Disaster Recovery Overview
Disaster recovery is the deployment of Paragon Automation cluster at two different geographical locations. Disaster recovery ensures that when the Paragon Pathfinder component in one Paragon Automation deployment goes down, Paragon Pathfinder service is are available from the Paragon Pathfinder component in the second Paragon Automation deployment.
In a disaster recovery setup, you must independently configure network discovery (for example, BGP-LS, PCEP, and analytic streaming) and independently perform tasks such as discovering devices and configuring playbooks, on both the Paragon Automation deployments.
A federated exchange configured on the messaging bus synchronizes the two deployments for:
-
Topology-related changes (changes related to addition, modification and deletion of nodes, links, and LSPs)
-
LSP optimization
-
Resetting the topology
-
Adding or removing LSP delegation
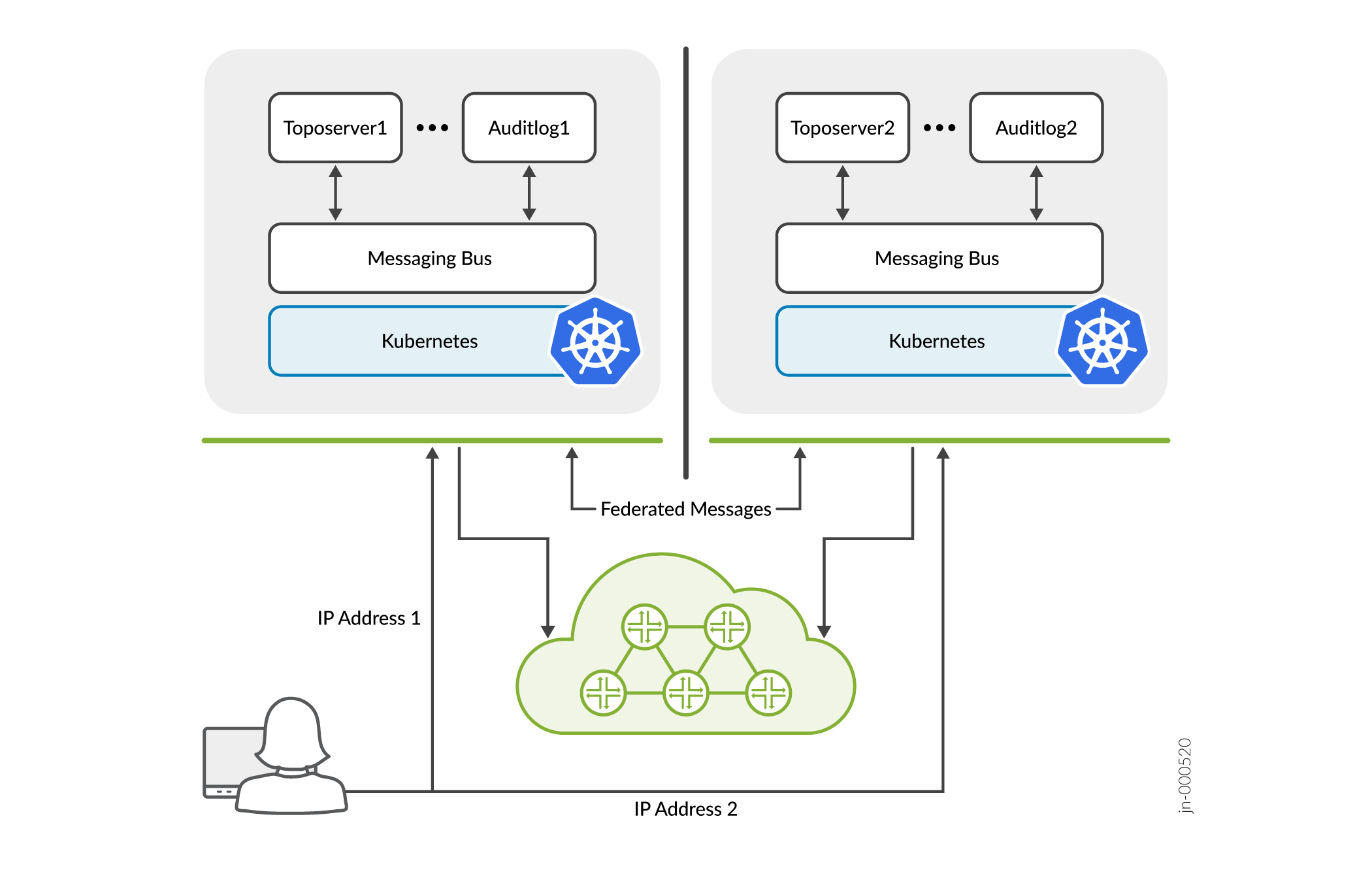
The topology servers in the deployments send beacons over a federated exchange which help in detecting failure of either of the deployments and avoid unsynchronized changes. By default, the topology servers send beacons once every 5 seconds.
- You can provision or modify only path computation client (PCC)-delegated LSPs in a disaster recovery setup. Provisioning or modification of PCC-controlled LSPs and path computation element (PCE)-initiated LSPs is not supported .
-
NETCONF is not supported in a disaster recovery setup.
-
You must run device collection task for delegated LSPs to appear correctly on both the deployments. Otherwise, the LSP appears as PCC-controlled in the deployment without the delegation bit and modifying the LSP from the deployment without the delegation bit results in an error.
For a disaster recovery setup, you must configure the following flags in the Pathfinder Settings (Configuration > Network Settings > Pathfinder Settings):
-
source-of-truth (optional)
-
use-federated-exchange (mandatory)
-
toposerver-beacon-interval (optional)
-
sync-topology-after-failure (optional)
For information on configuring the Pathfinder settings, see Modify Pathfinder Settings From the GUI.
Fig shows the disaster recovery architecture, where Paragon Pathfinder is deployed at two different geographical locations to manage the same network. Both the sites have active BGP Link State (BGP-LS), Path Computation Element Protocol (PCEP), BGP Monitoring Protocol (BMP), and SSH sessions to the network. The deployments communicate with the network through a federated exchange. Both the deployments are in active-active state and synchronize changes within a few seconds. For information on configuring disaster recovery, see Configure Disaster Recovery for Paragon Pathfinder.
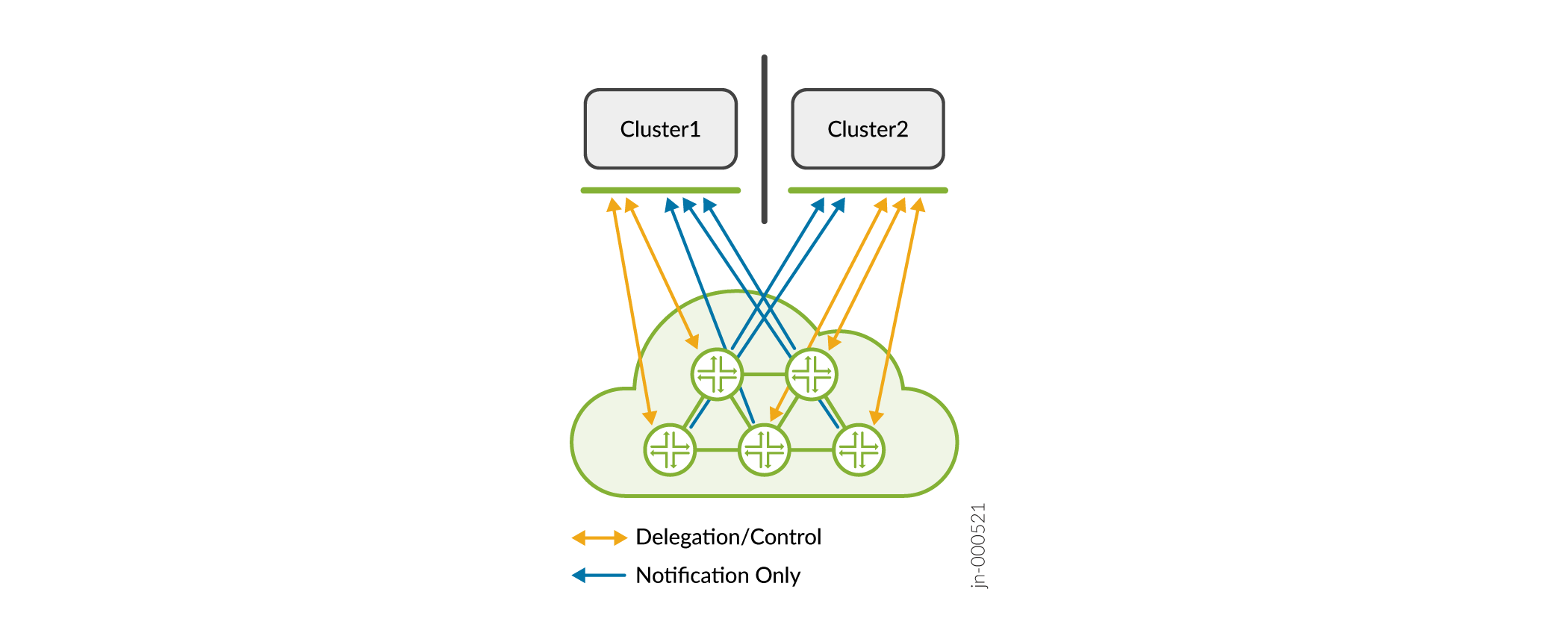
In a disaster recovery setup, we recommend that you specify one of the deployments as the
primary deployment by configuring the delegation priority for the path
computation element (PCE). All delegated LSPs send their delegation bit to the PCE in the
primary deployment. To configure delegation priority for a PCE, see delegation-priority.
Figure shows the PCEP connectivity between the Paragon Pathfinder deployments (clusters) at two different locations and the network. The LSPs are delegated to either cluster 1 or cluster 2. Notifications related to the LSPs are reported to both the clusters.
Failure Scenarios
The following failure scenarios are possible:
-
The primary deployment fails and PCC sends delegation bit to the PCE in the secondary deployment.
When the primary deployment fails, the topology server in the secondary deployment goes into safe mode preventing input of any change related to topology. This ensures that the topology information in the deployments does not go out of synchronization. A notification indicating that the Paragon Pathfinder component is in safe mode is displayed at the top of the Topology page (Network > Topology).
If you want to make changes while the primary deployment is down and not sending a beacon, enable the source-of-truth flag in Paragon Pathfinder settings (Configuration > Network Settings > Pathfinder Settings) on the secondary deployment. See Modify Pathfinder Settings From the GUI for details. After you bring the primary deployment up, disable the source-of-truth flag on the primary deployment (if enabled) so that the primary deployment synchronizes with the secondary deployment to obtain all changes that were made through the secondary deployment. After the synchronization, we recommend that you disable the source-of-truth flag on the secondary deployment.
-
Federated exchange fails.
The federated exchange transfers messages between the individual deployments. If the federated exchange fails, Paragon Pathfinder component goes into safe mode. A notification indicating that the Paragon Pathfinder component is in safe mode is displayed at the top of the Topology page (Network > Topology). To check if the federated exchange is up or not, execute the following command on any deployment:
root@davinci-master-c1:~# kubectl exec -it -n northstar rabbitmq-0 -- rabbitmqctl list_parameters
An output in the below format indicates that the federated exchange is up.
Listing runtime parameters for vhost "/" ... component name value federation-upstream my-upstream {"expires":30000,"uri":"amqps://northstar:6rchz9eHGy@10.52.33.97?cacertfile=/opt/bitnami/rabbitmq/certs/ca_certificate.pem&verify=verify_none"}If the federated exchange fails, you must troubleshoot and bring the federated exchange up to manage the network.
After you bring the federated exchange up, the topology servers at the primary deployment and the secondary deployment synchronize any changes to the topology.
