SCTP on the AGF
Next Generation Application Protocol (NGAP) on the Access Gateway Function (AGF) uses the Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP) to transport NGAP messages. NGAP messages provide control plane signaling between the AGF and the Access and Mobility Management Functions (AMFs). NGAP support TNLA usage type and weight factor. SCTP is a transport layer protocol that provides the mechanism for reliable, in-sequence transport of data between endpoints. The endpoints form a unique Transport Layer Network Association (TNLA), that enables seamless communication between nodes. For more information on SCTP, see SCTP Overview.
The AGF uses the configured values in the services agf amf hierarchy to
initiate a static TNLA with the AMF.
The AMF can dynamically request TNLAs to be added or deleted between the AGF and AMF by sending an NGAP AMF configuration update message. The TNLA specifies whether the TNLA will be used for NGAP UE associated signaling, non-UE associated signaling, or both. The AMF specifies the TNLA’s usage type and the weight factor when the TNLA is established. The AMF can dynamically modify the TNLAs usage type or weight factor as needed.
AGF supports the following :
- Multihoming support where one or both endpoints of a SCTP association can have more than one bound IP address.
-
Separate routing instances for each AMF. SCTP communications occurs in the configured AMF routing instance. If a routing instance is not configured, AGF uses the default routing-instance.
-
Up to 10 TNLAs with each AMF. The initial TNLA is a static TNLA. Subsequent TNLAs added by the AMF are dynamic TNLAs.
-
Load balancing of user equipment (UE) across all TNLAs that support UE-associated signaling.
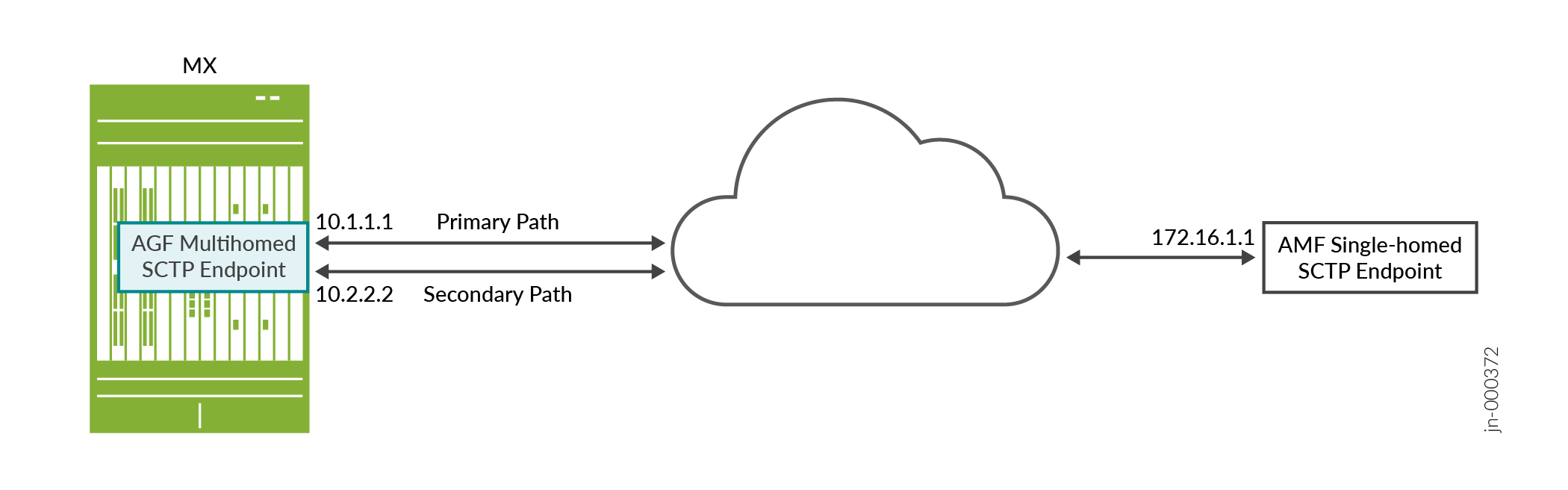
Figure 1 shows a multihomed AGF SCTP endpoint and a single-homed AMF SCTP endpoint. SCTP maintains multiple packet paths between SCTP endpoints. One of the packet paths is designated as the primary path by the SCTP implementation. If the primary path fails, SCTP switches to the secondary path.
Configure the initial TNLA with the AMFs in the [edit services agf amf]
hierarchy.
The following sample configuration shows AGF requesting a TNLA that supports both UE and non-UE associated signalling with a default weight factor of 128.
amf amf1 {
node-id 0;
ip-address 172.16.1.1; # AMF IP address
port 38412; # AMF port number (Defaults to 38412)
local-endpoint {
ip-address 10.1.1.1; # AGF IP address
ip-address 10.2.2.2; # AGF IP address
port 37100; # AGF port number (Defaults to a Junos selected ephemeral port)
initial-tnla-weight-factor 128;
}
default-amf;
}