Solution Design and Architecture
This validated design focuses on validating a reliable network design that enables the campus and branch locations to connect to the private enterprise data center and the Internet. Figure 1 shows a typical large enterprise network. The WAN edge routers in the remote locations use MPLS tunnels to connect to the enterprise data center WAN edge router at the enterprise headquarters network. An MPLS WAN core network enables redundant high-performance delivery of the centralized services running in the headquarters data center and provides access to the Internet. The VPLS, L2CKT, and L3VPN services are popular L2/L3 VPN connection methods that enterprises use for the MPLS overlay. The enterprise WAN uses OSPF as the IGP, and LDP for MPLS label distribution. Since the WAN transport network must be resilient and robust, MPLS-related high availability protocols such as FA, Bi-Directional Forwarding Detection (BFD), and Equal Cost Multi-Path (ECMP) are used.
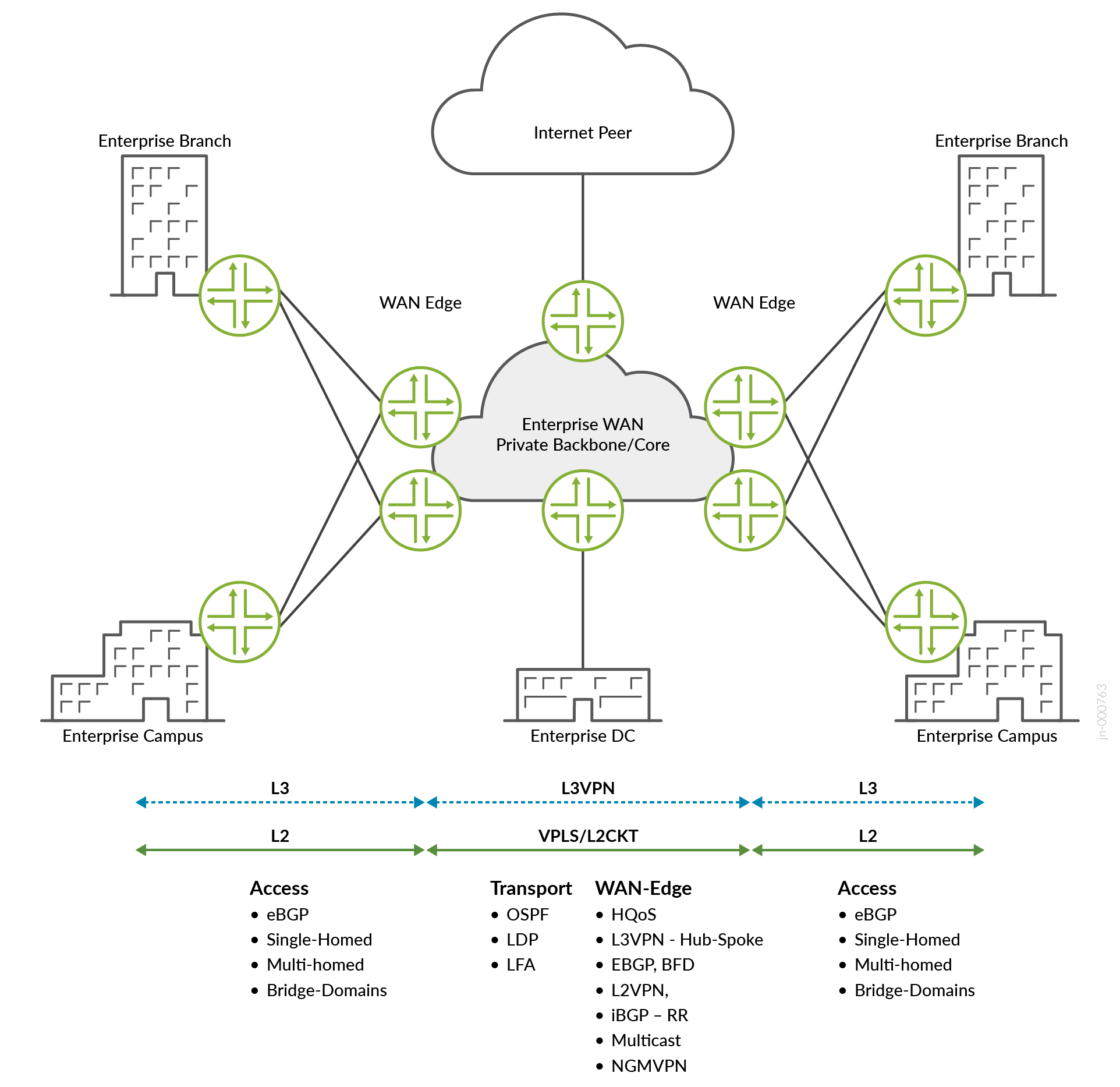
The building blocks of this validated design include: (see Figure 1):
- L2VPN Services
- BGP-VPLS, L2Circuit
- Multihomed Single-Active and Single-Homed
- L3VPN Services with VRRP (Active/Standby)
- L3VPN many-to-many and Hub-Spoke deployment
- HQOS at the IFD Level
- Native multicast
- LDP for label distribution
- Loop Free Alternate (LFA) Fast Reroute
- Internal BGP (IBGP) between Provider Edge (PE) and Route-Reflector (RR) node
- NG-MVPN with S-PMSI
- Fast failover and detection mechanism
- LFA/FRR
- BFD
- OAM
- ECMP
