst size to each of the following rate pairs:
Shaping rate and guaranteed rate
Guaranteed high (GH) and guaranteed medium (GM)
Excess high (EH) and excess low (EL)
Guaranteed low (GL)
To calculate the burst size for each pair, the system:
Uses the configured burst-size if only one of the pair is configured.
Uses the lesser of the two burst sizes if both values are configured.
Uses the next lower power of two.
To calculate the minimum burst size, the system uses the greater of the two rates.
Change History Table
Feature support is determined by the platform and release you are using. Use Feature Explorer to determine if a feature is supported on your platform.
