ON THIS PAGE
Example: Redistributing OSPF Routes into IS-IS
This example shows how to redistribute OSPF routes into an IS-IS network.
Requirements
No special configuration beyond device initialization is required before configuring this example.
Overview
Export policy can be applied to IS-IS to facilitate route redistribution.
Junos OS does not support the application of import policy for link-state routing protocols like IS-IS because such policies can lead to inconsistent link-state database (LSDB) entries, which in turn can result in routing inconstancies.
In this example, OSPF routes 192.168.0/24 through 192.168.3/24 are redistributed into IS-IS area 49.0002 from Device R2.
In addition, policies are configured to ensure that Device R1 can reach destinations on the 10.0.0.44/30 network, and that Device R3 can reach destinations on the 10.0.0.36/30 network. This enables end-to-end reachability.
Figure 1 shows the topology used in this example.
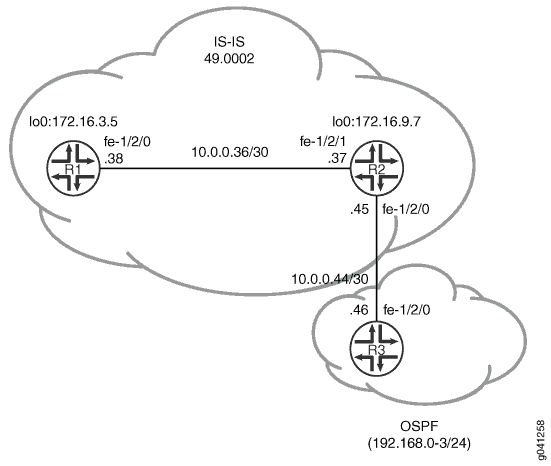
CLI Quick Configuration shows the configuration for all of the devices in Figure 1. The section #configuration759__isis-redist-ospf-step-by-step-r2 describes the steps on Device R2. #configuration759__isis-redist-ospf-step-by-step-r3 describes the steps on Device R3.
Topology
Configuration
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure
this example, copy the following commands, paste them into a text
file, remove any line breaks, change any details necessary to match
your network configuration, and then copy and paste the commands into
the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
Device R1
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 description to-R7 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.38/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 172.16.3.5/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0002.0172.0016.0305.00 set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/0.0 set protocols isis interface lo0.0
Device R2
set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 description to-R5 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.37/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 description to-OSPF-network set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.45/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 172.16.9.7/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0002.0172.0016.0907.00 set protocols isis export ospf-isis set protocols isis export send-direct-to-isis-neighbors set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/1.0 set protocols isis interface lo0.0 set protocols ospf export send-direct-to-ospf-neighbors set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.1 interface fe-1/2/0.0 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.1 interface lo0.0 passive set policy-options policy-statement ospf-isis term 1 from protocol ospf set policy-options policy-statement ospf-isis term 1 from route-filter 192.168.0.0/22 longer set policy-options policy-statement ospf-isis term 1 then accept set policy-options policy-statement send-direct-to-isis-neighbors from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement send-direct-to-isis-neighbors from route-filter 10.0.0.44/30 exact set policy-options policy-statement send-direct-to-isis-neighbors then accept set policy-options policy-statement send-direct-to-ospf-neighbors from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement send-direct-to-ospf-neighbors from route-filter 10.0.0.36/30 exact set policy-options policy-statement send-direct-to-ospf-neighbors then accept
Device R3
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.46/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.1.1/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.2.1/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.3.1/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.1/32 set protocols ospf export ospf set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.1 interface fe-1/2/0.0 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.1 interface lo0.0 passive set policy-options policy-statement ospf term 1 from protocol static set policy-options policy-statement ospf term 1 then accept set routing-options static route 192.168.0.0/24 discard set routing-options static route 192.168.1.0/24 discard set routing-options static route 192.168.3.0/24 discard set routing-options static route 192.168.2.0/24 discard
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure Device R2:
Configure the network interfaces.
[edit interfaces] user@R2# set fe-1/2/1 unit 0 description to-R5 user@R2# set fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.37/30 user@R2# set fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family iso user@R2# set fe-1/2/0 unit 0 description to-OSPF-network user@R2# set fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.45/30 user@R2# set lo0 unit 0 family inet address 172.16.9.7/32 user@R2# set lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0002.0172.0016.0907.00
Configure IS-IS on the interface facing Device R1 and the loopback interface.
[edit protocols isis] user@R2# set interface fe-1/2/1.0 user@R2# set interface lo0.0
Configure the policy that enables Device R1 to reach the 10.0.0.44/30 network.
[edit policy-options policy-statement send-direct-to-isis-neighbors] user@R2# set from protocol direct user@R2# set from route-filter 10.0.0.44/30 exact user@R2# set then accept
Apply the policy that enables Device R1 to reach the 10.0.0.44/30 network.
[edit protocols isis] user@R2# set export send-direct-to-isis-neighbors
Configure OSPF on the interfaces.
[edit protocols ospf] user@R2# set area 0.0.0.1 interface fe-1/2/0.0 user@R2# set area 0.0.0.1 interface lo0.0 passive
Configure the OSPF route redistribution policy.
[edit policy-options policy-statement ospf-isis term 1] user@R2# set from protocol ospf user@R2# set from route-filter 192.168.0.0/22 longer user@R2# set then accept
Apply the OSPF route redistribution policy to the IS-IS instance.
[edit protocols isis] user@R2# set export ospf-isis
Configure the policy that enables Device R3 to reach the 10.0.0.36/30 network.
[edit policy-options policy-statement send-direct-to-ospf-neighbors] user@R2# set from protocol direct user@R2# set from route-filter 10.0.0.36/30 exact user@R2# set then accept
Apply the policy that enables Device R3 to reach the 10.0.0.36/30 network.
[edit protocols ospf] user@R2# set export send-direct-to-ospf-neighbors
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following example requires you to navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For information about navigating the CLI, see Using the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode in the CLI User Guide.
To configure multi-level IS-IS:
Configure the network interfaces.
Multiple addresses are configured on the loopback interface to simulate multiple route destinations.
[edit interfaces] user@R3# set fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.46/30 user@R3# set lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.1.1/32 user@R3# set lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.2.1/32 user@R3# set lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.3.1/32 user@R3# set lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.1/32
Configure static routes to the loopback interface addresses.
These are the routes that are redistributed into IS-IS.
[edit routing-options static] user@R3# set route 192.168.0.0/24 discard user@R3# set route 192.168.1.0/24 discard user@R3# set route 192.168.3.0/24 discard user@R3# set route 192.168.2.0/24 discard
Configure OSPF on the interfaces.
[edit protocols ospf area 0.0.0.1] user@R3# set interface fe-1/2/0.0 user@R3# set interface lo0.0 passive
Configure the OSPF policy to export the static routes.
[edit policy-options policy-statement ospf term 1] user@R3# set from protocol static user@R3# set then accept
Apply the OSPF export policy.
[edit protocols ospf] user@R3# set export ospf
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show interfaces, show protocols, show policy-options, and show routing-options commands. If the output does not display the intended configuration,
repeat the instructions in this example to correct the configuration.
Device R2
user@R2# show interfaces
fe-1/2/1 {
unit 0 {
description to-R5;
family inet {
address 10.0.0.37/30;
}
family iso;
}
}
fe-1/2/0 {
unit 0 {
description to-OSPF-network;
family inet {
address 10.0.0.45/30;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 172.16.9.7/32;
}
family iso {
address 49.0002.0172.0016.0907.00;
}
}
}
user@R2# show protocols
isis {
export [ ospf-isis send-direct-to-isis-neighbors ];
interface fe-1/2/1.0;
interface lo0.0;
}
ospf {
export send-direct-to-ospf-neighbors;
area 0.0.0.1 {
interface fe-1/2/0.0;
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
}
}
user@R2# show policy-options
policy-statement ospf-isis {
term 1 {
from {
protocol ospf;
route-filter 192.168.0.0/22 longer;
}
then accept;
}
}
policy-statement send-direct-to-isis-neighbors {
from {
protocol direct;
route-filter 10.0.0.44/30 exact;
}
then accept;
}
policy-statement send-direct-to-ospf-neighbors {
from {
protocol direct;
route-filter 10.0.0.36/30 exact;
}
then accept;
}
Device R3
user@R3# show interfaces
fe-1/2/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.0.0.46/30;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.168.1.1/32;
address 192.168.2.1/32;
address 192.168.3.1/32;
address 192.168.0.1/32;
}
}
}
user@R3# show protocols
ospf {
export ospf;
area 0.0.0.1 {
interface fe-1/2/0.0;
interface lo0.0 {
passive;
}
}
}
user@R3# show policy-options
policy-statement ospf {
term 1 {
from protocol static;
then accept;
}
}
user@R3# show routing-options
static {
route 192.168.0.0/24 discard;
route 192.168.1.0/24 discard;
route 192.168.3.0/24 discard;
route 192.168.2.0/24 discard;
}
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Verification
Confirm that the configuration is working properly.
Verifying OSPF Route Advertisement
Purpose
Make sure that the expected routes are advertised by OSPF.
Action
From operational mode on Device R2, enter the show
route protocol ospf command.
user@R2> show route protocol ospf
inet.0: 15 destinations, 15 routes (15 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
192.168.0.0/24 *[OSPF/150] 03:54:21, metric 0, tag 0
> to 10.0.0.46 via fe-1/2/0.0
192.168.0.1/32 *[OSPF/10] 03:54:21, metric 1
> to 10.0.0.46 via fe-1/2/0.0
192.168.1.0/24 *[OSPF/150] 03:54:21, metric 0, tag 0
> to 10.0.0.46 via fe-1/2/0.0
192.168.1.1/32 *[OSPF/10] 03:54:21, metric 1
> to 10.0.0.46 via fe-1/2/0.0
192.168.2.0/24 *[OSPF/150] 03:54:21, metric 0, tag 0
> to 10.0.0.46 via fe-1/2/0.0
192.168.2.1/32 *[OSPF/10] 03:54:21, metric 1
> to 10.0.0.46 via fe-1/2/0.0
192.168.3.0/24 *[OSPF/150] 03:54:21, metric 0, tag 0
> to 10.0.0.46 via fe-1/2/0.0
192.168.3.1/32 *[OSPF/10] 03:54:21, metric 1
> to 10.0.0.46 via fe-1/2/0.0
224.0.0.5/32 *[OSPF/10] 03:56:03, metric 1
MultiRecv
iso.0: 1 destinations, 1 routes (1 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)Meaning
The 192.168/16 routes are advertised by OSPF.
Verifying Route Redistribution
Purpose
Make sure that the expected routes are redistributed from OSPF into IS-IS.
Action
From operational mode on Device R1, enter the show
route protocol isis command.
user@R1> show route protocol isis
inet.0: 13 destinations, 13 routes (13 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
10.0.0.44/30 *[IS-IS/160] 03:45:24, metric 20
> to 10.0.0.37 via fe-1/2/0.0
172.16.9.7/32 *[IS-IS/15] 03:49:46, metric 10
> to 10.0.0.37 via fe-1/2/0.0
192.168.0.0/24 *[IS-IS/160] 03:49:46, metric 10
> to 10.0.0.37 via fe-1/2/0.0
192.168.0.1/32 *[IS-IS/160] 03:49:46, metric 11, tag2 1
> to 10.0.0.37 via fe-1/2/0.0
192.168.1.0/24 *[IS-IS/160] 03:49:46, metric 10
> to 10.0.0.37 via fe-1/2/0.0
192.168.1.1/32 *[IS-IS/160] 03:49:46, metric 11, tag2 1
> to 10.0.0.37 via fe-1/2/0.0
192.168.2.0/24 *[IS-IS/160] 03:49:46, metric 10
> to 10.0.0.37 via fe-1/2/0.0
192.168.2.1/32 *[IS-IS/160] 03:49:46, metric 11, tag2 1
> to 10.0.0.37 via fe-1/2/0.0
192.168.3.0/24 *[IS-IS/160] 03:49:46, metric 10
> to 10.0.0.37 via fe-1/2/0.0
192.168.3.1/32 *[IS-IS/160] 03:49:46, metric 11, tag2 1
> to 10.0.0.37 via fe-1/2/0.0
iso.0: 1 destinations, 1 routes (1 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)Meaning
The 192.168/16 routes are redistributed into IS-IS.
Verifying Connectivity
Purpose
Check that Device R1 can reach the destinations on Device R3.
Action
From operational mode, enter the ping command.
user@R1> ping 192.168.1.1 PING 192.168.1.1 (192.168.1.1): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 192.168.1.1: icmp_seq=0 ttl=63 time=2.089 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.1.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=63 time=1.270 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.1.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=63 time=2.135 ms
Meaning
These results confirm that Device R1 can reach the destinations in the OSPF network.
