ON THIS PAGE
Example: Configuring Remote LFA over LDP Tunnels in IS-IS Networks
This example shows how to configure remote LFA for LDP tunnels in an IS-IS network for extending backup protection.
Requirements
This example uses the following hardware and software components:
-
Six routers with IS-IS protocol and LDP enabled on the connected interfaces.
-
Junos OS running on all devices.
Before you configure remote LFA over LDP tunnels in IS-IS networks, make sure of the following:
-
LDP is enabled on the loopback interface. Without a loopback interface, LDP targeted adjacency cannot be formed. Remote LFA cannot be configured without LDP targeted adjacency.
-
Remote LFA must allow asymmetric remote neighbor discovery, that is, it must send periodic targeted hellos to the router that initiated the remote neighbor for LDP auto targeted adjacency.
-
Link protection or node-link protection must be configured on the point of local repair (PLR).
Overview
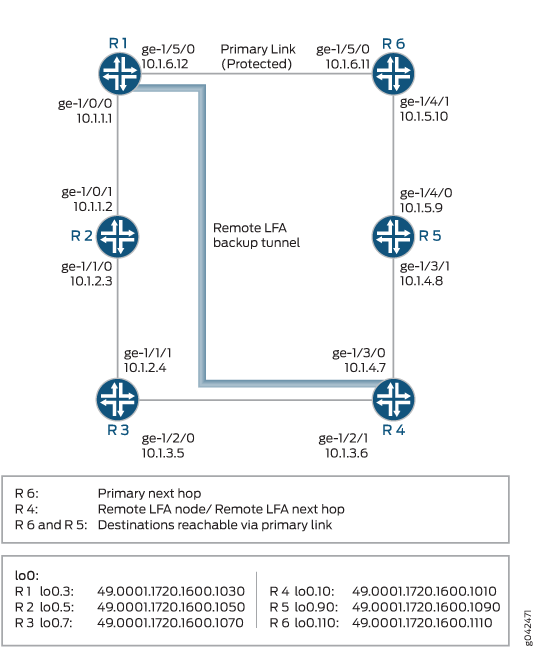
The example includes six routers in a ring topology. Configure the IS-IS protocol on the directly connected interfaces. Device R1 is the PLR. This example verifies that Junos OS updates the routing table of Device R1 with LDP next-hop routes as the backup route.
Topology
Figure 1 shows the topology used in this example.
Configuration
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the following commands, paste them into a
text file, remove any line breaks, change any details necessary to match your
network configuration, copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the
[edit] hierarchy level, and then enter
commit from configuration mode.
Router R1
set interfaces ge-1/0/0 unit 1 description R1->R2 set interfaces ge-1/0/0 unit 1 family inet address 10.1.1.1/24 set interfaces ge-1/0/0 unit 1 family iso set interfaces ge-1/0/0 unit 1 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/5/0 unit 12 description R1->R6 set interfaces ge-1/5/0 unit 12 family inet address 10.1.6.12/24 set interfaces ge-1/5/0 unit 12 family iso set interfaces ge-1/5/0 unit 12 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 3 family inet address 10.255.102.128/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 3 family iso address 49.0001.1720.1600.1030.00 set protocols isis interface ge-1/0/0.1 set protocols isis interface ge-1/5/0.12 link-protection set protocols isis interface lo0.12 passive set protocols isis interface all level 2 metric 10 set protocols isis interface fxp0.0 disable set protocols isis spf-options delay 1000 set protocols isis interface all node-link-protection set protocols isis backup-spf-options remote-backup-calculation set protocols isis backup-spf-options node-link-degradation set protocols mpls interface all set protocols mpls interface fxp0.0 disable set protocols ldp interface all set protocols ldp interface fxp0.0 disable set protocols ldp auto-targeted-session set protocols ldp auto-targeted-session teardown-delay 60 set protocols ldp auto-targeted-session maximum-sessions 20 set protocols ldp deaggregate set policy-options policy-statement ecmp term 1 then load-balance per-packet set routing-options forwarding-table export ecmp
Router R2
set interfaces ge-1/0/1 unit 2 description R2>R1 set interfaces ge-1/0/1 unit 2 family inet address 10.1.1.2/24 set interfaces ge-1/0/1 unit 2 family iso set interfaces ge-1/0/1 unit 2 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/1/0 unit 3 description R2->R3 set interfaces ge-1/1/0 unit 3 family inet address 10.1.2.3/24 set interfaces ge-1/1/0 unit 3 family iso set interfaces ge-1/1/0 unit 3 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 5 family inet address 10.255.102.178/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 5 family iso address 49.0001.1720.1600.1050.00 set protocols isis interface ge-1/0/1.2 set protocols isis interface ge-1/1/0.3 set protocols isis interface lo0.3 passive set protocols isis interface all level 2 metric 10 set protocols isis interface fxp0.0 disable set protocols isis spf-options delay 1000 set protocols mpls interface all set protocols mpls interface fxp0.0 disable set protocols ldp interface all set protocols ldp interface fxp0.0 disable set protocols ldp auto-targeted-session set protocols ldp auto-targeted-session teardown-delay 60 set protocols ldp auto-targeted-session maximum-sessions 20 set protocols ldp deaggregate
Router R3
set interfaces ge-1/1/1 unit 4 description R3->R2 set interfaces ge-1/1/1 unit 4 family inet address 10.1.2.4/24 set interfaces ge-1/1/1 unit 4 family iso set interfaces ge-1/1/1 unit 4 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 5 description R3->R4 set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 5 family inet address 10.1.3.5/24 set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 5 family iso set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 5 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 7 family inet address 10.255.102.146/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 7 family iso address 49.0001.1720.1600.1070.00 set protocols isis interface ge-1/1/1.4 set protocols isis interface ge-1/2/0.5 set protocols isis interface lo0.5 passive set protocols isis interface all level 2 metric 10 set protocols isis interface fxp0.0 disable set protocols isis spf-options delay 1000 set protocols mpls interface all set protocols mpls interface fxp0.0 disable set protocols ldp interface all set protocols ldp interface fxp0.0 disable set protocols ldp auto-targeted-session set protocols ldp auto-targeted-session teardown-delay 60 set protocols ldp auto-targeted-session maximum-sessions 20 set protocols ldp deaggregate
Router R4
set interfaces ge-1/2/1 unit 6 description R4->R3 set interfaces ge-1/2/1 unit 6 family inet address 10.1.3.6/24 set interfaces ge-1/2/1 unit 6 family iso set interfaces ge-1/2/1 unit 6 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/3/0 unit 7 description R4->R5 set interfaces ge-1/3/0 unit 7 family inet address 10.1.4.7/24 set interfaces ge-1/3/0 unit 7 family iso set interfaces ge-1/3/0 unit 7 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 10 family inet address 10.255.102.156/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 10 family iso address 49.0001.1720.1600.1010.00 set protocols isis interface ge-1/2/1.6 set protocols isis interface ge-1/3/0.7 set protocols isis interface lo0.7 passive set protocols isis interface all level 2 metric 10 set protocols isis interface fxp0.0 disable set protocols isis spf-options delay 1000 set protocols mpls interface all set protocols mpls interface fxp0.0 disable set protocols ldp interface all set protocols ldp interface fxp0.0 disable set protocols ldp auto-targeted-session set protocols ldp auto-targeted-session teardown-delay 60 set protocols ldp auto-targeted-session maximum-sessions 20 set protocols ldp deaggregate
Router R5
set interfaces ge-1/3/1 unit 8 description R5->R4 set interfaces ge-1/3/1 unit 8 family inet address 10.1.4.8/24 set interfaces ge-1/3/1 unit 8 family iso set interfaces ge-1/3/1 unit 8 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/4/0 unit 9 description R5->R6 set interfaces ge-1/4/0 unit 9 family inet address 10.1.5.9/24 set interfaces ge-1/4/0 unit 9 family iso set interfaces ge-1/4/0 unit 9 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 90 family inet address 10.255.102.166/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 90 family iso address 49.0001.1720.1600.1090.00 set protocols isis interface ge-1/3/1.8 set protocols isis interface ge-1/4/0.9 set protocols isis interface lo0.9 passive set protocols isis interface all level 2 metric 10 set protocols isis interface fxp0.0 disable set protocols isis spf-options delay 1000 set protocols mpls interface all set protocols mpls interface fxp0.0 disable set protocols ldp interface all set protocols ldp interface fxp0.0 disable set ldp auto-targeted-session set ldp auto-targeted-session teardown-delay 60 set ldp auto-targeted-session maximum-sessions 20 set protocols ldp deaggregate
Router R6
set interfaces ge-1/4/1 unit 10 description R6->R5 set interfaces ge-1/4/1 unit 10 family inet address 10.1.5.10/24 set interfaces ge-1/4/1 unit 10 family iso set interfaces ge-1/4/1 unit 10 family mpls set interfaces ge-1/5/0 unit 11 description R6->R1 set interfaces ge-1/5/0 unit 11 family inet address 10.1.6.11/24 set interfaces ge-1/5/0 unit 11 family iso set interfaces ge-1/5/0 unit 11 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 110 family inet address 10.255.102.136/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 110 family iso address 49.0001.1720.1600.1110.00 set protocols isis interface ge-1/4/1.10 set protocols isis interface ge-1/5/0.11 set protocols isis interface lo0.11 passive set protocols isis interface all level 2 metric 10 set protocols isis interface fxp0.0 disable set protocols isis spf-options delay 1000 set protocols mpls interface all set protocols mpls interface fxp0.0 disable set protocols ldp interface all set protocols ldp interface fxp0.0 disable set protocols ldp auto-targeted-session teardown-delay 60 set protocols ldp auto-targeted-session maximum-sessions 20 set protocols ldp deaggregate
Configuring Device R1
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following example requires that you navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For information about navigating the CLI, see Using the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode in the CLI User Guide.
Repeat this procedure except Step 4 and 5 for every Juniper Networks router in the IGP domain, modifying the appropriate interface names, addresses, and any other parameters.
To configure Device R1:
-
Configure the interfaces.
[edit interfaces] user@R1# set ge-1/0/0 unit 1 description R1->R2 user@R1# set ge-1/0/0 unit 1 family inet address 10.1.1.1/24 user@R1# set ge-1/0/0 unit 1 family iso user@R1# set ge-1/0/0 unit 1 family mpls user@R1# set ge-1/5/0 unit 12 description R1->R6 user@R1# set ge-1/5/0 unit 12 family inet address 10.1.6.12/24 user@R1# set ge-1/5/0 unit 12 family iso user@R1# set ge-1/5/0 unit 12 family mpls
-
Assign a loopback address to the device.
[edit interfaces lo0 unit 3] user@R1# set family inet address 10.255.102.128/32 user@R1# set family iso address 49.0001.1720.1600.1030.00
-
Configure the IS-IS interface for level 2 and the metric value on all the interfaces, and enable link protection on the protected interface.
[edit protocols isis] user@R1# set interface all level 2 metric 10 user@R1# set interface lo0.12 passive user@R1# set interface fxp0.0 disable user@R1# set interface ge-1/0/0.1 user@R1# set interface ge-1/5/0.12 link-protection
-
Enable IS-IS node-link protection, which also automatically extends backup coverage to all LDP label-switched paths.
[edit protocols isis] user@R1# set spf-options delay 1000 user@R1# set interface all node-link-protection
-
Enable remote LFA backup which calculates the backup next hop using dynamic LDP label-switched path.
(Optional) When you include the node link degradation statement even if node protection LFA is not configured for a given destination, the device uses the configured link protection LFA as the backup for the primary link.
[edit protocols isis] user@R1# set backup-spf-options remote-backup-calculation user@R1# set backup-spf-options node-link-degradation
-
Configure MPLS to use LDP label-switched paths for all interfaces on the device.
[edit protocols] user@R1# set mpls interface all user@R1# set mpls interface fxp0.0 disable user@R1# set ldp interface all user@R1# set ldp interface fxp0.0 disable
-
Specify a time interval for which the targeted LDP sessions are kept up when the remote LFA goes down, and specify a maximum number of automatically, targeted LDP sessions to optimize the use of memory.
[edit protocols ldp] user@R1# set auto-targeted-session user@R1# set auto-targeted-session teardown-delay 60 user@R1# set auto-targeted-session maximum-sessions 20
-
(Optional) Enable forwarding equivalence class (FEC) deaggregation, which results in faster global convergence.
[edit protocols ldp] user@R1# set deaggregate
-
To enable Packet Forwarding Engine local repair, establish a policy that forces the routing protocol process to install all the next hops for a given route.
This policy ensures that the backup route is installed in the forwarding table used by the Packet Forwarding Engine to forward traffic to a given destination.
[edit policy-options] user@R1# set policy-options policy-statement ecmp term 1 user@R1# set then load-balance per-packet
-
Apply the policy to the forwarding table of the local router with the export statement.
[edit routing-options forwarding-table] user@R1# set export ecmp
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration by entering the show interfaces, show protocols, show policy-options, and show routing-options commands. If the output does not display the intended configuration, repeat the instructions in this example to correct the configuration.
user@R1# show interfaces
ge-1/0/0 {
unit 1 {
description R1->R2;
family inet {
address 10.1.1.1/24;
}
family iso;
family mpls;
}
}
ge-1/5/0 {
unit 12 {
description R1->R6;
family inet {
address 10.1.6.12/24;
}
family iso;
family mpls;
}
}
lo0 {
unit 10 {
family inet {
address 10.255.102.128/32;
}
family iso {
address 49.0001.1720.1600.1030.00;
}
}
}
user@R1# show protocols
mpls {
interface all;
interface fxp0.0 {
disable;
}
}
isis {
spf-options delay 1000;
backup-spf-options {
remote-backup-calculation;
node-link-degradation;
}
interface ge-1/0/0.1;
interface ge-1/5/0.12; {
link-protection;
}
interface all {
node-link-protection;
level 2 metric 10;
}
interface fxp0.0 {
disable;
}
interface lo0.12 {
passive;
}
}
ldp {
auto-targeted-session {
teardown-delay 60;
maximum-sessions 20;
}
deaggregate;
interface all;
interface fxp0.0 {
disable;
}
}
user@R1# show policy-options
policy-options {
policy-statement ecmp {
term 1 {
then {
load-balance per-packet;
}
}
}
}
user@R1# show routing-options
forwarding-table {
export ecmp;
}
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from the
configuration mode.
Verification
Confirm that the configuration is working properly.
- Verifying the Routes
- Verifying the IS-IS Routes
- Verifying the LDP Routes
- Verifying the Designated Backup Path Node
Verifying the Routes
Purpose
Verify that the expected routes are learned.
Action
On Device R1, from operational mode, run the show route command to display the routes in the routing table.
user@R1> show route 10.1.4/24
inet.0: 14 destinations, 14 routes (14 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
10.1.4.0/24 *[IS-IS/15] 11:37:58, metric 30
> to 10.1.6.11 via ge-1/5/0
to 10.1.1.2 via ge-1/0/0, Push 299824
user@R1> show route 10.1.4/24 detail
inet.0: 14 destinations, 14 routes (14 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
10.1.4.0/24 (1 entry, 1 announced)
State: <FlashAll>
*IS-IS Preference: 15
Level: 1
Next hop type: Router, Next hop index: 262154
Address: 0x98047cc
Next-hop reference count: 8
Next hop: 10.1.6.11 via ge-1/5/0 weight 0x1, selected
Session Id: 0x14b
Next hop: 10.1.1.2 via ge-1/0/0 weight 0x101 uflags Remote neighbor path
Label operation: Push 299824
Label TTL action: prop-ttl
Load balance label: Label 299824: None;
Session Id: 0x142
State:<Active Int>
Age: 11:38:00
Metric: 30
Validation State: unverified
Task: IS-IS
Announcement bits (3): 0-LDP 1-IS-IS 3-KRT
AS path: I Meaning
The output shows all the routes in the routing table of Device R1.
Verifying the IS-IS Routes
Purpose
Display all the LDP backup routes in the IS-IS routing table of Device R1.
Action
On Device R1, from operational mode, run the show isis route command to display the routes in the IS-IS routing table.
user@R1> show isis route
IS-IS routing table Current version: L1: 558 L2: 564
IPv4/IPv6 Routes
----------------
Prefix L Version Metric Type Interface NH Via Backup Score
10.1.2.0/24 1 558 20 int lt-1/2/0.1 IPV4 tp3-R2
10.1.3.0/24 1 558 30 int lt-1/2/0.1 IPV4 tp3-R2
10.1.4.0/24 1 558 30 int lt-1/2/0.12 IPV4 tp3-R6
lt-1/2/0.1 LSP LDP->tp3-R4(10.255.102.156)
10.1.5.0/24 1 558 20 int lt-1/2/0.12 IPV4 tp3-R6
lt-1/2/0.1 LSP LDP->tp3-R4(10.255.102.156)
10.255.102.136/32 1 558 10 int lt-1/2/0.12 IPV4 tp3-R6
lt-1/2/0.1 LSP LDP->tp3-R4(10.255.102.156)
10.255.102.146/32 1 558 20 int lt-1/2/0.1 IPV4 tp3-R2
10.255.102.156/32 1 558 30 int lt-1/2/0.1 IPV4 tp3-R2
lt-1/2/0.12 IPV4 tp3-R6
10.255.102.166/32 1 558 20 int lt-1/2/0.12 IPV4 tp3-R6
lt-1/2/0.1 LSP LDP->tp3-R4(10.255.102.156)
10.255.102.178/32 1 558 10 int lt-1/2/0.1 IPV4 tp3-R2
Meaning
The output shows all the LDP backup routes in the IS-IS routing table of Device R1.
Verifying the LDP Routes
Purpose
Verify the automatically targeted LDP routes.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show ldp session auto-targeted detail command.
user@R1> show ldp session auto-targeted detail
Address: 10.255.102.156, State: Operational, Connection: Open, Hold time: 21
Session ID: 10.255.102.128:0--10.255.102.156:0
Next keepalive in 1 seconds
Passive, Maximum PDU: 4096, Hold time: 30, Neighbor count: 1
Neighbor types: auto-targeted
Keepalive interval: 10, Connect retry interval: 1
Local address: 10.255.102.128, Remote address: 10.255.102.156
Up for 11:38:23
Capabilities advertised: none
Capabilities received: none
Protection: disabled
Session flags: none
Local - Restart: disabled, Helper mode: enabled
Remote - Restart: disabled, Helper mode: enabled
Local maximum neighbor reconnect time: 120000 msec
Local maximum neighbor recovery time: 240000 msec
Local Label Advertisement mode: Downstream unsolicited
Remote Label Advertisement mode: Downstream unsolicited
Negotiated Label Advertisement mode: Downstream unsolicited
MTU discovery: disabled
Nonstop routing state: Not in sync
Next-hop addresses received:
10.1.3.6
10.1.4.7
10.255.102.156
Meaning
The output shows automatically targeted LDP next hops.
Verifying the Designated Backup Path Node
Purpose
Display the remote LFA next hop determined for a given destination.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show isis backup spf results command.
user@R1> show isis backup spf results R6
IS-IS level 1 SPF results:
R6.00
Primary next-hop: ge-1/5/0, IPV4, R6, SNPA: 0:5:85:88:f0:bc
Root: R6, Root Metric: 10, Metric: 0, Root Preference: 0x0
Not eligible, IPV4, Reason: Primary next-hop link fate sharing
Root: R2, Root Metric: 10, Metric: 20, Root Preference: 0x0
track-item: R6.00-00
track-item: R1.00-00
Not eligible, IPV4, Reason: Path loops
Root: R4, Root Metric: 30, Metric: 20, Root Preference: 0x0
track-item: R6.00-00
track-item: R4.00-00
Eligible, Backup next-hop: ge-1/0/0, LSP, LDP->R4(10.255.102.156), Prefixes: 2
1 nodes
IS-IS level 2 SPF results:
R6.00
Primary next-hop: ge-1/5/0, IPV4, R6, SNPA: 0:5:85:88:f0:bc
Root: R6, Root Metric: 10, Metric: 0, Root Preference: 0x0
Not eligible, IPV4, Reason: Primary next-hop link fate sharing
Root: R2, Root Metric: 10, Metric: 20, Root Preference: 0x0
track-item: R6.00-00
track-item: R1.00-00
Not eligible, IPV4, Reason: Path loops
Root: R4, Root Metric: 30, Metric: 20, Root Preference: 0x0
track-item: R6.00-00
track-item: R4.00-00
Eligible, Backup next-hop: ge-1/0/0, LSP, LDP->R4(10.255.102.156), Prefixes: 0
1 nodes
Meaning
The output indicates whether a specific interface or node has been designated as a remote backup path and why.
