Implementing Threat Policy on VMWare NSX
VMWare NSX Integration with Policy Enforcer and Juniper ATP Cloud Overview
Juniper Networks Advanced Threat Prevention Cloud (Juniper ATP Cloud) identifies the infected virtual machines (VMs) running on VMWare NSX and tags these VMs as infected. This is based on a malware file exchange from the infected VMs and/or based on the Command and Control communication with known botnet sites on the internet.
Based on this identification of infected or compromised hosts, you can take one of the following actions:
-
Enable additional security features such as Layer-7 Application Firewall and Intrusion Prevention (IPS) leveraging vSRX
-
Enforce Layer-2 to Layer-4 controls using NSX Distributed Firewall
-
Leverage NSX integration with Host-Based security vendors (https://www.vmware.com/products/nsx/technology-partners.html) to take host-based security actions such as running antivirus or anti malware features on the infected VMs.
Policy Enforcer provides a set of Connector APIs for the third-party adaptors. The NSX Connector integrates with the Policy Enforcer using these APIs to enable enforcement of the infected hosts policy on Secure Fabric. For NSX connectors, the NSX Manager , its associated vCenter, and an edge firewall form the Secure Fabric.
The following topology shows how NSX Manager and the edge firewall create a Secure Fabric to use with Policy Enforcer.
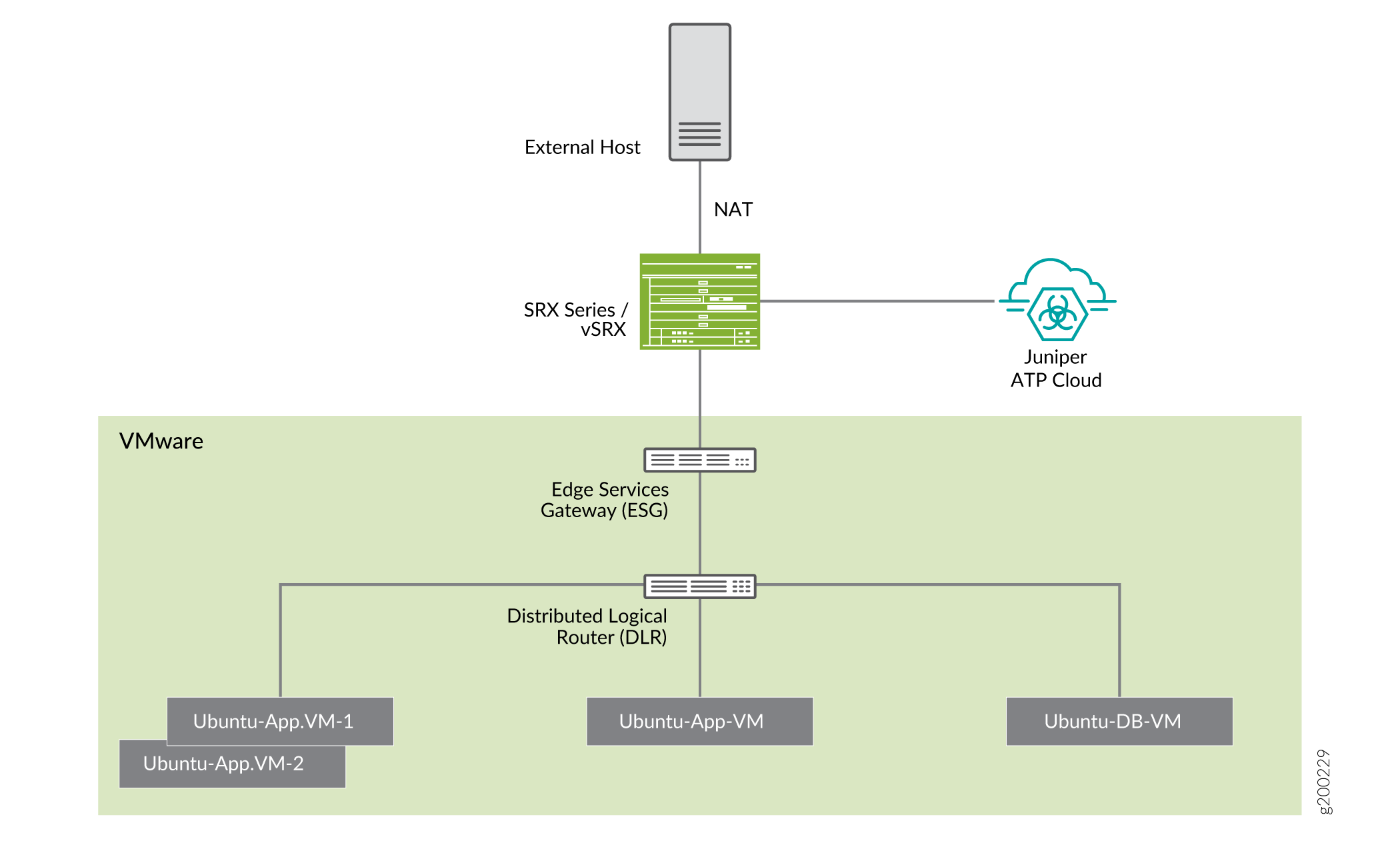
Within the NSX Manager, the virtual machines (VM) connect to logical networks, shown as green and yellow colour logical networks, as shown in Figure 1. The logical switches connect to each other using a Distributed Logical Router(DLR). To form the Secure Fabric, configure the edge service gateway (ESG) to point to SRX Series devices or vSRX as the gateway for the networks hosted on NSX. This is implemented by establishing IBGP session between ESG and vSRX or SRX Series device. This ensures that all the north-south traffic passes through the vSRX edge firewall. The vSRX edge gateway is enrolled with Juniper ATP Cloud for the traffic inspection.
If NAT services are required, it must be configured on the vSRX and not on the ESG. Configure NAT services using the following CLI commands.
set security nat source rule-set trust-to-untrust from
zone trust
set security nat source rule-set trust-to-untrust to zone
untrust
set security nat source rule-set trust-to-untrust rule
snat-rule match source-address 0.0.0.0/0
set security nat source rule-set trust-to-untrust rule
snat-rule then source-nat interface
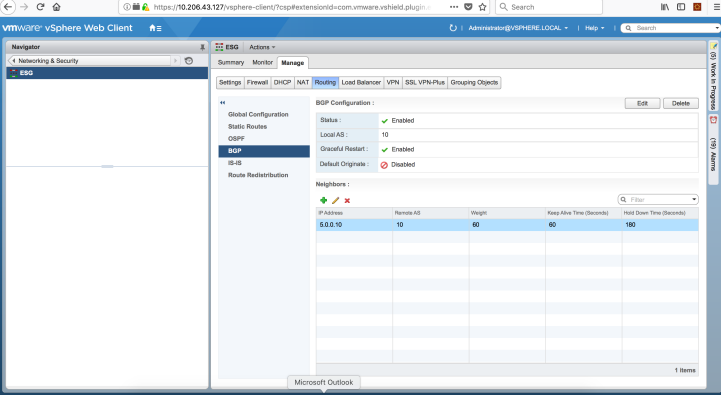
To establish a BGP session, use the following configuration commands:
set routing-options autonomous-system 10
set protocols bgp group nsx neighbor 5.0.0.2 peer-as 10
You can view the BGP configuration in VMWare vCenter Server, as shown in Figure 2.
You can register the NSX Manager with Security Director only when the Policy Enforcer is configured. The NSX micro service is bundled with the Policy Enforcer VM. However, the NSX micro service is packaged as a standalone rpm, so that the NSX micro service upgrade and patches can be performed independent of the Policy Enforcer VM.
- Implementation of Infected Hosts Policy Overview for VMware NSX
- Registering NSX Micro Service as Policy Enforcer Connector Instance Overview
Implementation of Infected Hosts Policy Overview for VMware NSX
The vSRX or SRX Series devices running as an edge firewall is enrolled to send all the suspected traffic to Juniper ATP Cloud.
The following steps explain the high-level workflow:
-
If an infection is detected, Juniper ATP Cloud notifies the Policy Enforcer about the infected IP addresses
-
If the infected IP address belongs to Secure Fabric associated with the NSX domain, Policy Enforcer calls the NSX plugin APIs to notify the NSX Connector about the list of infected IP addresses
-
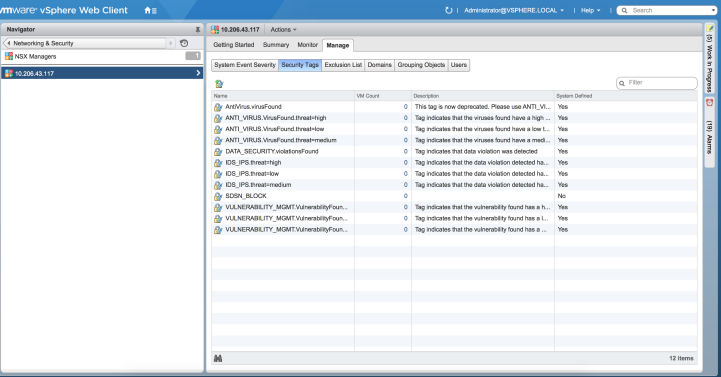
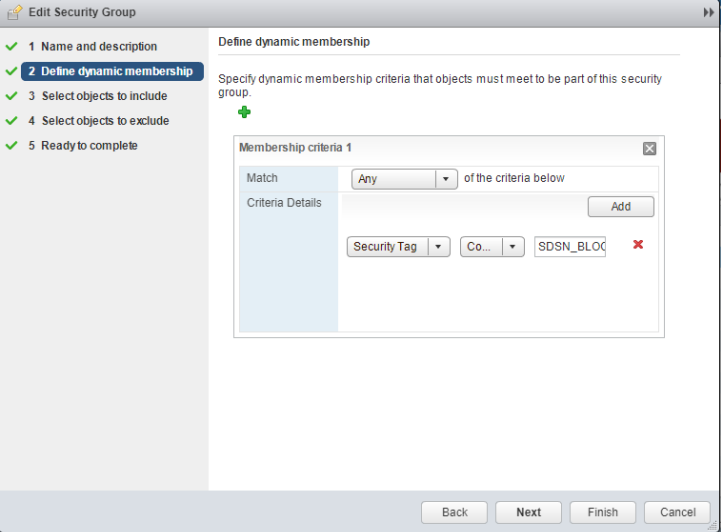
NSX service will then retrieve the VM corresponding to the IP addresses sent and then calls the NSX API to tag to an appropriate VM with a security tag, SDSN_BLOCK.
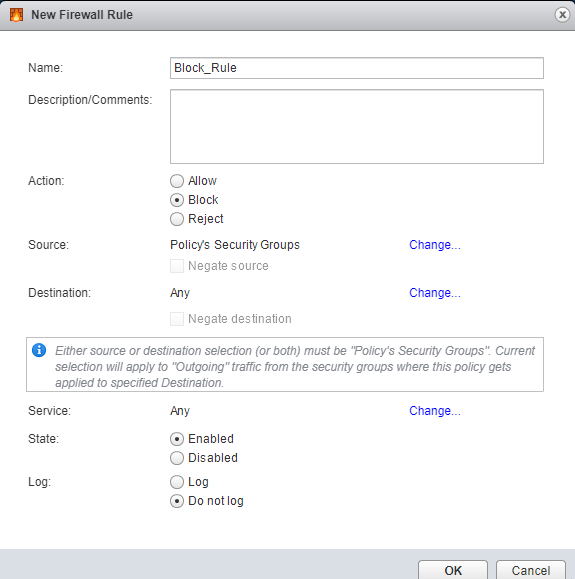
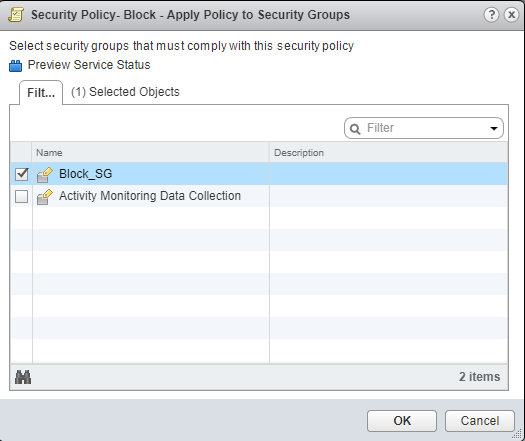
You can then create a policy to block the infected hosts using the SDSN_BLOCK tag by creating VMWare Distributed Firewall (DFW) rules. The block policy consists of two rules for ingress block and egress block. The ingress block rule applies to any traffic originating from a security group composed of VMs tagged with a block tag to any destination. Similarly, the egress block rule applies to any traffic destined to security group composed of VMs tagged with block tag from any source.
The creation of security groups associated with the SDSN_BLOCK tag, creation of ingress and egress block rules, and the action to take on the matching packets must be configured by the VMWare administrators. The NSX Connector will simply apply the SDSN_BLOCK tag on the infected VM.
Registering NSX Micro Service as Policy Enforcer Connector Instance Overview
The integration of each NSX manager discovered in Security Director with Policy Enforcer is triggered automatically.
The automatic registration of a connector instance involves the following steps:
-
Discovering the NSX Manager in Security Director. This triggers an auto creation of the Policy Enforcer connector instance.
-
Secure Fabric is created to manage the discovered NSX Manager.
-
Creation of threat prevention policy requires the knowledge of Juniper ATP Cloud realm and the edge firewall device. These are taken as inputs from the user.
Before You Begin
Before you begin to configure NSX with Policy Enforcer, configure the infected hosts workflow in VMWare vCenter Server.
Infected Hosts Workflow in VMware vCenter Server
To block the infected hosts:
Configuring VMware NSX with Policy Enforcer
The following steps explain configuring VMWare NSX with Policy Enforcer:
Example: Creating a Firewall Rule in VMWare vCenter Server Using SDSN_BLOCK Tag
The following example shows the firewall rule creation using the SDSN_BLOCK security tag: