Related Documentation
Example: Configuring BGP Autodiscovery for LDP VPLS
This example describes how to configure BGP autodiscovery for LDP VPLS, as specified in forwarding equivalency class (FEC) 129. FEC 129 uses BGP autodiscovery to convey endpoint information, so you do not need to manually configure pseudowires.
Requirements
This example uses the following hardware and software components:
- Four MX Series 3D Universal Edge Routers
- Junos OS Release 10.4R2 or later
If you are using M Series or T Series routers, the PE routers must have either virtual loopback tunnel (vt) interfaces or label-switched interfaces (LSIs). On M Series and T Series routers, VPLS uses tunnel-based PICs to create virtual ports on vt interfaces. If you do not have a tunnel-based PIC installed on your M Series or T Series router, you can still configure VPLS by using LSIs to support the virtual ports. Use of LSIs requires Ethernet-based PICs installed in an Enhanced Flexible PIC Concentrator (FPC).
You do not need to use routers for the CE devices. For example, the CE devices can be EX Series Ethernet Switches.
Overview
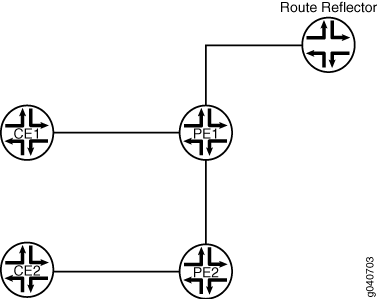
All PE routers in a VPLS network operate like a large, distributed Ethernet switch to provide Layer 2 services to attached devices. This example shows a minimum configuration for PE routers and CE devices to create an autodiscovered VPLS network. The topology consists of five routers: two PE routers, two CE routers, and an optional route reflector (RR). The PE routers use BGP to autodiscover two different VPLS instances that are configured on both PE routers. Then the PE routers use LDP to automatically signal two pseudowires between the discovered end points. Finally, the PE routers bring up both VPLS instances for forwarding traffic. Each CE device is configured with two VLANs, with each VLAN belonging to different VPLS instances in the PE routers.
This example includes the following settings:
- auto-discovery-only—Allows the router
to process only the autodiscovery network layer reachability information
(NLRI) update messages for LDP-based Layer 2 VPN and VPLS update messages
(BGP_L2VPN_AD_NLRI) (FEC 129). Specifically, the auto-discovery-only statement notifies the routing process (rpd) to expect autodiscovery-related
NLRI messages so that information can be deciphered and used by LDP
and VPLS. You can configure this statement at the global, group, and
neighbor levels for BGP. The auto-discovery-only statement
must be configured on all PE routers in the VPLS. If you configure
route reflection, the auto-discovery-only statement is
also required on P routers that act as the route reflector in supporting
FEC 129-related updates.
The signaling statement is not included in this example but is discussed here for completeness. The signaling statement allows the router to process only the BGP_L2VPN_NLRIs used for BGP-based Layer 2 VPNs (FEC 128).
For interoperation scenarios in which a PE router must support both types of NLRI (FEC 128 and FEC 129), you can configure both the signaling statement and the auto-discovery-only statement. For example, a single PE router might need to process a combination of BGP-signaled virtual private wire service (VPWS) and LDP-signaled VPLS assisted by BGP autodiscovery. Configuring both the signaling statement and the auto-discovery-only statement together allows both types of signaling to run independently. The signaling statement is supported at the same hierarchy levels as the auto-discovery-only statement.
- cluster—Configuring a route reflector is optional for FEC 129 autodiscovered PE routers. In this example, the cluster statement configures Router RR to be a route reflector in the IBGP group. For inbound updates, BGP autodiscovery NLRI messages are accepted if the router is configured to be a route reflector or if the keep all statement is configured in the IBGP group.
- l2vpn-id—Specifies a globally unique
Layer 2 VPN community identifier for the instance. This statement
is configurable for routing instances of type vpls.
You can configure the following formats for the community identifier:
- Autonomous system (AS) number format—l2vpn-id:as-number:2-byte-number. For example: l2vpn-id:100:200. The AS number can be in the range from 1 through 65,535.
- IPv4 format—l2vpn-id:ip-address:2-byte-number. For example: l2vpn-id:10.1.1.1:2.
- vrf-target—Defines the import and export route targets for the NLRI. You must either configure the vrf-target statement or the vrf-import and vrf-export statements to define the instance import and export policy or the import and export route targets for the NLRI. This example uses the vrf-target statement.
- route-distinguisher—Forms part of the
BGP autodiscovery NLRI and distinguishes to which VPN or VPLS routing
instance each route belongs. Each route distinguisher is a 6-byte
value. You must configure a unique route distinguisher for each routing
instance.
You can configure the following formats for the route distinguisher:
- AS number format—as-number:2-byte-number
- IPv4 format—ip-address:2-byte-number
Two notable statements are included in this example. These statements are important for interoperability with other vendors’ equipment. The interoperability statements are not necessary for the topology that is used in this example, but they are included for completeness.
The interoperability statements are as follows:
- input-vlan-map pop—Removes an outer VLAN tag from the top of the VLAN tag stack.
- output-vlan-map push—Adds an outer VLAN tag in front of the existing VLAN tag.
Topology Diagram
Figure 1 shows the topology used in this example.
Figure 1: BGP Autodiscovery for LDP VPLS
Configuration
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure BGP autodiscovery for LDP VPLS, copy the following commands, remove any line breaks, and then paste the commands into the CLI of each device.
On Router PE1:
On Device CE1:
On Router PE2:
On Device CE2:
On Router RR:
Router PE1
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure Router PE1:
Configure the interfaces, the interface encapsulation, and the protocol families.
[edit]user@PE1# edit interfaces[edit interfaces]user@PE1# set ge-0/1/0 encapsulation flexible-ethernet-servicesuser@PE1# set ge-0/1/0 unit 100 encapsulation vlan-vplsuser@PE1# set ge-0/1/0 unit 100 family vplsuser@PE1# set ge-0/1/0 unit 200 encapsulation vlan-vplsuser@PE1# set ge-0/1/0 unit 200 family vplsuser@PE1# set ge-0/1/1 unit 0 description "PE1 to PE2"user@PE1# set ge-0/1/1 unit 0 family inet address 8.0.40.100/24user@PE1# set ge-0/1/1 unit 0 family isouser@PE1# set ge-0/1/1 unit 0 family mplsuser@PE1# set ge-0/3/0 unit 0 description "PE1 to RR"user@PE1# set ge-0/3/0 unit 0 family inet address 8.0.70.100/24user@PE1# set ge-0/3/0 unit 0 family isouser@PE1# set ge-0/3/0 unit 0 family mplsuser@PE1# set lo0 unit 0 family inet address 8.0.0.100/32Configure the VLANs.
[edit interfaces]user@PE1# set ge-0/1/0 vlan-tagginguser@PE1# set ge-0/1/0 unit 100 vlan-id 100user@PE1# set ge-0/1/0 unit 100 input-vlan-map popuser@PE1# set ge-0/1/0 unit 100 output-vlan-map pushuser@PE1# set ge-0/1/0 unit 200 vlan-id 200user@PE1# exitConfigure the protocol-independent properties.
We recommend that the router ID be the same as the local address. (See the local-address statement in Step 4.)
[edit]user@PE1# edit routing-options[edit routing-options]user@PE1# set router-id 8.0.0.100user@PE1# set autonomous-system 100user@PE1# exitConfigure IBGP, including the auto-discovery-only statement.
[edit]user@PE1# edit protocols[edit protocols]user@PE1# set bgp group int type internaluser@PE1# set bgp group int local-address 8.0.0.100user@PE1# set bgp group int family l2vpn auto-discovery-onlyuser@PE1# set bgp group int neighbor 8.0.0.107Configure MPLS, LDP, and an IGP.
[edit protocols]user@PE1# set mpls interface lo0.0user@PE1# set mpls interface alluser@PE1# set mpls interface fxp0.0 disableuser@PE1# set isis level 1 disableuser@PE1# set isis interface alluser@PE1# set isis interface fxp0.0 disableuser@PE1# set isis interface lo0.0user@PE1# set ldp interface alluser@PE1# set ldp interface fxp0.0 disableuser@PE1# set ldp interface lo0.0user@PE1# exit- Configure the routing instances.
The no-tunnel-services statement is required if you are using LSI interfaces for VPLS instead of vt interfaces.
[edit]user@PE1# edit routing-instances[edit routing-instances]user@PE1# set vpls100 instance-type vplsuser@PE1# set vpls100 interface ge-0/1/0.100user@PE1# set vpls100 route-distinguisher 8.0.0.100:100user@PE1# set vpls100 l2vpn-id l2vpn-id:100:100user@PE1# set vpls100 vrf-target target:100:100user@PE1# set vpls100 protocols vpls no-tunnel-servicesuser@PE1# set vpls200 instance-type vplsuser@PE1# set vpls200 interface ge-0/1/0.200user@PE1# set vpls200 route-distinguisher 8.0.0.100:200user@PE1# set vpls200 l2vpn-id l2vpn-id:100:200user@PE1# set vpls200 vrf-target target:100:208user@PE1# set vpls200 protocols vpls no-tunnel-services If you are done configuring the device, commit the configuration.
[edit]user@PE1# commit
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration by entering the show interfaces, show protocols, show routing-options, and show routing-instances commands. If the output does not display the intended configuration, repeat the instructions in this example to correct the configuration.
Device CE1
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure Device CE1:
Configure interface addresses and the interface maximum transmission unit (MTU).
[edit]user@CE1# edit interfaces[edit interfaces]user@CE1# set ge-1/2/1 mtu 1400user@CE1# set ge-1/2/1 unit 100 family inet address 3.0.100.103/24user@CE1# set ge-1/2/1 unit 200 family inet address 3.0.200.103/24Configure VLANs.
[edit interfaces]user@CE1# set ge-1/2/1 vlan-tagginguser@CE1# set ge-1/2/1 unit 100 vlan-id 100user@CE1# set ge-1/2/1 unit 200 vlan-id 200user@CE1# exitConfigure an IGP.
user@CE1# edit protocols[edit protocols]user@CE1# set ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/1.100user@CE1# set ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/1.200user@CE1# exitIf you are done configuring the device, commit the configuration.
[edit]user@CE1# commit
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration by entering the show interfaces and show protocols commands. If the output does not display the intended configuration, repeat the instructions in this example to correct the configuration.
Router PE2
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure Router PE2:
Configure the interfaces, the interface encapsulation, and the protocol families.
[edit]user@PE2# edit interfaces[edit interfaces]user@PE2# set ge-1/1/0 encapsulation flexible-ethernet-servicesuser@PE2# set ge-1/1/0 unit 100 encapsulation vlan-vplsuser@PE2# set ge-1/1/0 unit 100 family vplsuser@PE2# set ge-1/1/0 unit 200 encapsulation vlan-vplsuser@PE2# set ge-1/1/0 unit 200 family vplsuser@PE2# set ge-1/2/1 unit 0 description "PE2 to PE1"user@PE2# set ge-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 8.0.40.104/24user@PE2# set ge-1/2/1 unit 0 family isouser@PE2# set ge-1/2/1 unit 0 family mplsuser@PE2# set lo0 unit 0 family inet address 8.0.0.104/32Configure the VLANs.
[edit interfaces]user@PE2# set ge-1/1/0 vlan-tagginguser@PE2# set ge-1/1/0 unit 100 vlan-id 100user@PE2# set ge-1/1/0 unit 100 input-vlan-map popuser@PE2# set ge-1/1/0 unit 100 output-vlan-map pushuser@PE2# set ge-1/1/0 unit 200 vlan-id 200user@PE2# exit- Configure the protocols-independent properties.
We recommend that the router ID be the same as the local address. (See the local-address statement in Step 4.)
[edit]user@PE2# edit routing-options[edit routing-options]user@PE2# set router-id 8.0.0.104user@PE2# set autonomous-system 100 Configure IBGP, including the auto-discovery-only statement.
[edit]user@PE2# edit protocols[edit protocols]user@PE2# set bgp group int type internaluser@PE2# set bgp group int local-address 8.0.0.104user@PE2# set bgp group int family l2vpn auto-discovery-onlyuser@PE2# set bgp group int neighbor 8.0.0.107Configure MPLS, LDP, and an IGP.
[edit protocols]user@PE2# set mpls interface lo0.0user@PE2# set mpls interface alluser@PE2# set mpls interface fxp0.0 disableuser@PE2# set isis level 1 disableuser@PE2# set isis interface ge-1/2/1.0user@PE2# set isis interface lo0.0user@PE2# set ldp interface alluser@PE2# set ldp interface fxp0.0 disableuser@PE2# set ldp interface lo0.0user@PE2# exit- Configure the routing instances.
The no-tunnel-services statement is required if you are using LSI interfaces for VPLS instead of vt interfaces.
[edit]user@PE2# edit routing-instances[edit routing-instances]user@PE2# set vpls100 instance-type vplsuser@PE2# set vpls100 interface ge-1/1/0.100user@PE2# set vpls100 route-distinguisher 8.0.0.104:100user@PE2# set vpls100 l2vpn-id l2vpn-id:100:100user@PE2# set vpls100 vrf-target target:100:100user@PE2# set vpls100 protocols vpls no-tunnel-servicesuser@PE2# set vpls200 instance-type vplsuser@PE2# set vpls200 interface ge-1/1/0.200user@PE2# set vpls200 route-distinguisher 8.0.0.104:200user@PE2# set vpls200 l2vpn-id l2vpn-id:100:200user@PE2# set vpls200 vrf-target target:100:208user@PE2# set vpls200 protocols vpls no-tunnel-services If you are done configuring the device, commit the configuration.
[edit]user@PE2# commit
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration by entering the show interfaces, show protocols, show routing-options, and show routing-instances commands. If the output does not display the intended configuration, repeat the instructions in this example to correct the configuration.
Device CE2
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure Device CE2:
Configure VLAN interfaces.
[edit]user@CE2# edit interfaces ge-1/1/0[edit interfaces ge-1/1/0]user@CE2# set vlan-tagginguser@CE2# set mtu 1400user@CE2# set unit 100 vlan-id 100user@CE2# set unit 100 family inet address 3.0.100.105/24user@CE2# set unit 200 vlan-id 200user@CE2# set unit 200 family inet address 3.0.200.105/24user@CE2# exitConfigure OSPF on the interfaces.
[edit]user@CE2# edit protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0[edit protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0]user@CE2# set interface ge-1/1/0.100user@CE2# set interface ge-1/1/0.200user@CE2# exitIf you are done configuring the device, commit the configuration.
[edit]user@CE2# commit
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration by entering the show interfaces and show protocols commands. If the output does not display the intended configuration, repeat the instructions in this example to correct the configuration.
Router RR
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure Router RR:
Configure interface addresses and the protocol families.
[edit]user@RR# edit interfaces[edit interfaces]user@RR# set ge-1/3/2 unit 0 description "RR to PE1"user@RR# set ge-1/3/2 unit 0 family inet address 8.0.70.107/24user@RR# set ge-1/3/2 unit 0 family isouser@RR# set ge-1/3/2 unit 0 family mplsuser@RR# set lo0 unit 0 family inet address 8.0.0.107/32user@RR# exitConfigure the autonomous systems and the router ID.
[edit]user@RR# edit routing-options[edit routing-options]user@RR# set autonomous-system 100user@RR# set router-id 8.0.0.107user@RR# exitConfigure BGP and set this router to be the route reflector. Route reflection is optional for FEC 129.
[edit]user@RR# edit protocols bgp group int[edit protocols bgp group int]user@RR# set type internaluser@RR# set local-address 8.0.0.107user@RR# set family l2vpn auto-discovery-onlyuser@RR# set cluster 107.107.107.107user@RR# set neighbor 8.0.0.100user@RR# set neighbor 8.0.0.104user@RR# exitConfigure IS-IS for the IGP.
[edit]user@RR# edit protocols isis[edit protocols isis]user@RR# set level 1 disableuser@RR# set interface alluser@RR# set interface fxp0.0 disableuser@RR# set interface lo0.0user@RR# exitConfigure LDP for the MPLS signaling protocol.
[edit]user@RR# edit protocols ldp[edit protocols ldp]user@RR# set interface alluser@RR# set interface fxp0.0 disableuser@RR# set interface lo0.0user@RR# exitIf you are done configuring the device, commit the configuration.
[edit]user@RR# commit
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration by entering the show interfaces, show protocols, and show routing-options commands. If the output does not display the intended configuration, repeat the instructions in this example to correct the configuration.
Verification
To verify the operation, use the following commands:
- show route extensive
- show route advertising-protocol bgp neighbor
- show route receive-protocol bgp neighbor
- show route table bgp.l2vpn.0
- show route table vpls100.l2vpn.0
- show route table vpls200.l2vpn.0
- show vpls connections extensive
- show vpls mac-table detail
- show vpls statistics
AD in the routing table output indicates autodiscovery NLRI.


