User Access on Logical Systems
Example: Configuring Logical System Administrators
This example shows how to configure logical system administrators.
Requirements
You must be the primary administrator to assign system administrators to logical systems.
Overview
The primary administrator can assign one or more system administrators to each logical system. Logical system administrators are confined to the context of the logical system to which they are assigned. This means that logical system administrators cannot access any global configuration statements. This also means that command output is restricted to the context to which the logical system administrators are assigned.
Configuring a user account for each logical system helps in navigating the CLI. This enables you to log in to each logical system and be positioned within the root of that logical system as if you were in the root of a physical router.
In this example, LS1Admin has full permissions on Logical System LS1.
In this example, LS2Admin has the ability to view Logical System LS2 but not to change the configuration.
Diagram
Figure 1 shows how logical system administration works.
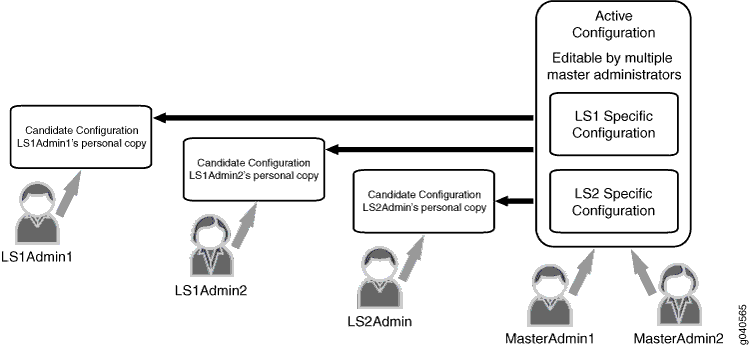
Configuration
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks,
change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
set logical-systems LS1 set logical-systems LS2 set system login class admin1 logical-system LS1 set system login class admin2 logical-system LS2 set system login class admin1 permissions all set system login class admin2 permissions view set system login user LS1Admin class admin1 set system login user LS2Admin class admin2
Procedure
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following example requires you to navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For information about navigating the CLI, see Using the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode in the CLI User Guide.
To assign logical system administrators to a logical systems:
Configure the logical systems.
[edit] user@host# set logical-systems LS1 user@host# set logical-systems LS2
Create the login classes and assign logical systems to the classes.
[edit] user@host# set system login class admin1 logical-system LS1 user@host# set system login class admin2 logical-system LS2
Assign permissions to the login classes.
[edit] user@host# set system login class admin1 permissions all user@host# set system login class admin2 permissions view
Assign users to the login classes.
[edit] user@host# set system login user LS1Admin class admin1 user@host# set system login user LS2Admin class admin2
If you are done configuring the device, commit the configuration.
[edit] user@host# commit
Verification
To verify that the configuration is working
properly, issue the show cli authorization command to view permissions for the current user.
