무선 관리
Juniper Mist AI 기반 무선 리소스 관리(RRM)는 주니퍼 AP와 Juniper Mist 클라우드 모두에서 사용할 수 있는 머신 러닝 기술을 설명합니다. RRM은 기본적으로 활성화되며 대부분의 최적화는 백그라운드에서 자동으로 수행됩니다.
클라우드에서 RRM은 WLAN 또는 사이트의 여러 AP에서 데이터를 수집하며, 다음 비디오와 같이 용량 SLE와 같은 SLE(Service Level Expectations)의 일부로 수집됩니다.
Radio frequency environments are inherently complex and therefore challenging to control and optimize for the efficient transmission of data. Since the inception of radio frequency, or RF, radio resource management, also known as RRM, has been a long-standing technique used to optimize the RF radio waves that transmit network traffic in wireless LANs. However, multiple interference sources like walls, buildings, and people combined with the air servings of transmission medium make RRM a challenging technique to master.
Traditionally, site surveys have been used to determine the optimal placement of Wi-Fi access points and settings for transmit power, channels, and bandwidth. However, these manual approaches can't account for the dynamic nature of the environment when the wireless network is in use, with people and devices entering or leaving and moving about. Additionally, this challenge is compounded with random RF interferences from sources like microwave ovens, radios, and aircraft radar, to name a few.
But what if the wireless network itself could perform RRM on its own? What if it could detect and respond to both interference sources, as well as the movement of people and devices, and adjust the radio settings in real time to provide the best possible wireless service? That's exactly what Juniper has done with the AI-driven MIST wireless solution, using advanced machine learning techniques. Specifically, MIST uses reinforcement learning to perform RRM. In a nutshell, a reinforcement learning machine, or agent, learns through an iterative trial and error process in an effort to achieve the correct result.
It's rewarded for actions that lead to the correct result, while receiving penalties for actions leading to an incorrect result. The machine learns by favoring actions that result in rewards. With MIST wireless, the reinforcement learning machine's value function is based on three main factors that lead to a good user experience.
Coverage, capacity, and connectivity. A value function can be thought of as an expected return based on the actions taken. The machine can execute five different actions to optimize the value function.
These are adjusting the band setting between the two wireless bands of 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz, increasing or decreasing the transmit power of the AP's radios, switching to a different channel within the band, adjusting a channel's bandwidth, and switching the BSS color, which is a new knob available to 11 AX access points. RRM will select actions with maximum future rewards for a site. Future rewards are evaluated by a value function.
The various actions taken by the learning machine, such as the increase of transmit power or switching the band from 2.4 GHz to 5 GHz, together represent a policy, which is a map the machine builds based on multiple trial and error cycles as it collects rewards, modeling actions that maximize the value function. Again, keep in mind that the value function represents good wireless user experience. As time goes on, even if random changes occur in the environment, the machine learns as it strives to maximize the value function.
The benefits of using reinforcement learning are obvious. A MIST wireless network customizes the RRM policy per site, creating a unique wireless coverage environment akin to a well-tailored suit. While large organizations with multiple sites replicate their many locations as copy exact, these sites will naturally experience variances despite best efforts.
Reinforcement learning easily fixes this, delivering real-time, actively adjusting, custom wireless environments. We hope this episode helped to uncover some of the magic and mystery behind our AI-driven network solutions.
RRM은 지속적인 강화 학습을 적용하여 최대 30일 분량의 성능 데이터를 분석합니다. 따라서 하루, 일주일 또는 한 달 동안 발생하는 이벤트 기반 추세를 식별하여 일종의 이웃 장치로부터 빈번한 간섭이 발생하는 것으로 관찰된 채널의 우선 순위를 낮출 수 있습니다. 긴 기준선을 만드는 것 외에도 이러한 지속적인 관찰 및 학습은 정적 Wi-Fi 구현에 상속되는 시스템 드리프트 및 수동 개입을 방지하는 역할을 합니다.
개별 AP 수준에서 RRM은 채널 간섭과 같은 이벤트에 대응하여 최적의 채널 최적화를 보장합니다. 또한 레이더 공격에 자동으로 즉시 반응하고 전송 전력 또는 채널 사용량을 조정할 수 있습니다.
| 글로벌 RRM |
로컬 RRM |
|---|---|
| 예약은 사이트별로 야간에 자동으로 실행됩니다. |
로컬 이벤트에 대응(AP 기준) |
| 라디오 대역별로 수동이 트리거됩니다. |
클라우드 독립적 |
| 강화 학습 사용 |
Ad Hoc – 필요에 따라 실행 |
| 여러 날에 걸친 데이터 세트를 활용하여 정보에 입각한 의사 결정 |
다음 이벤트를 포함합니다.
|
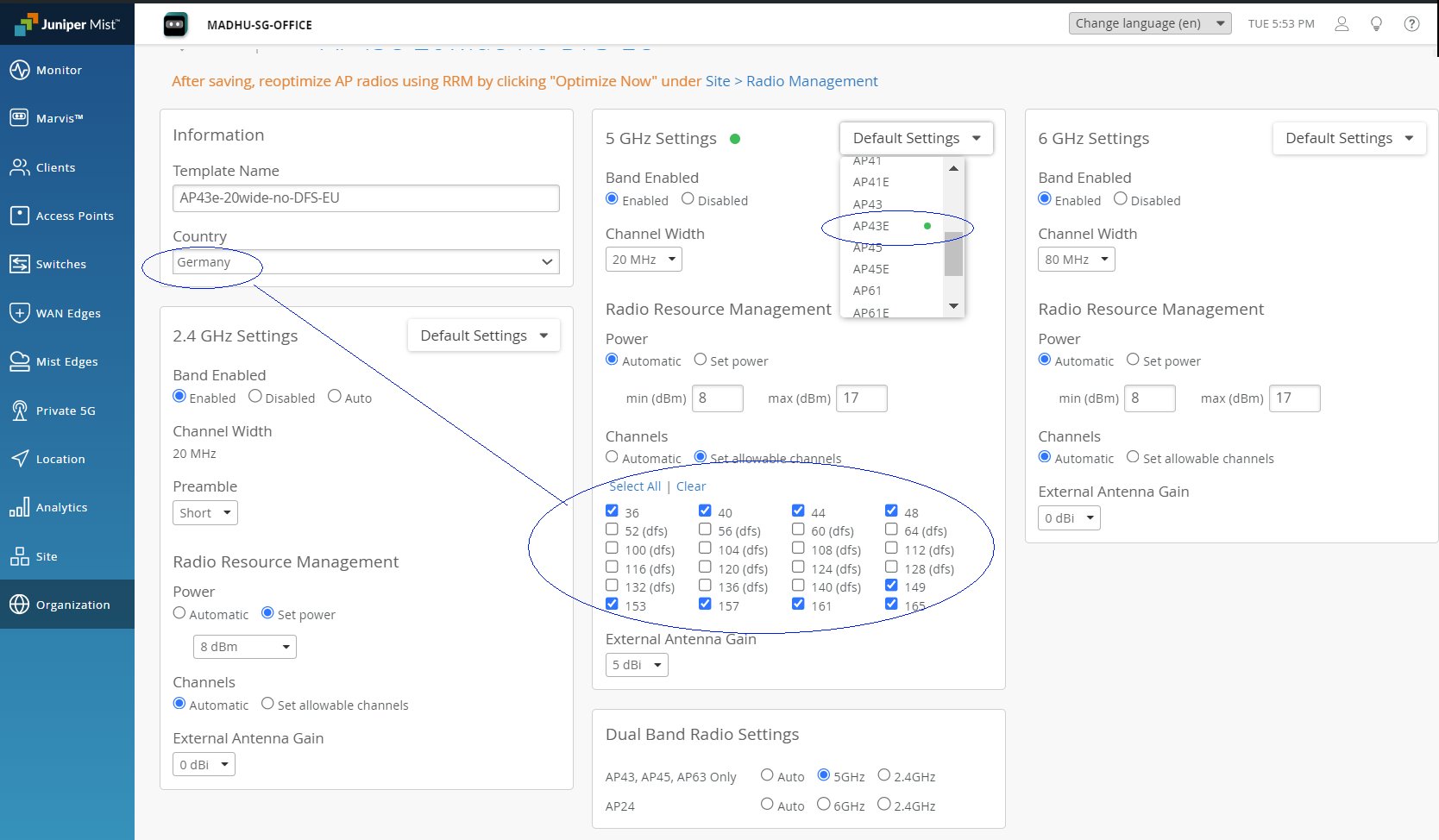
RRM의 또 다른 기능은 듀얼 밴드 무선 관리입니다. 여기서 RRM은 AP의 세 번째(또는 네 번째) 라디오를 활용하여 불필요한 2.4GHz 라디오를 식별하고 자동으로 5GHz 대역(또는 6GHz)으로 변환합니다. 이는 고밀도 환경에서 특히 유용하며, 인접 AP가 전송 전력을 증가시키지 않고 발생합니다.
듀얼 밴드를 관리하기 위해 로컬 RRM은 인접 AP와 함께 작동하여 2.4GHz 무선 신호 강도 및 밀도(주어진 영역에서 전송하는 2.4GHz 무선 송수신기 수)를 평가합니다. 특정 AP 모델이 듀얼 밴드를 지원하지 않는 경우, RRM은 트래픽을 5GHz 대역으로 구동하도록 변환하는 대신 2.4GHz 라디오를 비활성화할 수 있습니다. 라디오 관리(듀얼 밴드)를 참조하십시오.
조직 수준과 구성의 사이트 수준 모두에서 비활성화할 라디오를 수동으로 구성하고 채널 폭과 가용성을 설정하는 등의 작업을 수행하여 자동 설정을 재정의할 수 있습니다.
그림 1에서 볼 수 있듯이 일부 기본값은 국가 선택과 관련이 있습니다.