Overview of MAC Mobility
MAC mobility describes the scenario where a host moves from one Ethernet segment to another segment in the EVPN network. Provider Edge (PE) devices discover the host MAC address from its local interfaces or from remote PE devices. When a PE device learns of a new local MAC address, it sends a MAC advertisement route message to other devices in the network. During this time, there are two advertised routes and the PE devices in the EVPN network must decide which of the MAC advertisement messages to use.
To determine the correct MAC address location, PE devices use the MAC mobility extended community field, as defined in RFC 7432, in the MAC advertisement route message. The MAC mobility extended community includes a static flag and a sequence number. The static flag identifies pinned MAC addresses that should not be relocated. The sequence number identifies newer MAC advertisement messages. Starting at 0, the sequence number is incremented for every MAC address mobility event. PE devices running Junos OS apply the following precedence order in determining the MAC advertisement route to use:
-
Advertisement routes with a local pinned MAC address (static MAC address).
-
Advertisement routes with a remote pinned MAC address (static MAC address).
-
Advertisement routes with a higher sequence number.
When there are two advertisement route messages for pinned MAC addresses with different routes or two advertisement route messages with the same sequence number, the local device chooses the advertisement route message from the PE device with the lower IP address.
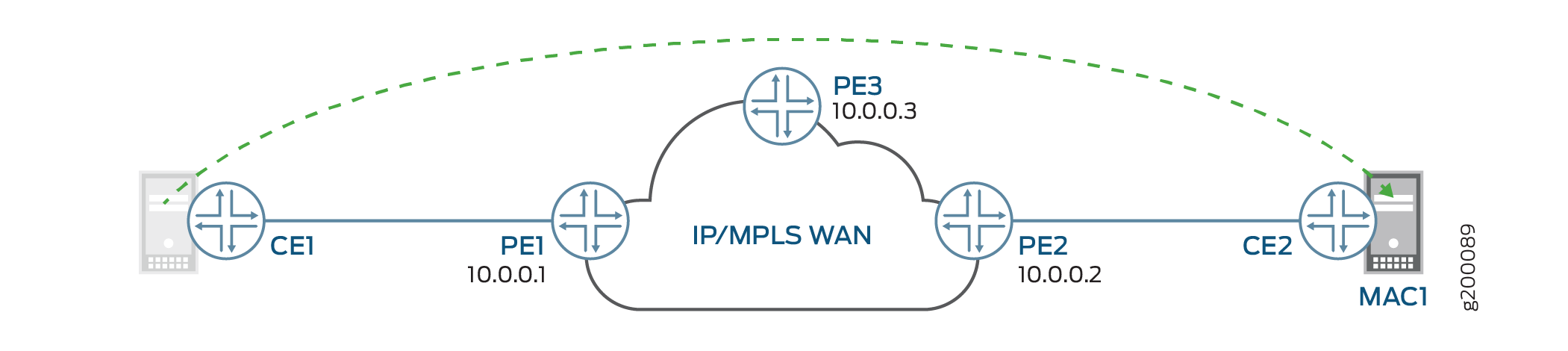
Figure 1 illustrates a network where a MAC address is relocated from PE1 to PE2. Before the move, a MAC advertisement route message sent by PE1 has the active route for all PE devices in the network. After the relocation, PE2 learns of the new local MAC address and sends an updated MAC advertisement route message. Table 1 lists the action taken by each PE device based on the two MAC advertisements. The PE device generates a syslog message when it encounters conflicts with a pinned MAC address.
Table 1 includes use cases with pinned MAC addresses. These use cases do not apply to PE devices that do not support MAC pinning. To determine whether or not MAC pinning is supported by a particular Juniper Networks device or Junos OS release, see Feature Explorer.
|
MAC Advertisement |
PE1 |
PE2 |
PE3 |
|---|---|---|---|
|
PE1: MAC address with a sequence number (n). PE2: MAC address with the sequence number incremented by one (n+1). |
Install the remote MAC advertisement route from PE2 because it has a higher sequence number (n+1). |
Advertise the local MAC route because it has a higher sequence number (n+1). |
Install the remote MAC advertisement route from PE2 because it has a higher sequence number (n+1). |
|
PE1: MAC address with a sequence number (n). PE2: MAC address with the same sequence number (n). |
Advertise the local MAC route because PE1 has the lower IP address (10.0.0.1). |
Install the remote MAC advertisement route from PE1 because PE1 has the lower IP address (10.0.0.1). |
Use the MAC advertisement route from PE1 because PE1 has the lower IP address (10.0.0.1). |
|
PE1: Pinned MAC address with the static bit set. PE2: MAC address and a sequence number (n). |
Advertise the local MAC route because it is a pinned MAC address. Generate a syslog message. |
Install the remote MAC advertisement route from PE1 because it is a pinned MAC address. |
Use the MAC advertisement route from PE1 because it is a pinned MAC address. Generate a syslog message. |
|
PE1: MAC address with a sequence number (n). PE2: Pinned MAC address with the static bit set. |
Install the remote the MAC advertisement route from PE2 because it is a pinned MAC address. |
Advertise local MAC route because it is a pinned MAC address. Generate a syslog message. |
Install the remote MAC advertisement route from PE2 because it is a pinned MAC address. |
|
PE1: Pinned MAC address with static bit set. PE2: Pinned MAC address with static bit set. |
Advertise the local MAC route because it is a local pinned MAC address. Generate a syslog message. |
Advertise the local MAC route because it is a local pinned MAC address. Generate a syslog message. |
Use the MAC advertisement route from PE1 because PE1 has the lower IP address (10.0.0.1). Generate a syslog message. |
Junos supports MAC mobility automatically by default. To disable
MAC mobility, use the set protocols evpn mac-mobility no-sequence-numbers statement.
