Supported Protocols on an IRB Interface in EVPN-VXLAN
EVPN-VXLAN provides logical layer 2 connectivity over a layer 3 network. It is a logical overlay that is decoupled from the underlay network. The layer 2 subnets in the EVPN-VXLAN network are uniquely identified by the virtual network identifier (VNI) where devices configured with the same VNI are considered to be in the same logical subnet. The devices in the same logical subnet can communicate directly with each other when they are connected to the same virtural gateway. To route traffic when devices with different VNIs are connected to the same gateway, you must configure an IRB interface on the VXLAN gateway to route traffic. This allows protocol adjacencies to be established between the layer 3 gateway IRB interface and customer edge devices in the following scenarios:
-
Support networking functions when there are firewalls or load balancers connected between the host and the gateway device.
-
Support inter-VNI routing when VNIs for the same tenant extend across data centers.
Figure 1 illustrates a simple leaf-spine (centrally-routed bridging overlay) topology in an EVPN-VXLAN network with the VXLAN gateway on spine devices. For host 1 to communicate with hosts in other VNIs, you must configure the IRB interfaces on the VXLAN gateway on the spine devices.
When configuring an ESI interface for multihomed devices, Junos OS only supports routing protocols that are configured on an IRB in the all-active multihoming mode in a centrally-routed bridging overlay EVPN-VXLAN network.
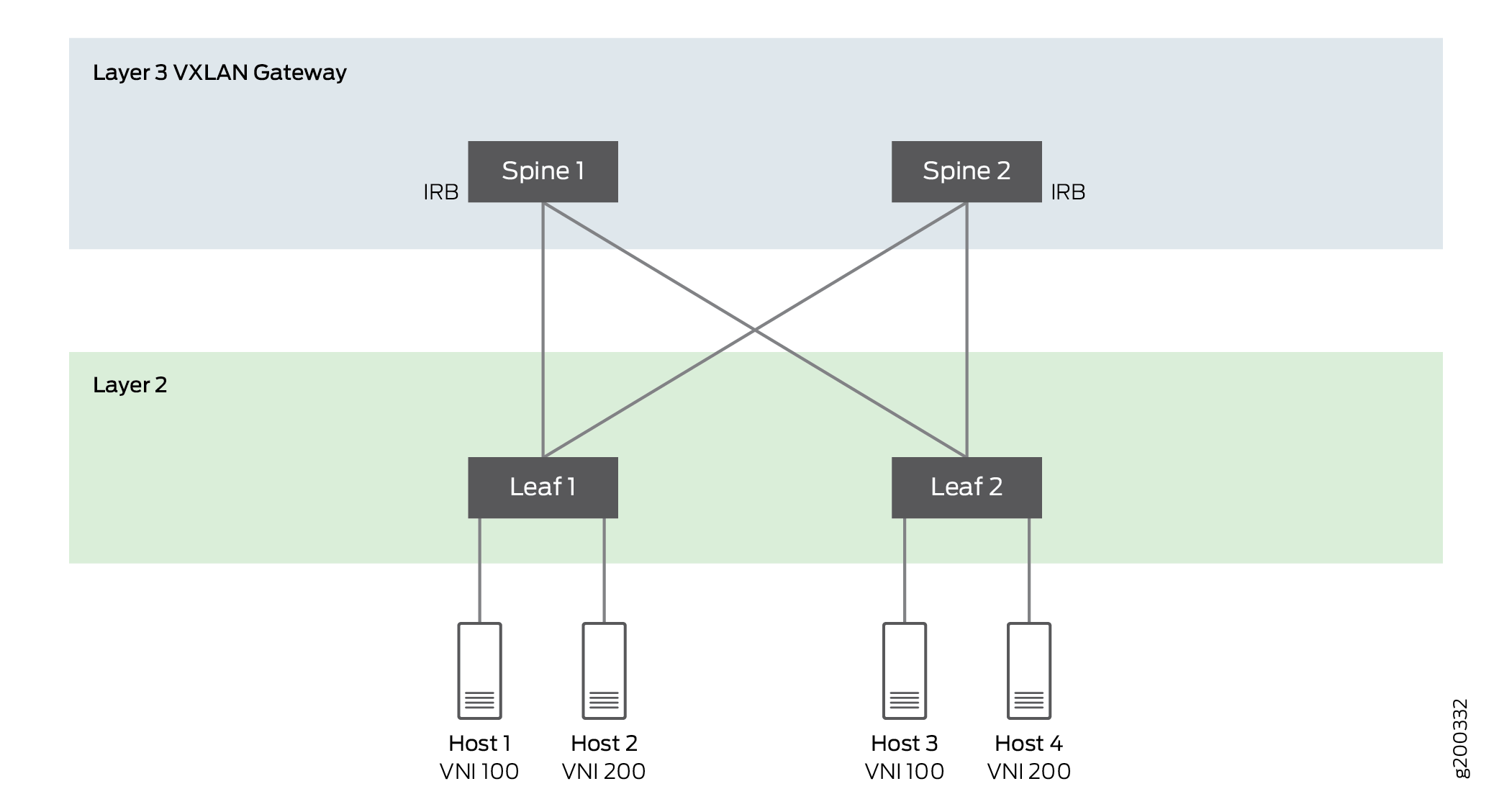
Figure 2 illustrates a collapsed leaf-spine (edge-routed bridging) topology with VXLAN gateways on leaf devices. For host 1 to communicate with hosts in other VNIs, you must configure IRB interfaces on the VXLAN gateway on the leaf devices.
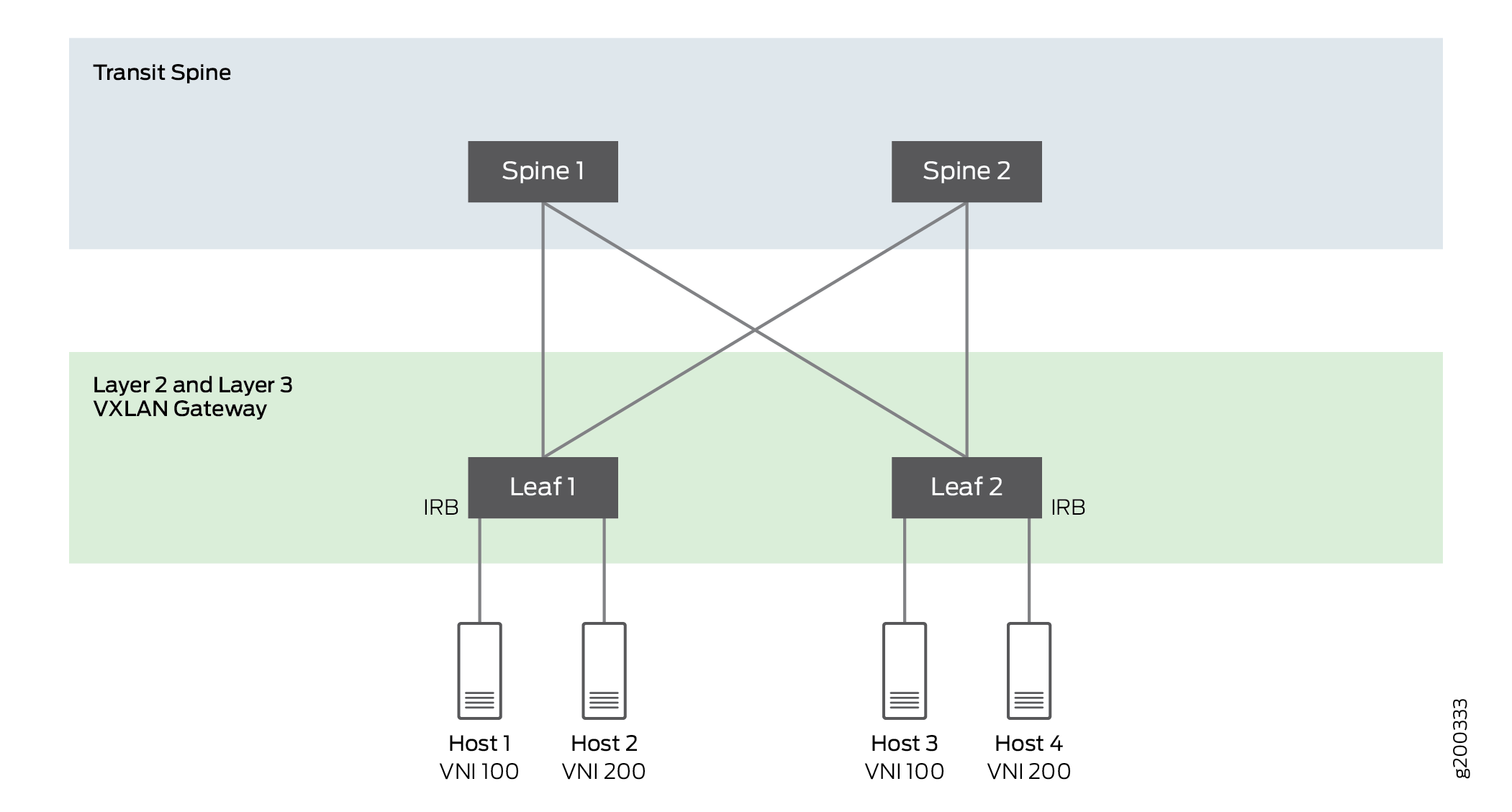
Junos OS supports the following protocols on the IRB in the EVPN-VXLAN overlay network:
-
OSPF
-
IS-IS
-
BGP (eBGP and iBGP)
-
Bidirectional forwarding detection (BFD) support for ISIS, OSPF, BGP and static routing.
