Related Documentation
- EX, J, MX, T Series
- show ingress-replication mvpn
- M, MX, T Series
- Configuring Routing Instances for an MBGP MVPN
- mpls-internet-multicast
- ingress-replication
- create-new-ucast-tunnel
- M, MX, SRX, T Series
- label-switched-path-template
Example: Configuring Ingress Replication for IP Multicast Using MBGP MVPNs
Requirements
The routers used in this example are Juniper Networks M Series Multiservice Edge Routers, T Series Core Routers, or MX Series 3D Universal Edge Routers running Junos OS Release 10.4 or later. When using ingress replication for IP multicast, each participating router must be configured with BGP for control plane procedures and with ingress replication for the data provider tunnel, which forms a full mesh of MPLS point-to-point LSPs. The ingress replication tunnel can be selective or inclusive, depending on the configuration of the provider tunnel in the routing instance.
Overview
The ingress-replication provider tunnel type uses unicast tunnels between routers to create a multicast distribution tree.
The mpls-internet-multicast routing instance type uses ingress replication provider tunnels to carry IP multicast data between routers through an MPLS cloud, using MBGP (or Next Gen) MVPN. Ingress replication can also be configured when using MVPN to carry multicast data between PE routers.
The mpls-internet-multicast routing instance is a non-forwarding instance used only for control plane procedures. It does not support any interface configurations. Only one mpls-internet-multicast routing instance can be defined for a logical system. All multicast and unicast routes used for IP multicast are associated only with the default routing instance (inet.0), not with a configured routing instance. The mpls-internet-multicast routing instance type is configured for the default master instance on each router, and is also included at the [edit protocols pim] hierarchy level in the default instance.
For each mpls-internet-multicast routing instance, the ingress-replication statement is required under the provider-tunnel statement and also under the [edit routing-instances routing-instance-name provider-tunnel selective group source] hierarchy level.
When a new destination needs to be added to the ingress replication provider tunnel, the resulting behavior differs depending on how the ingress replication provider tunnel is configured:
- create-new-ucast-tunnel—When this statement is configured, a new unicast tunnel to the destination is created, and is deleted when the destination is no longer needed. Use this mode for RSVP LSPs using ingress replication.
- label-switched-path-template—When this statement is configured, an LSP template is used for the for the point-to-multipoint LSP for ingress replication.
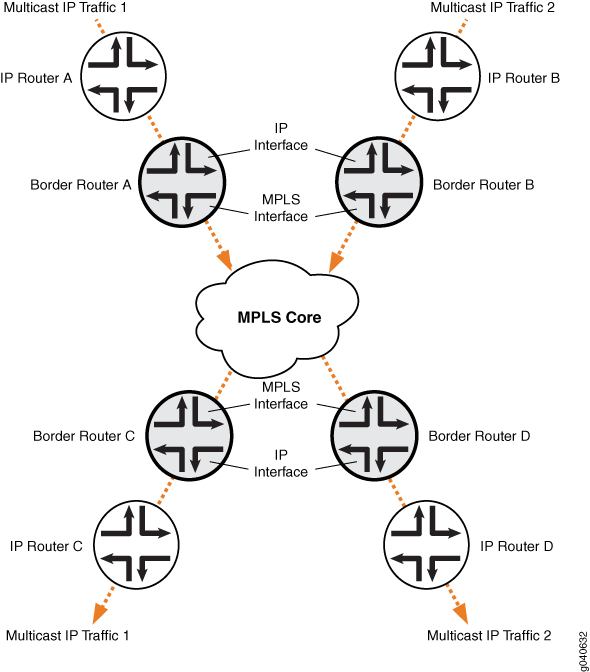
The IP topology consists of routers on the edge of the IP multicast domain. Each router has a set of IP interfaces configured toward the MPLS cloud and a set of interfaces configured toward the IP routers. See Figure 1. Internet multicast traffic is carried between the IP routers, through the MPLS cloud, using ingress replication tunnels for the data plane and a full-mesh IBGP session for the control plane.
Figure 1: Internet Multicast Topology
Configuration
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks, change any details necessary to match your network configuration, and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
Border Router C
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following example requires you to navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For information about navigating the CLI, see Using the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode in the CLI User Guide.
The following example shows how to configure ingress replication on an IP multicast instance with the routing instance type mpls-internet-multicast. Additionally, this example shows how to configure a selective provider tunnel that selects a new unicast tunnel each time a new destination needs to be added to the multicast distribution tree.
This example shows the configuration of the link between Border Router C and edge IP Router C, from which Border Router C receives PIM join messages.
- Enable MPLS.[edit protocols mpls]user@Border_Router_C# set ipv6-tunnelinguser@Border_Router_C# set interface all
- Configure a signaling protocol, such as RSVP or LDP.[edit protocols ldp]user@Border_Router_C# set interface all
- Configure a full-mesh of IBGP peering sessions.[edit protocols bgp group ibgp]user@Border_Router_C# set type internaluser@Border_Router_C# set local-address 10.255.10.61user@Border_Router_C# set neighbor 10.255.10.97user@Border_Router_C# set neighbor 10.255.10.55user@Border_Router_C# set neighbor 10.255.10.57user@Border_Router_C# set neighbor 10.255.10.59user@Border_Router_C# set export to-bgp
- Configure the multiprotocol BGP-related settings so that
the BGP sessions carry the necessary NLRI.[edit protocols bgp group ibgp]user@Border_Router_C# set family inet unicastuser@Border_Router_C# set family inet-vpn anyuser@Border_Router_C# set family inet6 unicastuser@Border_Router_C# set family inet6-vpn anyuser@Border_Router_C# set family inet-mvpn signalinguser@Border_Router_C# set family inet6-mvpn signaling
- Configure an interior gateway protocol (IGP).
This example shows a dual stacking configuration with OSPF and OSPF version 3 configured on the interfaces.
[edit protocols ospf3]user@Border_Router_C# set area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0user@Border_Router_C# set area 0.0.0.0 interface so-1/3/1.0user@Border_Router_C# set area 0.0.0.0 interface so-0/3/0.0
[edit protocols ospf]user@Border_Router_C# set traffic-engineeringuser@Border_Router_C# set area 0.0.0.0 interface fxp0.0 disableuser@Border_Router_C# set area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0user@Border_Router_C# set area 0.0.0.0 interface so-1/3/1.0user@Border_Router_C# set area 0.0.0.0 interface so-0/3/0.0 - Configure a global PIM instance on the interface facing
the edge device.
PIM is not configured in the core.
[edit protocols pim]user@Border_Router_C# set rp static address 15.10.10.2user@Border_Router_C# set rp static address 2::15:10:10:2user@Border_Router_C# set interface fe-0/1/0.0user@Border_Router_C# set mpls-internet-multicast - Configure the ingress replication provider tunnel to create
a new unicast tunnel each time a destination needs to be added to
the multicast distribution tree.[edit routing-instances test]user@Border_Router_C# set instance-type mpls-internet-multicastuser@Border_Router_C# set provider-tunnel ingress-replication label-switched-pathuser@Border_Router_C# set protocols mvpn

Note: Alternatively, use the label-switched-path-template statement to configure a point-to-point LSP for the ingress tunnel.
Configure the point-to-point LSP to use the default template settings (this is needed only when using RSVP tunnels). For example:
[edit routing-instances test provider-tunnel]user@Border_Router_C# set ingress-replication label-switched-path label-switched-path-template default-templateuser@Border_Router_C# set selective group 232.1.1.1/32 source 192.168.195.145/32 ingress-replication label-switched-path - Commit the configuration.user@Border_Router_C# commit
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration by issuing the show protocols and show routing-instances command. If the output does not display the intended configuration, repeat the instructions in this example to correct the configuration.
Verification
Confirm that the configuration is working properly. The following operational output is for LDP ingress replication SPT-only mode. The multicast source behind IP Router B. The multicast receiver is behind IP Router C.
- Checking the Ingress Replication Status on Border Router C
- Checking the Routing Table for the MVPN Routing Instance on Border Router C
- Checking the MVPN Neighbors on Border Router C
- Checking the PIM Join Status on Border Router C
- Checking the Multicast Route Status on Border Router C
- Checking the Ingress Replication Status on Border Router B
- Checking the Routing Table for the MVPN Routing Instance on Border Router B
- Checking the MVPN Neighbors on Border Router B
- Checking the PIM Join Status on Border Router B
- Checking the Multicast Route Status on Border Router B
Checking the Ingress Replication Status on Border Router C
Purpose
Use the show ingress-replication mvpn command to check the ingress replication status.
Action
user@Border_Router_C> show ingress-replication
mvpnIngress Tunnel: mvpn:1
Application: MVPN
Unicast tunnels
Leaf Address Tunnel-type Mode State
10.255.10.61 P2P LSP Existing Up
Meaning
The ingress replication is using a point-to-point LSP, and is in the Up state.
Checking the Routing Table for the MVPN Routing Instance on Border Router C
Purpose
Use the show route table command to check the route status.
Action
user@Border_Router_C> show route table test.mvpntest.mvpn.0: 5 destinations, 7 routes (5 active, 1 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
1:0:0:10.255.10.61/240
*[BGP/170] 00:45:55, localpref 100, from 10.255.10.61
AS path: I, validation-state: unverified
> via so-2/0/1.0
1:0:0:10.255.10.97/240
*[MVPN/70] 00:47:19, metric2 1
Indirect
5:0:0:32:192.168.195.106:32:224.1.1.1/240
*[PIM/105] 00:06:35
Multicast (IPv4) Composite
[BGP/170] 00:06:35, localpref 100, from 10.255.10.61
AS path: I, validation-state: unverified
> via so-2/0/1.0
6:0:0:1000:32:15.10.10.2:32:224.1.1.1/240
*[PIM/105] 00:07:03
Multicast (IPv4) Composite
7:0:0:1000:32:192.168.195.106:32:224.1.1.1/240
*[MVPN/70] 00:06:35, metric2 1
Multicast (IPv4) Composite
[PIM/105] 00:05:35
Multicast (IPv4) Composite
test.mvpn-inet6.0: 2 destinations, 2 routes (2 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
1:0:0:10.255.10.61/432
*[BGP/170] 00:45:55, localpref 100, from 10.255.10.61
AS path: I, validation-state: unverified
> via so-2/0/1.0
1:0:0:10.255.10.97/432
*[MVPN/70] 00:47:19, metric2 1
Indirect
Meaning
The expected routes are populating the test.mvpn routing table.
Checking the MVPN Neighbors on Border Router C
Purpose
Use the show mvpn neighbor command to check the neighbor status.
Action
user@Border_Router_C> show mvpn neighborMVPN instance:
Legend for provider tunnel
S- Selective provider tunnel
Legend for c-multicast routes properties (Pr)
DS -- derived from (*, c-g) RM -- remote VPN route
Family : INET
Instance : test
MVPN Mode : SPT-ONLY
Neighbor Inclusive Provider Tunnel
10.255.10.61 INGRESS-REPLICATION:MPLS Label 16:10.255.10.61
MVPN instance:
Legend for provider tunnel
S- Selective provider tunnel
Legend for c-multicast routes properties (Pr)
DS -- derived from (*, c-g) RM -- remote VPN route
Family : INET6
Instance : test
MVPN Mode : SPT-ONLY
Neighbor Inclusive Provider Tunnel
10.255.10.61 INGRESS-REPLICATION:MPLS Label 16:10.255.10.61
Checking the PIM Join Status on Border Router C
Purpose
Use the show pim join extensive command to check the PIM join status.
Action
user@Border_Router_C> show pim join extensiveInstance: PIM.master Family: INET
R = Rendezvous Point Tree, S = Sparse, W = Wildcard
Group: 224.1.1.1
Source: *
RP: 15.10.10.2
Flags: sparse,rptree,wildcard
Upstream interface: Local
Upstream neighbor: Local
Upstream state: Local RP
Uptime: 00:07:49
Downstream neighbors:
Interface: ge-3/0/6.0
15.10.10.2 State: Join Flags: SRW Timeout: Infinity
Uptime: 00:07:49 Time since last Join: 00:07:49
Number of downstream interfaces: 1
Group: 224.1.1.1
Source: 192.168.195.106
Flags: sparse
Upstream protocol: BGP
Upstream interface: Through BGP
Upstream neighbor: Through MVPN
Upstream state: Local RP, Join to Source, No Prune to RP
Keepalive timeout: 69
Uptime: 00:06:21
Number of downstream interfaces: 0
Instance: PIM.master Family: INET6
R = Rendezvous Point Tree, S = Sparse, W = Wildcard
Checking the Multicast Route Status on Border Router C
Purpose
Use the show multicast route extensive command to check the multicast route status.
Action
user@Border_Router_C> show multicast route extensiveInstance: master Family: INET
Group: 224.1.1.1
Source: 192.168.195.106/32
Upstream interface: lsi.0
Downstream interface list:
ge-3/0/6.0
Number of outgoing interfaces: 1
Session description: NOB Cross media facilities
Statistics: 18 kBps, 200 pps, 88907 packets
Next-hop ID: 1048577
Upstream protocol: MVPN
Route state: Active
Forwarding state: Forwarding
Cache lifetime/timeout: forever
Wrong incoming interface notifications: 0
Uptime: 00:07:25
Instance: master Family: INET6
Checking the Ingress Replication Status on Border Router B
Purpose
Use the show ingress-replication mvpn command to check the ingress replication status.
Action
user@Border_Router_B> show ingress-replication
mvpnIngress Tunnel: mvpn:1
Application: MVPN
Unicast tunnels
Leaf Address Tunnel-type Mode State
10.255.10.97 P2P LSP Existing Up
Meaning
The ingress replication is using a point-to-point LSP, and is in the Up state.
Checking the Routing Table for the MVPN Routing Instance on Border Router B
Purpose
Use the show route table command to check the route status.
Action
user@Border_Router_B> show route table test.mvpntest.mvpn.0: 5 destinations, 7 routes (5 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
1:0:0:10.255.10.61/240
*[MVPN/70] 00:49:26, metric2 1
Indirect
1:0:0:10.255.10.97/240
*[BGP/170] 00:48:22, localpref 100, from 10.255.10.97
AS path: I, validation-state: unverified
> via so-1/3/1.0
5:0:0:32:192.168.195.106:32:224.1.1.1/240
*[PIM/105] 00:09:02
Multicast (IPv4) Composite
[BGP/170] 00:09:02, localpref 100, from 10.255.10.97
AS path: I, validation-state: unverified
> via so-1/3/1.0
7:0:0:1000:32:192.168.195.106:32:224.1.1.1/240
*[PIM/105] 00:09:02
Multicast (IPv4) Composite
[BGP/170] 00:09:02, localpref 100, from 10.255.10.97
AS path: I, validation-state: unverified
> via so-1/3/1.0
test.mvpn-inet6.0: 2 destinations, 2 routes (2 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
1:0:0:10.255.10.61/432
*[MVPN/70] 00:49:26, metric2 1
Indirect
1:0:0:10.255.10.97/432
*[BGP/170] 00:48:22, localpref 100, from 10.255.10.97
AS path: I, validation-state: unverified
> via so-1/3/1.0
Meaning
The expected routes are populating the test.mvpn routing table.
Checking the MVPN Neighbors on Border Router B
Purpose
Use the show mvpn neighbor command to check the neighbor status.
Action
user@Border_Router_B> show mvpn neighborMVPN instance:
Legend for provider tunnel
S- Selective provider tunnel
Legend for c-multicast routes properties (Pr)
DS -- derived from (*, c-g) RM -- remote VPN route
Family : INET
Instance : test
MVPN Mode : SPT-ONLY
Neighbor Inclusive Provider Tunnel
10.255.10.97 INGRESS-REPLICATION:MPLS Label 16:10.255.10.97
MVPN instance:
Legend for provider tunnel
S- Selective provider tunnel
Legend for c-multicast routes properties (Pr)
DS -- derived from (*, c-g) RM -- remote VPN route
Family : INET6
Instance : test
MVPN Mode : SPT-ONLY
Neighbor Inclusive Provider Tunnel
10.255.10.97 INGRESS-REPLICATION:MPLS Label 16:10.255.10.97
Checking the PIM Join Status on Border Router B
Purpose
Use the show pim join extensive command to check the PIM join status.
Action
user@Border_Router_B> show pim join extensiveInstance: PIM.master Family: INET
R = Rendezvous Point Tree, S = Sparse, W = Wildcard
Group: 224.1.1.1
Source: 192.168.195.106
Flags: sparse,spt
Upstream interface: fe-0/1/0.0
Upstream neighbor: Direct
Upstream state: Local Source
Keepalive timeout: 0
Uptime: 00:09:39
Downstream neighbors:
Interface: Pseudo-MVPN
Uptime: 00:09:39 Time since last Join: 00:09:39
Number of downstream interfaces: 1
Instance: PIM.master Family: INET6
R = Rendezvous Point Tree, S = Sparse, W = Wildcard
Checking the Multicast Route Status on Border Router B
Purpose
Use the show multicast route extensive command to check the multicast route status.
Action
user@Border_Router_B> show multicast route extensiveInstance: master Family: INET
Group: 224.1.1.1
Source: 192.168.195.106/32
Upstream interface: fe-0/1/0.0
Downstream interface list:
so-1/3/1.0
Number of outgoing interfaces: 1
Session description: NOB Cross media facilities
Statistics: 18 kBps, 200 pps, 116531 packets
Next-hop ID: 1048580
Upstream protocol: MVPN
Route state: Active
Forwarding state: Forwarding
Cache lifetime/timeout: forever
Wrong incoming interface notifications: 0
Uptime: 00:09:43
Related Documentation
- EX, J, MX, T Series
- show ingress-replication mvpn
- M, MX, T Series
- Configuring Routing Instances for an MBGP MVPN
- mpls-internet-multicast
- ingress-replication
- create-new-ucast-tunnel
- M, MX, SRX, T Series
- label-switched-path-template
Published: 2013-03-21
Related Documentation
- EX, J, MX, T Series
- show ingress-replication mvpn
- M, MX, T Series
- Configuring Routing Instances for an MBGP MVPN
- mpls-internet-multicast
- ingress-replication
- create-new-ucast-tunnel
- M, MX, SRX, T Series
- label-switched-path-template


