ON THIS PAGE
Example: Rewriting CoS Information at the Network Border to Enforce CoS Strategies
This example shows how to rewrite (remark) class-of-service (CoS) values at the network border to enforce your internal CoS strategies. This is typically done when the CoS values of the inbound traffic at the network border cannot be trusted, or the values do not match your internal network’s CoS strategy.
A thorough explanation of the CoS rewriting and its underlying algorithms is beyond the scope of this document. For more information about traffic policing, and CoS in general, refer to QOS-Enabled Networks—Tools and Foundations by Miguel Barreiros and Peter Lundqvist. This book is available at many online booksellers and at www.juniper.net/books .
Requirements
To verify this procedure, this example uses a traffic generator. The traffic generator can be hardware-based or it can be software running on a server or host machine.
The functionality in this procedure is widely supported on devices that run Junos OS. The example shown here was tested and verified on MX Series routers running a supported Junos OS release.
Overview
The purpose of this example is to demonstrate CoS rewriting at a network border to convey the traffics’s CoS profile to the next-hop router, based on the forwarding class and packet loss priority (PLP) assigned to the traffic. CoS information rewriting is performed as the last step before a packet is transmitted onto the egress network.
In this example the rewriting is done when sending traffic from the host connected to Device R1 to the host connected to Device R2. The information required for rewriting the CoS parameters in the other direction is not included in this example. However, you can use the rewriting information in Device R1 (making changes for the interfaces used) and apply it to Device R2 to achieve bidirectional CoS rewriting.
Junos OS contains several default rewrite rules that might meet your requirements. You display
them with the show class-of-service rewrite-rule command. Table 1 shows a partial list of
the default rewrite rule mapping.
|
Map from Forwarding Class |
PLP Value |
MAP to DSCP/DSCP IPv6/EXP/IP Code Point Aliases |
|---|---|---|
|
expedited-forwarding |
low |
ef |
|
expedited-forwarding |
high |
ef |
|
assured-forwarding |
low |
af11 |
|
assured-forwarding |
high |
af12(DSCP/DSCP IPv6/EXP) |
|
best-effort |
low |
be |
|
best-effort |
high |
be |
|
network-control |
low |
nc1/cs6 |
|
network-control |
high |
nc2/cs7 |
You can also define your own custom rewrite-rules table, or use a mixture of the default rewrite-rules and a custom table that you create. This example uses default rewrite-rules.
Topology
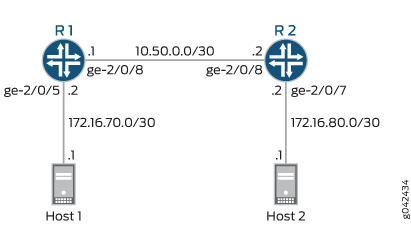
This example uses the topology in Figure 1.
This video explains the topics used in this example. We recommend that you watch the video before proceeding.
Configuration
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example,
copy the following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any
line breaks, change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
Device R1
set interfaces ge-2/0/5 description to-Host set interfaces ge-2/0/5 unit 0 family inet address 172.16.70.2/30 set interfaces ge-2/0/5 unit 0 family inet filter input mf-classifier set interfaces ge-2/0/8 description to-R2 set interfaces ge-2/0/8 unit 0 family inet address 10.50.0.1/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 description looback-interface set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.13.1/32 set class-of-service forwarding-classes queue 0 BE-data set class-of-service forwarding-classes queue 1 Premium-data set class-of-service forwarding-classes queue 2 voice set class-of-service forwarding-classes queue 3 NC set class-of-service interfaces ge-2/0/8 scheduler-map test-map set class-of-service interfaces ge-2/0/8 unit 0 rewrite-rules dscp IPv4-rewrite-table set class-of-service rewrite-rules dscp IPv4-rewrite-table forwarding-class BE-data loss-priority low code-point be set class-of-service rewrite-rules dscp IPv4-rewrite-table forwarding-class Premium-data loss-priority low code-point ef set class-of-service scheduler-maps test-map forwarding-class BE-data scheduler BE-data set class-of-service scheduler-maps test-map forwarding-class Premium-data scheduler Prem-data set class-of-service schedulers BE-data transmit-rate 1m set class-of-service schedulers BE-data buffer-size percent 25 set class-of-service schedulers BE-data priority low set class-of-service schedulers Prem-data transmit-rate 1m set class-of-service schedulers Prem-data buffer-size percent 25 set class-of-service schedulers Prem-data priority high set firewall family inet filter mf-classifier term BE-data from protocol tcp set firewall family inet filter mf-classifier term BE-data from port 80 set firewall family inet filter mf-classifier term BE-data then count BE-data set firewall family inet filter mf-classifier term BE-data then forwarding-class BE-data set firewall family inet filter mf-classifier term Prem-data from protocol tcp set firewall family inet filter mf-classifier term Prem-data from port 12345 set firewall family inet filter mf-classifier term Prem-data then count Prem-data set firewall family inet filter mf-classifier term Prem-data then forwarding-class Premium-data set firewall family inet filter mf-classifier term accept then accept set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-2/0/5.0 passive set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0 passive set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-2/0/8.0
Device R2
set interfaces ge-2/0/7 description to-Host set interfaces ge-2/0/7 unit 0 family inet address 172.16.80.1/30 set interfaces ge-2/0/8 description to-R1 set interfaces ge-2/0/8 unit 0 family inet address 10.50.0.2/30 set interfaces ge-2/0/8 unit 0 family inet filter input mf-classifier set interfaces unit 0 description looback-interface set interfaces unit 0 family inet address 192.168.14.1/32 set firewall family inet filter mf-classifier term BE-data from dscp be set firewall family inet filter mf-classifier term BE-data then count BE-data set firewall family inet filter mf-classifier term Premium-data from dscp ef set firewall family inet filter mf-classifier term Premium-data then count Premium-data set firewall family inet filter mf-classifier term accept then accept set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-2/0/7.0 passive set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0 passive set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-2/0/8.0
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following example requires you to navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For instructions on how to do that, see Using the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode in the Junos OS CLI User Guide.
To configure Device R1:
Configure the device interfaces.
[edit ] user@R1# set interfaces ge-2/0/5 description to-Host user@R1# set interfaces ge-2/0/5 unit 0 family inet address 172.16.70.2/30 user@R1# set interfaces ge-2/0/5 unit 0 family inet filter input mf-classifier user@R1# set interfaces ge-2/0/8 description to-R2 user@R1# set interfaces ge-2/0/8 unit 0 family inet address 10.50.0.1/30 user@R1# set interfaces lo0 unit 0 description looback-interface user@R1# set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.13.1/32
Configure the firewall parameters.
[edit ] user@R1# set firewall family inet filter mf-classifier term BE-data from protocol tcp user@R1# set firewall family inet filter mf-classifier term BE-data from port 80 user@R1# set firewall family inet filter mf-classifier term BE-data then count BE-data user@R1# set firewall family inet filter mf-classifier term BE-data then forwarding-class BE-data user@R1# set firewall family inet filter mf-classifier term Prem-data from protocol tcp user@R1# set firewall family inet filter mf-classifier term Prem-data from port 12345 user@R1# set firewall family inet filter mf-classifier term Prem-data then count Prem-data user@R1# set firewall family inet filter mf-classifier term Prem-data then forwarding-class Premium-data user@R1# set firewall family inet filter mf-classifier term accept then accept
Configure the class-of-service parameters.
[edit ] user@R1# set class-of-service forwarding-classes queue 0 BE-data user@R1# set class-of-service forwarding-classes queue 1 Premium-data user@R1# set class-of-service forwarding-classes queue 2 voice user@R1# set class-of-service forwarding-classes queue 3 NC user@R1# set class-of-service interfaces ge-2/0/8 scheduler-map test-map user@R1# set class-of-service interfaces ge-2/0/8 unit 0 rewrite-rules dscp IPv4-rewrite-table user@R1# set class-of-service rewrite-rules dscp IPv4-rewrite-table forwarding-class BE-data loss-priority low code-point be user@R1# set class-of-service rewrite-rules dscp IPv4-rewrite-table forwarding-class Premium-data loss-priority low code-point ef user@R1# set class-of-service scheduler-maps test-map forwarding-class BE-data scheduler BE-data user@R1# set class-of-service scheduler-maps test-map forwarding-class Premium-data scheduler Prem-data user@R1# set class-of-service schedulers BE-data transmit-rate 1m user@R1# set class-of-service schedulers BE-data buffer-size percent 25 user@R1# set class-of-service schedulers BE-data priority low user@R1# set class-of-service schedulers Prem-data transmit-rate 1m user@R1# set class-of-service schedulers Prem-data buffer-size percent 25 user@R1# set class-of-service schedulers Prem-data priority high
Configure OSPF.
[edit protocols ospf] user@R1# set area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-2/0/5.0 passive user@R1# set area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0 passive user@R1# set area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-2/0/8.0
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure Device R2:
Configure the device interface.
[edit ] user@R1# set interfaces ge-2/0/7 description to-Host user@R1# set interfaces ge-2/0/7 unit 0 family inet address 172.16.80.1/30 user@R1# set interfaces ge-2/0/8 description to-R1 user@R1# set interfaces ge-2/0/8 unit 0 family inet address 10.50.0.2/30 user@R2# set interfaces ge-2/0/8 unit 0 family inet filter input mf-classifier user@R1# set interfaces unit 0 description looback-interface user@R1# set interfaces unit 0 family inet address 192.168.14.1/32
Configure the firewall parameters.
[edit ] user@R2# set firewall family inet filter mf-classifier term BE-data from dscp be user@R2# set firewall family inet filter mf-classifier term BE-data then count BE-data user@R2# set firewall family inet filter mf-classifier term Premium-data from dscp ef user@R2# set firewall family inet filter mf-classifier term Premium-data then count Premium-data user@R2# set firewall family inet filter mf-classifier term accept then accept
Configure OSPF.
[edit protocols ospf] user@R1# set area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-2/0/7.0 passive user@R1# set area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0 passive user@R1# set area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-2/0/8.0
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show interfaces, show firewall, show class-of-service , and show protocols ospf commands. If the output does not display the intended configuration,
repeat the instructions in this example to correct the configuration.
user@R1 show interfaces
ge-2/0/5 {
description to-Host;
unit 0 {
family inet {
filter {
input mf-classifier;
}
address 172.16.70.2/30;
}
}
}
ge-2/0/8 {
description to-R2;
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.50.0.1/30;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 0 {
description looback-interface;
family inet {
address 192.168.13.1/32;
}
}
}
user@R1 show firewall
family inet {
filter mf-classifier {
term BE-data {
from {
protocol tcp;
port 80;
}
then {
count BE-data;
forwarding-class BE-data;
}
}
term Prem-data {
from {
protocol tcp;
port 12345;
}
then {
count Prem-data;
forwarding-class Premium-data;
}
}
term accept {
then accept;
}
}
}
user@R1 show class-of-service
forwarding-classes {
queue 0 BE-data;
queue 1 Premium-data;
queue 2 voice;
queue 3 NC;
}
interfaces {
ge-2/0/8 {
scheduler-map test-map;
unit 0 {
rewrite-rules {
dscp IPv4-rewrite-table;
}
}
}
}
rewrite-rules {
dscp IPv4-rewrite-table {
forwarding-class BE-data {
loss-priority low code-point be;
}
forwarding-class Premium-data {
loss-priority low code-point ef;
}
}
}
scheduler-maps {
test-map {
forwarding-class BE-data scheduler BE-data;
forwarding-class Premium-data scheduler Prem-data;
}
}
schedulers {
BE-data {
transmit-rate 1m;
buffer-size percent 25;
priority low;
}
Prem-data {
transmit-rate 1m;
buffer-size percent 25;
priority high;
}
}
user@R1# show protocols ospf
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface ge-2/0/5.0 {
passive;
}
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
interface ge-2/0/8.0;
}
If you are done configuring Device R1, enter commit from configuration mode.
user@R2# show interfaces
ge-2/0/7 {
unit 0 {
description to-Host;
family inet {
address 172.16.80.2;
}
}
}
ge-2/0/8 {
description to-R1;
unit 0 {
family inet {
filter {
input mf-classifier;
}
address 10.50.0.2/30;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 0 {
description looback-interface;
family inet {
address 192.168.14.1/32;
}
}
}
user@R2# show firewall
family inet {
filter mf-classifier {
term BE-data {
from {
dscp be;
}
then count BE-data;
}
term Premium-data {
from {
dscp ef;
}
then count Premium-data;
}
term accept {
then accept;
}
}
}
user@R2# show protocols ospf
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface ge-2/0/7.0 {
passive;
}
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
interface ge-2/0/8.0;
}
If you are done configuring Device R2, enter commit from configuration mode.
Verification
Confirm that the configuration is working properly.
- Clearing the Firewall Counters
- Sending Traffic into the Network from TCP HTTP Ports 80 and 12345 and Monitoring the Results
Clearing the Firewall Counters
Purpose
Confirm that the firewall counters are cleared.
Action
On Devices R1 and R2, run the clear firewall all command to reset the firewall counters to 0.
user@R1> clear firewall all user@R2> clear firewall all
Sending Traffic into the Network from TCP HTTP Ports 80 and 12345 and Monitoring the Results
Purpose
Send traffic from the host connected to Device 1 into the network so that it can be monitored by the firewall on Device R1 and Device R2.
Action
Use a traffic generator to send 20 TCP packets with a source port of 80 into the network.
The -s flag sets the source port. The -k flag causes the source port to remain steady at 80 instead of incrementing. The -c flag sets the number of packets to 20. The -d flag sets the packet size.
[User@host]# hping 172.16.80.1 -c 20 -s 80 -k -d 300 HPING 172.16.80.1 (eth1 172.16.80.1): NO FLAGS are set, 40 headers + 0 data bytes len=46 ip=172.16.80.1 ttl=62 DF id=0 sport=0 flags=RA seq=0 win=0 rtt=0.9 ms . . . --- 172.16.80.1 hping statistic --- 20 packets transmitted, 20 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 0.9/9501.4/19002.4 ms
Use a traffic generator to send 20 TCP packets with a source port of 12345 into the network.
[User@host]# hping 172.16.80.1 -c 20 -s 12345 -k -d 300 HPING 172.16.80.1 (eth1 172.16.80.1): NO FLAGS are set, 40 headers + 0 data bytes len=46 ip=172.16.80.1 ttl=62 DF id=0 sport=0 flags=RA seq=0 win=0 rtt=0.3 ms . . . --- 172.16.80.1 hping statistic --- 20 packets transmitted, 20 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 0.3/9501.5/19002.7 ms
On Device R1, check the firewall counters by using the
show firewallcommand.user@R1> show firewall Filter: mf-classifier Counters: Name Bytes Packets BE-data 800 20 Prem-data 800 20
On Device R2, check the firewall counters using the
show firewallcommand.user@R2> show firewall Filter: mf-classifier Counters: Name Bytes Packets BE-data 800 20 Premium-data 800 20
Meaning
Device R1 correctly set the code point for TCP packets to port 12345 to bf. Device R1 correctly set the code point for TCP packets to port 80 to ef. Device R2 correctly recognized the code point for TCP packets to port 12345 as bf. Device R2 correctly recognized the code point for TCP packets to port 80 as ef.
