Passive Monitoring
Understanding Passive Monitoring
Passive monitoring is a type of network monitoring used to passively capture traffic from monitoring interfaces. When you enable passive monitoring, the device accepts and monitors traffic on the interface and forwards the traffic to monitoring tools like IDS servers and packet analyzers, or other devices such as routers or end node hosts.
Passive Monitoring Benefits
-
Provides filtering capabilities for monitoring ingress and egress traffic at the Internet point of presence (PoP) where security networks are attached.
Guidelines for Configuring Passive Monitoring
-
You can only configure passive monitoring at the interface level. Configuration per VLAN or logical interface is not supported.
-
A passive monitoring interface cannot be an aggregated Ethernet (AE) interface.
-
Monitoring tools or devices must be directly connected to the switch or router.
-
Packets with more than two MPLS labels and more than two VLAN tags are dropped.
-
Exception packets such as IP packet options, router alert, and TTL expiry packets are treated as regular traffic.
-
Ethernet encapsulation is not supported.
-
MPLS family is supported on the PTX10001-36MR, PTX10004, and PTX10008 routers.
-
Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) is not supported on the AE bundle connected to the monitoring tool or device.
Example: Configuring Passive Monitoring
This example shows how to configure passive monitoring on QFX10000 switches.
- Requirements
- Overview
- Configuration
- Verification
- Sample Configuration for PTX10001-36MR, PTX10004, and PTX10008 Routers
Requirements
This example uses the following hardware and software components:
-
Two routers (R1 and R2)
-
One QFX10002 switch
-
Two devices, directly connected to the switch
-
Junos OS Release 18.4R1 or later
Overview
This example describes how to configure passive monitoring on the switch.
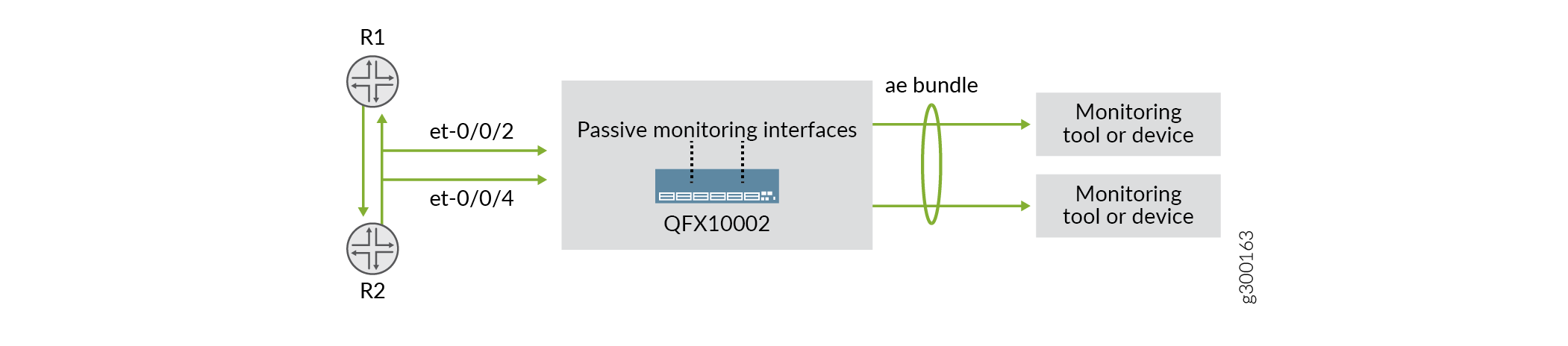
In Figure 1, et-0/0/2 and
et-0/0/4 are configured as passive monitoring interfaces. Packets coming
into the network are exchanged between Router 1 (R1) and Router 2 (R2) in two directions (R1
to R2, R2 to R1) and are sent to the monitored interfaces. When traffic is received, a
firewall filter transfers all packets to a routing instance and forwards the packets to the
monitoring tools. The interfaces are then grouped into a single logical interface, known as
a link aggregation group (LAG) or AE bundle. This enables the traffic to be evenly
distributed across the monitoring tools effectively increasing the uplink bandwidth. If one
interface fails, the bundle continues to carry traffic over the remaining interfaces.
Optionally, you can apply symmetric hashing over the passive monitor interfaces for load
balancing traffic to the monitoring tools. This allows ingress and egress traffic of the
same flow to be sent out through the same monitored interface. To configure symmetric
hashing, include the no-incoming-port option under the [edit
forwarding-options enhanced-hash-key] hierarchy. Symmetric hashing is enabled and
disabled at the global level only. Per protocol hashing is not supported.
Topology
Configuration
The following example requires you to navigate various levels in the CLI hierarchy. For information about navigating the CLI, see Using the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode.
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the following commands, paste them into a text
file, remove any line breaks, change any details necessary to match your network
configuration, copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit]
hierarchy level, and then enter commit from configuration mode.
set interfaces et-0/0/2 passive-monitor-mode set interfaces et-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet filter input pm set interfaces et-0/0/4 passive-monitor-mode set interfaces et-0/0/4 unit 0 family inet filter input pm1 set firewall family inet filter pm1 term t1 from interface et-0/0/4.0 set firewall family inet filter pm1 term t1 then count c1 set firewall family inet filter pm1 term t1 then routing-instance pm_inst set firewall family inet filter pm term t1 from interface et-0/0/2.0 set firewall family inet filter pm term t1 then count c3 set firewall family inet filter pm term t1 then routing-instance pm_inst set routing-instances pm_inst instance-type virtual-router set routing-instances pm_inst interface ae0.0 set routing-instances pm_inst routing-options static route 0.0.0.0/0 next-hop 198.51.100.1 set interfaces xe-0/0/9:0 ether-options 802.3ad ae0 set interfaces xe-0/0/9:1 ether-options 802.3ad ae0 set interfaces ae0 unit 0 family inet address 198.51.100.2/24 arp 198.51.100.1 mac 00:10:94:00:00:05 set routing-instances pm_inst interface ae0.0 set forwarding-options enhanced-hash-key inet no-incoming-port
Configuring Passive Monitoring
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure passive monitoring:
-
Configure passive-monitor mode on the switch interfaces:
[edit]] user@switch# set interfaces et-0/0/2 passive-monitor-mode set interfaces et-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet filter input pm set interfaces et-0/0/4 passive-monitor-mode set interfaces et-0/0/4 unit 0 family inet filter input pm1
-
Configure a
family inetfirewall filter on the passive monitor interfaces to forward the traffic to a routing instance. Supported filter actions areaccept, reject, count, routing-instance.[edit] user@switch# set firewall family inet filter pm1 term t1 from interface et-0/0/4.0 set firewall family inet filter pm1 term t1 then count c1 set firewall family inet filter pm1 term t1 then routing-instance pm_inst set firewall family inet filter pm term t1 from interface et-0/0/2.0 set firewall family inet filter pm term t1 then count c3 set firewall family inet filter pm term t1 then routing-instance pm_inst
-
Create a routing-instance with a static route that points to the devices.
[edit] user@switch# set routing-instances pm_inst instance-type virtual-router set routing-instances pm_inst interface ae0.0 set routing-instances pm_inst routing-options static route 0.0.0.0/0 next-hop 198.51.100.1
-
Configure an AE bundle on the passive monitoring interfaces.
[edit] user@switch# set interfaces xe-0/0/9:0 ether-options 802.3ad ae0 set interfaces xe-0/0/9:1 ether-options 802.3ad ae0 set interfaces ae0 unit 0 family inet address 198.51.100.2/24 arp 198.51.100.1 mac 00:10:94:00:00:05 set routing-instances pm_inst interface ae0.0
-
(Optional) Configure symmetric hashing.
[edit] user@switch# set forwarding-options enhanced-hash-key inet no-incoming-port
-
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration by entering the
show interfacescommand. If the command output does not display the intended configuration, repeat the instructions in this example to correct it. -
If you are done configuring the interfaces, enter
commitfrom configuration mode.
Verification
Confirm that the configuration is working properly.
Verify the Passive Monitoring Configuration
Purpose
Verify that passive monitoring is working on the interfaces. If the interface output
shows No-receive and No-transmit, this means that
passive monitoring is working.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show
interfaces command to view the passive monitoring interfaces.
user@host> show interfaces et-0/0/2
Physical interface: et-0/0/2, Enabled, Physical link is Up
Interface index: 146, SNMP ifIndex: 515
Link-level type: Ethernet, MTU: 1514, LAN-PHY mode, Speed: 40Gbps, BPDU Error: None, Loop Detect PDU Error: None, Ethernet-Switching Error: None, MAC-REWRITE Error: None,
Loopback: Disabled, Source filtering: Disabled, Flow control: Disabled, Media type: Fiber
Device flags : Present Running
Interface flags: SNMP-Traps No-receive No-transmit Internal: 0x4000
Link flags : None
CoS queues : 8 supported, 8 maximum usable queues
Current address: 3c:61:04:75:3c:5d, Hardware address: 3c:61:04:75:3c:5d
Last flapped : 2018-05-17 11:19:05 PDT (00:17:55 ago)
Input rate : 0 bps (0 pps)
Output rate : 0 bps (0 pps)
Active alarms : None
Active defects : None
PCS statistics Seconds
Bit errors 0
Errored blocks 0
Ethernet FEC Mode : NONE
Ethernet FEC statistics Errors
FEC Corrected Errors 0
FEC Uncorrected Errors 0
FEC Corrected Errors Rate 0
FEC Uncorrected Errors Rate 0
PRBS Statistics : Disabled
Interface transmit statistics: Disabled
user@host show interfaces et-0/0/4
Physical interface: et-0/0/4, Enabled, Physical link is Up
Interface index: 146, SNMP ifIndex: 515
Link-level type: Ethernet, MTU: 1514, LAN-PHY mode, Speed: 40Gbps, BPDU Error: None, Loop Detect PDU Error: None, Ethernet-Switching Error: None, MAC-REWRITE Error: None,
Loopback: Disabled, Source filtering: Disabled, Flow control: Disabled, Media type: Fiber
Device flags : Present Running
Interface flags: SNMP-Traps No-receive No-transmit Internal: 0x4000
Link flags : None
CoS queues : 8 supported, 8 maximum usable queues
Current address: 3c:61:04:75:3c:5d, Hardware address: 3c:61:04:75:3c:5d
Last flapped : 2018-05-17 11:19:05 PDT (00:18:17 ago)
Input rate : 0 bps (0 pps)
Output rate : 0 bps (0 pps)
Active alarms : None
Active defects : None
PCS statistics Seconds
Bit errors 0
Errored blocks 0
Ethernet FEC Mode : NONE
Ethernet FEC statistics Errors
FEC Corrected Errors 0
FEC Uncorrected Errors 0
FEC Corrected Errors Rate 0
FEC Uncorrected Errors Rate 0
PRBS Statistics : Disabled
Interface transmit statistics: Disabled
Verify Symmetric Hashing
Purpose
Verify the output for symmetric hashing. The incoming port fields for
inet,inet6 and L2 should all be set to No.
Action
From configuration mode, enter the show forwarding-options
enhanced-hash-key command.
Slot 0
Seed value for Hash function 0: 3626023417
Seed value for Hash function 1: 3626023417
Seed value for Hash function 2: 3626023417
Seed value for Hash function 3: 3626023417
Inet settings:
--------------
IPV4 dest address: Yes
IPV4 source address: Yes
L4 Dest Port: Yes
L4 Source Port: Yes
Incoming port: No
Inet6 settings:
--------------
IPV6 dest address: Yes
IPV6 source address: Yes
L4 Dest Port: Yes
L4 Source Port: Yes
Incoming port: No
L2 settings:
------------
Dest Mac address: No
Source Mac address: No
Vlan Id: Yes
Inner-vlan Id: No
Incoming port: No
GRE settings:
-------------
Key: No
Protocol: No
MPLS settings:
--------------
MPLS Enabled: Yes
VXLAN settings:
---------------
VXLAN VNID: No
Sample Configuration for PTX10001-36MR, PTX10004, and PTX10008 Routers
The following is a sample configuration for the PTX10001-36MR, PTX10004, and PTX10008 routers with family mpls support.
set interfaces et-0/0/13 passive-monitor-mode set interfaces et-0/0/13 passive-monitor-mode set interfaces et-0/0/13 unit 0 family inet filter input ipv4pmFilter set interfaces et-0/0/13 unit 0 family inet6 filter input ipv6pmFilter set interfaces et-0/0/13 unit 0 family mpls filter input mplspmFilter set interfaces et-0/0/5 ether-options 802.3ad ae0 set interfaces et-0/0/7 ether-options 802.3ad ae0 set interfaces ae0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.1.1/24 arp 192.168.1.10 mac 00:00:00:11:11:11 set interfaces ae0 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001:db8:1::1/64 ndp 2001:db8:1::10 mac 00:00:00:11:11:11 set routing-instances pm_inst routing-options rib pm_inst.inet6.0 static route 0::0/0 next-hop 2001:db8:1::10 set routing-instances pm_inst routing-options static route 0.0.0.0/0 next-hop 192.168.1.10 set routing-instances pm_inst instance-type virtual-router set routing-instances pm_inst interface ae0.0 set firewall family inet filter ipv4pmFilter term t1 then count C1 set firewall family inet filter ipv4pmFilter term t1 then routing-instance pm_inst set firewall family inet6 filter ipv6pmFilter term t2 then count C2 set firewall family inet6 filter ipv6pmFilter term t2 then routing-instance pm_inst set firewall family mpls filter ipv4pmfilter term t1 then count C1 set firewall family mpls filter ipv4pmfilter term t1 then routing-instance pm_inst set firewall family mpls filter ipv4pmfilter term t1 from ip-version ipv4 ip-protocol-except 255 set firewall family mpls filter ipv6pmfilter term t2 then count C2 set firewall family mpls filter ipv6pmfilter term t2 then routing-instance pm_inst set firewall family mpls filter ipv6pmfilter term t2 from ip-version ipv6 next-header-except 255
Change History Table
Feature support is determined by the platform and release you are using. Use Feature Explorer to determine if a feature is supported on your platform.
