ON THIS PAGE
Example: Configuring IS-IS IPv4 and IPv6 Unicast Topologies
This example shows how to configure IS-IS to calculate an alternate IPv6 unicast topology, in addition to the normal IPv4 unicast topology.
Requirements
No special configuration beyond device initialization is required before configuring this example.
Overview
This example focuses on IPv4 and IPv6 unicast topologies. The IS-IS interface metrics for the IPv4 topology can be configured independently of the IPv6 metrics. You can also selectively disable interfaces from participating in the IPv6 topology while continuing to participate in the IPv4 topology. This enables you to exercise control over the paths that unicast data takes through a network.
To enable an IPv6 unicast topology for IS-IS, include the ipv6-unicast statement:
isis {
topologies {
ipv6-unicast;
}
}
To configure a metric for the IPv6 unicast topology, include
the ipv6-unicast-metric statement:
isis {
interface interface-name {
level level-number {
ipv6-unicast-metric number;
}
}
}
To exclude an interface from the IPv6 unicast topologies for
IS-IS, include the no-ipv6-unicast statement:
isis {
interface interface-name {
no-ipv6-unicast;
}
}
Figure 1 shows the topology used in this example. The black lines indicate link membership in the IPv6 topology. The gray lines indicate membership to the IPv4 topology. Using regular TLVs, it would not be possible to build multiple topologies and run an SPF calculation based on them. The multitopology extensions describe an extension to carry the set of supported protocols in the hello packet. After activating multitopology routing support on a link, the link carries all the topologies that the underlying circuit is able to relay.
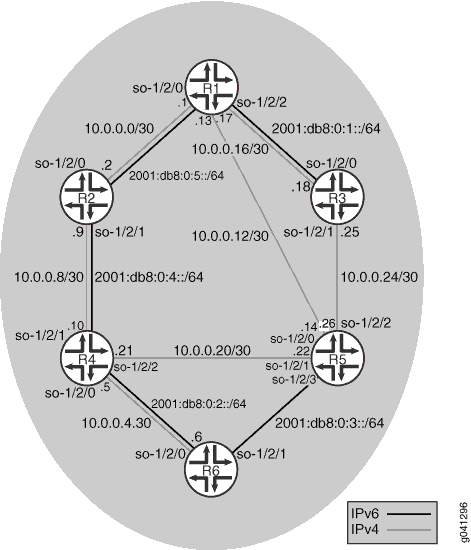
CLI Quick Configuration shows the configuration for all of the devices in Figure 1. The section #configuration340__isis-ipv6-mtr-step-by-step describes the steps on Device R1.
Configuration
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure
this example, copy the following commands, paste them into a text
file, remove any line breaks, change any details necessary to match
your network configuration, and then copy and paste the commands into
the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
Device R1
set interfaces so-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.1/30 set interfaces so-1/2/0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces so-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001:db8:0:5::/64 eui-64 set interfaces so-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.13/30 set interfaces so-1/2/1 unit 0 family iso set interfaces so-1/2/2 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.17/30 set interfaces so-1/2/2 unit 0 family iso set interfaces so-1/2/2 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001:db8:0:1::/64 eui-64 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.1/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0002.0192.0168.0001.00 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001:db8::1/128 set protocols isis topologies ipv6-unicast set protocols isis interface so-1/2/0.0 set protocols isis interface so-1/2/1.0 no-ipv6-unicast set protocols isis interface so-1/2/2.0 set protocols isis interface lo0.0
Device R2
set interfaces so-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.2/30 set interfaces so-1/2/0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces so-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001:db8:0:5::/64 eui-64 set interfaces so-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.9/30 set interfaces so-1/2/1 unit 0 family iso set interfaces so-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001:db8:0:4::/64 eui-64 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.2/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0002.0192.0168.0002.00 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001:db8::2/128 set protocols isis topologies ipv6-unicast set protocols isis interface so-1/2/0.2 set protocols isis interface so-1/2/1.0 set protocols isis interface lo0.0
Device R3
set interfaces so-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.18/30 set interfaces so-1/2/0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces so-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001:db8:0:1::/64 eui-64 set interfaces so-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.25/30 set interfaces so-1/2/1 unit 0 family iso set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.3/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0002.0192.0168.0003.00 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001:db8::3/128 set protocols isis topologies ipv6-unicast set protocols isis interface so-1/2/0.0 set protocols isis interface so-1/2/1.0 no-ipv6-unicast set protocols isis interface lo0.0
Device R4
set interfaces so-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.5/30 set interfaces so-1/2/0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces so-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001:db8:0:2::/64 eui-64 set interfaces so-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.10/30 set interfaces so-1/2/1 unit 0 family iso set interfaces so-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001:db8:0:1::/64 eui-64 set interfaces so-1/2/2 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.21/30 set interfaces so-1/2/2 unit 0 family iso set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.4/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0002.0192.0168.0004.00 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001:db8::4/128 set protocols isis topologies ipv6-unicast set protocols isis interface so-1/2/0.0 set protocols isis interface so-1/2/1.0 set protocols isis interface so-1/2/2.0 no-ipv6-unicast set protocols isis interface lo0.0
Device R5
set interfaces so-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.14/30 set interfaces so-1/2/0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces so-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.22/30 set interfaces so-1/2/1 unit 0 family iso set interfaces so-1/2/2 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.26/30 set interfaces so-1/2/2 unit 0 family iso set interfaces so-1/2/3 unit 0 family iso set interfaces so-1/2/3 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001:db8:0:3::/64 eui-64 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.5/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0002.0192.0168.0005.00 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001:db8::5/128 set protocols isis topologies ipv6-unicast set protocols isis interface so-1/2/0.0 no-ipv6-unicast set protocols isis interface so-1/2/1.0 no-ipv6-unicast set protocols isis interface so-1/2/2.0 no-ipv6-unicast set protocols isis interface so-1/2/3.0 set protocols isis interface lo0.0
Device R6
set interfaces so-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.6/30 set interfaces so-1/2/0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces so-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001:db8:0:2::/64 eui-64 set interfaces so-1/2/1 unit 0 family iso set interfaces so-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001:db8:0:3::/64 eui-64 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.6/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0002.0192.0168.0006.00 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001:db8::6/128 set protocols isis topologies ipv6-unicast set protocols isis interface so-1/2/0.0 set protocols isis interface so-1/2/1.0 set protocols isis interface lo0.0
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following example requires you to navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For information about navigating the CLI, see Using the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode in the CLI User Guide.
To configure an alternate IPv6 unicast topology:
Configure the interfaces.
[edit interfaces] user@R1# set so-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.1/30 user@R1# set so-1/2/0 unit 0 family iso user@R1# set so-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001:db8:0:5::/64 eui-64 user@R1# set so-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.13/30 user@R1# set so-1/2/1 unit 0 family iso user@R1# set so-1/2/2 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.17/30 user@R1# set so-1/2/2 unit 0 family iso user@R1# set so-1/2/2 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001:db8:0:1::/64 eui-64 user@R1# set lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.1/32 user@R1# set lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0002.0192.0168.0001.00 user@R1# set lo0 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001:db8::1/128
Enable IS-IS on the interfaces.
[edit protocols isis] user@R1# set interface so-1/2/0.0 user@R1# set interface so-1/2/1.0 user@R1# set interface so-1/2/2.0 user@R1# set interface lo0.0
Enable multitopology routing on the IS-IS interfaces.
The
ipv6-unicaststatement enables multitopology IS-IS routing on all interfaces that havefamily isoandfamily inet6configured and are listed at the[edit protocols isis interface]hierarchy level.[edit protocols isis] user@R1# set topologies ipv6-unicast
Disable IPv6 unicast support on a given interface.
If you do not want to run multitopology IS-IS routing for IPv6 on a given interface, you can disable multitopology routing by including the
no-ipv6-unicaststatement in the IS-IS interface configuration.[edit protocols isis] user@R1# set interface so-1/2/1.0 no-ipv6-unicast
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show interfaces and show protocols commands. If the output does not display the intended configuration,
repeat the instructions in this example to correct the configuration.
user@R1# show interfaces
so-1/2/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.0.0.1/30;
}
family iso;
family inet6 {
address 2001:db8:0:5::/64 {
eui-64;
}
}
}
}
so-1/2/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.0.0.13/30;
}
family iso;
}
}
so-1/2/2 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.0.0.17/30;
}
family iso;
family inet6 {
address 2001:db8:0:1::/64 {
eui-64;
}
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.168.0.1/32;
}
family iso {
address 49.0002.0192.0168.0001.00;
}
family inet6 {
address 2001:db8::1/128;
}
}
}
user@R1# show protocols
isis {
topologies ipv6-unicast;
interface so-1/2/0.0;
interface so-1/2/1.0 {
no-ipv6-unicast;
}
interface so-1/2/2.0;
interface lo0.0;
}
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Verification
Confirm that the configuration is working properly.
- Checking the Topologies on Neighbors
- Checking the IS-IS SPF Calculations
- Checking the Tcpdump Output
Checking the Topologies on Neighbors
Purpose
Determine what topologies are supported on neighboring IS-IS devices.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show isis adjacency
detail command.
user@R1> show isis adjacency detail R2 Interface: so-1/2/0.0, Level: 3, State: Up, Expires in 24 secs Priority: 0, Up/Down transitions: 1, Last transition: 05:28:16 ago Circuit type: 3, Speaks: IP, IPv6 Topologies: Unicast, IPV6-Unicast Restart capable: Yes, Adjacency advertisement: Advertise IP addresses: 10.0.0.2 IPv6 addresses: fe80::2a0:a514:0:24c R5 Interface: so-1/2/1.0, Level: 3, State: Up, Expires in 21 secs Priority: 0, Up/Down transitions: 1, Last transition: 05:27:47 ago Circuit type: 3, Speaks: IP, IPv6 Topologies: Unicast Restart capable: Yes, Adjacency advertisement: Advertise IP addresses: 10.0.0.14 R3 Interface: so-1/2/2.0, Level: 3, State: Up, Expires in 22 secs Priority: 0, Up/Down transitions: 1, Last transition: 05:27:25 ago Circuit type: 3, Speaks: IP, IPv6 Topologies: Unicast, IPV6-Unicast Restart capable: Yes, Adjacency advertisement: Advertise IP addresses: 10.0.0.18 IPv6 addresses: fe80::2a0:a514:0:124c
Meaning
As expected, the adjacency with Device R5 only supports the IPv4 unicast topology, while the adjacencies with Device R2 and Device R3 support both the IPv4 and IPv6 topologies.
Checking the IS-IS SPF Calculations
Purpose
Verify that separate SPF calculations are being run for IPv4 and IPv6.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show isis spf
brief command.
user@R1> show isis spf brief IPV4 Unicast IS-IS level 1 SPF results: Node Metric Interface NH Via SNPA R6.00 20 so-1/2/1.0 IPV4 R5 R4.00 20 so-1/2/0.0 IPV4 R2 R5.00 10 so-1/2/1.0 IPV4 R5 R3.00 10 so-1/2/2.0 IPV4 R3 R2.00 10 so-1/2/0.0 IPV4 R2 R1.00 0 6 nodes IPV4 Unicast IS-IS level 2 SPF results: Node Metric Interface NH Via SNPA R6.00 20 so-1/2/1.0 IPV4 R5 R4.00 20 so-1/2/0.0 IPV4 R2 R5.00 10 so-1/2/1.0 IPV4 R5 R3.00 10 so-1/2/2.0 IPV4 R3 R2.00 10 so-1/2/0.0 IPV4 R2 R1.00 0 6 nodes IPV6 Unicast IS-IS level 1 SPF results: Node Metric Interface NH Via SNPA R5.00 40 so-1/2/0.0 IPV6 R2 R6.00 30 so-1/2/0.0 IPV6 R2 R4.00 20 so-1/2/0.0 IPV6 R2 R3.00 10 so-1/2/2.0 IPV6 R3 R2.00 10 so-1/2/0.0 IPV6 R2 R1.00 0 6 nodes IPV6 Unicast IS-IS level 2 SPF results: Node Metric Interface NH Via SNPA R5.00 40 so-1/2/0.0 IPV6 R2 R6.00 30 so-1/2/0.0 IPV6 R2 R4.00 20 so-1/2/0.0 IPV6 R2 R3.00 10 so-1/2/2.0 IPV6 R3 R2.00 10 so-1/2/0.0 IPV6 R2 R1.00 0 6 nodes
Meaning
As expected, SPF calculations are being performed for IPv4 and IPv6 topologies.
Checking the Tcpdump Output
Purpose
Verify that the link can be a member of both the IPv4 unicast topology and the IPv6 unicast topology.
Action
user@R1> monitor traffic detail interface so-1/2/0.0
[...]
15:52:35.719540 In IS-IS, length 82
p2p IIH, hlen: 20, v: 1, pdu-v: 1, sys-id-len: 6 (0), max-area: 3 (0)
source-id: 0192.0168.0002, holding time: 27s, Flags: [Level 1, Level 2]
circuit-id: 0x01, PDU length: 82
Point-to-point Adjacency State TLV #240, length: 15
Adjacency State: Up (0)
Extended Local circuit-ID: 0x00000054
Neighbor System-ID: 0192.0168.0001
Neighbor Extended Local circuit-ID: 0x00000043
Protocols supported TLV #129, length: 2
NLPID(s): IPv4 (0xcc), IPv6 (0x8e)
IPv4 Interface address(es) TLV #132, length: 4
IPv4 interface address: 10.0.0.2
IPv6 Interface address(es) TLV #232, length: 16
IPv6 interface address: fe80::2a0:a514:0:24c
Area address(es) TLV #1, length: 4
Area address (length: 3): 49.0002
Restart Signaling TLV #211, length: 3
Flags [none], Remaining holding time 0s
Multi Topology TLV #229, length: 4
IPv4 unicast Topology (0x000), Flags: [none]
IPv6 unicast Topology (0x002), Flags: [none]
Meaning
The IS-IS hello (IIH) packet shows that IPv4 and IPv6 are supported. The hello packet lists valid IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, and therefore the routing device can create valid next-hop entries. The supported protocols are listed in the multitopology TLV #229.
