VPN Monitoring and Diagnostics
The VPN Module together with the Online Module provides you with VPN monitoring and diagnostics capabilities for a live router network.
This feature requires the Online Module.
This feature requires the Online Module. First you would need to perform network data collection using the Task Manager . Upon completion of network configuration collection, the program constructs the network model that includes all the configured VPNs in the network.
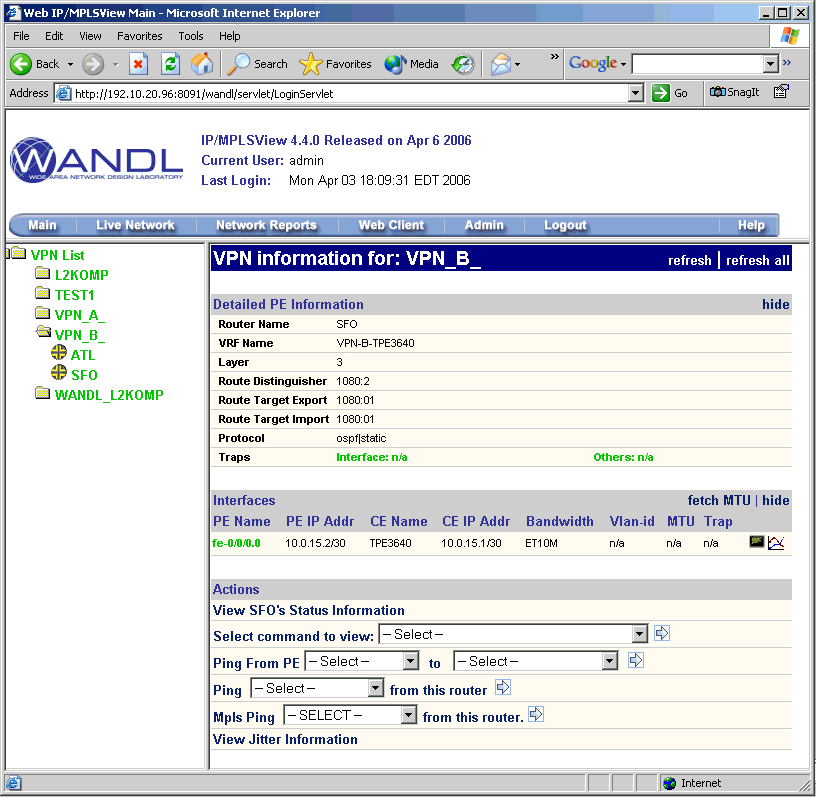
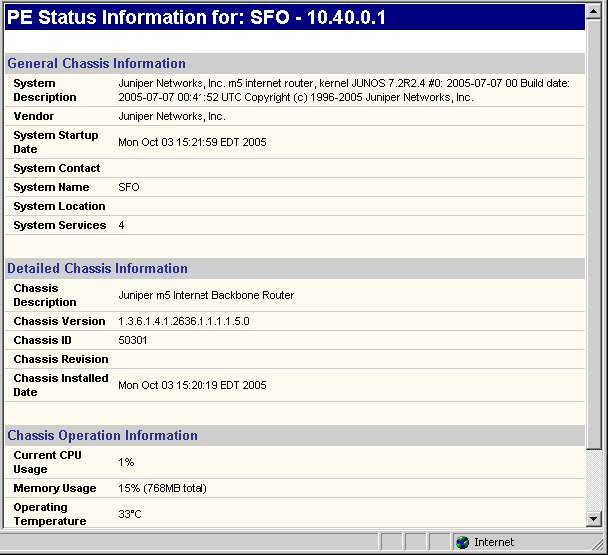
For a PE router, you may run “show” commands (accessible via the Run CLI... menu by right-clicking on a node in the topology map). Click the arrow next to the Commands list to select a VPN category to view the available CLI commands for VPNs.
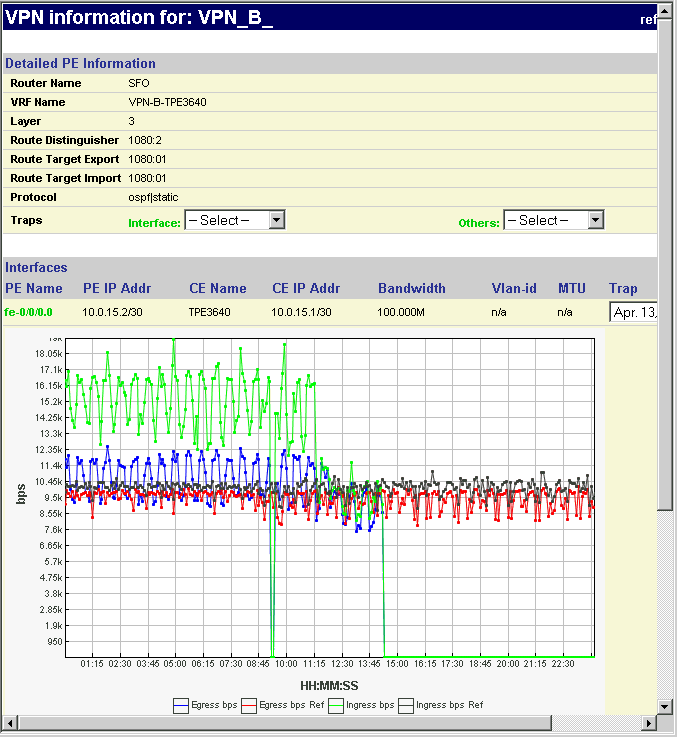
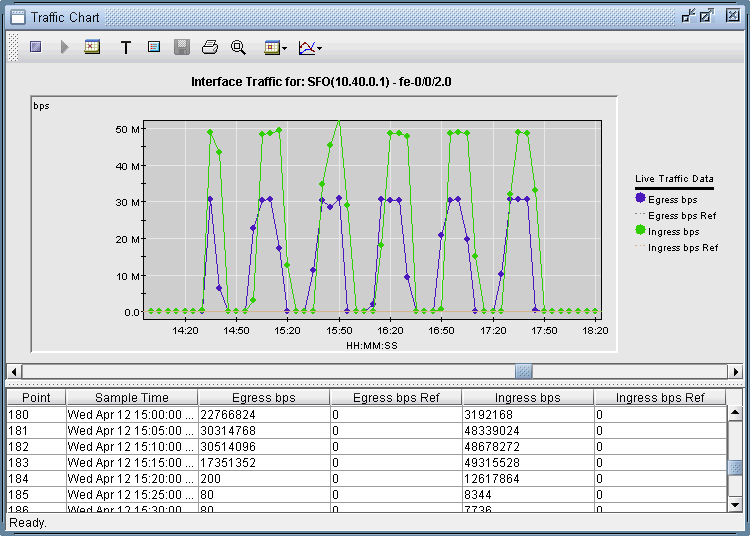
To observe the network traffic condition (e.g. between PE and CE), periodic sampling of interface traffic statistics is performed by the Task Manager. The collected interface data can then be accessed in the form or reports and charts. The following figure shows a PE->CE interface traffic chart for router SFO.
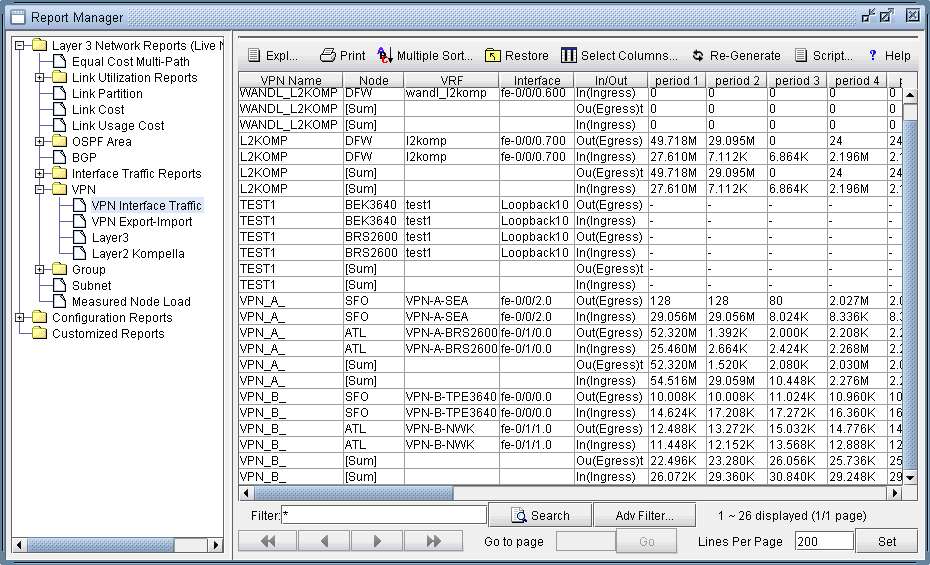
In the Report Manager, a VPN Interface Traffic report is available under Network Reports > VPN that lets you see the interface traffic for each node of each VPN, as shown in the following figure.
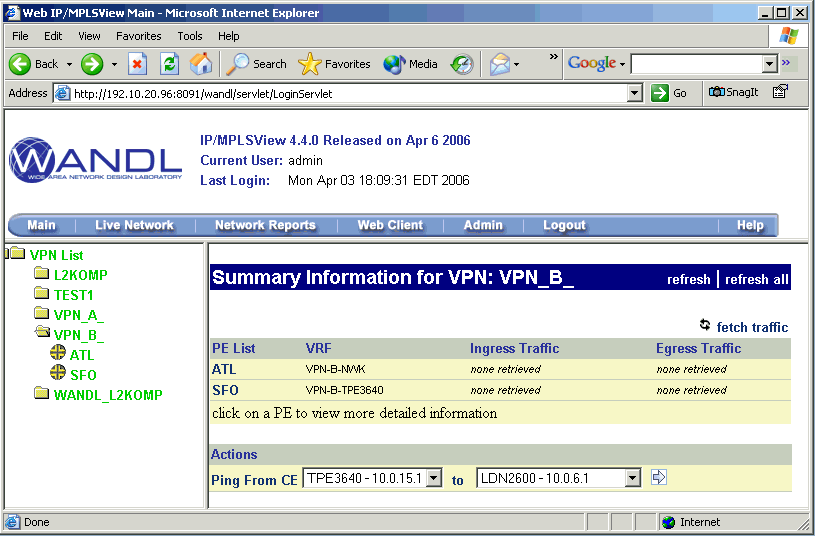
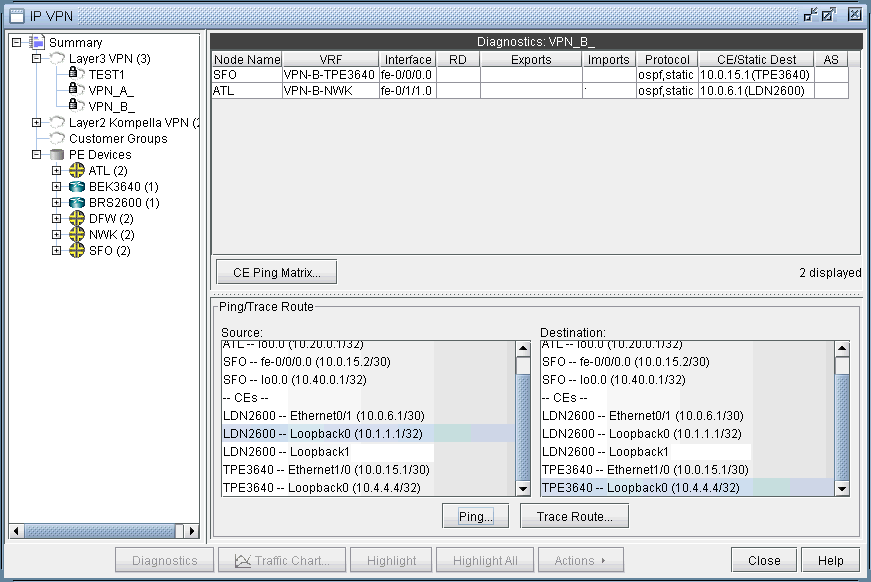
To verify connectivity and to measure delay and loss, you can also perform VPN diagnostics (e.g., CE-CE Ping and Traceroute) as shown in the following figures.
From the right-click menu of the VPNView topology, you can many functions (e.g. path tracing, running CLI commands, and connect to device).
With Java Web Start installed, you may also perform VPN monitoring and diagnostic functions from a web browser, as well as to access VPN-related reports and charts. The following figures are meant illustrate just some of the web features available.