Inter-Chassis Stateful Synchronization for Long Lived NAT, Stateful Firewall, and IDS Flows for Next Gen Services
Inter-Chassis Stateful Synchronization Overview
Stateful synchronization replicates the state of long-lived NAT, stateful firewall, and IDS sessions on the primary services PIC and sends it to the backup services PIC, which is on a different MX Series chassis. By default, long lived sessions are defined as having been active on the services PIC for at least 180 seconds, though you can configure this to a higher value.
The following restrictions apply:
NAPT44 is the only translation type supported.
Replicating state information for the port block allocation (PBA), endpoint-independent mapping (EIM), or endpoint-independent filters (EIF) features are supported supported for Next Gen Services.
When configuring a service set for NAT, stateful firewall, or IDS that belongs to a stateful synchronization setup, you must use a next-hop service set, and the NAT, stateful firewall, and IDS configurations for the service set must be identical on both MX Series chassis.
Figure 1 shows the stateful synchronization topology.
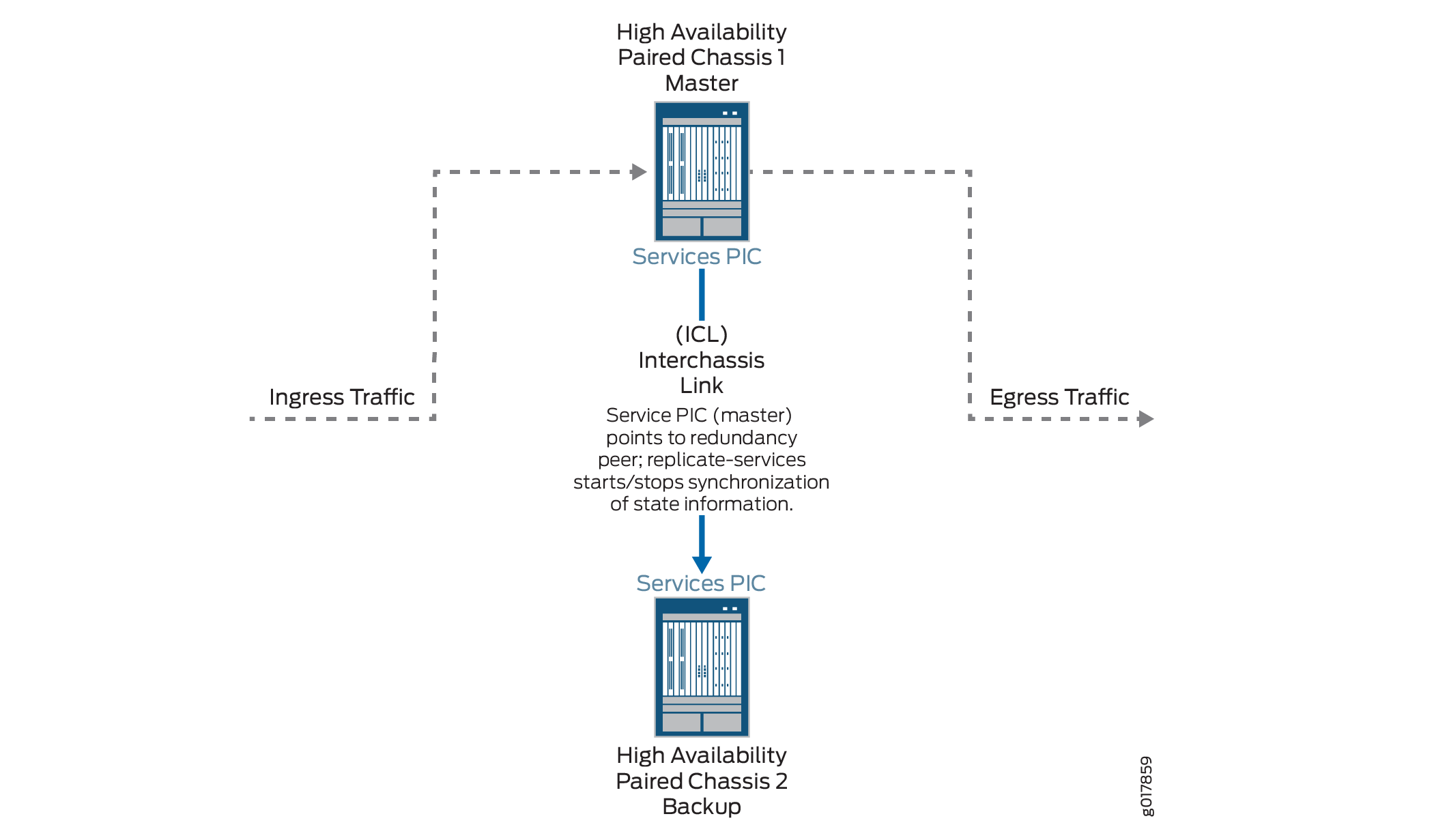
Benefits
Interchassis stateful synchronization of the services session state allows uninterrupted services when a switchover occurs from a services PIC on one chassis to a services PIC on another chassis.
Configuring Inter-Chassis Stateful Synchronization for Long- Lived NAT, Stateful Firewall, and IDS Flows for Next Gen Services
- Configuring Inter-Chassis Stateful Synchronization for Next Gen Services with non-AMS Interface
- Configuring Inter-Chassis Stateful Synchronization for Next Gen Services with AMS Interface
Configuring Inter-Chassis Stateful Synchronization for Next Gen Services with non-AMS Interface
To configure stateful synchronization inter-chassis high availability for NAT, stateful firewall, and IDS flows for Next Gen Services when the services interfaces are not AMS, perform the following configuration steps on each chassis of the high availability pair.
Configuring Inter-Chassis Stateful Synchronization for Next Gen Services with AMS Interface
To configure stateful synchronization inter-chassis high availability for NAT, stateful firewall, and IDS flows for Next Gen Services for an AMS services interface, perform the following configuration steps on each chassis of the high availability pair.
