Example: Configure sFlow for EVPN-VXLAN Networks
Use this example to configure and use sFlow monitoring for EVPN-VXLAN traffic with an IPv4 underlay on switches.
Requirements
This example uses the following hardware and software components:
- A QFX10002-60C, QFX10002, QFX10008, or QFX10016 switch.
- Junos OS Release 21.3R1, 21.2R2 and later.
This example assumes that you already have an EVPN-VXLAN with an IPv4 underlay based network and want to enable sFlow monitoring on a switch.
Overview and Topology
In this example, you enable sFlow inspection for an existing and working EVPN-VXLAN network traffic with IPv4 underlay.
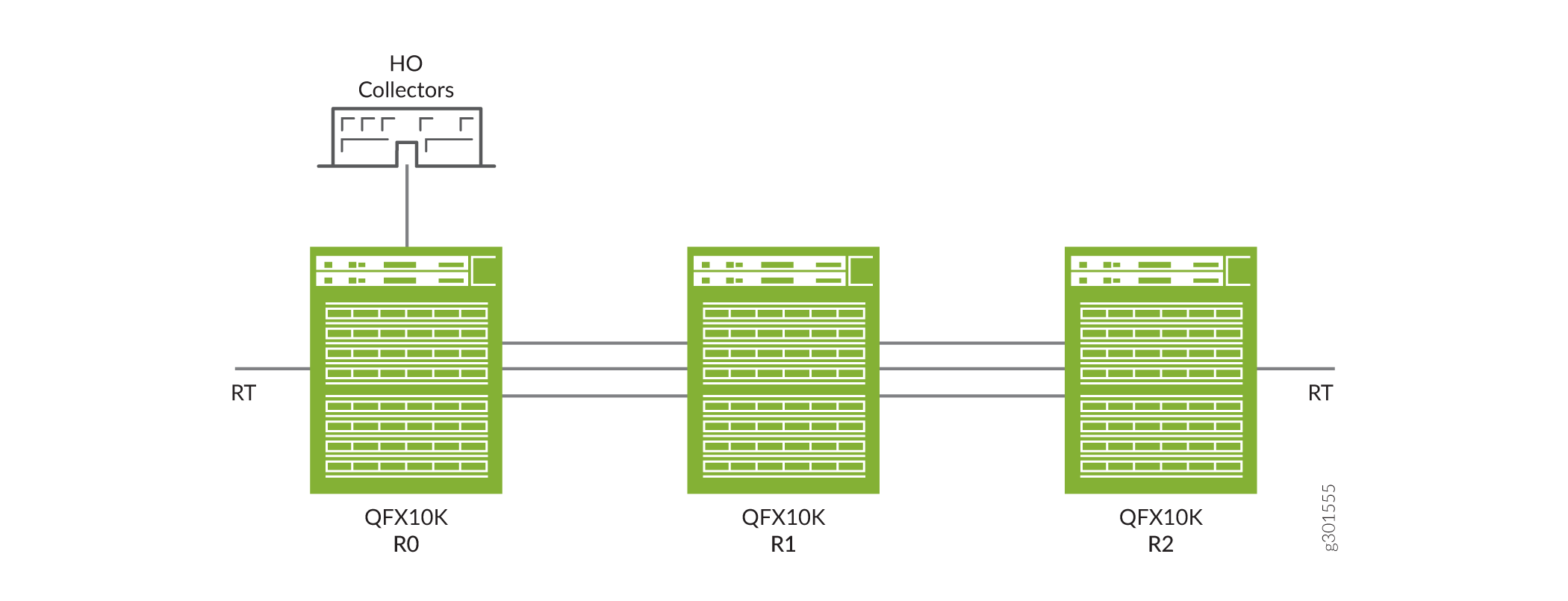
Topology
Figure 1 depicts the sFlow support in an EVPN-VXLAN network environment with an IPv4 underlay. In this topology, the sFlow agent performs packet sampling and gathers interface statistics, and then combines the information into UDP datagrams that are sent to sFlow collectors. You can connect an sFlow collector to the switch through the management network or data network. The sFlow program on the switch looks up the next-hop address for the specified collector IP address to determine whether the collector is reachable by way of the management network or data network.
You should configure sFlow on the physical port of your hardware switch and logical interface where the VTEPs (virtual port) are configured and not on VTEPs itself. When you configure sFlow on fabric facing interface, the underlay traffic along with VXLAN traffic is sampled. You can configure sFlow on any of the R0, R1, or R2 devices mentioned in the topology.
For information about basic EVPN-VXLAN underaly configuration, refer to Configuring an EVPN-VXLAN Centrally-Routed Bridged Overlay.
Configuration
Use the following steps to configure sFlow technology on your switch with EVPN-VXLAN network:
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example on your switch, copy the following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks, change any details necessary to match your network configuration, and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
[edit protocols sflow] set polling-interval 20 set sample-rate ingress 10 set source-ip 10.1.12.0 set collector 10.102.70.200set interfaces et-0/0/1.1 sample-rate ingress 100 egress 100
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure sFlow technology:
-
Specify in seconds how often the sFlow agent polls the interface:
[edit protocols sflow] user@switch# set polling-interval 0
-
Specify the rate at which ingress packets must be sampled:
[edit protocols sflow] user@switch# set sample-rate ingress 100
-
Configure the source IP address:
[edit protocols sflow] user@switch# set source-ip 10.1.12.0
-
Configure the IP address of the collector:
[edit protocols sflow] user@switch# set collector 192.168.200.100
-
Enable sFlow technology on a specific interface:
[edit protocols sflow] user@switch# set interfaces et-0/0/1.1 sample rate ingress 100 egress 100
-
Commit the configuration:
[edit protocols sflow] user@switch# commit
Results
Check the results of the configuration:
[edit]
user@switch# show protocols sflow
agent-id 10.1.12.0/24;
polling-interval 0;
sample-rate {
ingress 16000;
egress 16000;
}
collector 192.168.200.100;
interfaces et-0/0/54.1 {
sample-rate {
ingress 100;
egress 100;
}
}
interfaces et-0/0/56.0;
interfaces et-0/0/57.1 {
sample-rate {
ingress 100;
egress 100;
}
}
Verification
To confirm that the sFlow configuration is enabled and correct.
Verify Configured sFlow Technology
Purpose
Verify the sFlow monitoring is enabled for an EVPN-VXLAN network.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show protocols sflow command.
user@switch> show protocols sflow sFlow : Enabled Adaptive fallback : Disabled Sample limit : 300 packets/second Sample limit Threshold : 0 packets/second Polling interval : 0 second Sample rate egress : 1:2048: Disabled Sample rate ingress : 1:100: Enabled Agent ID : 10.1.12.0/24 Source IP address : 10.1.12.0
