Service Chain Version 2 with Port Tuple
Starting with Contrail 3.0, the user can create a port-tuple object for binding service instances to ports.
Overview of Port Tuple
In previous versions of Contrail, when a service instance is created for a virtual machine (VM)-based service, the service monitor creates one or more VM objects and creates a port for each VM object. Each VM object is a placeholder for binding a service instance to a port. The VM object also acts as a placeholder for the instance ID when using equal-cost multipath (ECMP).
Using the VM object as a placeholder doesn't add value beyond binding information between the service instance object and the port objects. By using a port-tuple object, the service instance can be linked directly to the port objects, eliminating the need to create a VM object. This simplifies the implementation of service instance objects, and also allows integration with Heat templates.
With a port-tuple object, the user can create ports and pass the port information when creating a service instance. The ports can be created as part of a VM launch from Nova or without using a VM launch. The ports are linked to a port-tuple object that is a child of a service instance. This functionality can also be leveraged in Heat stacks. See Figure 1.
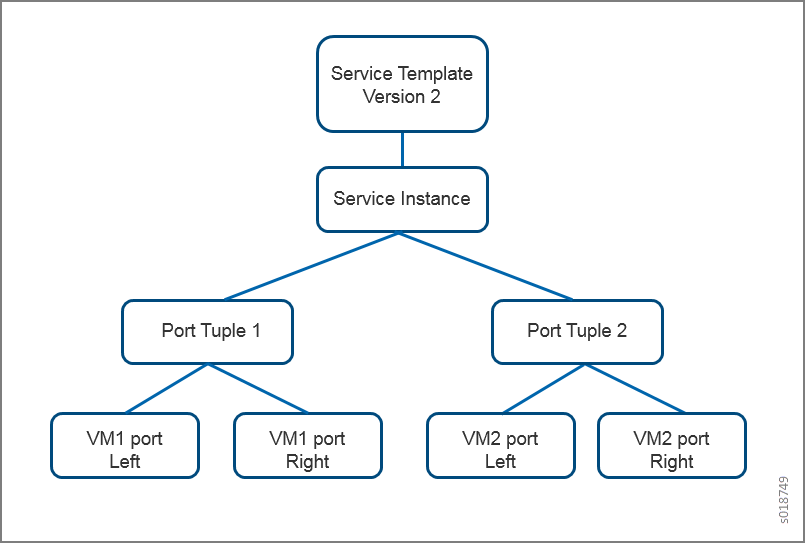
Service Chain Version 2 Sample Workflow
With Contrail service templates Version 2, the user can create ports and bind them to a VM-based or container-based service instance, by means of a port-tuple object. All objects created with the Version 2 service template are visible to the Contrail Heat engine, and are managed by Heat.
The following shows the basic workflow steps for creating a port tuple and service instance that will be managed by Heat:
Create a service template. Select 2 in the Version field.
Create a service instance for the service template just created.
Create a port-tuple object.
Create ports, using Nova VM launch or without a VM launch.
Label each port as
left, right, mgmt, and so on, and add the ports to the port-tuple object.Use a unique label for each of the ports in a single port tuple. The labels
leftandrightare used for forwarding.Link the port tuple to a service instance.
Launch the service instance. This creates the necessary objects in the Contrail database.
Port-tuple is not supported on transparent service instance, whether active/active, active/standby, or scale-out.
- Service Chain with Equal-Cost Multipath in Active-Active Mode
- Service Chain Active-Standby Mode with Allowed Address Pair
- Service Chain with Static Route Table
Service Chain with Equal-Cost Multipath in Active-Active Mode
Equal-cost multipath (ECMP) can be used to distribute traffic
across VMs. To support ECMP in the service chain, create multiple
port tuples within the same service instance. The labels should be
the same for the VM ports in each port tuple. For example, if port
tuple 1 uses the labels left and right, then port tuple 2 in the same service instance
should also use the labels left and right for its ports.
When there are multiple port tuples, the default mode of operation
is active-active.
Service Chain Active-Standby Mode with Allowed Address Pair
To support active-standby mode, you
must configure an allowed address pair on the interfaces. The active-standby is used as the high availability mode
in the allowed address pair. The allowed address pair is configured
as part of the service instance for a particular VM port label. For
example, if the allowed address pair is configured in a service instance
for the port with the label left, then
all of the port-tuple VM ports with the label left will use the allowed address pair high availability mode.
Allowed Address Pair
An allowed address pair extension is an OpenStack feature supported by Contrail.
By default, there is no way to specify additional MAC/IP address pairs that are allowed to pass through a port in Neutron, because ports are locked down to their MAC address and the fixed IPs associated with their port for anti-spoofing reasons. This locking can sometimes prevent protocols such as VRRP from providing a high availability failover strategy. Using the allowed address pair extension enables additional IP/MAC pairs to be allowed through ports in Neutron.
In Contrail, you can configure allowed address pairs in the service instance configuration, using Configure > Services > Service Instances > Allowed Address Pair, see Figure 2.
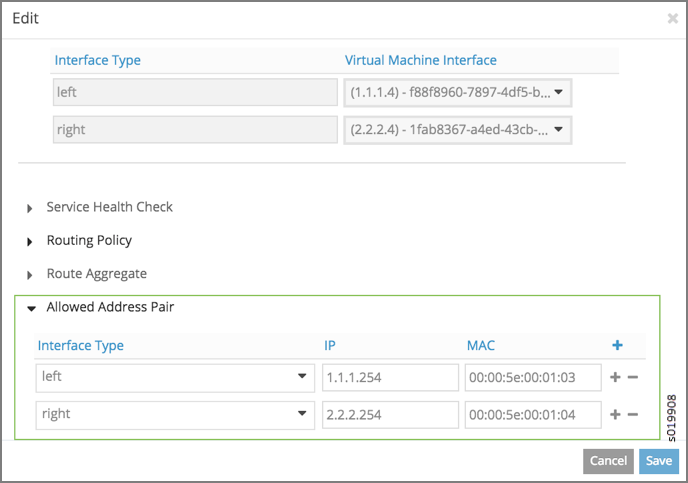
For more information about OpenStack allowed address pairs, see https://docs.openstack.org/dragonflow/latest/specs/allowed_address_pairs.html.
Service Chain with Static Route Table
The service chain Version 2 also supports static route tables.
A static route table is configured similar to how the allowed address
pair is configured, except with using the label right. The route table will be attached to the correct VM ports of the
port tuples, based on the configuration of the port with the label right.
Service Chain with Health Check
Service chain Version 2 also allows service instance health check configuration on a per interface label. This is used to monitor the health of the service.
For more information about the service instance health check, see Service Instance Health Checks.
