Example: Configuring a Routing Policy for AS Path Prepending
This example shows how to configure a routing policy to prepend the AS path on specific routes advertised by BGP.
Requirements
Before you begin, make sure your router interfaces and protocols are correctly configured. We provide the interface and BGP protocol configuration used in this document.
This example was updated and re-validated on Junos release 22.1R1.
Overview
In this example, you create a routing policy called prependpolicy1 and a term called prependterm1. The routing policy prepends AS number 65001 three times to routes that match the 172.16.0.0/12, 192.168.0.0/16, and 10.0.0.0/8 prefixes, when the mask length is equal to or longer than the specified mask. The result is a match occurs when the route's mask length is equal to or longer than the specified network mask. The prependpolicy1 policy is applied as an export policy to the BGP routes advertised by R1 in AS 65001 to R2 in AS number 65000. Routes that don't match the specified prefix ranges do not undergo AS path prepending.
Topology
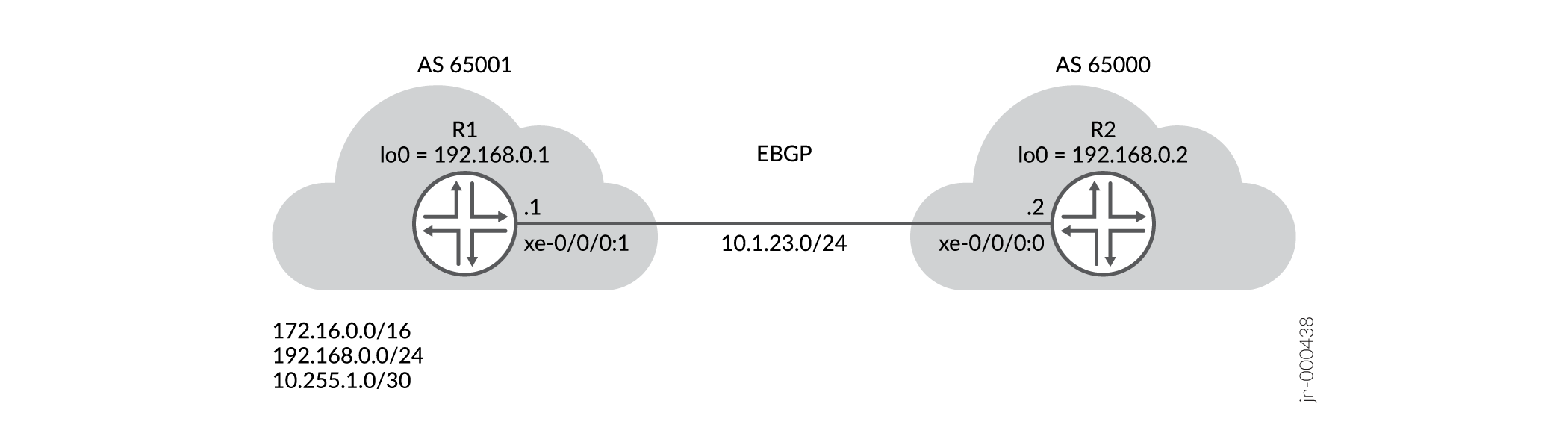
In the topology EBGP peering is configured between R1 and R2. Direct interface peering to the 10.1.23.0/24 subnet addresses is used. R1 belongs to AS number 65001 and is configured to prepend its AS number to a specific set of matching routes when advertised to R2.
By adding AS numbers to the AS path the route becomes less likely to be selected for forwarding. This might be done by the owner of AS 65001 to reduce the amount of ingress traffic it receives from the operator of AS 65000.
In this example we demonstrate AS path prepending through an export policy. You can also use an import policy to match on routes for attribute manipulation. In general its a best practice to only prepend your local AS number to routes. Prepending AS numbers that belong to remote networks can lead to unexpected results.
For details on BGP paths selection see Understanding BGP Path Selection.
Configuration
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
In this section we focus on the configuration of the R1 device. Refer to the appendix for the complete configurations of all devices used in this example.
To quickly configure this example, copy the following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks, change any details necessary to match your network configuration, and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
In this example we assign three test prefixes to an unused interface on R1. A
fourth test prefix is assigned to R1's loopback address. This provides four
direct routes that can be advertised into BGP. Our policy uses a combination
of protocol direct and route-filter
statements to control which prefixes undergo AS path prepending.
set system host-name R1 set interfaces xe-0/0/0:1 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.23.1/24 set interfaces xe-0/0/0:0 unit 0 family inet address 10.255.1.1/30 set interfaces xe-0/0/0:0 unit 0 family inet address 172.16.0.1/24 set interfaces xe-0/0/0:0 unit 0 family inet address 10.200.1.1/24 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.1/32 set policy-options policy-statement prependpolicy1 term prependterm1 from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement prependpolicy1 term prependterm1 from route-filter 172.16.0.0/16 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement prependpolicy1 term prependterm1 from route-filter 192.168.0.0/24 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement prependpolicy1 term prependterm1 from route-filter 10.255.1.0/24 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement prependpolicy1 term prependterm1 then as-path-prepend "65001 65001 65001" set policy-options policy-statement prependpolicy1 term prependterm1 then accept set policy-options policy-statement prependpolicy1 term else from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement prependpolicy1 term else from route-filter 10.200.0.0/16 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement prependpolicy1 term else then accept set routing-options autonomous-system 65001 set routing-options router-id 192.168.0.1 set protocols bgp group ebgp type external set protocols bgp group ebgp export prependpolicy1 set protocols bgp group ebgp peer-as 65000 set protocols bgp group ebgp neighbor 10.1.23.2
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following steps requires you to navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For instructions on how to do that, see Use the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode in the Junos OS CLI User Guide.
To create a routing policy that prepends AS numbers to specific routes:
-
Configure the peering and loopback interfaces.
user@R1# [edit] set interfaces xe-0/0/0:1 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.23.1/24 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.1/32
-
Configure the AS number, RID, and the external BGP peer group. You define the prependpolicy1 policy in the next step. The policy is applied as an export policy to affect the routes advertised by R1.
user@R1# [edit] set routing-options autonomous-system 65001 set routing-options router-id 192.168.0.1 set protocols bgp group ebgp type external set protocols bgp group ebgp export prependpolicy1 set protocols bgp group ebgp peer-as 65000 set protocols bgp group ebgp neighbor 10.1.23.2
-
Configure the prependpolicy1 policy. The use of
or-longerswitch to the route filter statements allows a match when the mask length is equal to or longer than the specified mask. Other options likeexactmatch only when the prefix and mask lengths are equal. The else term demonstrates how a route that does not match the prependterm1 term is advertised without AS path prepending by matching the else term.user@R1# [edit] set policy-options policy-statement prependpolicy1 term prependterm1 from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement prependpolicy1 term prependterm1 from route-filter 172.16.0.0/16 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement prependpolicy1 term prependterm1 from route-filter 192.168.0.0/24 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement prependpolicy1 term prependterm1 from route-filter 10.255.1.0/24 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement prependpolicy1 term prependterm1 then as-path-prepend "65001 65001 65001" set policy-options policy-statement prependpolicy1 term prependterm1 then accept set policy-options policy-statement prependpolicy1 term else from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement prependpolicy1 term else from route-filter 10.200.0.0/16 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement prependpolicy1 term else then accept
Note:When you enter multiple AS numbers, you must separate each number with a space. Enclose the string of AS numbers in double quotation marks.
-
Define test routes. In our sample topology we assign prefixes to an unused interface that is operationally up. This provides direct routes for BGP to advertise for testing the operation of the export policy.
user@R1# [edit] set interfaces xe-0/0/0:0 unit 0 family inet address 10.255.1.1/30 set interfaces xe-0/0/0:0 unit 0 family inet address 172.16.0.1/24 set interfaces xe-0/0/0:0 unit 0 family inet address 10.200.1.1/24
Results
Confirm your configuration by entering the show policy-options, show protocols bgp, show routing-options, and show interfaces commands from configuration mode. If the output does not display the intended configuration, repeat the configuration instructions in this example to correct it.
user@R1#[edit]
user@R1# show policy-options
policy-statement prependpolicy1 {
term prependterm1 {
from {
protocol direct;
route-filter 172.16.0.0/16 orlonger;
route-filter 192.168.0.0/24 orlonger;
route-filter 10.255.1.0/24 orlonger;
}
then {
as-path-prepend "65001 65001 65001";
accept;
}
}
term else {
from {
protocol direct;
route-filter 10.200.0.0/16 orlonger;
}
then accept;
}
}
[edit]
user@R1# show protocols bgp
group ebgp {
type external;
export direct;
peer-as 65000;
neighbor 10.1.23.2;
}
[edit]
user@R1# show routing-options
autonomous-system 65001;
router-id 192.168.0.1
user@R1# show interfaces xe-0/0/0:0
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.255.1.1/30;
address 172.16.0.1/24;
address 10.200.1.1/24;
}
}
[edit]
user@R1# show interfaces xe-0/0/0:1
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.1.23.1/24;
}
}
[edit]
user@R1# show interfaces lo0
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.168.0.1/32;
}
}If you are done configuring the R1 device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Verification
To confirm that the configuration is working properly, perform these tasks:
- Verifying the AS Prepending Policy
- Verifying Routing Policy Application and BGP Peering
- Verify AS Path Prepending
Verifying the AS Prepending Policy
Purpose
Verify that the policy is configured on the device, and that the appropriate routes are specified to prepend with AS numbers.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show policy prependpolicy1 command.
user@R1> show policy prependpolicy1
Policy prependpolicy1: [CHANGED/RESOLVED/]
Term prependterm1:
from proto Direct
route filter:
172.16.0.0/16 orlonger
192.168.0.0/24 orlonger
10.255.1.0/24 orlonger
then aspathprepend 65001 65001 65001 accept
Term else:
from proto Direct
route filter:
10.200.0.0/16 orlonger
then accept
The policy displays the correct match conditions and actions.
Verifying Routing Policy Application and BGP Peering
Purpose
Verify the routing policy is applied as an export policy to the EBGP peer group. This step also confirms the BGP session to R2 is correctly established.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show bgp neighbor 10.1.23.2 command.
user@R1> show bgp neighbor 10.1.23.2 Peer: 10.1.23.2+49642 AS 65000 Local: 10.1.23.1+179 AS 65001 Group: ebgp Routing-Instance: master Forwarding routing-instance: master Type: External State: Established Flags: <Sync> Last State: OpenConfirm Last Event: RecvKeepAlive Last Error: None Export: [ prependpolicy1 ] Options: <PeerAS Refresh> Options: <GracefulShutdownRcv> Holdtime: 90 Preference: 170 Graceful Shutdown Receiver local-preference: 0 Number of flaps: 1 Last flap event: RecvNotify Error: 'Cease' Sent: 0 Recv: 1 Peer ID: 192.168.0.2 Local ID: 192.168.0.1 Active Holdtime: 90 . . . Input messages: Total 2498 Updates 1 Refreshes 0 Octets 47510 Output messages: Total 2500 Updates 3 Refreshes 0 Octets 47620 Output Queue[1]: 0 (inet.0, inet-unicast)
The command output confirms the BGP session is established and that R1 has applied the prependpolicy1 policy as export.
Verify AS Path Prepending
Purpose
Verify the export policy works as design to prepend AS numbers to matching routes.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show route protocol bgp command on R2. Alternatively, use the show route advertising-protocol bgp 10.1.23.2 at R1 to display details about the routes it advertises to R2.
user@R2> show route protocol bgp
inet.0: 14 destinations, 14 routes (14 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
10.200.1.0/24 *[BGP/170] 00:04:46, localpref 100
AS path: 65001 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.1.23.1 via xe-0/0/0:0.0
10.255.1.0/30 *[BGP/170] 00:04:46, localpref 100
AS path: 65001 65001 65001 65001 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.1.23.1 via xe-0/0/0:0.0
172.16.0.0/24 *[BGP/170] 00:04:46, localpref 100
AS path: 65001 65001 65001 65001 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.1.23.1 via xe-0/0/0:0.0
192.168.0.1/32 *[BGP/170] 00:04:46, localpref 100
AS path: 65001 65001 65001 65001 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 10.1.23.1 via xe-0/0/0:0.0
The routes show the expected AS path prepending. Note that the 10.200.1.0/24 route only has one instance of AS number 65001. This route does not match the route filter statements in the prependterm1 of the prependpolicy1 policy and so does not undergo any prepending.
R1's view of the BGP routes it advertises to R2 is provided for completeness:
user@R1> show route advertising-protocol bgp 10.1.23.2
inet.0: 16 destinations, 16 routes (16 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
Prefix Nexthop MED Lclpref AS path
* 10.200.1.0/24 Self I
* 10.255.1.0/30 Self 65001 65001 65001 [65001] I
* 172.16.0.0/24 Self 65001 65001 65001 [65001] I
* 192.168.0.1/32 Self 65001 65001 65001 [65001] IAppendix Full Configurations
The full configuration for R1.
set system host-name R1 set interfaces xe-0/0/0:0 unit 0 family inet address 10.255.1.1/30 set interfaces xe-0/0/0:0 unit 0 family inet address 172.16.0.1/24 set interfaces xe-0/0/0:0 unit 0 family inet address 10.200.1.1/24 set interfaces xe-0/0/0:1 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.23.1/24 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.1/32 set policy-options policy-statement prependpolicy1 term prependterm1 from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement prependpolicy1 term prependterm1 from route-filter 172.16.0.0/16 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement prependpolicy1 term prependterm1 from route-filter 192.168.0.0/24 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement prependpolicy1 term prependterm1 from route-filter 10.255.1.0/24 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement prependpolicy1 term prependterm1 then as-path-prepend "65001 65001 65001" set policy-options policy-statement prependpolicy1 term prependterm1 then accept set policy-options policy-statement prependpolicy1 term else from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement prependpolicy1 term else from route-filter 10.200.0.0/16 orlonger set policy-options policy-statement prependpolicy1 term else then accept set routing-options router-id 192.168.0.1 set routing-options autonomous-system 65001 set protocols bgp group ebgp type external set protocols bgp group ebgp export prependpolicy1 set protocols bgp group ebgp peer-as 65000 set protocols bgp group ebgp neighbor 10.1.23.2
The full configuration for R2.
set system host-name R2 set interfaces xe-0/0/0:0 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.23.2/24 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.2/32 set routing-options router-id 192.168.0.2 set routing-options autonomous-system 65000 set protocols bgp group ebgp type external set protocols bgp group ebgp peer-as 65001 set protocols bgp group ebgp neighbor 10.1.23.1
