Validation Framework
Test Bed Topology
In this JVD, two physical topologies are leveraged for standalone (Figure 1) and redundant configurations (Figure 2) are able to address all four deployment scenarios as described in Supported Platforms. As mentioned in the configuration example section, some key elements need to be put in place, like a consistent network IP address scheme, the BGP peering between the MX Series Router, the external Gateway (if any), and with each SRX/vSRX Series Firewalls.
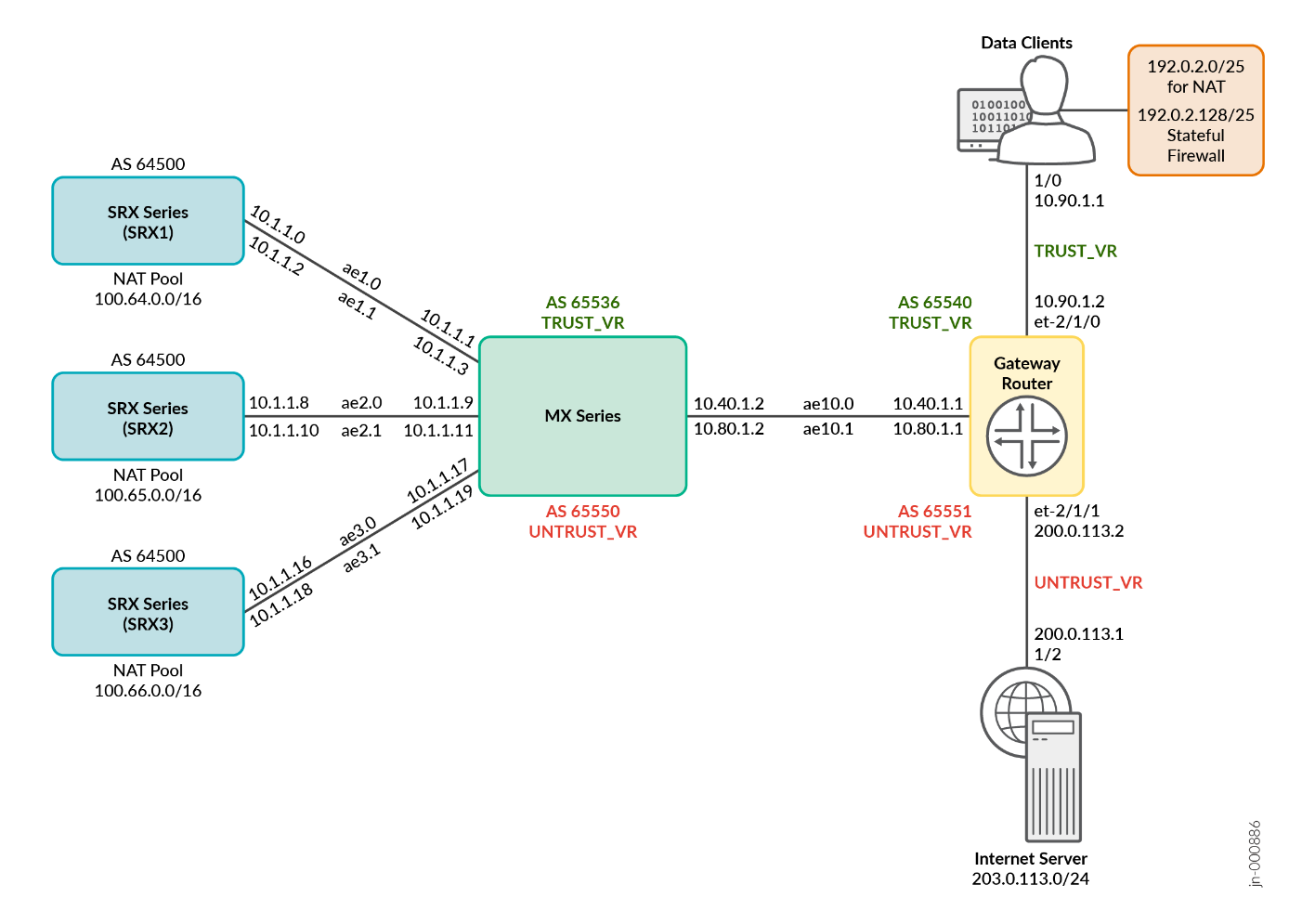
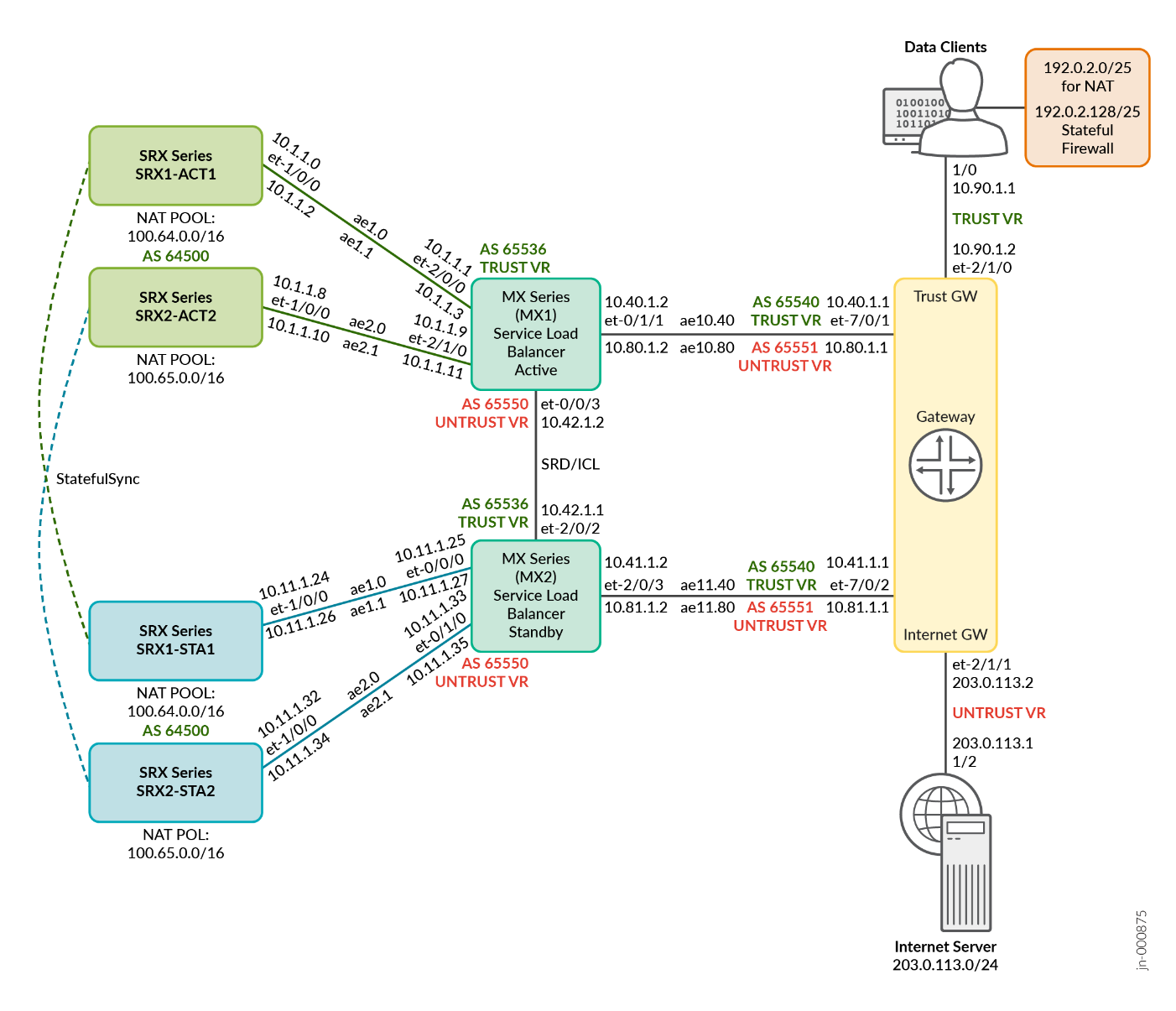
Supported Platforms
To review the software versions and platforms on which this JVD was validated by Juniper Networks, see the Validated Platforms and Software section in this document.
Tested Optics
The Fiber optic transceivers used in that test bed are:
- QSFP-100GBASE-SR4: between MX304 and SRX4600s
- QSFP28-100G-AOC-3M: between MX304 and servers hosting vSRXs
This JVD has been validated with the fiber optics reference above, but the technical validation is larger regarding hardware compatible optics, see those refs on Juniper’s Hardware Compatibility Tool.
- For SRX4600: https://apps.juniper.net/hct/product/?prd=SRX4600
- For MX304: https://apps.juniper.net/hct/product/?prd=MX304
- For MX10004: https://apps.juniper.net/hct/product/?prd=MX10004
vSRX Setup and Sizing
This JVD focuses only on the functional aspect of the solution. It does not matter whether powerful servers are tested for hosting the vSRX(s), as well as the size of vSRX used here. For real time performances, high end servers (like Dell or HPE servers with Intel Gold or AMK 9K CPUs, 256GB RAM and ConnectX6 or X7 or later interfaces) with large vSRX sizes are proposed (like 16 vCPU and 32GB RAM). For more information about vSRX requirements, see Juniper documentation:
or
