ON THIS PAGE
Example: Configuring Multitopology Routing to Provide Redundancy for Multicast Traffic over Separate Network Paths
This example shows how to use multitopology routing (MTR) to provide redundancy for multicast traffic over separate network paths. That is, two multicast sources send the same multicast stream, yet for redundancy purposes in the case of link failure, the two streams use disjoint paths.
Note there is no standard defined at this time for using MTR extensions to PIM.
Requirements
No special configuration beyond device initialization is required before configuring this example.
Overview
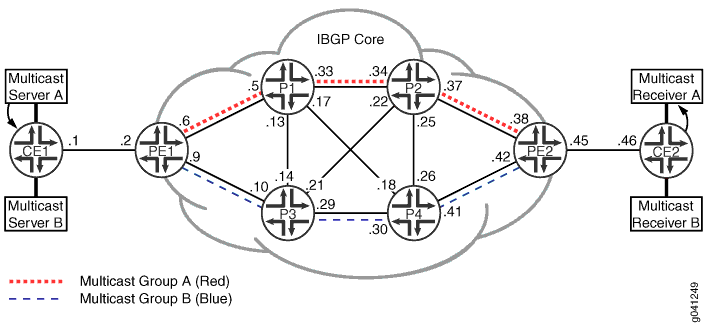
Assume that each source providing redundant multicast streams, S1 and S2, have different IP subnet addresses. Each source sends multicast traffic using different groups: G1 and G2. Further, assume that S1 and S2 are attached to the same customer edge (CE) device and use BGP to announce routes to the provider edge (PE) router.
For a complete set of configurations for all of the devices in the topology, see CLI Quick Configuration. The remainder of the example focuses on Device CE1 and Device PE1.
Figure 1 shows the sample topology.
Configuration
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this
example, copy the following commands, paste them into a text file,
remove any line breaks, change any details necessary to match your
network configuration, and then copy and paste the commands into the
CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
Device CE1
set interfaces fe-0/1/0 fastether-options loopback set interfaces fe-0/1/0 unit 0 family inet address 11.19.130.1/24 set interfaces fe-0/1/0 unit 0 family inet address 11.19.131.1/24 set interfaces fe-0/1/0 unit 0 family inet address 11.19.132.1/24 set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 1 description to-PE1 set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 1 family inet address 10.0.0.1/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 97 family inet address 10.255.165.97/32 primary set protocols bgp group ebgp type external set protocols bgp group ebgp local-address 10.0.0.1 set protocols bgp group ebgp family inet unicast set protocols bgp group ebgp family inet multicast set protocols bgp group ebgp export set_community set protocols bgp group ebgp export inject_directs set protocols bgp group ebgp peer-as 100 set protocols bgp group ebgp neighbor 10.0.0.2 set protocols pim interface fe-0/1/0.0 mode sparse set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/0.1 mode sparse set policy-options policy-statement inject_directs term a from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement inject_directs term a from interface fe-0/1/0.0 set policy-options policy-statement inject_directs term a then next policy set policy-options policy-statement inject_directs term a then accept set policy-options policy-statement inject_directs term b then reject set policy-options policy-statement set_community term a from route-filter 11.19.130.0/24 exact set policy-options policy-statement set_community term a from route-filter 11.19.131.0/24 exact set policy-options policy-statement set_community term a then community add red set policy-options policy-statement set_community term a then accept set policy-options policy-statement set_community term b from route-filter 11.19.132.0/24 exact set policy-options policy-statement set_community term b from route-filter 11.19.133.0/24 exact set policy-options policy-statement set_community term b then community add blue set policy-options policy-statement set_community term b then accept set policy-options policy-statement set_community term default then accept set policy-options community blue members target:50:50 set policy-options community red members target:40:40 set routing-options interface-routes rib-group inet if-rib set routing-options static route 10.0.0.0/16 next-hop 10.0.0.2 set routing-options rib-groups inet.2 import-rib inet.0 set routing-options rib-groups if-rib import-rib inet.0 set routing-options rib-groups if-rib import-rib inet.2 set routing-options rib-groups if-rib import-policy inject_directs set routing-options autonomous-system 101
Device CE2
set interfaces fe-0/1/1 unit 0 set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 46 description to-PE2 set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 46 family inet address 10.0.0.46/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 20 family inet address 10.255.165.20/32 primary set protocols bgp group ebgp type external set protocols bgp group ebgp local-address 10.0.0.46 set protocols bgp group ebgp peer-as 100 set protocols bgp group ebgp neighbor 10.0.0.45 set routing-options autonomous-system 102
Device PE1
set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 2 description to-CE1 set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 2 family inet address 10.0.0.2/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/1 unit 6 description to-P1 set interfaces ge-1/2/1 unit 6 family inet address 10.0.0.6/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/2 unit 9 description to-P3 set interfaces ge-1/2/2 unit 9 family inet address 10.0.0.9/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 93 family inet address 10.255.165.93/32 primary set interfaces lo0 unit 93 family inet address 1.1.1.30/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 93 family inet address 2.2.2.30/32 set protocols bgp group ibgp type internal set protocols bgp group ibgp local-address 10.255.165.93 set protocols bgp group ibgp family inet unicast set protocols bgp group ibgp family inet multicast set protocols bgp group ibgp export nhs_test set protocols bgp group ibgp export nhs_inet0_self set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.255.165.111 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.255.165.203 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.255.165.113 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.255.165.95 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.255.165.99 set protocols bgp group ebgp type external set protocols bgp group ebgp local-address 10.0.0.2 set protocols bgp group ebgp family inet unicast set protocols bgp group ebgp family inet multicast set protocols bgp group ebgp peer-as 101 set protocols bgp group ebgp neighbor 10.0.0.1 set protocols ospf topology red topology-id 126 set protocols ospf topology blue topology-id 52 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/1.6 metric 10 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/1.6 topology blue metric 1 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/1.6 topology red set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/2.9 metric 10 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/2.9 topology red metric 1 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/2.9 topology blue set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.93 passive set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface 1.1.1.30 topology red set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface 1.1.1.30 topology blue disable set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface 2.2.2.30 topology blue set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface 2.2.2.30 topology red disable set protocols pim rib-group inet mcast-rib set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/0.2 mode sparse set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/1.6 mode sparse set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/2.9 mode sparse set policy-options policy-statement nhs_inet0_self term a from protocol bgp set policy-options policy-statement nhs_inet0_self term a from rib inet.0 set policy-options policy-statement nhs_inet0_self term a then next-hop self set policy-options policy-statement nhs_test term a from protocol bgp set policy-options policy-statement nhs_test term a from community red set policy-options policy-statement nhs_test term a then next-hop 1.1.1.30 set policy-options policy-statement nhs_test term a then next policy set policy-options policy-statement nhs_test term a then accept set policy-options policy-statement nhs_test term b from protocol bgp set policy-options policy-statement nhs_test term b from community blue set policy-options policy-statement nhs_test term b then next-hop 2.2.2.30 set policy-options policy-statement nhs_test term b then next policy set policy-options policy-statement nhs_test term b then accept set policy-options policy-statement nhs_test term c then next-hop self set policy-options community blue members target:50:50 set policy-options community red members target:40:40 set routing-options rib-groups mcast-rib import-rib inet.2 set routing-options autonomous-system 100 set routing-options resolution rib inet.2 resolution-ribs :red.inet.0 set routing-options resolution rib inet.2 resolution-ribs :blue.inet.0 set routing-options topologies family inet topology red set routing-options topologies family inet topology blue
Device PE2
set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 38 description to-P2 set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 38 family inet address 10.0.0.38/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/1 unit 42 description to-P4 set interfaces ge-1/2/1 unit 42 family inet address 10.0.0.42/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/2 unit 45 description to-CE2 set interfaces ge-1/2/2 unit 45 family inet address 10.0.0.45/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 203 family inet address 10.255.165.203/32 primary set interfaces lo0 unit 203 family inet address 1.1.1.40/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 203 family inet address 2.2.2.40/32 set protocols bgp group ibgp type internal set protocols bgp group ibgp local-address 10.255.165.203 set protocols bgp group ibgp family inet unicast set protocols bgp group ibgp family inet multicast set protocols bgp group ibgp export nhs_test set protocols bgp group ibgp export nhs_inet0_self set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.255.165.111 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.255.165.93 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.255.165.113 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.255.165.95 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.255.165.99 set protocols bgp group ebgp type external set protocols bgp group ebgp local-address 10.0.0.45 set protocols bgp group ebgp family inet unicast set protocols bgp group ebgp family inet multicast set protocols bgp group ebgp peer-as 102 set protocols bgp group ebgp neighbor 10.0.0.46 set protocols ospf topology red topology-id 126 set protocols ospf topology blue topology-id 52 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/0.38 metric 10 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/0.38 topology blue metric 1 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/0.38 topology red set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/1.42 metric 10 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/1.42 topology red metric 1 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/1.42 topology blue set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.203 passive set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface 1.1.1.40 topology red set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface 1.1.1.40 topology blue disable set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface 2.2.2.40 topology red disable set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface 2.2.2.40 topology blue set protocols pim rib-group inet mcast-rib set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/0.38 mode sparse set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/1.42 mode sparse set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/2.45 mode sparse set policy-options policy-statement nhs then next-hop self set policy-options policy-statement nhs_inet0_self term a from protocol bgp set policy-options policy-statement nhs_inet0_self term a from rib inet.0 set policy-options policy-statement nhs_inet0_self term a then next-hop self set policy-options policy-statement nhs_test term a from protocol bgp set policy-options policy-statement nhs_test term a from community red set policy-options policy-statement nhs_test term a then next-hop 1.1.1.40 set policy-options policy-statement nhs_test term a then next policy set policy-options policy-statement nhs_test term a then accept set policy-options policy-statement nhs_test term b from protocol bgp set policy-options policy-statement nhs_test term b from community blue set policy-options policy-statement nhs_test term b then next-hop 2.2.2.40 set policy-options policy-statement nhs_test term b then next policy set policy-options policy-statement nhs_test term b then accept set policy-options policy-statement nhs_test term c then next-hop self set policy-options community blue members target:50:50 set policy-options community red members target:40:40 set routing-options rib-groups mcast-rib import-rib inet.2 set routing-options autonomous-system 100 set routing-options resolution rib inet.2 resolution-ribs :red.inet.0 set routing-options resolution rib inet.2 resolution-ribs :blue.inet.0 set routing-options topologies family inet topology red set routing-options topologies family inet topology blue
Device P1
set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 5 description to-PE1 set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 5 family inet address 10.0.0.5/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/1 unit 13 description to-P3 set interfaces ge-1/2/1 unit 13 family inet address 10.0.0.13/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/2 unit 17 description to-P4 set interfaces ge-1/2/2 unit 17 family inet address 10.0.0.17/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/3 unit 33 description to-P2 set interfaces ge-1/2/3 unit 33 family inet address 10.0.0.33/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 99 family inet address 10.255.165.99/32 primary set protocols bgp group ibgp type internal set protocols bgp group ibgp local-address 10.255.165.99 set protocols bgp group ibgp family inet unicast set protocols bgp group ibgp family inet multicast set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.255.165.93 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.255.165.111 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.255.165.203 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.255.165.95 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.255.165.113 set protocols ospf topology red topology-id 126 set protocols ospf topology blue topology-id 52 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/3.33 metric 10 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/3.33 topology red set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/3.33 topology blue metric 1 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/2.17 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/1.13 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/0.5 metric 10 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/0.5 topology red set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/0.5 topology blue metric 1 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.99 passive set protocols pim rib-group inet mcast-rib set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/3.33 mode sparse set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/2.17 mode sparse set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/1.13 mode sparse set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/0.5 mode sparse set routing-options rib-groups mcast-rib import-rib inet.2 set routing-options autonomous-system 100 set routing-options topologies family inet topology red set routing-options topologies family inet topology blue
Device P2
set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 22 description to-P3 set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 22 family inet address 10.0.0.22/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/1 unit 25 description to-P4 set interfaces ge-1/2/1 unit 25 family inet address 10.0.0.25/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/2 unit 34 description to-P1 set interfaces ge-1/2/2 unit 34 family inet address 10.0.0.34/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/3 unit 37 description to-PE2 set interfaces ge-1/2/3 unit 37 family inet address 10.0.0.37/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 113 family inet address 10.255.165.113/32 primary set protocols bgp group ibgp type internal set protocols bgp group ibgp local-address 10.255.165.113 set protocols bgp group ibgp family inet unicast set protocols bgp group ibgp family inet multicast set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.255.165.93 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.255.165.111 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.255.165.203 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.255.165.95 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.255.165.99 set protocols ospf topology red topology-id 126 set protocols ospf topology blue topology-id 52 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/2.34 metric 10 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/2.34 topology red set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/2.34 topology blue metric 1 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/0.22 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/1.25 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/3.37 metric 10 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/3.37 topology red set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/3.37 topology blue metric 1 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.113 passive set protocols pim rib-group inet mcast-rib set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/2.34 mode sparse set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/0.22 mode sparse set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/1.25 mode sparse set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/3.37 mode sparse set routing-options rib-groups mcast-rib import-rib inet.2 set routing-options autonomous-system 100 set routing-options topologies family inet topology red set routing-options topologies family inet topology blue
Device P3
set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 10 description to-PE1 set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 10 family inet address 10.0.0.10/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/1 unit 14 description to-P1 set interfaces ge-1/2/1 unit 14 family inet address 10.0.0.14/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/2 unit 21 description to-P2 set interfaces ge-1/2/2 unit 21 family inet address 10.0.0.21/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/3 unit 29 description to-P4 set interfaces ge-1/2/3 unit 29 family inet address 10.0.0.29/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 111 family inet address 10.255.165.111/32 primary set protocols bgp group ibgp type internal set protocols bgp group ibgp local-address 10.255.165.111 set protocols bgp group ibgp family inet unicast set protocols bgp group ibgp family inet multicast set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.255.165.93 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.255.165.113 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.255.165.203 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.255.165.95 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.255.165.99 set protocols ospf topology red topology-id 126 set protocols ospf topology blue topology-id 52 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/3.29 metric 10 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/3.29 topology red metric 1 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/3.29 topology blue set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/2.21 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/1.14 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/0.10 metric 10 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/0.10 topology red metric 1 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/0.10 topology blue set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.111 passive set protocols pim rib-group inet mcast-rib set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/3.29 mode sparse set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/2.21 mode sparse set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/1.14 mode sparse set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/0.10 mode sparse set routing-options rib-groups mcast-rib import-rib inet.2 set routing-options autonomous-system 100 set routing-options topologies family inet topology red set routing-options topologies family inet topology blue
Device P4
set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 18 description to-P1 set interfaces ge-1/2/0 unit 18 family inet address 10.0.0.18/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/1 unit 26 description to-P2 set interfaces ge-1/2/1 unit 26 family inet address 10.0.0.26/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/2 unit 30 description to-P3 set interfaces ge-1/2/2 unit 30 family inet address 10.0.0.30/30 set interfaces ge-1/2/3 unit 41 description to-PE2 set interfaces ge-1/2/3 unit 41 family inet address 10.0.0.41/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 95 family inet address 10.255.165.95/32 primary set protocols bgp group ibgp type internal set protocols bgp group ibgp local-address 10.255.165.95 set protocols bgp group ibgp family inet unicast set protocols bgp group ibgp family inet multicast set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.255.165.93 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.255.165.113 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.255.165.203 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.255.165.111 set protocols bgp group ibgp neighbor 10.255.165.99 set protocols ospf topology red topology-id 126 set protocols ospf topology blue topology-id 52 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/2.30 metric 10 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/2.30 topology red metric 1 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/2.30 topology blue set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/0.18 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/1.26 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/3.41 metric 10 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/3.41 topology red metric 1 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-1/2/3.41 topology blue set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.95 passive set protocols pim rib-group inet mcast-rib set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/2.30 mode sparse set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/0.18 mode sparse set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/1.26 mode sparse set protocols pim interface ge-1/2/3.41 mode sparse set routing-options rib-groups mcast-rib import-rib inet.2 set routing-options autonomous-system 100 set routing-options topologies family inet topology red set routing-options topologies family inet topology blue
Configuring Device CE1
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following example requires you to navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For information about navigating the CLI, see Using the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode in the Junos OS CLI User Guide.
To configure Device CE1:
Configure the interfaces.
For demonstration purposes, the example places an Ethernet interface into loopback mode and configures several addresses on this loopback interface. The addresses are then announced to the network as direct routes. These routes simulate a group of BGP routes with communities attached.
[edit interfaces] user@CE1# set fe-0/1/0 fastether-options loopback user@CE1# set fe-0/1/0 unit 0 family inet address 11.19.130.1/24 user@CE1# set fe-0/1/0 unit 0 family inet address 11.19.131.1/24 user@CE1# set fe-0/1/0 unit 0 family inet address 11.19.132.1/24 user@CE1# set ge-1/2/0 unit 1 description to-PE1 user@CE1# set ge-1/2/0 unit 1 family inet address 10.0.0.1/30 user@CE1# set lo0 unit 97 family inet address 10.255.165.97/32 primary
Configure the external BGP (EBGP) connection to Device PE1.
The CE router nearest to the multicast servers announces the multicast source IP addresses to the PE routers using EBGP. The source addresses are announced with both family inet unicast and family inet multicast, thus causing the BGP route to be added to the default routing table, inet.0, and to the multicast routing table, inet.2. Both sets of routes are injected by the PE router into IBGP.
[edit protocols bgp group ebgp] user@CE1# set type external user@CE1# set local-address 10.0.0.1 user@CE1# set family inet unicast user@CE1# set family inet multicast user@CE1# set peer-as 100 user@CE1# set neighbor 10.0.0.2
Configure PIM on the interfaces.
[edit protocols pim] user@CE1# set interface fe-0/1/0.0 mode sparse user@CE1# set interface ge-1/2/0.1 mode sparse
Configure the routing policy that announces the addresses that are configured on interface fe-0/1/0.
[edit policy-options policy-statement inject_directs] user@CE1# set term a from protocol direct user@CE1# set term a from interface fe-0/1/0.0 user@CE1# set term a then next policy user@CE1# set term a then accept user@CE1# set term b then reject
Configure the routing policy that tags some routes with the red community attribute and other routes with the blue community attribute.
The CE router advertises routes through EBGP to the PE router. These routes are advertised as BGP family inet multicast routes with communities set for two different groups. Policies identify the two groups of BGP routes.
[edit policy-options policy-statement set_community term a] user@CE1# set from route-filter 11.19.130.0/24 exact user@CE1# set from route-filter 11.19.131.0/24 exact user@CE1# set then community add red user@CE1# set then accept [edit policy-options policy-statement set_community term b] user@CE1# set from route-filter 11.19.132.0/24 exact user@CE1# set from route-filter 11.19.133.0/24 exact user@CE1# set then community add blue user@CE1# set then accept [edit policy-options policy-statement set_community term default] user@CE1# set then accept [edit policy-options] user@CE1# set community blue members target:50:50 user@CE1# set community red members target:40:40
Apply the set_community export policy so that the direct routes are exported into BGP.
Apply the inject_directs export policy to announce the addresses that are configured on interface fe-0/1/0.
[edit protocols bgp group ebgp] user@CE1# set export set_community user@CE1# set export inject_directs
Use rib-groups to simulate a group of BGP routes with communities attached and announced as multicast routes.
This configuration creates a multicast routing table and causes PIM to use the multicast routing table inet.2.
[edit routing-options] user@CE1# set interface-routes rib-group inet if-rib user@CE1# set static route 10.0.0.0/16 next-hop 10.0.0.2 [edit routing-options rib-groups] user@CE1# set inet.2 import-rib inet.0 user@CE1# set if-rib import-rib inet.0 user@CE1# set if-rib import-rib inet.2 user@CE1# set if-rib import-policy inject_directs
Configure the autonomous system (AS) number.
[edit routing-options] user@CE1# set autonomous-system 101
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show interfaces, show protocols, show policy-options, and show routing-options commands. If the output does not display the intended configuration,
repeat the instructions in this example to correct the configuration.
user@CE1# show interfaces
fe-0/1/0 {
fastether-options {
loopback;
}
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 11.19.130.1/24;
address 11.19.131.1/24;
address 11.19.132.1/24;
}
}
}
ge-1/2/0 {
unit 1 {
description to-PE1;
family inet {
address 10.0.0.1/30;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 97 {
family inet {
address 10.255.165.97/32 {
primary;
}
}
}
}
user@CE1# show protocols
bgp {
group ebgp {
type external;
local-address 10.0.0.1;
family inet {
unicast;
multicast;
}
export [ set_community inject_directs ];
peer-as 100;
neighbor 10.0.0.2;
}
}
pim {
interface fe-0/1/0.0 {
mode sparse;
}
interface ge-1/2/0.1 {
mode sparse;
}
}
user@CE1# show policy-options
policy-statement inject_directs {
term a {
from {
protocol direct;
interface fe-0/1/0.0;
}
then {
next policy;
accept;
}
}
term b {
then reject;
}
}
policy-statement set_community {
term a {
from {
route-filter 11.19.130.0/24 exact;
route-filter 11.19.131.0/24 exact;
}
then {
community add red;
accept;
}
}
term b {
from {
route-filter 11.19.132.0/24 exact;
route-filter 11.19.133.0/24 exact;
}
then {
community add blue;
accept;
}
}
term default {
then accept;
}
}
community blue members target:50:50;
community red members target:40:40;
user@CE1# show routing-options
interface-routes {
rib-group inet if-rib;
}
static {
route 10.0.0.0/16 next-hop 10.0.0.2;
}
rib-groups {
inet.2 {
import-rib inet.0;
}
if-rib {
import-rib [ inet.0 inet.2 ];
import-policy inject_directs;
}
}
autonomous-system 101;
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Configuring Device PE1
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following example requires you to navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For information about navigating the CLI, see Using the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode in the Junos OS CLI User Guide.
To configure Device PE1:
Configure the interfaces.
[edit interfaces] user@PE1# set ge-1/2/0 unit 2 description to-CE1 user@PE1# set ge-1/2/0 unit 2 family inet address 10.0.0.2/30 user@PE1# set ge-1/2/1 unit 6 description to-P1 user@PE1# set ge-1/2/1 unit 6 family inet address 10.0.0.6/30 user@PE1# set ge-1/2/2 unit 9 description to-P3 user@PE1# set ge-1/2/2 unit 9 family inet address 10.0.0.9/30 user@PE1# set lo0 unit 93 family inet address 10.255.165.93/32 primary
Configure secondary addresses, 1.1.1.30 and 2.2.2.30.
A specific protocol next-hop IP address is required for each topology on each router injecting IBGP routes. You can configure multiple secondary loopback IP addresses on a router to be used as protocol next-hop addresses. This configuration shows nonprimary IP addresses 1.1.1.30/32 and 2.2.2.30/32 configured on loopback interface lo0 for use in the red and blue topologies, respectively.
A group of BGP routes associated with a routing topology use the same unique protocol next hop. For instance, if you configure a PE router to handle two routing topologies, then you would also configure two unique nonprimary addresses under loopback interface lo0.
[edit interfaces] user@PE1# set lo0 unit 93 family inet address 1.1.1.30/32 user@PE1# set lo0 unit 93 family inet address 2.2.2.30/32
Associate each nonprimary loopback IP address with a topology for inclusion in the associated topology routing table.
Configure the loopback IP address and topology under an OSPF interface statement. You must specifically disable all other topologies known to OSPF for two reasons. First, the loopback address specific to a topology must reside in only one topology routing table. Second, once the topology is added to OSPF, the topology defaults to being enabled on all subsequent interfaces under OSPF.
The Device PE1 configuration places the loopback address 1.1.1.30/32 into the OSPF database as a stub route under this router�s OSPF Router-LSA. It belongs to the red and default topologies, but not to the blue topology. The loopback address 1.1.1.30/32 is installed in the remote core routers� topology routing tables inet.0 and :red.inet.0, (but not in :blue.inet.0). Use a similar configuration for the blue loopback address 2.2.2.30/32.
[edit protocols ospf] user@PE1# set topology red topology-id 126 user@PE1# set topology blue topology-id 52 [edit protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0] user@PE1# set interface 1.1.1.30 topology red user@PE1# set interface 1.1.1.30 topology blue disable user@PE1# set interface 2.2.2.30 topology blue user@PE1# set interface 2.2.2.30 topology red disable
Enable OSPF on the interfaces, and configure specific OSPF link metrics on topologies to identify paths and build trees to different servers.
Links can support all routing topologies to provide backup should a primary multicast path fail.
When a multicast tree gets built through PIM join messages directed toward the source, it follows the most preferred path. A multicast tree to a different multicast source (in a different routing topology) can create another tree along a different path.
[edit protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0] user@PE1# set interface ge-1/2/1.6 metric 10 user@PE1# set interface ge-1/2/1.6 topology blue metric 1 user@PE1# set interface ge-1/2/1.6 topology red user@PE1# set interface ge-1/2/2.9 metric 10 user@PE1# set interface ge-1/2/2.9 topology red metric 1 user@PE1# set interface ge-1/2/2.9 topology blue user@PE1# set interface lo0.93 passive
Create the multicast routing table inet.2, and configure PIM to use the inet.2 routing table.
Set up a separate routing table for multicast lookups. It is populated with routes from inet.2. The inet.2 routing table is populated by routes of type multicast.
[edit routing-options] user@PE1# set rib-groups mcast-rib import-rib inet.2
Configure PIM to use the routes in inet.2.
[edit protocols pim] user@PE1# set rib-group inet mcast-rib
Enable PIM on the interfaces.
[edit protocols pim] user@PE1# set interface ge-1/2/0.2 mode sparse user@PE1# set interface ge-1/2/1.6 mode sparse user@PE1# set interface ge-1/2/2.9 mode sparse
Configure the router to perform route resolution on protocol next hops using specified routing tables.
The protocol next hop is used to determine the forwarding next-hop interface out of which to forward PIM join messages. This configuration directs inet.2 route resolution to use topology routing tables :red.inet.0 and :blue.inet.0 for protocol next-hop IP address lookups.
You can specify up to two routing tables in the resolution configuration. A key element to this solution is that the protocol next-hop address resides in only one topology routing table. That is, the protocol next hop belongs to a remote PE secondary loopback address and is injected into only one topology routing table. The route resolution scheme first checks routing table :red.inet.0 for the protocol next-hop address. If the address is found, it uses this entry. If it is not found, the resolution scheme checks routing table :blue.inet.0. Hence, only one topology routing table is used for each protocol nexthop address.
[edit routing-options resolution rib inet.2] user@PE1# set resolution-ribs :red.inet.0 user@PE1# set resolution-ribs :blue.inet.0
Configure the autonomous system (AS) number.
[edit routing-options] user@PE1# set autonomous-system 100
Configure BGP.
[edit protocols bgp group ibgp] user@PE1# set type internal user@PE1# set local-address 10.255.165.93 user@PE1# set family inet unicast user@PE1# set family inet multicast user@PE1# set neighbor 10.255.165.111 user@PE1# set neighbor 10.255.165.203 user@PE1# set neighbor 10.255.165.113 user@PE1# set neighbor 10.255.165.95 user@PE1# set neighbor 10.255.165.99 [edit protocols bgp group ebgp] user@PE1# set type external user@PE1# set local-address 10.0.0.2 user@PE1# set family inet unicast user@PE1# set family inet multicast user@PE1# set peer-as 101 user@PE1# set neighbor 10.0.0.1
Set the protocol next hop when exporting EBGP routes into IBGP.
Configure the ingress Device PE1 router to set the BGP route�s protocol next-hop address when exporting the route into IBGP.
BGP uses an export policy to set the next hop when injecting the EBGP routes into IBGP.
This configuration is an export policy where there are three possibilities of next hops being set. Route 1.1.1.30 is associated with the red topology. Route 2.2.2.30 is associated with the blue topology. For the default next-hop self policy, the primary loopback address 10.255.165.93 on Device PE1 is used.
The nhs_test policy sets the protocol next-hop based on the community in the BGP update.
[edit policy-options] user@PE1# set community blue members target:50:50 user@PE1# set community red members target:40:40 [edit policy-options policy-statement nhs_test term a] user@PE1# set from protocol bgp user@PE1# set from community red user@PE1# set then next-hop 1.1.1.30 user@PE1# set then next policy user@PE1# set then accept [edit policy-options policy-statement nhs_test term b] user@PE1# set from protocol bgp user@PE1# set from community blue user@PE1# set then next-hop 2.2.2.30 user@PE1# set then next policy user@PE1# set then accept user@PE1# set policy-options policy-statement nhs_test term c then next-hop self [edit policy-options policy-statement nhs_inet0_self term a] user@PE1# set from protocol bgp user@PE1# set from rib inet.0 user@PE1# set then next-hop self
Apply the next-hop self policies to the IBGP sessions.
[edit protocols bgp group ibgp] user@PE1# set export nhs_test user@PE1# set export nhs_inet0_self
Configure the voice and video topologies, which enable you to use these topologies with OSPF and BGP.
The names voice and video are local to the router. The names are not propagated beyond this router. However, for management purposes, a consistent naming scheme across routers in a multitopology environment is convenient.
[edit routing-options topologies family inet] user@PE1# set topology red user@PE1# set topology blue
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show interfaces, show protocols, and show routing-options, and show policy-options commands. If the output does not display the intended configuration,
repeat the instructions in this example to correct the configuration.
user@PE1# show interfaces
ge-1/2/0 {
unit 2 {
description to-CE1;
family inet {
address 10.0.0.2/30;
}
}
}
ge-1/2/1 {
unit 6 {
description to-P1;
family inet {
address 10.0.0.6/30;
}
}
}
ge-1/2/2 {
unit 9 {
description to-P3;
family inet {
address 10.0.0.9/30;
}
}
}
lo0 {
unit 93 {
family inet {
address 10.255.165.93/32 {
primary;
}
address 1.1.1.30/32;
address 2.2.2.30/32;
}
}
}
user@PE1# show protocols
bgp {
group ibgp {
type internal;
local-address 10.255.165.93;
family inet {
unicast;
multicast;
}
export [ nhs_test nhs_inet0_self ];
neighbor 10.255.165.111;
neighbor 10.255.165.203;
neighbor 10.255.165.113;
neighbor 10.255.165.95;
neighbor 10.255.165.99;
}
group ebgp {
type external;
local-address 10.0.0.2;
family inet {
unicast;
multicast;
}
peer-as 101;
neighbor 10.0.0.1;
}
}
ospf {
topology red topology-id 126;
topology blue topology-id 52;
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface ge-1/2/1.6 {
metric 10;
topology blue metric 1;
topology red;
}
interface ge-1/2/2.9 {
metric 10;
topology red metric 1;
topology blue;
}
interface lo0.93 {
passive;
}
interface 1.1.1.30 {
topology red;
topology blue disable;
}
interface 2.2.2.30 {
topology blue;
topology red disable;
}
}
}
pim {
rib-group inet mcast-rib;
interface ge-1/2/0.2 {
mode sparse;
}
interface ge-1/2/1.6 {
mode sparse;
}
interface ge-1/2/2.9 {
mode sparse;
}
}
user@PE1# show policy-options
policy-statement nhs_inet0_self {
term a {
from {
protocol bgp;
rib inet.0;
}
then {
next-hop self;
}
}
}
policy-statement nhs_test {
term a {
from {
protocol bgp;
community red;
}
then {
next-hop 1.1.1.30;
next policy;
accept;
}
}
term b {
from {
protocol bgp;
community blue;
}
then {
next-hop 2.2.2.30;
next policy;
accept;
}
}
term c {
then {
next-hop self;
}
}
}
community blue members target:50:50;
community red members target:40:40;
user@PE1# show routing-options
rib-groups {
mcast-rib {
import-rib inet.2;
}
}
autonomous-system 100;
resolution {
rib inet.2 {
resolution-ribs [ :red.inet.0 :blue.inet.0 ];
}
}
topologies {
family inet {
topology red;
topology blue;
}
}
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Verification
Confirm that the configuration is working properly.
- Checking the IBGP routes in inet.2
- Verifying the Routes
- Checking the Resolving BGP Next Hops
- Examining the Protocol Next Hop
- Verifying the OSPF Neighbor
- Checking the Router LSA
- Checking How Traffic Traverses the Network
Checking the IBGP routes in inet.2
Purpose
Make sure that the routes injected into IBGP by Device PE1 have next hops that are based on the topology to which they belong.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show route table extensive command.
user@PE1> show route 11.19.130.0/24 table inet.2 extensive
inet.2: 3 destinations, 3 routes (3 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
11.19.130.0/24 (1 entry, 1 announced)
TSI:
Page 0 idx 0 Type 1 val 93e9768
Flags: Nexthop Change
Nexthop: 1.1.1.30
Localpref: 100
AS path: [100] 101 I
Communities: target:40:40
Path 11.19.130.0 from 10.0.0.1 Vector len 4. Val: 0
*BGP Preference: 170/-101
Next hop type: Router, Next hop index: 1180
Address: 0x94003ec
Next-hop reference count: 16
Source: 10.0.0.1
Next hop: 10.0.0.1 via lt-1/2/0.2, selected
Session Id: 0x380004
State: <Active Ext>
Local AS: 100 Peer AS: 101
Age: 22
Validation State: unverified
Task: BGP_101.10.0.0.1+58346
Announcement bits (1): 0-BGP_RT_Background
AS path: 101 I
Communities: target:40:40
Accepted
Localpref: 100
Router ID: 10.255.165.97Meaning
This output shows an IBGP route in the inet.2 routing table, as seen from Device PE1. The route was originally injected into IBGP by Device PE1, where the next hop was set based on the topology to which the route belonged. The BGP community value determined the topology association.
The route 11.19.130/24 belongs to the red topology because it has a community value of target:40:40. The protocol next hop is 1.1.1.30, and the forwarding next hop is ge-1/2/1.42.
Verifying the Routes
Purpose
Make sure that the routes are in the expected routing tables and that the expected communities are attached to the routes.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show route detail command on Device
PE1.
user@PE1> show route 11.19.130.0/24 detail
inet.0: 29 destinations, 30 routes (29 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
11.19.130.0/24 (1 entry, 1 announced)
*BGP Preference: 170/-101
Next hop type: Router, Next hop index: 812
Address: 0xb9f064c
Next-hop reference count: 22
Source: 10.0.0.1
Next hop: 10.0.0.1 via fe-1/2/0.2, selected
Session Id: 0x600004
State: <Active Ext>
Local AS: 100 Peer AS: 101
Age: 3d 21:44:07
Task: BGP_101.10.0.0.1+51873
Announcement bits (3): 0-KRT 3-BGP_RT_Background 4-Resolve tree 3
AS path: 101 I
Communities: target:40:40
Accepted
Localpref: 100
Router ID: 10.255.165.97
Secondary Tables: :voice.inet.0
:voice.inet.0: 16 destinations, 16 routes (16 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
11.19.130.0/24 (1 entry, 1 announced)
*BGP Preference: 170/-101
Next hop type: Router, Next hop index: 812
Address: 0xb9f064c
Next-hop reference count: 22
Source: 10.0.0.1
Next hop: 10.0.0.1 via fe-1/2/0.2, selected
Session Id: 0x600004
State: <Secondary Active IndepResolution Ext>
Local AS: 100 Peer AS: 101
Age: 3d 21:44:07
Task: BGP_101.10.0.0.1+51873
Announcement bits (2): 0-KRT 1-Resolve tree 1
AS path: 101 I
Communities: target:40:40
Accepted
Localpref: 100
Router ID: 10.255.165.97
Primary Routing Table inet.0
Meaning
This output shows BGP route 11.19.130.0/24 with community value target:40:40. Because the route matches the criteria for the voice topology, it is added to both the default and voice topology routing tables (inet.0 and :voice.inet.0). Device PE1 learns the route from Device CE1 through EBGP and then injects the route into IBGP.
Checking the Resolving BGP Next Hops
Purpose
Check the protocol next hop and forwarding next hop.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show route detail command on Device
PE2.
user@PE2> show route 11.19.130.0/24 detail
inet.0: 29 destinations, 30 routes (29 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
11.19.130.0/24 (1 entry, 1 announced)
*BGP Preference: 170/-101
Next hop type: Indirect
Address: 0xb9f0e04
Next-hop reference count: 12
Source: 10.255.165.93
Next hop type: Router, Next hop index: 262153
Next hop: 10.0.0.37 via fe-1/2/0.38
Session Id: 0x700004
Next hop: 10.0.0.41 via fe-1/2/1.42, selected
Session Id: 0x700005
Protocol next hop: 10.255.165.93
Indirect next hop: bb8c000 262154 INH Session ID: 0x700007
State: <Active Int Ext>
Local AS: 100 Peer AS: 100
Age: 3d 4:27:40 Metric2: 30
Task: BGP_100.10.255.165.93+179
Announcement bits (3): 0-KRT 3-BGP_RT_Background 4-Resolve tree 3
AS path: 101 I
Communities: target:40:40
Accepted
Localpref: 100
Router ID: 10.255.165.93
Secondary Tables: :voice.inet.0
:voice.inet.0: 16 destinations, 16 routes (16 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
11.19.130.0/24 (1 entry, 1 announced)
*BGP Preference: 170/-101
Next hop type: Indirect
Address: 0xb9f0f34
Next-hop reference count: 6
Source: 10.255.165.93
Next hop type: Router, Next hop index: 1188
Next hop: 10.0.0.37 via fe-1/2/0.38, selected
Session Id: 0x700004
Protocol next hop: 10.255.165.93
Indirect next hop: bb8c1d8 262177 INH Session ID: 0x700007
State: <Secondary Active IndepResolution Int Ext>
Local AS: 100 Peer AS: 100
Age: 3d 2:00:20 Metric2: 30
Task: BGP_100.10.255.165.93+179
Announcement bits (2): 0-KRT 1-Resolve tree 1
AS path: 101 I
Communities: target:40:40
Accepted
Localpref: 100
Router ID: 10.255.165.93
Primary Routing Table inet.0Meaning
A typical IBGP core has BGP routes with protocol next hops that resolve using the underlying IGP routes. IBGP routes in a topology routing table have protocol next-hop IP addresses. By default, the same topology routing table is used to look up and resolve the protocol next-hop IP address to a forwarding next hop. This output from Device PE2 shows the same BGP route as seen in the previous example: 11.19.130.0/24. The route is being shown from a different perspective, that is, from Device PE2 as an IBGP route. Similarly, this IBGP route is added to both inet.0 and :voice.inet.0 on Device PE2. However, while each route has the same protocol next hop, each route has a different forwarding next hop (ge-0/0/3.0 instead of ge-0/1/4.0). The reason for this difference is when the protocol next-hop IP address 10.255.165.93 is resolved, it uses the corresponding routing table (inet.0 or :voice.inet.0) to look up the protocol next hop.
Examining the Protocol Next Hop
Purpose
Check the protocol next hop and forwarding next hop.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show route command on Device PE2.
user@PE2> show route 10.255.165.93
inet.0: 29 destinations, 30 routes (29 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
10.255.165.93/32 *[OSPF/10] 3d 04:37:26, metric 30
> to 10.0.0.37 via fe-1/2/0.38
to 10.0.0.41 via fe-1/2/1.42
:voice.inet.0: 16 destinations, 16 routes (16 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
10.255.165.93/32 *[OSPF/10] 3d 02:10:04, metric 30
> to 10.0.0.37 via fe-1/2/0.38
:video.inet.0: 16 destinations, 16 routes (16 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
10.255.165.93/32 *[OSPF/10] 3d 02:03:16, metric 30
> to 10.0.0.41 via fe-1/2/1.42Meaning
This output from Device PE2 shows the protocol next hop of 11.19.130.0/24, which is IP address 10.255.165.93, thus further demonstrating how IBGP route 11.19.130.0/24 resolves its protocol next hop. The forwarding next hops of 10.255.165.93 match the IBGP forwarding next hops of route 11.19.130/24 as shown in the previous example. Observe here that the IP address 10.255.165.93 is also in routing table :video.inet.0. This address is the loopback address of Device PE1, and as such, resides in all three routing tables. This example also shows how traffic entering Device PE2 destined to 11.19.130.0/24 exits different interfaces depending on its associated topology. The actual traffic is marked in such a way that a firewall filter can direct the traffic to use a particular topology routing table.
Verifying the OSPF Neighbor
Purpose
Make sure that the expected topologies are enabled on the OSPF neighbor.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show (ospf | ospf3) neighbor extensive command on Device P2.
user@P2> show ospf neighbor 10.0.0.21 extensive Address Interface State ID Pri Dead 10.0.0.21 fe-1/2/0.22 Full 10.255.165.111 128 39 Area 0.0.0.0, opt 0x52, DR 10.0.0.22, BDR 10.0.0.21 Up 3d 06:09:50, adjacent 3d 06:09:50 Topology default (ID 0) -> Bidirectional Topology video (ID 52) -> Bidirectional
Meaning
This Device P2 output shows OSPF neighbor PE2 (10.0.0.21), where multitopology OSPF default and video are participants. The Bidirectional flag shows that the neighbor is configured using the same multitopology OSPF ID.
Checking the Router LSA
Purpose
Check the links where video and voice topologies are enabled.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show ospf database extensive command
on Device P2.
user@P2> show ospf database lsa-id 10.255.165.203 extensive
OSPF database, Area 0.0.0.0
Type ID Adv Rtr Seq Age Opt Cksum Len
Router 10.255.165.203 10.255.165.203 0x80000063 1552 0x22 0xdff3 80
bits 0x0, link count 3
id 10.255.165.203, data 255.255.255.255, Type Stub (3)
Topology count: 2, Default metric: 0
Topology video (ID 52) -> Metric: 0
Topology voice (ID 126) -> Metric: 0
id 10.0.0.38, data 10.0.0.38, Type Transit (2)
Topology count: 2, Default metric: 10
Topology video (ID 52) -> Metric: 200
Topology voice (ID 126) -> Metric: 10
id 10.0.0.42, data 10.0.0.42, Type Transit (2)
Topology count: 1, Default metric: 10
Topology video (ID 52) -> Metric: 10
Topology default (ID 0)
Type: Transit, Node ID: 10.0.0.42
Metric: 10, Bidirectional
Type: Transit, Node ID: 10.0.0.38
Metric: 10, Bidirectional
Topology video (ID 52)
Type: Transit, Node ID: 10.0.0.42
Metric: 10, Bidirectional
Type: Transit, Node ID: 10.0.0.38
Metric: 200, Bidirectional
Topology voice (ID 126)
Type: Transit, Node ID: 10.0.0.38
Metric: 10, Bidirectional
Aging timer 00:34:08
Installed 00:25:49 ago, expires in 00:34:08, sent 00:25:47 ago
Last changed 3d 01:45:51 ago, Change count: 10Meaning
This Device P2 output shows the Router-LSA originated by Device PE2. The LSA shows links where video and voice topologies are enabled (in addition to the default topology).
Checking How Traffic Traverses the Network
Purpose
Make sure that the expected paths are used.
Action
From operational mode, enter the traceroute command on Device CE1.
The first example output shows that a traceroute over the voice topology goes from Device CE1 to Device CE2 where DSCPs are set. The routes are resolved over :voice.inet.0. This traceroute path follows the voice path CE1-PE1-P1-P2-PE2-CE2.
user@CE1> traceroute 11.19.140.1 source 11.19.130.1 tos 160 traceroute to 11.19.140.1 (11.19.140.1) from 11.19.130.1, 30 hops max, 40 byte packets 1 10.0.0.2 (10.0.0.2) 2.015 ms 1.924 ms 1.770 ms 2 10.0.0.5 (10.0.0.5) 1.890 ms 1.010 ms 0.974 ms 3 10.0.0.34 (10.0.0.34) 0.986 ms 1.031 ms 0.973 ms 4 10.0.0.38 (10.0.0.38) 1.213 ms 1.065 ms 1.154 ms 5 11.19.140.1 (11.19.140.1) 1.696 ms 4.286 ms 1.332 ms
This output shows a traceroute from Device CE1 to Device CE2 for voice where no DSCPs are set. The routes are resolved over inet.0, and the resulting path is different from the previous case where the DSCPs are set. This traceroute path follows the default path CE1-PE1-P4-PE2-CE2.
user@CE1> traceroute 11.19.140.1 source 11.19.130.1 traceroute to 11.19.140.1 (11.19.140.1) from 11.19.130.1, 30 hops max, 40 byte packets 1 10.0.0.2 (10.0.0.2) 1.654 ms 1.710 ms 1.703 ms 2 10.0.0.5 (10.0.0.5) 1.790 ms 1.045 ms 0.975 ms 3 10.0.0.18 (10.0.0.18) 0.989 ms 1.041 ms 0.983 ms 4 10.0.0.42 (10.0.0.42) 0.994 ms 1.036 ms 1.002 ms 5 11.19.140.1 (11.19.140.1) 1.329 ms 2.248 ms 2.225 ms
This output shows a traceroute from Device CE1 to Device CE2 for video traffic where the firewall filter is based on the destination address. The routes are resolved over :video.inet.0. This traceroute follows the video path CE1-PE1-P3-P4-PE2-CE2.
user@CE1> traceroute 11.19.142.1 source 11.19.132.1 traceroute to 11.19.142.1 (11.19.142.1) from 11.19.132.1, 30 hops max, 40 byte packets 1 10.0.0.2 (10.0.0.2) 1.126 ms 1.300 ms 0.995 ms 2 10.0.0.10 (10.0.0.10) 0.981 ms 1.018 ms 0.991 ms 3 10.0.0.30 (10.0.0.30) 0.997 ms 1.886 ms 1.952 ms 4 10.0.0.42 (10.0.0.42) 1.800 ms 1.038 ms 0.980 ms 5 11.19.142.1 (11.19.142.1) 1.367 ms 1.352 ms 1.328 ms
This output shows a traceroute from Device CE1 to Device CE2 for video where DSCPs are set. The DSCP bits are directing Device PE1 to use the topology table :voice.inet.0. Because there is no entry in the voice routing table for the video routes, traffic is dropped.
user@CE1> traceroute 11.19.142.1 source 11.19.132.1 tos 160 traceroute to 11.19.142.1 (11.19.142.1) from 11.19.132.1, 30 hops max, 40 byte packets 1 10.0.0.2 (10.0.0.2) 1.135 ms !N 1.007 ms !N 0.954 ms !N
