ON THIS PAGE
Example: Configuring Layer 2 Mapping for IS-IS
This example shows how to configure Layer 2 mapping for IS-IS, that is, mapping a Layer 2 MAC address to the IPv4 address of the forwarding next hop. Layer 2 mapping minimizes traffic loss, provides better security, and reduces Layer 2 resolution processing on core links while activating an Ethernet link.
Requirements
This example uses the following hardware and software components:
Two routers
Junos OS running on all the devices
Overview
Layer 2 mapping ensures that the forwarding next-hop resolution is topology-driven rather than traffic-driven. IS-IS LAN and point-to-point Hellos supply all relevant Layer 2 and Layer 3 binding address information for address resolution. The device at the receiving end can use the information to populate the ARP or neighbor discovery cache of the kernel even before the route installation time. When Layer 2 mapping is enabled, IS-IS installs ARP or neighbor discovery next-hop entries into the forwarding table. Because this provides Layer 2 next-hop bindings ahead of time, IS-IS networks do not experience traffic loss while bringing up a link.
Topology
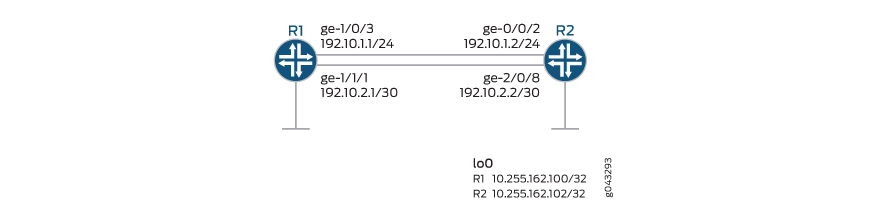
In Figure 1, Router R1 is connected to Router R2. Layer 2 mapping is enabled on Router R1. Router R2 receives the Layer 2 information from Router R1 and updates the forwarding table.
Configuration
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks,
change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy
level, and then enter commit from configuration mode.
Router R1
set interfaces ge-1/0/3 description R0–>R1_1 set interfaces ge-1/0/3 unit 0 family inet address 192.10.1.1/24 set interfaces ge-1/0/3 unit 0 family iso set interfaces ge-1/0/3 unit 0 family inet6 address 0000:0000:0000:0000:192:10:1:1/120 set interfaces ge-1/0/3 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/0/7 description R0–>RT0 set interfaces ge-1/0/7 unit 0 family inet address 193.1.1.1/30 set interfaces ge-1/0/7 unit 0 family iso set interfaces ge-1/0/7 unit 0 family inet6 address 0000:0000:0000:0000:193:1:1:1/120 set interfaces ge-1/0/7 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/1/1 description R0–>R1_2 set interfaces ge-1/1/1 unit 0 family inet address 192.10.2.1/30 set interfaces ge-1/1/1 unit 0 family iso set interfaces ge-1/1/1 unit 0 family inet6 address 0000:0000:0000:0000:192:10:2:1/120 set interfaces ge-1/1/1 unit 0 family mpls set lo0 unit 0 family inet address 10.255.162.100/32 set routing-options router-id 10.255.162.100 set protocols rsvp interface all set protocols rsvp interface lo0.0 set protocols rsvp interface fxp0.0 disable set protocols mpls interface all set protocols mpls interface lo0.0 set protocols mpls interface fxp0.0 disable set protocols isis layer2-map set protocols isis interface ge-1/0/3.0 level 2 disable set protocols ldp interface all set protocols ldp interface fxp0.0 disable set protocols ldp interface lo0.0
Router R2
set interfaces ge-0/0/2 descriptionR0–>R1_1 set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet address 192.10.1.2/24 set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family iso set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet6 address 0000:0000:0000:0000:192:10:1:2/120 set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-2/0/3 description R1–>RT0 set interfaces ge-2/0/3 unit 0 family inet address 193.2.1.1/30 set interfaces ge-2/0/3 unit 0 family iso set interfaces ge-2/0/3 unit 0 family inet6 address 0000:0000:0000:0000:193:2:1:1/120 set interfaces ge-2/0/3 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces ge-2/0/8 description R0–>R1_2 set interfaces ge-2/0/8 unit 0 family inet address 192.10.2.2/30 set interfaces ge-2/0/8 unit 0 family iso set interfaces ge-2/0/8 unit 0 family inet6 address 0000:0000:0000:0000:192:10:2:2/120 set interfaces ge-2/0/8 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 10.255.162.102/32 set routing-options router-id 10.255.162.109 set protocols rsvp interface all set protocols rsvp interface lo0.0 set protocols rsvp interface fxp0.0 disable set protocols mpls interface all set protocols mpls interface lo0.0 set protocols mpls interface fxp0.0 disable set protocols isis interface ge-0/0/2.0 level 2 disable set protocols ldp interface all set protocols ldp interface fxp0.0 disable set protocols ldp interface lo0.0
Procedure
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following example requires that you navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For information about navigating the CLI, see Using the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode in the Junos OS CLI User Guide.
To configure Layer 2 mapping on Router R1:
Repeat this procedure for Router 2 after modifying the appropriate interface names, addresses, and other parameters.
Configure the device interfaces.
[edit interfaces] user@R1# set ge-1/0/3 description R0–>R1_1 user@R1# set ge-1/0/3 unit 0 family inet address 192.10.1.1/24 user@R1# set ge-1/0/3 unit 0 family iso user@R1# set ge-1/0/3 unit 0 family inet6 address 0000:0000:0000:0000:192:10:1:1/120 user@R1# set ge-1/0/3 unit 0 family mpls user@R1# set ge-1/0/7 description R0–>RT0 user@R1# set ge-1/0/7 unit 0 family inet address 193.1.1.1/30 user@R1# set ge-1/0/7 unit 0 family iso user@R1# set ge-1/0/7 unit 0 family inet6 address 0000:0000:0000:0000:193:1:1:1/120 user@R1# set ge-1/0/7 unit 0 family mpls user@R1# set ge-1/1/1 description R0–>R1_2 user@R1# set ge-1/1/1 unit 0 family inet address 192.10.2.1/30 user@R1# set ge-1/1/1 unit 0 family iso user@R1# set ge-1/1/1 unit 0 family inet6 address 0000:0000:0000:0000:192:10:2:1/120 user@R1# set ge-1/1/1 unit 0 family mpls
Configure the loopback interface.
[edit interfaces] user@R1# set lo0 unit 0 family inet address 10.255.162.100/32
Configure the router id.
[edit routing-options] user@R1# set router-id 10.255.162.100
Configure RSVP, MPLS, and LDP on all interfaces excluding the management interface.
[edit protocols] user@R1# set rsvp interface all user@R1# set rsvp interface lo0.0 user@R1# set rsvp interface fxp0.0 disable user@R1# set mpls interface all user@R1# set mpls interface lo0.0 user@R1# set mpls interface fxp0.0 disable user@R1# set ldp interface all user@R1# set ldp interface fxp0.0 disable user@R1# set ldp interface lo0.0
Enable Layer 2 mapping.
[edit protocols] user@R1# set isis layer2-map
Disable level 2 IS-IS on interface ge-1/0/3.0.
[edit protocols] user@R1# set isis interface ge-1/0/3.0 level 2 disable
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show interfaces, show protocols, and show routing-options commands. If the output does
not display the intended configuration, repeat the instructions in
this example to correct the configuration.
[edit]
user@R1# show interfaces
ge-1/0/3 {
description 0–>R1_1;
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.10.1.1/24;
}
family iso;
family inet6 {
address 0000:0000:0000:0000:192:10:1:1/120;
}
family mpls;
}
}
ge-1/0/7 {
description R0–>RT0;
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 193.1.1.1/30;
}
family iso;
family inet6 {
address 0000:0000:0000:0000:193:1:1:1/120;
}
family mpls;
}
}
ge-1/1/1 {
description R0–>R1_2;
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.10.2.1/30;
}
family iso;
family inet6 {
address 0000:0000:0000:0000:192:10:2:1/120;
}
family mpls;
}
}
lo0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.255.162.100/32;
}
}
}
[edit]
user@R1# show protocols
rsvp {
interface all;
interface lo0.0;
interface fxp0.0 {
disable;
}
}
mpls {
interface all;
interface lo0.0;
interface fxp0.0 {
disable;
}
}
isis {
layer2-map;
}
ldp {
interface all;
interface fxp0.0 {
disable;
}
interface lo0.0;
}
[edit] user@R1# show routing-options router-id 10.255.162.100;
If you are done configuring the device, commit the configuration.
user@R1# commit
Verification
Confirm that the configuration is working properly.
- Verifying IS-IS Adjacencies
- Verifying That Layer 2 Mapping Is Enabled
- Verifying That the Layer 2 Address Is Mapped
Verifying IS-IS Adjacencies
Purpose
Verify that the expected adjacencies have formed between Router R1 and Router R2.
Action
From operational mode, run the show isis adjacency command on Router R1.
user@R1> show isis adjacency Interface System L State Hold (secs) SNPA ge-1/0/3.0 R2 1 Up 8 88:e0:f3:5e:e8:2
Meaning
The interface ge-1/0/3.0 on Router R1 has established adjacency with Router R2.
Verifying That Layer 2 Mapping Is Enabled
Purpose
Verify that Layer 2 mapping is enabled on Router R1.
Action
From operational mode, run the show isis interface detail command on Router R1.
user@R1> show isis interface detail
IS-IS interface database:
ge-1/0/3.0
Index: 196612, State: 0x6, Circuit id: 0x1, Circuit type: 1
LSP interval: 100 ms, CSNP interval: 10 s
Adjacency advertisement: Advertise, Layer2-map: Enabled
Level Adjacencies Priority Metric Hello (s) Hold (s) Designated Router
1 1 64 10 9.000 27 R2.02 (not us)
2 0 64 10 Disabled
Meaning
The output confirms that Layer 2 mapping is enabled on Router R1.
Verifying That the Layer 2 Address Is Mapped
Purpose
Display Layer 3 next hop and the mapped data link address in the kernel for the routing instances.
Action
From operational mode, run the show isis layer2-map command on Router R1.
user@R1> show isis layer2-map Layer2 mapping database for instance master IP Address Interface SNPA Refresh State 192.10.1.2 ge-1/0/3.0 88:e0:f3:5e:e8:2 00:11:54 fe80::8ae0:f3ff:fe5e:e802 ge-1/0/3.0 88:e0:f3:5e:e8:2 00:04:02 IPv4 records: 1 IPv6 records: 1
Meaning
The Layer 2 MAC address of the next hop is mapped to the IP address of interface ge-1/0/3.0 in the kernel.
