NETCONF Sessions over Outbound HTTPS
Client applications can establish Network Configuration Protocol (NETCONF) sessions using outbound HTTPS on supported devices running Junos OS Release 20.2.
This topic discusses how to establish NETCONF sessions using outbound HTTPS on devices running Junos OS Release 20.2. For information about establishing NETCONF and shell sessions using enhanced outbound HTTPS, see NETCONF and Shell Sessions over Enhanced Outbound HTTPS.
Understanding NETCONF Sessions over Outbound HTTPS
- Benefits of NETCONF Sessions over Outbound HTTPS
- NETCONF Sessions over Outbound HTTPS Overview
- Connection Workflow for Sessions over Outbound HTTPS
Benefits of NETCONF Sessions over Outbound HTTPS
-
Enable NETCONF client applications to manage devices that are not accessible through other protocols.
-
Enable remote management of devices using certificate-based authentication for the outbound HTTPS client.
NETCONF Sessions over Outbound HTTPS Overview
You can establish NETCONF sessions over outbound HTTPS between supported Junos devices and a network management system. A NETCONF session over outbound HTTPS enables you to remotely manage devices that might not be accessible through other protocols such as SSH. This might happen, for example, if the device is behind a firewall, and the firewall or another security tool blocks those protocols. HTTPS, on the other hand, uses a standard port, which is typically allowed outbound in most environments.
On supported devices, Junos OS includes a Juniper Extension Toolkit (JET) application that supports establishing a NETCONF session using outbound HTTPS. The JET application uses the gRPC framework to connect to the outbound HTTPS client, which consists of a gRPC server running on the network management system. gRPC is a language-agnostic, open-source remote procedure call (RPC) framework. Figure 1 illustrates the outbound HTTPS setup in its simplest form.
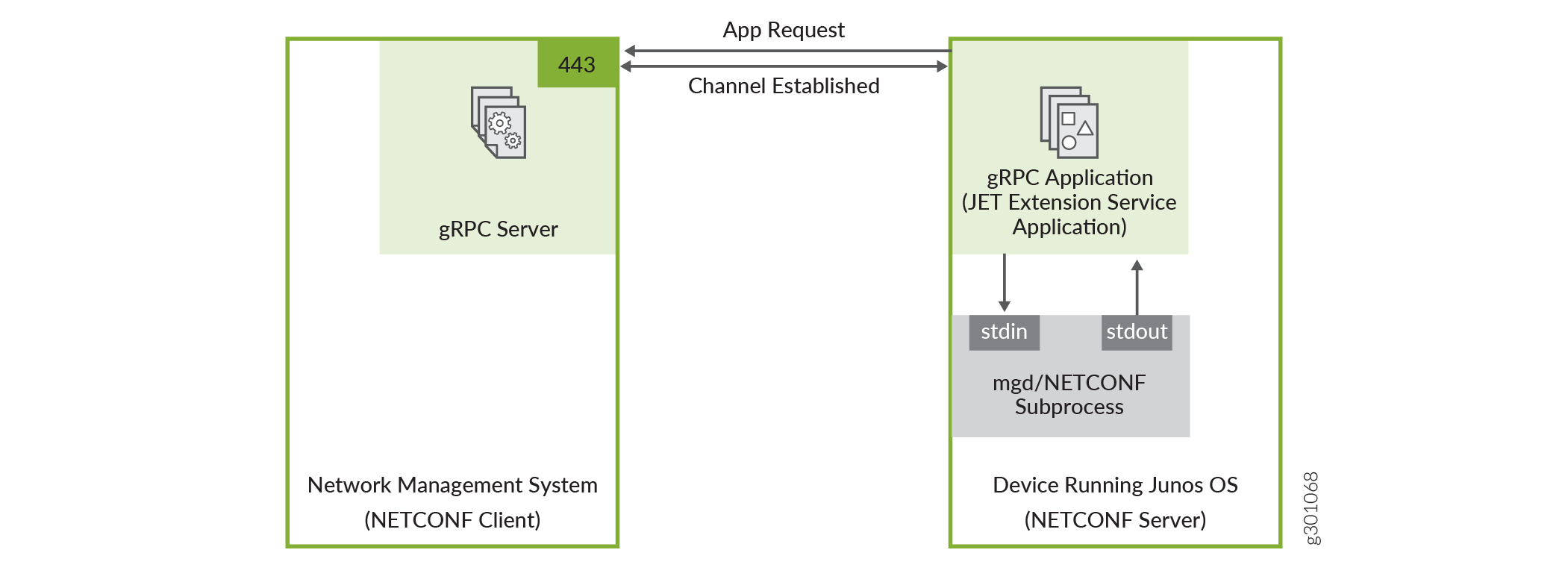
In this scenario, the gRPC server acts as the NETCONF client, and the JET application is the gRPC client and NETCONF server. The gRPC server listens for connection requests on the specified port, which defaults to port 443. You configure the JET application as an extension service. The relevant connection and authentication information is passed to the script. While the script runs, it automatically attempts to connect to the gRPC server on the configured host and port.
The JET application and gRPC server establish a persistent HTTPS connection over a TLS-encrypted gRPC session. The JET application authenticates the gRPC server using an X.509 digital certificate, and if the authentication is successful, the requested NETCONF session is established over this connection. The NETCONF operations execute under the account privileges of the user configured for the extension service application.
The outbound HTTPS connection uses an X.509 digital certificate to authenticate the gRPC server. A digital certificate is an electronic means for verifying your identity through a trusted third party, known as a certificate authority or certification authority (CA). A certificate authority issues digital certificates, which can be used to establish a secure connection between two endpoints through certificate validation. The X.509 standard defines the format for the certificate. To establish a NETCONF session over outbound HTTPS on supported Junos devices, the gRPC server must have a valid X.509 certificate.
The basic outbound HTTPS feature provides support for connecting to a single outbound HTTPS client and configuring one gRPC server for that client. Server authentication must use a self-signed X.509 certificate. You can establish a single NETCONF session over the connection.
Connection Workflow for Sessions over Outbound HTTPS
In a NETCONF session over outbound HTTPS, the gRPC server running on the network management system acts as the NETCONF client, and the JET application on the Junos device is the gRPC client and NETCONF server.
The gRPC client and server perform the following actions to establish a NETCONF session over outbound HTTPS:
-
The gRPC server listens for incoming connections on the specified port, or if no port is specified, on the default port 443.
-
The gRPC client initiates a TCP/IP connection with the configured gRPC server and port.
-
The gRPC client sends a TLS
ClientHellomessage to initiate the TLS handshake. -
The gRPC server sends a
ServerHellomessage and its certificate. -
The gRPC client verifies the identity of the gRPC server.
-
The NETCONF session is established.
-
The server and client exchange NETCONF
<hello>messages. -
The NETCONF client application performs operations as needed.
How to Establish a NETCONF Session over Outbound HTTPS
You can use the JET application that is included as part of the Junos software image to establish a NETCONF session over outbound HTTPS between a network management system (NMS) and supported Junos devices. The JET application, configured as an extension service, initiates a connection to a gRPC server running on an NMS and establishes a persistent HTTPS connection over a TLS-encrypted gRPC session. The NETCONF session runs over this HTTPS connection. In this scenario, the gRPC server is the NETCONF client, and the JET application is the gRPC client and NETCONF server.
The following hardware and software are required for establishing a NETCONF session over outbound HTTPS:
-
Network management system running Python 3.5 or later
-
Device running Junos OS with upgraded FreeBSD Release 20.2 that also supports running JET applications
Note:For supported devices, see Feature Explorer NETCONF sessions over outbound HTTPS.
Figure 2 illustrates the setup referenced in the tasks that follow.
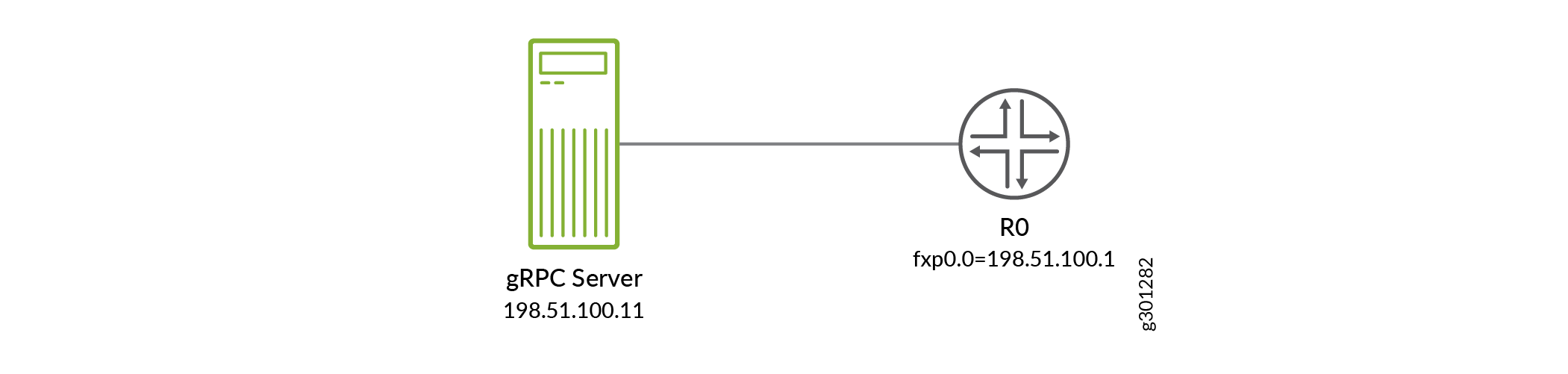
Before the client and server can establish a NETCONF session over outbound HTTPS, you must satisfy the requirements discussed in the following sections:
- Obtain an X.509 Certificate for the gRPC Server
- Set Up the gRPC Server
- Configure the User Account for the NETCONF User
- Configure the Outbound HTTPS Client
- Configure the Outbound HTTPS Extension Service on Junos Devices
- Start the NETCONF Session
Obtain an X.509 Certificate for the gRPC Server
The outbound HTTPS connection uses an X.509 public key certificate to authenticate the identity of the gRPC server running on the network management system. The gRPC stack supports the X.509 v3 certificate format.
The requirements for the gRPC server’s certificate are:
-
The certificate must be self-signed.
-
The certificate must define either the gRPC server’s hostname in the Common Name (CN) field, or it must define the gRPC server’s IP address in the SubjectAltName (SAN) IP Address field. The Junos device must use the same value to establish the connection to the server. If the certificate defines the SubjectAltName IP Address field, the device ignores the Common Name field during authentication.
-
The certificate must be PEM-encoded and use a .crt extension.
-
The certificate and its key must be named server.crt and server.key, respectively.
To use OpenSSL to obtain a certificate:
Set Up the gRPC Server
The network management system requires the following software:
-
Python 3.5 or later
The network management system and the JET application on the Junos device use the gRPC
framework to establish a persistent HTTPS connection over a TLS-encrypted gRPC session.
The network management system must have the gRPC stack installed and run a gRPC server
that listens on the specified port for the connection request. Juniper Networks provides
the necessary proto definition files and sample gRPC server application files in the
Juniper Networks
netconf-https-outbound
repository on GitHub.
This section sets up the gRPC server on a network management system running Ubuntu 18.04. If you are running a different operating system, use the commands appropriate for your OS.
To set up the gRPC server on a network management system running Ubuntu 18.04:
The gRPC server listens indefinitely on the specified port for incoming connections. After you configure the Junos device to connect to the gRPC server and a connection and session are established, you can perform NETCONF operations as appropriate.
Configure the User Account for the NETCONF User
To establish a NETCONF session over outbound HTTPS, you must create a user account locally on the Junos device. You use this account to perform the NETCONF operations on the device for that session. The JET application runs using the permissions configured for this account.
To create a user account on a Junos device:
Configure the Outbound HTTPS Client
The JET application can connect to only one outbound HTTPS client. You configure the connection and authentication information for the client as command-line arguments to the JET script. Table 1 outlines the arguments.
|
Argument |
Value |
|---|---|
|
|
The hostname or IPv4 address of the gRPC server to which the JET application connects. The argument value must match the hostname in the Common Name (CN) field or the IP address in the SubjectAltName IP address field in the gRPC server's certificate. |
|
|
(Optional) Port on which the JET application attempts to connect to the gRPC server. Omit this argument to use the default port 443. |
|
|
(Optional) The gRPC server's certificate contents between the
You can omit this argument if you instead copy the certificate to the /var/db/scripts/jet directory on the device. You must copy the certificate to the device for key sizes greater than 4096 bits. |
Before you begin, you will need the values for the script arguments, including:
-
The port on which the gRPC server is listening for connections.
-
The contents of the SubjectAltName IP Address field, or if there is no such field, the contents of the Common Name (CN) field in the gRPC server's certificate.
-
The contents of the gRPC server's certificate between
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----and-----END CERTIFICATE-----, omitting any newlines. This information is only required when you configure the certificate contents as a script argument instead of copying the certificate to the device running Junos OS.
To configure the outbound HTTPS client:
Configure the Outbound HTTPS Extension Service on Junos Devices
Junos releases that support NETCONF sessions over outbound HTTPS include a JET application and supporting files in the software image. Table 2 outlines the files, which are located in the /var/db/scripts/jet directory on the device.
|
Files |
Description |
|---|---|
|
nc_grpc_app.py |
JET application that uses the gRPC framework to establish a persistent HTTPS connection with a gRPC server running on the network management system. |
|
nc_grpc_pb2.py nc_grpc_pb2_grpc.py |
Required libraries |
To configure the Junos device for sessions over outbound HTTPS:
After the application successfully starts, it logs messages to the outbound_https.log file.
If the application does not automatically start after you commit the configuration,
review the log messages related to this application to troubleshoot the issue. In
Junos OS, issue the show log jet.log command.
Start the NETCONF Session
The gRPC server running on the network management system acts as the NETCONF client, and the JET application on the Junos device acts as the gRPC client and NETCONF server. After you start the gRPC server and JET application, the JET application attempts to connect to the gRPC server on the specified port. If the connection is successful, the gRPC client authenticates the gRPC server. If the server authentication is successful, the NETCONF session starts automatically.
To establish a NETCONF session over outbound HTTPS:
