Example: Configuring an RFC 2544-Based Benchmarking Test on an MX104 Router for UNI Direction of Ethernet Pseudowires
This example shows how to configure the RFC2544-based benchmarking test for the user-to-network interface (UNI) direction of an Ethernet pseudowire service that is enabled between two routers. The test detects and analyzes the performance of the interconnected routers.
Requirements
MX Series routers support only the reflector function in RFC2544-based benchmarking tests. This example uses the MX104 3D Universal Edge Router as the reflector. You can also configure benchmarking tests on MX80 Series routers and MX240, MX480, and MX960 Series routers with MPC1, MPC2, and 16-port 10-gigabit Ethernet MPC from Junos OS Release 16.1 or later. To configure RFC2544-based benchmarking tests on MX240, MX480, MX960 Series routers, see Enabling Support for RFC 2544-Based Benchmarking Tests on MX Series Routers.
This example uses the following hardware and software components:
-
An MX104 (reflector)
-
An ACX Series router (initiator)
-
Junos OS Release 13.3 or later
Overview
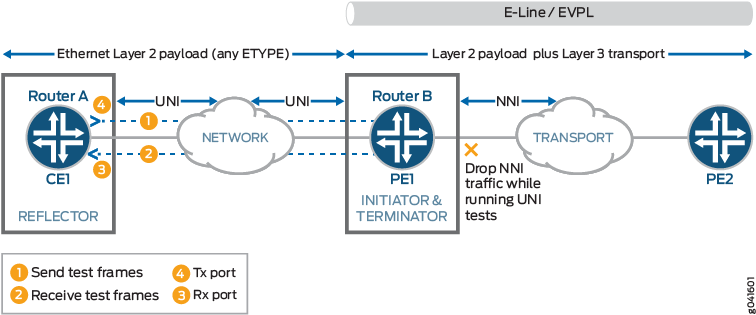
Consider a sample topology in which a router, Router A (MX104), functions as a
reflector of the test frames for an RFC 2544-based benchmarking test. The logical
customer edge (CE)-facing interface and inet family are configured
on Router A. Router A is not part of a pseudowire and therefore, a Layer 3 family
configuration is required on it. Router A, which is a customer edge device CE1 is
connected to Router B (ACX), which functions as a provider edge device PE1 over an
Ethernet pseudowire in the UNI direction with EtherType or Layer 2 Ethernet payload.
The logical interface, family, and UNI direction are configured on Router B. Router
B or PE1 is connected over an Ethernet pseudowire in the NNI direction to a provider
edge device at the remote site, PE2. The link between CE1 and PE1 is an Ethernet
Layer 2 network and it can be configured with any EtherType value. The link between
PE1 and PE2 is an Ethernet line (E-Line) or an Ethernet Private Line (EPL) that has
Layer 2 payload and Layer 3 transport sent over it. Router B or PE1 functions as an
initiator and terminator of the test frames that are sent to Router A and reflected
back from it.
This benchmarking test is used to compute the performance attributes in the user-to-network interface (UNI) direction of an Ethernet pseudowire service between Router A and Router B. Data traffic arriving from a network-to-network interface (NNI) toward the customer edge is ignored while the test is in progress. Packets from the CE are not sent toward the NNI because all packets are assumed to be test probes.
Figure 1 shows the sample topology to perform an RFC 2544 test for the UNI direction of an Ethernet pseudowire service.
Configuration
In this example, you configure the benchmarking test for the UNI direction of an Ethernet pseudowire service that is enabled between two routers to detect and analyze the performance of the interconnected routers.
- CLI Quick Configuration
- Configuring Benchmarking Test Parameters on Router B (Initiator and Terminator)
- Configuring Benchmarking Test Parameters on Router A (Reflector)
- Run the Benchmarking Test
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the following commands, paste them in a
text file, remove any line breaks, change any details necessary to match your
network configuration, and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the
[edit] hierarchy level:
Configuring Benchmarking Test Parameters on Router B (Initiator and Terminator)
set interfaces ge-0/0/0 vlan-tagging set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 vlan-id 101 set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 192.0.2.1/24 set services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking profiles test-profile throughput test-type throughput set services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking profiles test-profile throughput packet-size 64 set services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking profiles test-profile throughput test-duration 20m set services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking profiles test-profile throughput bandwidth-kbps 500 set services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking tests test-name test1 interface ge-0/0/0.0 set services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking tests test-name test1 test-profile throughput set services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking tests test-name test1 mode initiate-and-terminate set services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking tests test-name test1 family inet set services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking tests test-name test1 dest-address 192.0.2.2 set services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking tests test-name test1 udp-port 4001
Configuring Benchmarking Test Parameters on Router A (Reflector)
set interfaces ge-0/0/4 vlan-tagging set interfaces ge-0/0/4 unit 0 encapsulation vlan-ccc set interfaces ge-0/0/4 unit 0 vlan-id 101 set services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking tests test-name test1 interface ge-0/0/4.0 set services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking tests test-name test1 mode reflect set services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking tests test-name test1 mode family ccc set services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking tests test-name test1 direction uni
Configuring Benchmarking Test Parameters on Router B (Initiator and Terminator)
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following require you to navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For information about navigating the CLI, see Using the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode.
To configure the test parameters on Router B:
In configuration mode, go to the
[edit interfaces]hierarchy level:[edit] user@host# edit interfaces
Configure the interface on which the test must be run.
[edit interfaces] user@host# edit ge-0/0/0
Configure VLAN tagging for transmission and reception of 802.1Q VLAN-tagged frames.
[edit interfaces ge-0/0/0] user@host# set vlan-tagging
Configure a logical unit and specify the protocol family as
inet.[edit interfaces ge-0/0/0] user@host# edit unit 0 family inet
Specify the address for the logical interface.
[edit interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet] user@host# set address 192.0.2.1/24
Configure the VLAN ID on the logical interface as 101.
[edit interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0] user@host# set vlan-id 101
Go to the top level of the configuration command mode.
[edit interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0] user@host# top
In configuration mode, go to the
[edit services]hierarchy level.[edit] user@host# edit services
Configure a real-time performance monitoring service (RPM) instance.
[edit services] user@host# edit rpm
Configure an RFC 2544-based benchmarking test for the RPM instance.
[edit services rpm] user@host# edit rfc2544-benchmarking
Define a name for a test profile—for example, throughput.
[edit services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking] user@host# edit profiles test-profile throughput
Configure the type of test to be performed as throughput.
[edit services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking profiles test-profile throughput] user@host# set test-type throughput
Specify the size of the test packet as 64 bytes.
[edit services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking profiles test-profile throughput] user@host# set test-type packet-size 64
Specify the period for which the test is to be performed in hours, minutes, or seconds by specifying a number followed by the letter h (for hours), m (for minutes), or s (for seconds). In this example, you configure the period as 20 minutes.
[edit services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking profiles test-profile throughput] user@host# set test-type test-duration 20m
Define the theoretical maximum bandwidth for the test in kilobits per second, with a value from 1 Kbps through 1,000,000 Kbps.
[edit services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking profiles test-profile throughput] user@host# set test-type bandwidth-kbps 500
Enter the
upcommand to go the previous level in the configuration hierarchy.[edit services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking profiles test-profile throughput] user@host# up
Enter the
upcommand to go the previous level in the configuration hierarchy.[edit services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking profiles] user@host# up
Define a name for the test—for example, test1. The test name identifier can be up to 32 characters in length.
[edit services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking] user@host# edit tests test-name test1
Specify the name of the test profile—for example, throughput—to be associated with a particular test name.
[edit services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking tests test-name test1] user@host# set test-profile throughput
Specify the logical interface, ge-0/0/0.0, on which the RFC 2544-based benchmarking test is run.
[edit services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking tests test-name test1] user@host# set test-interface ge-0/0/0.0
Specify the test mode for the packets that are sent during the benchmarking test as
initiate-and-terminate.[edit services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking tests test-name test1] user@host# set mode initiate-and-terminate
Configure the address type family,
inet, for the benchmarking test.[edit services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking tests test-name test1] user@host# set family inet
Configure the destination IPv4 address for the test packets as 192.0.2.2.
[edit services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking tests test-name test1] user@host# set dest-address 192.0.2.2
Specify the UDP port of the destination to be used in the UDP header for the generated frames as 4001.
[edit services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking tests test-name test1] user@host# set udp-port 4001
Verify the Configuration and Commit
In configuration mode, confirm your configuration on Router B by entering the
show command. If the output does not display the
intended configuration, repeat the configuration instructions in this
example to correct it.
Benchmarking Test Parameters on Router B:
[edit]
user@host# show
[edit interfaces]
ge-0/0/0 {
vlan-tagging;
unit 0 {
vlan-id 101;
family inet {
address 192.0.2.1/24;
}
}
}
[edit services rpm]
rfc2544-benchmarking {
profiles {
test-profile throughput {
test-type throughput
packet-size 64;
test-duration 20m;
bandwidth-kbps 500;
}
}
tests {
test-name test1 {
interface ge-0/0/0.0;
test-profile throughput;
mode initiate-and-terminate;
family inet;
dest-address 192.0.2.2
udp-port 4001;
}
}
}
When the configuration is correct, commit the configuration:
[edit] user@host# commit
Configuring Benchmarking Test Parameters on Router A (Reflector)
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following require you to navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For information about navigating the CLI, see Using the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode.
To configure the test parameters on Router A:
In configuration mode, go to the
[edit interfaces]hierarchy level:[edit] user@host# edit interfaces
Configure the interface on which the test must be run.
[edit interfaces] user@host# edit ge-0/0/4
Configure VLAN tagging for transmission and reception of 802.1Q VLAN-tagged frames.
[edit interfaces ge-0/0/4] user@host# set vlan-tagging
Configure a logical unit for the interface.
[edit interfaces ge-0/0/4] user@host# edit unit 0
Specify the encapsulation for Ethernet VLAN circuits.
[edit interfaces ge-0/0/4 unit 0] user@host# set encapsulation vlan-ccc
Configure the VLAN ID as 101 on the logical interface.
[edit interfaces ge-0/0/4 unit 0] user@host# set vlan-id 101
Go to the top level of the configuration command mode.
[edit interfaces ge-0/0/4 unit 0] user@host# top
In configuration mode, go to the
[edit services]hierarchy level.[edit] user@host# edit services
Configure a real-time performance monitoring service (RPM) instance.
[edit services] user@host# edit rpm
Configure an RFC 2544-based benchmarking test for the RPM instance.
[edit services rpm] user@host# edit rfc2544-benchmarking
Define a name for the test—for example, test1. The test name identifier can be up to 32 characters in length.
[edit services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking] user@host# edit tests test-name test1
Specify the logical interface on which the RFC 2544-based benchmarking test is run.
[edit services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking tests test-name test1] user@host# set test-interface ge-0/0/4.0
Specify
reflectas the test mode for the packets that are sent during the benchmarking test.[edit services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking tests test-name test1] user@host# set mode reflect
Configure the address type family,
ccc, for the benchmarking test.[edit services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking tests test-name test1] user@host# set family ccc
Specify the direction of the interface on which the test must be run, which is UNI in this example.
[edit services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking tests test-name test1] user@host# set direction uni
Verify the Configuration and Commit
In configuration mode, confirm your configuration on Router A by entering the
show command. If the output does not display the
intended configuration, repeat the configuration instructions in this
example to correct it.
Benchmarking Test Parameters on Router A:
[edit]
user@host# show
[edit interfaces]
ge-0/0/4 {
vlan-tagging;
unit 0 {
encapsulation vlan-ccc;
vlan-id 101;
}
}
[edit services rpm]
rfc2544-benchmarking {
# Note, When in reflector mode, test profile is not needed
tests {
test-name test1 {
interface ge-0/0/4.0;
mode reflect;
family ccc;
direction uni;
}
}
}
When the configuration is correct, commit the configuration.
[edit] user@host# commit
Run the Benchmarking Test
-
Start the benchmarking test on the reflector (Router A).
user@host> test services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking test test1 start
The test stops automatically at the initiator (Router B) when the test successfully completes. After the test successfully completes at the initiator, stop the test at the reflector (Router A).
user@host> test services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking test test1 stop
Verifying the Benchmarking Test Results
Examine the results of the benchmarking test that is performed on the configured service between Router A and Router B.
Purpose
Verify that the necessary and desired statistical values are displayed for the benchmarking test that is run on the configured service between Router A and Router B.
Action
In operational mode, enter the show services rpm rfc2544-benchmarking
(aborted-tests | active-tests | completed-tests | summary) command
to display information about the results of each category or state of the RFC
2544-based benchmarking test, such as terminated tests, active tests, and
completed tests, for each real-time performance monitoring (RPM) instance.
Meaning
The output displays the details of the benchmarking test that was performed. For
more information about the show services rpm
rfc2544-benchmarking operational command, see show services
rpm rfc2544-benchmarking in the CLI Explorer.
