Example: Configuring IGMP Snooping on SRX Series Devices
You can enable IGMP snooping on a VLAN to constrain the flooding of IPv4 multicast traffic on a VLAN. When IGMP snooping is enabled, the device examines IGMP messages between hosts and multicast routers and learns which hosts are interested in receiving multicast traffic for a multicast group. Based on what it learns, the device then forwards multicast traffic only to those interfaces that are connected to relevant receivers instead of flooding the traffic to all interfaces.
This example describes how to configure IGMP snooping:
Requirements
This example uses the following hardware and software components:
One SRX Series Firewall
Junos OS Release 18.1R1
Before you configure IGMP snooping, be sure you have:
Configured a VLAN, v1, on the device
Assigned interfaces ge-0/0/1, ge-0/0/2, ge-0/0/3, and ge-0/0/4 to v1
Configured ge-0/0/3 as a trunk interface
Overview and Topology
IGMP snooping controls multicast traffic in a switched network. When IGMP snooping is not enabled, the SRX Series Firewall broadcasts multicast traffic out of all of its ports, even if the hosts on the network do not want the multicast traffic. With IGMP snooping enabled, the SRX Series Firewall monitors the IGMP join and leave messages sent from each connected host to a multicast router. This enables the SRX Series Firewall to keep track of the multicast groups and associated member ports. The SRX Series Firewall uses this information to make intelligent decisions and to forward multicast traffic to only the intended destination hosts.
Topology
The sample topology is illustrated in Figure 1.
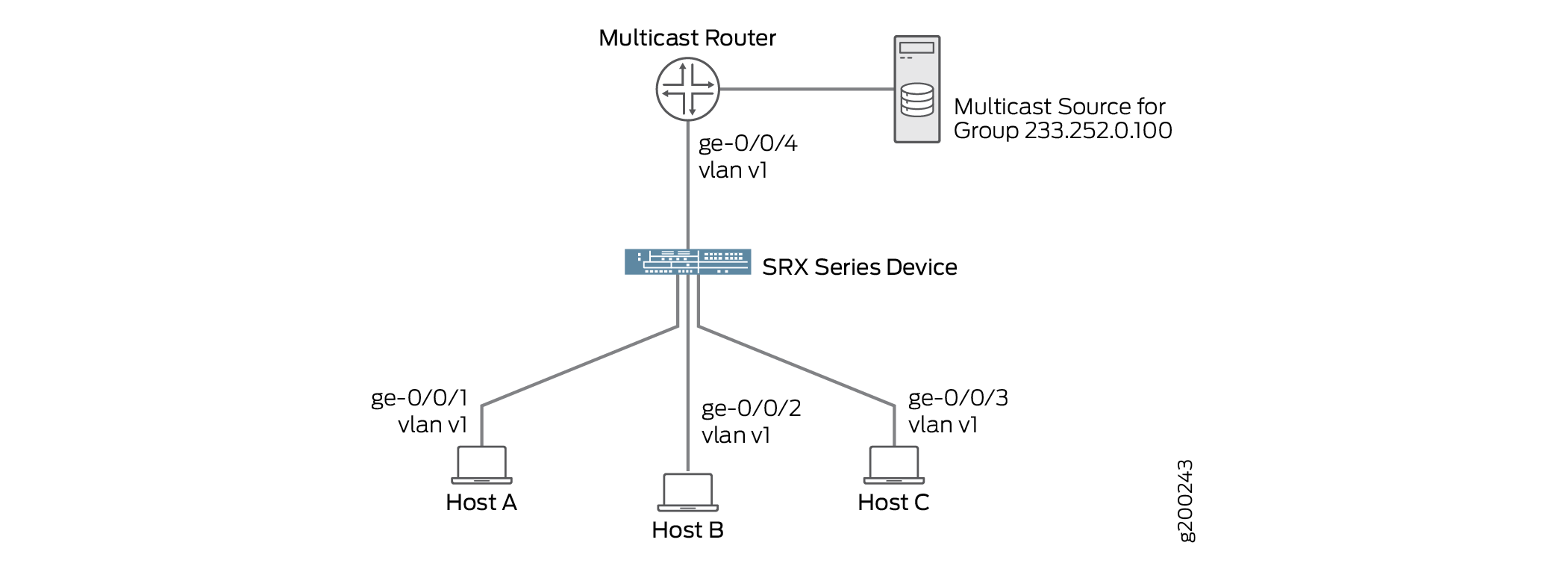
In this sample topology, the multicast router forwards multicast traffic to the device from the source when it receives a membership report for group 233.252.0.100 from one of the hosts—for example, Host B. If IGMP snooping is not enabled on vlan100, the device floods the multicast traffic on all interfaces in vlan100 (except for interface ge-0/0/2.0). If IGMP snooping is enabled on vlan100, the device monitors the IGMP messages between the hosts and router, allowing it to determine that only Host B is interested in receiving the multicast traffic. The device then forwards the multicast traffic only to interface ge-0/0/2.
Configuration
To configure IGMP snooping on a device:
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks,
change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy
level, and then enter commit from configuration mode.
set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode access set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members v1 set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode access set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members v1 set interfaces ge-0/0/3 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode trunk set interfaces ge-0/0/3 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members v1 set interfaces ge-0/0/4 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode access set interfaces ge-0/0/4 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members v1 set vlans v1 vlan-id 100 set protocols igmp-snooping vlan v1 query-interval 200 set protocols igmp-snooping vlan v1 query-response-interval 0.4 set protocols igmp-snooping vlan v1 query-last-member-interval 0.1 set protocols igmp-snooping vlan v1 robust-count 4 set protocols igmp-snooping vlan v1 immediate-leave set protocols igmp-snooping vlan v1 proxy set protocols igmp-snooping vlan v1 interface ge-0/0/1.0 host-only-interface set protocols igmp-snooping vlan v1 interface ge-0/0/1.0 group-limit 50 set protocols igmp-snooping vlan v1 interface ge-0/0/4.0 static group 233.252.0.100
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following example requires you to navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For instructions on how to do that, see Using the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode in the CLI User Guide.
To configure IGMP snooping:
Configure the access mode interfaces.
[edit] user@host# set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode access user@host# set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members v1 user@host# set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode access user@host# set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members v1 user@host# set interfaces ge-0/0/3 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode trunk user@host# set interfaces ge-0/0/3 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members v1 user@host# set interfaces ge-0/0/4 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode access user@host# set interfaces ge-0/0/4 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members v1
Configure the VLAN.
[edit] user@host# set vlans v1 vlan-id 100
Enable IGMP snooping and configure the device to serve as a proxy.
[edit] user@host# set protocols igmp-snooping vlan v1 proxy
Configure the limit for the number of multicast groups allowed on the ge-0/0/1.0 interface to 50.
[edit] user@host# set protocols igmp-snooping vlan v1 interface ge-0/0/1.0 group-limit 50
Configure the device to immediately remove a group membership from an interface when it receives a leave message from that interface without waiting for any other IGMP messages to be exchanged.
[edit] user@host# set protocols igmp-snooping vlan v1 immediate-leave
Statically configure interface ge-0/0/4 as a multicast-router interface.
[edit] user@host# set protocols igmp-snooping vlan v1 interface ge-0/0/4.0 static group 233.252.0.100
Configure an interface to be an exclusively host-facing interface (to drop IGMP query messages).
[edit] user@host# set protocols igmp-snooping vlan v1 interface ge-0/0/1.0 host-only-interface
Configure the IGMP message intervals and robustness count.
[edit] user@host# set protocols igmp-snooping vlan v1 query-interval 200 user@host# set protocols igmp-snooping vlan v1 query-response-interval 0.4 user@host# set protocols igmp-snooping vlan v1 query-last-member-interval 0.1 user@host# set protocols igmp-snooping vlan v1 robust-count 4
If you are done configuring the device, commit the configuration.
user@host# commit
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show protocols igmp-snooping command. If
the output does not display the intended configuration, repeat the
configuration instructions in this example to correct it.
[edit]
user@host# show protocols igmp-snooping
vlan v1 {
query-interval 200;
query-response-interval 0.4;
query-last-member-interval 0.1;
robust-count 4;
immediate-leave;
proxy;
interface ge-0/0/1.0 {
host-only-interface;
group-limit 50;
}
interface ge-0/0/4.0 {
static {
group 233.252.0.100;
}
}
}
Verifying IGMP Snooping Operation
To verify that IGMP snooping is operating as configured, perform the following task:
Displaying IGMP Snooping Information for VLAN v1
Purpose
Verify that IGMP snooping is enabled on vlan v1 and that ge-0/0/4 is recognized as a multicast-router interface.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show igmp snooping
membership command.
user@host> show igmp snooping membership Instance: default-switch Vlan: v1 Learning-Domain: default Interface: ge-0/0/4.0, Groups: 1 Group: 233.252.0.100 Group mode: Exclude Source: 0.0.0.0 Last reported by: Local Group timeout: 0 Type: Static
Meaning
By showing information for vlanv1, the command output confirms that IGMP snooping is configured on the VLAN. Interface ge-0/0/4.0 is listed as a multicast-router interface, as configured. Because none of the host interfaces are listed, none of the hosts are currently receivers for the multicast group.
