Supported Platforms
Routing VPN and Outgoing Internet Traffic Through the Same Interface and Routing Return Internet Traffic Through a Different Interface
In this example, the CE router sends VPN and Internet traffic through the same interface but receives return Internet traffic through a different interface. The PE router has a default route in the VRF table pointing to the main routing table inet.0. It routes the VPN public IP address pool (return Internet traffic) through a different interface in inet.0 (see Figure 1). The CE router still performs NAT functions.
Figure 1: VPN and Outgoing Internet Traffic Routed Through the Same Interface and Return Internet Traffic Routed Through a Different Interface
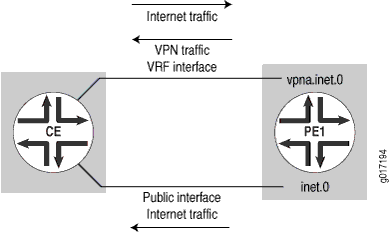
The following section shows how to route VPN and outgoing Internet traffic through the same interface and routing return Internet traffic through a different interface:
Configuration for Router PE1
This example has the same configuration as Router PE1 in Routing VPN and Internet Traffic Through Different Interfaces. It uses the topology shown in Routing VPN and Internet Traffic Through Different Interfaces. The default route to the VPN routing table is configured differently. At the [edit routing-instances routing-instance-name routing-options] hierarchy level, you configure a default static route that is installed in vpna.inet.0 and points to inet.0 for resolution:
You also need to change the configuration of Router CE1 (from the configuration that works with the configuration for Router PE1 described in Routing VPN and Internet Traffic Through Different Interfaces) to account for the differences in the configuration of the PE routers.


