Configuring Loop Detection for Duplicate MAC Addresses
Understanding Duplicate MAC Address Loop Detection
You can use duplicate MAC address loop detection to detect and resolve loops within the same broadcast domain in an EVPN fabric or between EVPN fabrics. A loop can occur when there is a backdoor path between two provider edge (PE) devices. Because of the backdoor path, PEs could forward a frame back and forth continuously.
There are two types of loops: local and global. A local loop occurs when there is a backdoor path within the same physical interface or between two attachment circuits (ACs) in the same network virtual interface (NVE). A backdoor path can occur when there is a Layer 2 connection between NVEs within an EVPN instance (EVI).
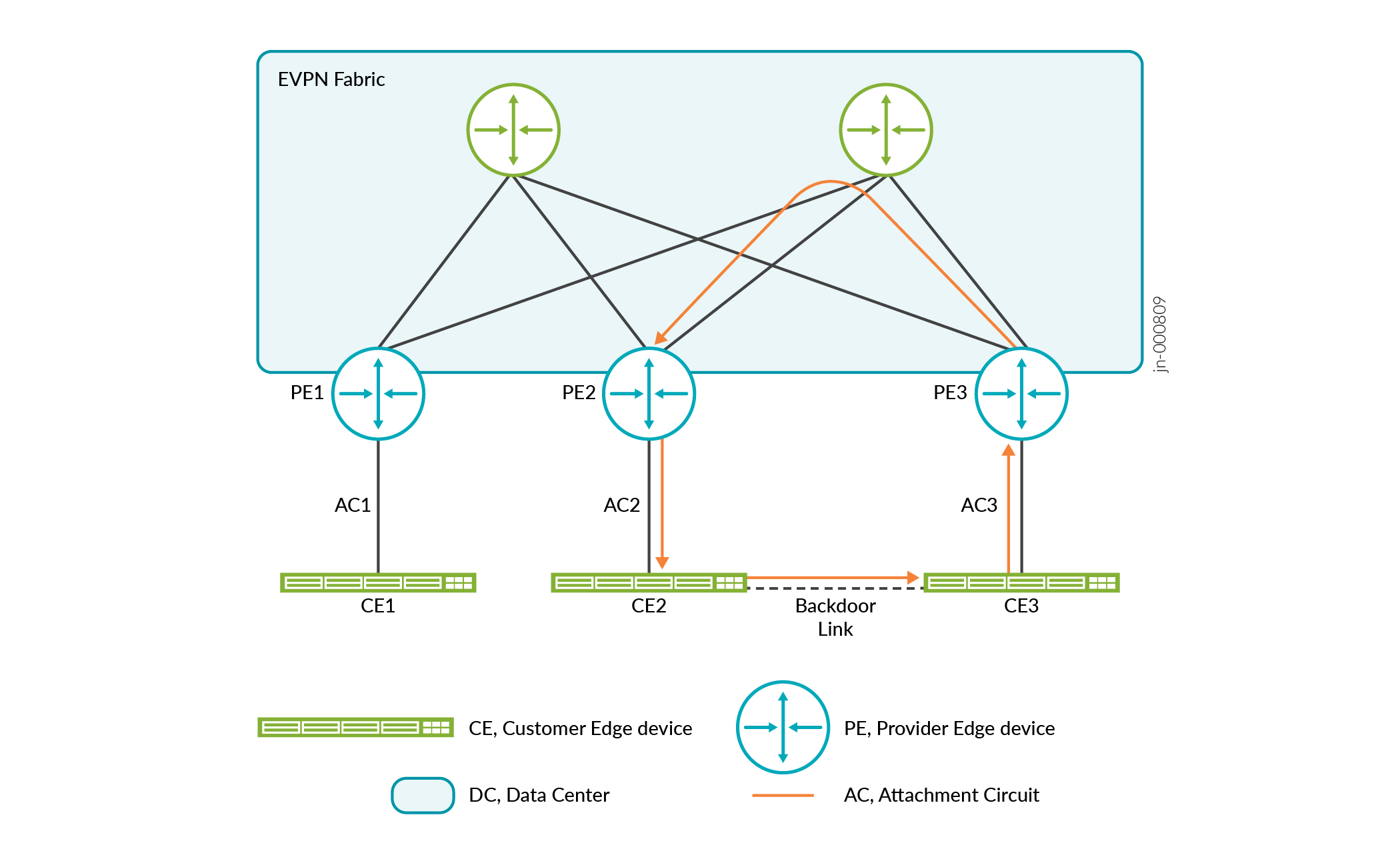
A global loop occurs when there is a backdoor link between two ACs in the same EVI, but the EVIs are located in different NVEs.
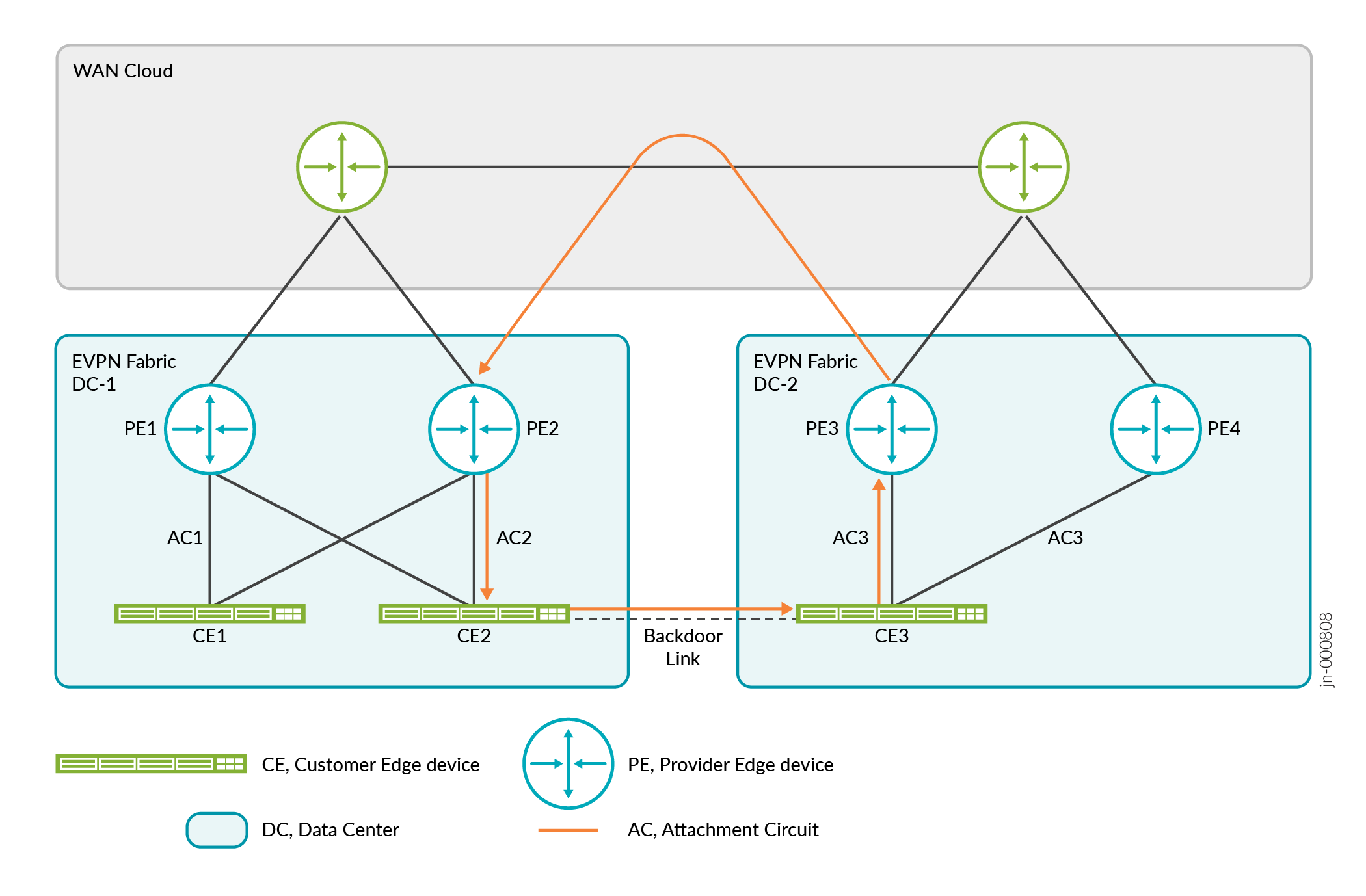
We have enhanced duplicate MAC detection to detect and resolve loops. You can resolve the loops by either blocking duplicate MAC addresses or shutting down the local interfaces associated with the duplicate MAC addresses. For duplicate MAC resolution to work, you also need to configure duplicate MAC address detection.
When a MAC address is marked as a duplicate MAC address, a PE device drops any packet that has a source address or destination address of the duplicate MAC address. Optionally, instead of dropping packets, you could configure a PE device to bring down the attachment circuit on which the frame was last seen.
To block duplicate MAC addresses and shut down their associated local interfaces, enable
the action <block | shutdown> statement at the [edit
routing-instances name protocols evpn duplicate-mac-detection] hierarchy. To
track local MAC address mobility movements, enable the include-local-moves
statement at the [edit routing-instances name protocols evpn
duplicate-mac-detection] hierarchy.
Sample Configurations
- Blocking Duplicate MAC Addresses
- Shutting Down Local Interfaces
- Manually Clearing Duplicate MAC Addresses
- Manually Recovering Interfaces that were Shut Down
Blocking Duplicate MAC Addresses
Here is a sample configuration that shows you how to block duplicate MAC addresses.
set routing-instances rtt1 protocols evpn duplicate-mac-detection detection-threshold 3 set routing-instances rtt1 protocols evpn duplicate-mac-detection detection-window 5 set routing-instances rtt1 protocols evpn duplicate-mac-detection auto-recovery-time 10 set routing-instances rtt1 protocols evpn duplicate-mac-detection action block set routing-instances rtt1 protocols evpn duplicate-mac-detection include-local-moves
Shutting Down Local Interfaces
Here is a sample configuration that shows you how to shut down the local interfaces that are associated with the duplicate MAC addresses.
set routing-instances rtt1 protocols evpn duplicate-mac-detection detection-threshold 3 set routing-instances rtt1 protocols evpn duplicate-mac-detection detection-window 5 set routing-instances rtt1 protocols evpn duplicate-mac-detection action shutdown set interfaces et-0/0/0 unit 0 family ethernet-switching recovery-timeout 10
Manually Clearing Duplicate MAC Addresses
To manually clear the duplicate MAC addresses, issue the clear evpn
duplicate-mac-suppression command.
You can also clear duplicate MAC addresses individually or per Layer 2 domain by issuing the
clear evpn duplicate-mac-suppression l2-domain-id or clear evpn
duplicate-mac-suppression mac-address commands.
Manually Recovering Interfaces that were Shut Down
To manually recover the interface that was shut down, issue the clear ethernet-switching
recovery-timeout command.
