RIP Timers
Understanding RIP Timers
RIP uses several timers to regulate its operation.
The update interval is the interval at which routes that are learned by RIP are advertised to neighbors. This timer controls the interval between routing updates. The update interval is set to 30 seconds, by default, with a small random amount of time added when the timer is reset. This added time prevents congestion that can occur if all routing devices update their neighbors simultaneously.
To configure the update time interval, include the update-interval statement:
update-interval seconds;
seconds can be a value from 10 through 60.
You can set a route timeout interval. If a route is not refreshed after being installed in the routing table by the specified time interval, the route is marked as invalid and is removed from the routing table after the hold-down period expires.
To configure the route timeout for RIP, include the route-timeout statement:
route-timeout seconds;
seconds can be a value from 30 through 360. The default value is 180 seconds.
RIP routes expire when either a route timeout limit is met or a route metric reaches infinity, and the route is no longer valid. However, the expired route is retained in the routing table for a specified period so that neighbors can be notified that the route has been dropped. This time period is set by configuring the hold-down timer. Upon expiration of the hold-down timer, the route is removed from the routing table.
To configure the hold-down timer for RIP, include the holddown statement:
holddown seconds;
seconds can be a value from 10 through 180. The default value is 120 seconds.
In Junos OS Release 11.1 and later, a retransmission timer is available for RIP demand circuits.
Generally, we recommend against changing the RIP timers, unless the effects of a change are well understood. The route timeout should be at least three times the update interval. Normally, the default values are best left in effect for standard operations.
Example: Configuring RIP Timers
This example shows how to configure the RIP update interval and how to monitor the impact of the change.
Requirements
No special configuration beyond device initialization is required before configuring this example.
Overview
In this example, Device R2 has an update interval of 60 seconds for its neighbor, Device R1, and an update interval of 10 seconds for its neighbor, Device R3.
This example is not necessarily practical, but it is shown for demonstration purposes. Generally, we recommend against changing the RIP timers, unless the effects of a change are well understood. Normally, the default values are best left in effect for standard operations.
An export policy is also shown because an export policy is required as part of the minimum configuration for RIP.
Figure 1 shows the topology used in this example.
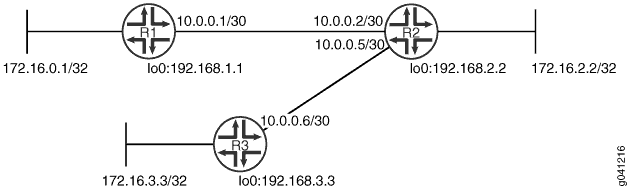
CLI Quick Configuration shows the configuration for all of the devices in Figure 1. The section #d53e65__d53e186 describes the steps on Device R2.
Topology
Configuration
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this
example, copy the following commands, paste them into a text file,
remove any line breaks, change any details necessary to match your
network configuration, and then copy and paste the commands into the
CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
Device R1
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 1 family inet address 10.0.0.1/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 1 family inet address 172.16.0.1/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 1 family inet address 192.168.1.1/32 set protocols rip group rip-group export advertise-routes-through-rip set protocols rip group rip-group neighbor fe-1/2/0.1 set policy-options policy-statement advertise-routes-through-rip term 1 from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement advertise-routes-through-rip term 1 from protocol rip set policy-options policy-statement advertise-routes-through-rip term 1 then accept
Device R2
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 2 family inet address 10.0.0.2/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 5 family inet address 10.0.0.5/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 2 family inet address 192.168.2.2/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 2 family inet address 172.16.2.2/32 set protocols rip group rip-group export advertise-routes-through-rip set protocols rip group rip-group neighbor fe-1/2/0.2 update-interval 60 set protocols rip group rip-group neighbor fe-1/2/1.5 update-interval 10 set policy-options policy-statement advertise-routes-through-rip term 1 from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement advertise-routes-through-rip term 1 from protocol rip set policy-options policy-statement advertise-routes-through-rip term 1 then accept
Device R3
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 6 family inet address 10.0.0.6/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 3 family inet address 192.168.3.3/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 3 family inet address 172.16.3.3/32 set protocols rip group rip-group export advertise-routes-through-rip set protocols rip group rip-group neighbor fe-1/2/0.6 set policy-options policy-statement advertise-routes-through-rip term 1 from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement advertise-routes-through-rip term 1 from protocol rip set policy-options policy-statement advertise-routes-through-rip term 1 then accept
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following example requires you to navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For information about navigating the CLI, see Using the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode in the CLI User Guide.
To configure the RIP update interval:
Configure the network interfaces.
This example shows multiple loopback interface addresses to simulate attached networks.
[edit interfaces] user@R2# set fe-1/2/0 unit 2 family inet address 10.0.0.2/30 user@R2# set fe-1/2/1 unit 5 family inet address 10.0.0.5/30 user@R2# set lo0 unit 2 family inet address 192.168.2.2/32 user@R2# set lo0 unit 2 family inet address 172.16.2.2/32
Configure different update intervals for the two RIP neighbors.
To configure RIP in Junos OS, you must configure a group that contains the interfaces on which RIP is enabled. You do not need to enable RIP on the loopback interface.
[edit protocols rip group rip-group] user@R2# set neighbor fe-1/2/0.2 update-interval 60 user@R2# set neighbor fe-1/2/1.5 update-interval 10
Create the routing policy to advertise both direct and RIP-learned routes.
[edit policy-options policy-statement advertise-routes-through-rip term 1] user@R2# set from protocol direct user@R2# set from protocol rip user@R2# set then accept
Apply the routing policy.
In Junos OS, you can only apply RIP export policies at the group level.
[edit protocols rip group rip-group] user@R2# set export advertise-routes-through-rip
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show interfaces, show protocols, and show policy-options commands. If the output does
not display the intended configuration, repeat the configuration instructions
in this example to correct it.
user@R2# show interfaces
fe-1/2/0 {
unit 2 {
family inet {
address 10.0.0.2/30;
}
}
}
fe-1/2/1 {
unit 5 {
family inet {
address 10.0.0.5/30;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 2 {
family inet {
address 192.168.2.2/32;
address 172.16.2.2/32;
}
}
}
user@R2# show protocols
rip {
group rip-group {
export advertise-routes-through-rip;
neighbor fe-1/2/0.2 {
update-interval 60;
}
neighbor fe-1/2/1.5 {
update-interval 10;
}
}
}
user@R2# show policy-options
policy-statement advertise-routes-through-rip {
term 1 {
from protocol [ direct rip ];
then accept;
}
}
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Verification
Confirm that the configuration is working properly.
- Checking the RIP Updates Sent by Device R2
- Checking the RIP Updates Received by Device R2
- Checking the RIP Updates Received by Device R3
Checking the RIP Updates Sent by Device R2
Purpose
Make sure that the RIP update packets are sent at the expected interval.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show rip statistics command.
user@R2> show rip statistics
RIPv2 info: port 520; holddown 120s.
rts learned rts held down rqsts dropped resps dropped
4 2 0 0
fe-1/2/0.2: 2 routes learned; 5 routes advertised; timeout 180s; update interval 60s
Counter Total Last 5 min Last minute
------- ----------- ----------- -----------
Updates Sent 123 5 1
Triggered Updates Sent 0 0 0
Responses Sent 0 0 0
Bad Messages 0 0 0
RIPv1 Updates Received 0 0 0
RIPv1 Bad Route Entries 0 0 0
RIPv1 Updates Ignored 0 0 0
RIPv2 Updates Received 244 10 2
RIPv2 Bad Route Entries 0 0 0
RIPv2 Updates Ignored 0 0 0
Authentication Failures 0 0 0
RIP Requests Received 0 0 0
RIP Requests Ignored 0 0 0
none 0 0 0
fe-1/2/1.5: 2 routes learned; 5 routes advertised; timeout 180s; update interval 10s
Counter Total Last 5 min Last minute
------- ----------- ----------- -----------
Updates Sent 734 32 6
Triggered Updates Sent 0 0 0
Responses Sent 0 0 0
Bad Messages 0 0 0
RIPv1 Updates Received 0 0 0
RIPv1 Bad Route Entries 0 0 0
RIPv1 Updates Ignored 0 0 0
RIPv2 Updates Received 245 11 2
RIPv2 Bad Route Entries 0 0 0
RIPv2 Updates Ignored 0 0 0
Authentication Failures 0 0 0
RIP Requests Received 0 0 0
RIP Requests Ignored 0 0 0
none 0 0 0Meaning
The update interval field shows that the interval is 60 seconds for Neighbor R1 and 10 seconds for Neighbor R3. The Updates Sent field shows that Device R2 is sending updates to Device R1 at roughly 1/6 of the rate that it is sending updates to Device R3.
Checking the RIP Updates Received by Device R2
Purpose
Make sure that the RIP update packets are sent at the expected interval.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show rip statistics command.
user@R1> show rip statistics
RIPv2 info: port 520; holddown 120s.
rts learned rts held down rqsts dropped resps dropped
5 0 0 0
fe-1/2/0.1: 5 routes learned; 2 routes advertised; timeout 180s; update interval 30s
Counter Total Last 5 min Last minute
------- ----------- ----------- -----------
Updates Sent 312 10 2
Triggered Updates Sent 2 0 0
Responses Sent 0 0 0
Bad Messages 0 0 0
RIPv1 Updates Received 0 0 0
RIPv1 Bad Route Entries 0 0 0
RIPv1 Updates Ignored 0 0 0
RIPv2 Updates Received 181 5 1
RIPv2 Bad Route Entries 0 0 0
RIPv2 Updates Ignored 0 0 0
Authentication Failures 0 0 0
RIP Requests Received 1 0 0
RIP Requests Ignored 0 0 0
none 0 0 0Meaning
The RIPv2 Updates Received field shows the number of updates received from Device R2.
Checking the RIP Updates Received by Device R3
Purpose
Make sure that the RIP update packets are sent at the expected interval.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show rip statistics command.
user@R3> show rip statistics
RIPv2 info: port 520; holddown 120s.
rts learned rts held down rqsts dropped resps dropped
5 0 0 0
fe-1/2/0.6: 5 routes learned; 2 routes advertised; timeout 180s; update interval 30s
Counter Total Last 5 min Last minute
------- ----------- ----------- -----------
Updates Sent 314 11 2
Triggered Updates Sent 1 0 0
Responses Sent 0 0 0
Bad Messages 0 0 0
RIPv1 Updates Received 0 0 0
RIPv1 Bad Route Entries 0 0 0
RIPv1 Updates Ignored 0 0 0
RIPv2 Updates Received 827 31 6
RIPv2 Bad Route Entries 0 0 0
RIPv2 Updates Ignored 0 0 0
Authentication Failures 0 0 0
RIP Requests Received 0 0 0
RIP Requests Ignored 0 0 0
none 0 0 0
Meaning
The RIPv2 Updates Received field shows the number of updates received from Device R2.
Change History Table
Feature support is determined by the platform and release you are using. Use Feature Explorer to determine if a feature is supported on your platform.
