| IKE Gateway |
|
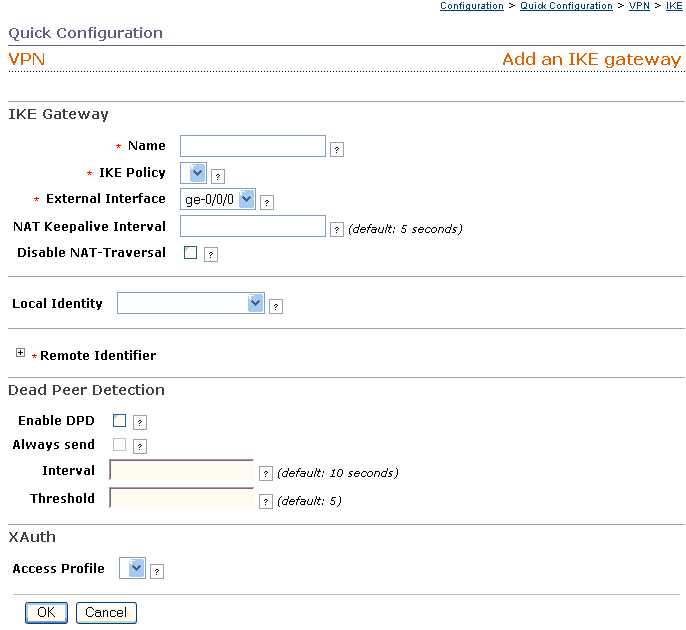
Name
|
Name of the destination peer gateway, specified as an alphanumeric
string
|
Enter a name.
|
|
IKE Policy
|
The IKE policy to be used for communication with the destination
peer gateway.
|
Select the IKE policy to use for the peer gateway
|
|
External Interface
|
Name of the interface to be used to send traffic to the IPsec
VPN.
|
Specify the outgoing interface for IKE SAs. This interface is
associated with a zone that acts as its carrier, providing firewall
security for it.
|
|
NAT Keepalive Interval
|
The interval at which NAT keepalive packets can be sent so that
NAT translation continues.
|
Specify a maximum interval in seconds at which NAT keepalive
packets can be sent.Range: 1 through 300 seconds.Default: 5 seconds.
|
|
Disable NAT Traversal
|
Disables UDP encapsulation of IPsec Encapsulating Security Payload
(ESP) packets, otherwise known as Network Address Translation Traversal
(NAT-T). NAT-T is enabled by default.
|
Click the check box to disable or enable.
|
|
Local Identity
|
The local IKE identity to send in the exchange with the destination
peer so that the destination peer can communicate with the local peer.
If you do not configure a local-identity, the device uses the IP address
corresponding to the local endpoint.You can identify the local identity
in either of the following ways:
- IP Address—IPv4 IP address to identify the dynamic
peer.
- Hostname—Fully qualified domain name (FQDN) to identify
the dynamic peer.
- User at Hostname—E-mail address to identify the
dynamic peer.
- Distinguished Name—Name to identify the dynamic
peer. The distinguished name appears in the subject line of the Public
Key Infrastructure (PKI) certificate. For example: Organization:
juniper, Organizational unit: slt, Common name: common.
|
Specify an IP address, hostname, user-at-hostname, or distinguished
name.
|
|
Remote Identifier
|
Provides information about remote peer.
|
Click the check box to expand the field.
|
|
Address
|
Static address or hostname of remote peer.
|
Specify one primary and up to four backups.
|
|
Dynamic
|
Dynamic address of remote peer.
|
Select.
|
|
Connections limit
|
Maximum number of concurrent connections allowed.
|
Specify the maximum number of concurrent users that can be connected
to the gateway. When the maximum number of connections is reached,
no more dynamic VPN endpoint dial-up users attempting to access an
IPsec VPN are allowed to begin Internet Key Exchange (IKE) negotiations.
|
|
IKE user type
|
- group-ike-id— E-mail address or fully qualified
domain name (FQDN) shared for a group of remote access users so that
each one does not need a separate IKE profile configured.
- shared-ike-id—Email address shared for a large number
of remote access users so that each one does not need a separate IKE
profile configured.
|
Select the type of IKE user for a remote access connection.
|
|
Remote id type
|
Type of identifier for remote peer.
|
Select IP Address, Hostname, User at hostname, or Distinguished
name.
|
|
IP Address
|
Use an IPv4 IP address to identify the dynamic peer.
|
Enter an IP address.
|
|
Hostname
|
Use a fully qualified domain name (FQDN) to identify the dynamic
peer.
|
Select and enter the FQDN.
|
|
User at hostname
|
Use an e-mail address to to identify the dynamic peer.
|
Select and enter the remote identity as an e-mail address.
|
|
Distinguished name
|
Use a distinguished name to identify the dynamic peer. The distinguished
name appears in the subject line of the Public Key Infrastructure
(PKI) certificate. For example: Organization: juniper, Organizational
unit: slt, Common name: common.
|
Select and specify a container or a wildcard.
|
|
container
|
The distinguished name of the remote peer.
|
Enter the distinguished name string exactly as it appears in
the certificate.
|
|
wildcard
|
All or part of the distinguished name of the remote peer.
|
Enter all or parts of a distinguished name, in any order.
|
| Dead Peer
Detection |
|
Enabled DPD
|
RFC 3706 Dead Peer Detection.
|
Click the check box.
|
|
Always Send
|
Instructs the device to send dead peer detection (DPD) requests
regardless of whether there is outgoing IPsec traffic to the peer.
|
Click the check box.
|
|
Interval
|
The amount of time that the peer waits for traffic from its
destination peer before sending a dead peer detection (DPD) request
packet.
|
Enter the interval at which to send DPD messages. Range: 1 through
60 seconds.
|
|
Threshold
|
The maximum number of unsuccessful dead peer detection (DPD)
requests that can be sent before the peer is considered unavailable.
|
Enter the maximum number of unsuccessful DPD requests to be
sent. Range: 1 through 5. Default: 5.
|
| XAuth |
|
Access Profile
|
Provides extended authentication (XAuth), in addition to IKE
authentication for remote users trying to access a VPN tunnel.
|
Select a previously created access profile to reference for
authentication information.
|