ON THIS PAGE
Configuring RSTP on Devices That Support Enhanced Layer 2 Software (ELS)
Example: Configuring Faster Convergence and Network Stability on ELS Devices with RSTP
Example: Faster Convergence and Improved Network Stability with RSTP on EX Series Switches
Forcing RSTP or VSTP to Run as IEEE 802.1D STP (CLI Procedure)
Configuring RSTP
Understanding RSTP
Juniper Networks products use Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) on the network side of devices by default to provide quicker convergence time than the base Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) does. RSTP identifies certain links as point to point. When a point-to-point link fails, the alternate link can transition to the forwarding state, which speeds up convergence.
Benefits of Using RSTP
Some benefits of using the original STP are:
RSTP is faster than STP.
Voice and video work better with RSTP than they do with STP.
RSTP supports more ports than MSTP or VSTP.
RSTP is backward compatible with STP; therefore, switches do not all have to run RSTP.
On MX Series and ACX Series routers, you can configure RSTP, MSTP, and VSTP instance interfaces as edge ports.
Why is RSTP the Default Spanning-Tree Protocol?
RSTP evolved from the original STP IEEE 802.1D protocol to provide faster spanning-tree reconvergence after a switch port, switch, or LAN failure. Where STP took up to 50 seconds to respond to topology changes, RSTP responds to changes within the timeframe of three hello BPDUs (bridge protocol data units), or 6 seconds. This is the primary reason that RSTP is the default spanning-tree configuration.
EX Series switches configured to use STP run RSTP force version 0, which is compatible with STP.
Configuring Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
You can configure Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) under the following hierarchy levels:
-
[edit logical-systems logical-system-name protocols]
-
[edit logical-systems logical-system-name routing-instances routing-instance-name protocols]
-
[edit protocols]
-
[edit routing-instances routing-instance-name protocols]
The routing instance type can be either virtual-switch or layer2-control.
To configure the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol:
Configuring RSTP on Devices That Support Enhanced Layer 2 Software (ELS)
The default spanning-tree protocol on devices that support ELS is Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP). RSTP provides faster convergence times than the original Spanning Tree Protocol (STP).You can configure VSTP and RSTP on a device at the same time. If you have configured MSTP on your device, you cannot configure RSTP on the device. You need to use this procedure only if another spanning-tree protocol is configured on your device.
To enable RSTP:
Example: Configuring Faster Convergence and Network Stability on ELS Devices with RSTP
This example uses Junos OS for EX Series switches with support for the Enhanced Layer 2 Software (ELS) configuration style. If your switch runs software that does not support ELS, see Example: Faster Convergence and Improved Network Stability with RSTP on EX Series Switches. For ELS details, see Using the Enhanced Layer 2 Software CLI.
EX Series switches use Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) by default to provide a loop-free topology.
When switches that support redundant Routing Engines use RSTP, it is important to keep RSTP synchronized on both Routing Engines so that no loss of service occurs after a Routing Engine switchover. Nonstop bridging protocol keeps Routing Engines synchronized.
This example describes how to configure RSTP and NSB on four EX Series switches:
- Requirements
- Overview and Topology
- Configuring RSTP and Nonstop Bridging on Switch 1
- Configuring RSTP and Nonstop Bridging on Switch 2
- Configuring RSTP and Nonstop Bridging on Switch 3
- Configuring RSTP and Nonstop Bridging on Switch 4
- Verification
Requirements
This example uses the following software and hardware components:
Junos OS Release 15.1 or later for EX Series switches
Four EX Series switches
Before you configure the switches for RSTP, be sure you have:
Installed and connected the four switches. See the hardware documentation for your switch.
Performed the initial software configuration on all switches. See Connecting and Configuring an EX Series Switch (CLI Procedure).
Overview and Topology
RSTP works by identifying certain links as point to point links and blocking other possible paths. When one of the point-to-point links fails, a designated alternate link transitions to the forwarding state and take over. Configuring nonstop bridging (NSB) on a switch with redundant Routing Engines keeps RSTP synchronized on both Routing Engines. This way, RSTP remains active immediately after a switchover because it is already synchronized to the backup Routing Engine. RSTP does not have to reconverge after a Routing Engine switchover when NSB is enabled because the neighbor devices do not detect an RSTP change on the switch. In this example, four EX Series switches are connected in the topology displayed in Figure 1 to create a loop-free topology with NSB applied to switches with dual Routing Engines.
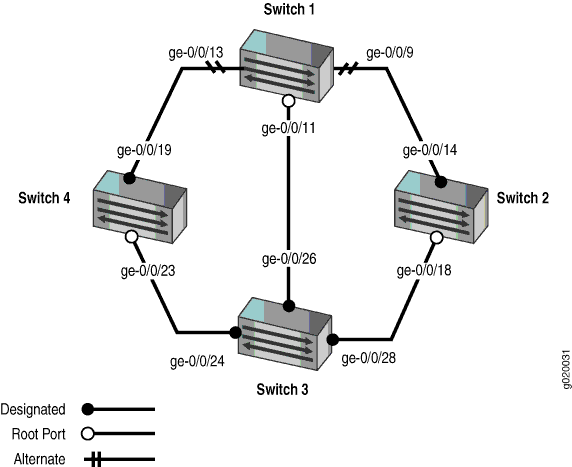
Table 1 shows the components of the topology for this example.
You can configure RSTP only on physical interfaces, not on logical interfaces.
Property |
Settings |
|---|---|
Switch 1 |
The following interfaces on Switch 1 are connected in this way:
|
Switch 2 |
The following interfaces on Switch 2 are connected in this way:
|
Switch 3 |
The following interfaces on Switch 3 are connected in this way:
|
Switch 4 |
The following interfaces on Switch 4 are connected in this way:
|
VLAN names and tag IDs |
voice-vlan, tag 10 employee-vlan, tag 20 guest-vlan, tag 30 camera-vlan, tag 40 |
This configuration example creates a loop-free topology between four EX Series switches using RSTP.
An RSTP topology contains ports that have specific roles:
The root port is responsible for forwarding data to the root bridge.
The alternate port is a standby port for the root port. When a root port goes down, the alternate port becomes the active root port.
The designated port forwards data to the downstream network segment or device.
The backup port is a backup port for the designated port. When a designated port goes down, the backup port becomes the active designated port and starts forwarding data.
You also can create a loop-free topology between the aggregation layer and the distribution layer using redundant trunk links. For more information about configuring redundant trunk links, see Example: Configuring Redundant Trunk Links for Faster Recovery on Devices with ELS Support.
Topology
Configuring RSTP and Nonstop Bridging on Switch 1
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure RSTP and nonstop bridging on Switch 1, copy the following commands and paste them into the switch terminal window:
[edit]
set vlans voice-vlan description “Voice VLAN”
set vlans voice-vlan vlan-id 10
set vlans employee-vlan description “Employee VLAN”
set vlans employee-vlan vlan-id 20
set vlans guest-vlan description “Guest VLAN”
set vlans guest-vlan vlan-id 30
set vlans camera-vlan description “Camera VLAN”
set vlans camera-vlan vlan-id 40
set interfaces ge-0/0/13 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40]
set interfaces ge-0/0/9 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40]
set interfaces ge-0/0/11 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40]
set interfaces ge-0/0/13 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode trunk
set interfaces ge-0/0/9 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode trunk
set interfaces ge-0/0/11 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode trunk
set protocols rstp bridge-priority 16k
set protocols rstp interface all cost 1000
set protocols rstp interface all mode point-to-point If Switch 1 includes dual Routing Engines, configure NSB. To quickly configure nonstop bridging on Switch 1, copy the following commands and paste them into the switch terminal window:
set chassis redundancy graceful-switchover set system commit synchronize set protocols layer2-control nonstop-bridging
NFX150 devices support only a single Routing Engine.
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure RSTP and nonstop bridging on Switch 1:
Configure the VLANs voice-vlan, employee-vlan, guest-vlan, and camera-vlan:
[edit vlans] user@switch1# set voice-vlan description “Voice VLAN” user@switch1# set voice-vlan vlan-id 10 user@switch1# set employee-vlan description “Employee VLAN” user@switch1# set employee-vlan vlan-id 20 user@switch1# set guest-vlan description “Guest VLAN” user@switch1# set guest-vlan vlan-id 30 user@switch1# set camera-vlan description “Camera VLAN” user@switch1# set camera-vlan vlan-id 40Configure the VLANs on the interfaces, including support for the Ethernet switching protocol:
[edit interfaces] user@switch1# set ge-0/0/13 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40] user@switch1# set ge-0/0/9 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40] user@switch1# set ge-0/0/11 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40]Configure the port mode for the interfaces:
[edit interfaces] user@switch1# set ge-0/0/13 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode trunk user@switch1# set ge-0/0/9 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode trunk user@switch1# set ge-0/0/11 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode trunk
Configure RSTP on the switch:
[edit protocols] user@switch1# rstp bridge-priority 16k user@switch1# rstp interface all cost 1000 user@switch1# rstp interface all mode point-to-point
Step-by-Step Procedure
If Switch 1 includes dual Routing Engines, configure nonstop bridging. To configure NSB on Switch 1:
Enable graceful Routing Engine switchover (GRES):
[edit chassis redundancy] user@switch1# set graceful-switchover
Configure the switch to always synchronize configuration changes between the Routing Engines:
[edit system] user@switch1# set commit synchronize
If you try to commit a configuration in which nonstop bridging is configured but synchronization of configuration changes is not configured, the configuration is not committed.
Enable nonstop bridging:
[edit protocols layer2-control] user@switch1# set nonstop-bridging
Note:This process enables NSB for all NSB-supported Layer 2 protocols on the switch, including RSTP.
Results
Check the results of the configuration:
user@switch1> show configuration
interfaces {
ge-0/0/13 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
interface-mode trunk;
vlan {
members [10 20 30 40];
}
}
}
}
ge-0/0/9 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
interface-mode trunk;
vlan {
members [10 20 30 40];
}
}
}
}
ge-0/0/11 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
interface-mode trunk;
vlan {
members [10 20 30 40];
}
}
}
}
}
protocols {
layer2-control {
nonstop-bridging;
}
rstp {
bridge-priority 16k;
interface ge-0/0/13 {
cost 1000;
mode point-to-point;
}
interface ge-0/0/9 {
cost 1000;
mode point-to-point;
}
interface ge-0/0/11 {
cost 1000;
mode point-to-point;
}
}
}
}
vlans {
voice-vlan {
vlan-id 10;
}
employee-vlan {
vlan-id 20;
}
guest-vlan {
vlan-id 30;
}
camera-vlan {
vlan-id 40;
}
}
system {
commit synchronize;
}
chassis {
redundancy {
graceful-switchover;
}
Configuring RSTP and Nonstop Bridging on Switch 2
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure RSTP and nonstop bridging on Switch 2, copy the following commands and paste them into the switch terminal window:
[edit]
set vlans voice-vlan description “Voice VLAN”
set vlans voice-vlan vlan-id 10
set vlans employee-vlan description “Employee VLAN”
set vlans employee-vlan vlan-id 20
set vlans guest-vlan description “Guest VLAN”
set vlans guest-vlan vlan-id 30
set vlans camera-vlan description “Camera VLAN”
set vlans camera-vlan vlan-id 40
set interfaces ge-0/0/14 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40]
set interfaces ge-0/0/18 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40]
set interfaces ge-0/0/14 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode trunk
set interfaces ge-0/0/18 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode trunk
set protocols rstp bridge-priority 32k
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/14 cost 1000
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/14 mode point-to-point
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/18 cost 1000
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/18 mode point-to-point Starting with Junos OS Release 15.1 for EX Series and QFX Series switches with support for the Enhanced Layer 2 Software (ELS) configuration style, you can configure spanning tree parameters globally on all spanning tree interfaces. See Configuring RSTP on EX Series Switches (CLI Procedure) for additional information.
If Switch 2 includes dual Routing Engines, configure NSB. To quickly configure nonstop bridging on Switch 2, copy the following commands and paste them into the switch terminal window:
set chassis redundancy graceful-switchover set system commit synchronize set protocols layer2-control nonstop-bridging
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure RSTP and nonstop bridging on Switch 2:
Configure the VLANs voice-vlan, employee-vlan, guest-vlan, and camera-vlan:
[edit vlans] user@switch2# set voice-vlan description “Voice VLAN” user@switch2# set voice-vlan vlan-id 10 user@switch2# set employee-vlan description “Employee VLAN” user@switch2# set employee-vlan vlan-id 20 user@switch2# set guest-vlan description “Guest VLAN” user@switch2# set guest-vlan vlan-id 30 user@switch2# set camera-vlan vlan-description “Camera VLAN” user@switch2# set camera-vlan vlan-id 40Configure the VLANs on the interfaces, including support for the Ethernet switching protocol:
[edit interfaces] user@switch2# set ge-0/0/14 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40] user@switch2# set ge-0/0/18 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40]Configure the port mode for the interfaces:
[edit interfaces] user@switch2# set ge-0/0/14 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode trunk user@switch2# set ge-0/0/18 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode trunk
Configure RSTP on the switch:
[edit protocols] user@switch2# rstp bridge-priority 32k user@switch2# rstp interface ge-0/0/14 cost 1000 user@switch2# rstp interface ge-0/0/14 mode point-to-point user@switch2# rstp interface ge-0/0/18 cost 1000 user@switch2# rstp interface ge-0/0/18 mode point-to-point
Step-by-Step Procedure
If Switch 2 includes dual Routing Engines, configure nonstop bridging. To configure NSB on Switch 2:
Enable graceful Routing Engine switchover (GRES):
[edit chassis redundancy] user@switch2# set graceful-switchover
Configure the switch to always synchronize configuration changes between the Routing Engines:
[edit system] user@switch2# set commit synchronize
If you try to commit a configuration in which nonstop bridging is configured but synchronization of configuration changes is not configured, the configuration is not committed.
Enable nonstop bridging:
[edit protocols layer2-control] user@switch2# set nonstop-bridging
Note:This process enables NSB for all NSB-supported Layer 2 protocols on the switch, including RSTP.
Results
Check the results of the configuration:
user@switch2> show configuration
interfaces {
ge-0/0/14 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
interface-mode trunk;
vlan {
members [10 20 30 40];
}
}
}
}
ge-0/0/18 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
interface-mode trunk;
vlan {
members [10 20 30 40];
}
}
}
}
}
protocols {
layer2-control {
nonstop-bridging;
}
rstp {
bridge-priority 32k;
interface ge-0/0/14 {
cost 1000;
mode point-to-point;
}
interface ge-0/0/18 {
cost 1000;
mode point-to-point;
}
}
}
}
vlans {
voice-vlan {
vlan-id 10;
}
employee-vlan {
vlan-id 20;
}
guest-vlan {
vlan-id 30;
}
camera-vlan {
vlan-id 40;
}
}
system {
commit synchronize;
}
chassis {
redundancy {
graceful-switchover;
}
Configuring RSTP and Nonstop Bridging on Switch 3
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure RSTP and nonstop bridging on Switch 3, copy the following commands and paste them into the switch terminal window:
[edit]
set vlans voice-vlan description “Voice VLAN”
set vlans voice-vlan vlan-id 10
set vlans employee-vlan description “Employee VLAN”
set vlans employee-vlan vlan-id 20
set vlans guest-vlan description “Guest VLAN”
set vlans guest-vlan vlan-id 30
set vlans camera-vlan description “Camera VLAN”
set vlans camera-vlan vlan-id 40
set interfaces ge-0/0/26 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40]
set interfaces ge-0/0/28 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40]
set interfaces ge-0/0/24 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40]
set interfaces ge-0/0/26 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode trunk
set interfaces ge-0/0/28 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode trunk
set interfaces ge-0/0/24 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode trunk
set protocols rstp bridge-priority 8k
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/26 cost 1000
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/26 mode point-to-point
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/28 cost 1000
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/28 mode point-to-point
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/24 cost 1000
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/24 mode point-to-point If Switch 3 includes dual Routing Engines, configure NSB. To quickly configure nonstop bridging on Switch 3, copy the following commands and paste them into the switch terminal window:
set chassis redundancy graceful-switchover set system commit synchronize set protocols layer2-control nonstop-bridging
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure RSTP and nonstop bridging on Switch 3:
Configure the VLANs voice-vlan, employee-vlan, guest-vlan, and camera-vlan:
[edit vlans] user@switch3# set voice-vlan description “Voice VLAN” user@switch3# set voice-vlan vlan-id 10 user@switch3# set employee-vlan description “Employee VLAN” user@switch3# set employee-vlan vlan-id 20 user@switch3# set guest-vlan description “Guest VLAN” user@switch3# set guest-vlan vlan-id 30 user@switch3# set camera-vlan description “Camera VLAN” user@switch3# set camera-vlan vlan-id 40Configure the VLANs on the interfaces, including support for the Ethernet switching protocol:
[edit interfaces] user@switch3# set ge-0/0/26 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40] user@switch3# set ge-0/0/28 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40] user@switch3# set ge-0/0/24 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40]Configure the port mode for the interfaces:
[edit interfaces] user@switch3# set ge-0/0/26 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode trunk user@switch3# set ge-0/0/28 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode trunk user@switch3# set ge-0/0/24 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode trunk
Configure RSTP on the switch:
[edit protocols] user@switch3# rstp bridge-priority 8k user@switch3# rstp interface ge-0/0/26 cost 1000 user@switch3# rstp interface ge-0/0/26 mode point-to-point user@switch3# rstp interface ge-0/0/28 cost 1000 user@switch3# rstp interface ge-0/0/28 mode point-to-point user@switch3# rstp interface ge-0/0/24 cost 1000 user@switch3# rstp interface ge-0/0/24 mode point-to-point
Step-by-Step Procedure
If Switch 3 includes dual Routing Engines, configure nonstop bridging. To configure NSB on Switch 3:
Enable graceful Routing Engine switchover (GRES):
[edit chassis redundancy] user@switch3# set graceful-switchover
Configure the switch to always synchronize configuration changes between the Routing Engines:
[edit system] user@switch3# set commit synchronize
If you try to commit a configuration in which nonstop bridging is configured but synchronization of configuration changes is not configured, the configuration is not committed.
Enable nonstop bridging:
[edit protocols layer2-control] user@switch3# set nonstop-bridging
Note:This process enables NSB for all NSB-supported Layer 2 protocols on the switch, including RSTP.
Results
Check the results of the configuration:
user@switch3> show configuration
interfaces {
ge-0/0/26 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
interface-mode trunk;
vlan {
members [10 20 30 40];
}
}
}
}
ge-0/0/28 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
interface-mode trunk;
vlan {
members [10 20 30 40];
}
}
}
}
ge-0/0/24 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
interface-mode trunk;
vlan {
members [10 20 30 40];
}
}
}
}
}
}
protocols {
layer2-control {
nonstop-bridging;
}
rstp {
bridge-priority 8k;
interface ge-0/0/26 {
cost 1000;
mode point-to-point;
}
interface ge-0/0/28 {
cost 1000;
mode point-to-point;
}
interface ge-0/0/24 {
cost 1000;
mode point-to-point;
}
}
bridge-priority 8k;
}
}
}
}
vlans {
voice-vlan {
vlan-id 10;
}
employee-vlan {
vlan-id 20;
}
guest-vlan {
vlan-id 30;
}
camera-vlan {
vlan-id 40;
}
}
system {
commit synchronize;
}
chassis {
redundancy {
graceful-switchover;
}
Configuring RSTP and Nonstop Bridging on Switch 4
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure RSTP and nonstop bridging on Switch 4, copy the following commands and paste them into the switch terminal window:
[edit]
set vlans voice-vlan description “Voice VLAN”
set vlans voice-vlan vlan-id 10
set vlans employee-vlan description “Employee VLAN”
set vlans employee-vlan vlan-id 20
set vlans guest-vlan description “Guest VLAN”
set vlans guest-vlan vlan-id 30
set vlans camera-vlan description “Camera VLAN”
set vlans camera-vlan vlan-id 40
set interfaces ge-0/0/23 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40]
set interfaces ge-0/0/19 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40]
set interfaces ge-0/0/23 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode trunk
set interfaces ge-0/0/19 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode trunk
set protocols rstp bridge-priority 16k
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/23 cost 1000
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/23 mode point-to-point
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/19 cost 1000
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/19 mode point-to-point If Switch 4 includes dual Routing Engines, configure NSB. To quickly configure nonstop bridging on Switch 4, copy the following commands and paste them into the switch terminal window:
set chassis redundancy graceful-switchover set system commit synchronize set protocols layer2-control nonstop-bridging
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure RSTP and nonstop bridging on Switch 4:
Configure the VLANs voice-vlan, employee-vlan, guest-vlan, and camera-vlan:
[edit vlans] user@switch4# set voice-vlan description “Voice VLAN” user@switch4# set voice-vlan vlan-id 10 user@switch4# set employee-vlan description “Employee VLAN” user@switch4# set employee-vlan vlan-id 20 user@switch4# set guest-vlan description “Guest VLAN” user@switch4# set guest-vlan vlan-id 30 user@switch4# set camera-vlan description “Camera VLAN” user@switch4# set camera-vlan vlan-id 40Configure the VLANs on the interfaces, including support for the Ethernet switching protocol:
[edit interfaces] user@switch4# set ge-0/0/23 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40] user@switch4# set ge-0/0/19 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40]Configure the port mode for the interfaces:
[edit interfaces] user@switch4# set ge-0/0/23 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode trunk user@switch4# set ge-0/0/19 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode trunk
Configure RSTP on the switch:
[edit protocols] user@switch4# rstp bridge-priority 16k user@switch4# rstp interface ge-0/0/23 cost 1000 user@switch4# rstp interface ge-0/0/23 mode point-to-point user@switch4# rstp interface ge-0/0/19 cost 1000 user@switch4# rstp interface ge-0/0/19 mode point-to-point
Step-by-Step Procedure
If Switch 4 includes dual Routing Engines, configure nonstop bridging. To configure NSB on Switch 4:
Enable graceful Routing Engine switchover (GRES):
[edit chassis redundancy] user@switch4# set graceful-switchover
Configure the switch to always synchronize configuration changes between the Routing Engines:
[edit system] user@switch4# set commit synchronize
If you try to commit a configuration in which nonstop bridging is configured but synchronization of configuration changes is not configured, the configuration is not committed.
Enable nonstop bridging:
[edit protocols layer2-control] user@switch4# set nonstop-bridging
Note:This process enables NSB for all NSB-supported Layer 2 protocols on the switch, including RSTP.
Results
Check the results of the configuration:
user@switch4> show configuration
interfaces {
ge-0/0/23 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
interface-mode trunk;
vlan {
members [10 20 30 40];
}
}
}
}
ge-0/0/19 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
interface-mode trunk;
vlan {
members [10 20 30 40];
}
}
}
}
}
protocols {
layer2-control {
nonstop-bridging;
}
rstp {
bridge-priority 16k;
interface ge-0/0/23 {
cost 1000;
mode point-to-point;
}
interface ge-0/0/19 {
cost 1000;
mode point-to-point;
}
}
}
}
vlans {
voice-vlan {
vlan-id 10;
}
employee-vlan {
vlan-id 20;
}
guest-vlan {
vlan-id 30;
}
camera-vlan {
vlan-id 40;
}
}
system {
commit synchronize;
}
chassis {
redundancy {
graceful-switchover;
}
Verification
To confirm that the configuration is working properly, perform these tasks on both Routing Engines:
- Verifying RSTP Configuration on Switch 1
- Verifying RSTP Configuration on Switch 2
- Verifying RSTP Configuration on Switch 3
- Verifying RSTP Configuration on Switch 4
Verifying RSTP Configuration on Switch 1
Purpose
Verify the RSTP configuration on Switch 1.
Action
Use the operational mode command:
user@switch1> show spanning-tree interface
Spanning tree interface parameters for instance 0
Interface Port ID Designated Designated Port State Role
port ID bridge ID Cost
ge-0/0/13 128:526 128:526 16384.0019e25040e0 1000 BLK ALT
ge-0/0/9 128:522 128:522 32768.0019e2503d20 1000 BLK ALT
ge-0/0/11 128:524 128:524 8192.0019e25051e0 1000 FWD ROOT
Meaning
The operational mode command show spanning-tree
interface shows that ge-0/0/13 is in a forwarding
state. The other interfaces on Switch 1 are blocking.
Verifying RSTP Configuration on Switch 2
Purpose
Use this procedure to verify the RSTP configuration on both Switch 2 Routing Engines.
Action
Use the operational mode command:
user@switch2> show spanning-tree interface
Spanning tree interface parameters for instance 0
Interface Port ID Designated Designated Port State Role
port ID bridge ID Cost
ge-0/0/14 128:527 128:527 32768.0019e2503d20 1000 FWD DESG
ge-0/0/18 128:529 128:529 8192.0019e25051e0 1000 FWD ROOT
Meaning
The operational mode command show spanning-tree
interface shows that ge-0/0/18 is in a forwarding
state and is the root port.
Verifying RSTP Configuration on Switch 3
Purpose
Use this procedure to verify the RSTP configuration on both Switch 3 Routing Engines.
Action
Use the operational mode commands:
user@switch3> show spanning-tree interface
Spanning tree interface parameters for instance 0
Interface Port ID Designated Designated Port State Role
port ID bridge ID Cost
ge-0/0/26 128:539 128:539 8192.0019e25051e0 1000 FWD DESG
ge-0/0/28 128:541 128:541 8192.0019e25051e0 1000 FWD DESG
ge-0/0/24 128:537 128:537 8192.0019e25051e0 1000 FWD DESG
Meaning
The operational mode command show spanning-tree
interface shows that no interface is the root interface.
Verifying RSTP Configuration on Switch 4
Purpose
Use this procedure to verify the RSTP configuration on both Switch 4 Routing Engines.
Action
Use the operational mode commands:
user@switch4> show spanning-tree interface
Spanning tree interface parameters for instance 0
Interface Port ID Designated Designated Port State Role
port ID bridge ID Cost
ge-0/0/23 128:536 128:536 8192.0019e25051e0 1000 FWD ROOT
ge-0/0/19 128:532 128:532 16384.0019e25040e0 1000 FWD DESG
Meaning
The operational mode command show spanning-tree
interface shows that interface ge-0/0/23 is the root
interface and forwarding.
Example: Faster Convergence and Improved Network Stability with RSTP on EX Series Switches
EX Series switches use Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) by default to provide a loop-free topology.
When switches that support redundant Routing Engines use RSTP, it is important to keep RSTP synchronized on both Routing Engines so that no loss of service occurs after a Routing Engine switchover. Nonstop bridging protocol keeps Routing Engines synchronized.
This example describes how to configure RSTP and NSB on four EX Series switches:
- Requirements
- Overview and Topology
- Configuring RSTP and Nonstop Bridging on Switch 1
- Configuring RSTP and Nonstop Bridging on Switch 2
- Configuring RSTP and Nonstop Bridging on Switch 3
- Configuring RSTP and Nonstop Bridging on Switch 4
- Verification
Requirements
This example uses the following hardware and software components:
Junos OS Release 11.3 or later for EX Series switches
Four EX Series switches
Before you configure the switches for RSTP, be sure you have:
Installed the four switches. See Connecting and Configuring an EX Series Switch (J-Web Procedure).
Performed the initial software configuration on all switches. See Installing and Connecting an EX3200 Switch.
Overview and Topology
RSTP works by identifying certain links as point to point links and blocking other possible paths. When one of the point-to-point links fails, a designated alternate link transitions to the forwarding state and take over. Configuring nonstop bridging (NSB) on a switch with redundant Routing Engines keeps RSTP synchronized on both Routing Engines. This way, RSTP remains active immediately after a switchover because it is already synchronized to the backup Routing Engine. RSTP does not have to reconverge after a Routing Engine switchover when NSB is enabled because the neighbor devices do not detect an RSTP change on the switch. In this example, four EX Series switches are connected in the topology displayed in Figure 2 to create a loop-free topology with NSB applied to switches with dual Routing Engines.

Table 2 shows the components of the topology for this example.
You can configure RSTP on logical or physical interfaces. This example shows RSTP configured on logical interfaces.
Property |
Settings |
|---|---|
Switch 1 |
The following interfaces on Switch 1 are connected in this way:
|
Switch 2 |
The following interfaces on Switch 2 are connected in this way:
|
Switch 3 |
The following interfaces on Switch 3 are connected in this way:
|
Switch 4 |
The following interfaces on Switch 4 are connected in this way:
|
VLAN names and tag IDs |
voice-vlan, tag 10 employee-vlan, tag 20 guest-vlan, tag 30 camera-vlan, tag 40 |
This configuration example creates a loop-free topology between four EX Series switches using RSTP.
An RSTP topology contains ports that have specific roles:
The root port is responsible for forwarding data to the root bridge.
The alternate port is a standby port for the root port. When a root port goes down, the alternate port becomes the active root port.
The designated port forwards data to the downstream network segment or device.
The backup port is a backup port for the designated port. When a designated port goes down, the backup port becomes the active designated port and starts forwarding data.
You also can create a loop-free topology between the aggregation layer and the distribution layer using redundant trunk links. For more information about configuring redundant trunk links, see Example: Configuring Redundant Trunk Links for Faster Recovery on EX Series Switches.
Topology
Configuring RSTP and Nonstop Bridging on Switch 1
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure RSTP and nonstop bridging on Switch 1, copy the following commands and paste them into the switch terminal window:
[edit]
set vlans voice-vlan description “Voice VLAN”
set vlans voice-vlan vlan-id 10
set vlans employee-vlan description “Employee VLAN”
set vlans employee-vlan vlan-id 20
set vlans guest-vlan description “Guest VLAN”
set vlans guest-vlan vlan-id 30
set vlans camera-vlan description “Camera VLAN”
set vlans camera-vlan vlan-id 40
set interfaces ge-0/0/13 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40]
set interfaces ge–0/0/9 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40]
set interfaces ge–0/0/11 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40]
set interfaces ge–0/0/13 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode trunk
set interfaces ge-0/0/9 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode trunk
set interfaces ge-0/0/11 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode trunk
set protocols rstp bridge-priority 16k
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/13.0 cost 1000
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/13.0 mode point-to-point
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/9.0 cost 1000
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/9.0 mode point-to-point
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/11.0 cost 1000
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/11.0 mode point-to-point If Switch 1 includes dual Routing Engines, configure NSB. To quickly configure nonstop bridging on Switch 1, copy the following commands and paste them into the switch terminal window:
set chassis redundancy graceful-switchover set system commit synchronize set ethernet-switching-options nonstop-bridging
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure RSTP and nonstop bridging on Switch 1:
Configure the VLANs voice-vlan, employee-vlan, guest-vlan, and camera-vlan:
[edit vlans] user@switch1# set voice-vlan description “Voice VLAN” user@switch1# set voice-vlan vlan-id 10 user@switch1# set employee-vlan description “Employee VLAN” user@switch1# set employee-vlan vlan-id 20 user@switch1# set guest-vlan description “Guest VLAN” user@switch1# set guest-vlan vlan-id 30 user@switch1# set camera-vlan description “Camera VLAN” user@switch1# set camera-vlan vlan-id 40Configure the VLANs on the interfaces, including support for the Ethernet switching protocol:
[edit interfaces] user@switch1# set ge-0/0/13 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40] user@switch1# set ge-0/0/9 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40] user@switch1# set ge-0/0/11 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40]Configure the port mode for the interfaces:
[edit interfaces] user@switch1# set ge-0/0/13 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode trunk user@switch1# set ge-0/0/9 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode trunk user@switch1# set ge-0/0/11 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode trunk
Configure RSTP on the switch:
[edit protocols] user@switch1# rstp bridge-priority 16k user@switch1# rstp interface ge-0/0/13.0 cost 1000 user@switch1# rstp interface ge-0/0/13.0 mode point-to-point user@switch1# rstp interface ge-0/0/9.0 cost 1000 user@switch1# rstp interface ge-0/0/9.0 mode point-to-point user@switch1# rstp interface ge-0/0/11.0 cost 1000 user@switch1# rstp interface ge-0/0/11.0 mode point-to-point
Step-by-Step Procedure
If Switch 1 includes dual Routing Engines, configure nonstop bridging. To configure NSB on Switch 1:
Enable graceful Routing Engine switchover (GRES):
[edit chassis redundancy] user@switch1# set graceful-switchover
Configure the switch to always synchronize configuration changes between the Routing Engines:
[edit system] user@switch1# set commit synchronize
If you try to commit a configuration in which nonstop bridging is configured but synchronization of configuration changes is not configured, the configuration is not committed.
Enable nonstop bridging:
[edit ethernet-switching-options] user@switch1# set nonstop-bridging
Note:This process enables NSB for all NSB-supported Layer 2 protocols on the switch, including RSTP.
Results
Check the results of the configuration:
user@switch1> show configuration
interfaces {
ge-0/0/13 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
port-mode trunk;
vlan {
members [10 20 30 40];
}
}
}
}
ge-0/0/9 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
port-mode trunk;
vlan {
members [10 20 30 40];
}
}
}
}
ge-0/0/11 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
port-mode trunk;
vlan {
members [10 20 30 40];
}
}
}
}
}
protocols {
rstp {
bridge-priority 16k;
interface ge-0/0/13.0 {
cost 1000;
mode point-to-point;
}
interface ge-0/0/9.0 {
cost 1000;
mode point-to-point;
}
interface ge-0/0/11.0 {
cost 1000;
mode point-to-point;
}
}
}
}
vlans {
voice-vlan {
vlan-id 10;
}
employee-vlan {
vlan-id 20;
}
guest-vlan {
vlan-id 30;
}
camera-vlan {
vlan-id 40;
}
}
system {
commit synchronize;
}
chassis {
redundancy {
graceful-switchover;
}
ethernet-switching-options {
nonstop-bridging;
}
Configuring RSTP and Nonstop Bridging on Switch 2
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure RSTP and nonstop bridging on Switch 2, copy the following commands and paste them into the switch terminal window:
[edit]
set vlans voice-vlan description “Voice VLAN”
set vlans voice-vlan vlan-id 10
set vlans employee-vlan description “Employee VLAN”
set vlans employee-vlan vlan-id 20
set vlans guest-vlan description “Guest VLAN”
set vlans guest-vlan vlan-id 30
set vlans camera-vlan description “Camera VLAN”
set vlans camera-vlan vlan-id 40
set interfaces ge-0/0/14 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40]
set interfaces ge-0/0/18 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40]
set interfaces ge-0/0/14 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode trunk
set interfaces ge-0/0/18 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode trunk
set protocols rstp bridge-priority 32k
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/14.0 cost 1000
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/14.0 mode point-to-point
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/18.0 cost 1000
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/18.0 mode point-to-point If Switch 2 includes dual Routing Engines, configure NSB. To quickly configure nonstop bridging on Switch 2, copy the following commands and paste them into the switch terminal window:
set chassis redundancy graceful-switchover set system commit synchronize set ethernet-switching-options nonstop-bridging
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure RSTP and nonstop bridging on Switch 2:
Configure the VLANs voice-vlan, employee-vlan, guest-vlan, and camera-vlan:
[edit vlans] user@switch2# set voice-vlan description “Voice VLAN” user@switch2# set voice-vlan vlan-id 10 user@switch2# set employee-vlan description “Employee VLAN” user@switch2# set employee-vlan vlan-id 20 user@switch2# set guest-vlan description “Guest VLAN” user@switch2# set guest-vlan vlan-id 30 user@switch2# set camera-vlan vlan-description “Camera VLAN” user@switch2# set camera-vlan vlan-id 40Configure the VLANs on the interfaces, including support for the Ethernet switching protocol:
[edit interfaces] user@switch2# set ge-0/0/14 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40] user@switch2# set ge-0/0/18 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40]Configure the port mode for the interfaces:
[edit interfaces] user@switch2# set ge-0/0/14 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode trunk user@switch2# set ge-0/0/18 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode trunk
Configure RSTP on the switch:
[edit protocols] user@switch2# rstp bridge-priority 32k user@switch2# rstp interface ge-0/0/14.0 cost 1000 user@switch2# rstp interface ge-0/0/14.0 mode point-to-point user@switch2# rstp interface ge-0/0/18.0 cost 1000 user@switch2# rstp interface ge-0/0/18.0 mode point-to-point
Step-by-Step Procedure
If Switch 2 includes dual Routing Engines, configure nonstop bridging. To configure NSB on Switch 2:
Enable graceful Routing Engine switchover (GRES):
[edit chassis redundancy] user@switch2# set graceful-switchover
Configure the switch to always synchronize configuration changes between the Routing Engines:
[edit system] user@switch2# set commit synchronize
If you try to commit a configuration in which nonstop bridging is configured but synchronization of configuration changes is not configured, the configuration is not committed.
Enable nonstop bridging:
[edit ethernet-switching-options] user@switch2# set nonstop-bridging
Note:This process enables NSB for all NSB-supported Layer 2 protocols on the switch, including RSTP.
Results
Check the results of the configuration:
user@switch2> show configuration
interfaces {
ge-0/0/14 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
port-mode trunk;
vlan {
members [10 20 30 40];
}
}
}
}
ge-0/0/18 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
port-mode trunk;
vlan {
members [10 20 30 40];
}
}
}
}
}
protocols {
rstp {
bridge-priority 32k;
interface ge-0/0/14.0 {
cost 1000;
mode point-to-point;
}
interface ge-0/0/18.0 {
cost 1000;
mode point-to-point;
}
}
}
}
vlans {
voice-vlan {
vlan-id 10;
}
employee-vlan {
vlan-id 20;
}
guest-vlan {
vlan-id 30;
}
camera-vlan {
vlan-id 40;
}
}
system {
commit synchronize;
}
chassis {
redundancy {
graceful-switchover;
}
ethernet-switching-options {
nonstop-bridging;
}
Configuring RSTP and Nonstop Bridging on Switch 3
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure RSTP and nonstop bridging on Switch 3, copy the following commands and paste them into the switch terminal window:
[edit]
set vlans voice-vlan description “Voice VLAN”
set vlans voice-vlan vlan-id 10
set vlans employee-vlan description “Employee VLAN”
set vlans employee-vlan vlan-id 20
set vlans guest-vlan description “Guest VLAN”
set vlans guest-vlan vlan-id 30
set vlans camera-vlan description “Camera VLAN”
set vlans camera-vlan vlan-id 40
set interfaces ge-0/0/26 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40]
set interfaces ge-0/0/28 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40]
set interfaces ge-0/0/24 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40]
set interfaces ge-0/0/26 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode trunk
set interfaces ge-0/0/28 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode trunk
set interfaces ge-0/0/24 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode trunk
set protocols rstp bridge-priority 8k
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/26.0 cost 1000
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/26.0 mode point-to-point
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/28.0 cost 1000
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/28.0 mode point-to-point
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/24.0 cost 1000
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/24.0 mode point-to-point If Switch 3 includes dual Routing Engines, configure NSB. To quickly configure nonstop bridging on Switch 3, copy the following commands and paste them into the switch terminal window:
set chassis redundancy graceful-switchover set system commit synchronize set ethernet-switching-options nonstop-bridging
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure RSTP and nonstop bridging on Switch 3:
Configure the VLANs voice-vlan, employee-vlan, guest-vlan, and camera-vlan:
[edit vlans] user@switch3# set voice-vlan description “Voice VLAN” user@switch3# set voice-vlan vlan-id 10 user@switch3# set employee-vlan description “Employee VLAN” user@switch3# set employee-vlan vlan-id 20 user@switch3# set guest-vlan description “Guest VLAN” user@switch3# set guest-vlan vlan-id 30 user@switch3# set camera-vlan description “Camera VLAN” user@switch3# set camera-vlan vlan-id 40Configure the VLANs on the interfaces, including support for the Ethernet switching protocol:
[edit interfaces] user@switch3# set ge-0/0/26 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40] user@switch3# set ge-0/0/28 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40] user@switch3# set ge-0/0/24 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40]Configure the port mode for the interfaces:
[edit interfaces] user@switch3# set ge-0/0/26 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode trunk user@switch3# set ge-0/0/28 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode trunk user@switch3# set ge-0/0/24 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode trunk
Configure RSTP on the switch:
[edit protocols] user@switch3# rstp bridge-priority 8k user@switch3# rstp interface ge-0/0/26.0 cost 1000 user@switch3# rstp interface ge-0/0/26.0 mode point-to-point user@switch3# rstp interface ge-0/0/28.0 cost 1000 user@switch3# rstp interface ge-0/0/28.0 mode point-to-point user@switch3# rstp interface ge-0/0/24.0 cost 1000 user@switch3# rstp interface ge-0/0/24.0 mode point-to-point
Step-by-Step Procedure
If Switch 3 includes dual Routing Engines, configure nonstop bridging. To configure NSB on Switch 3:
Enable graceful Routing Engine switchover (GRES):
[edit chassis redundancy] user@switch3# set graceful-switchover
Configure the switch to always synchronize configuration changes between the Routing Engines:
[edit system] user@switch3# set commit synchronize
If you try to commit a configuration in which nonstop bridging is configured but synchronization of configuration changes is not configured, the configuration is not committed.
Enable nonstop bridging:
[edit ethernet-switching-options] user@switch3# set nonstop-bridging
Note:This process enables NSB for all NSB-supported Layer 2 protocols on the switch, including RSTP.
Results
Check the results of the configuration:
user@switch3> show configuration
interfaces {
ge-0/0/26 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
port-mode trunk;
vlan {
members [10 20 30 40];
}
}
}
}
ge-0/0/28 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
port-mode trunk;
vlan {
members [10 20 30 40];
}
}
}
}
ge-0/0/24 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
port-mode trunk;
vlan {
members [10 20 30 40];
}
}
}
}
}
}
protocols {
rstp {
bridge-priority 8k;
interface ge-0/0/26.0 {
cost 1000;
mode point-to-point;
}
interface ge-0/0/28.0 {
cost 1000;
mode point-to-point;
}
interface ge-0/0/24.0 {
cost 1000;
mode point-to-point;
}
}
bridge-priority 8k;
}
}
}
}
vlans {
voice-vlan {
vlan-id 10;
}
employee-vlan {
vlan-id 20;
}
guest-vlan {
vlan-id 30;
}
camera-vlan {
vlan-id 40;
}
}
system {
commit synchronize;
}
chassis {
redundancy {
graceful-switchover;
}
ethernet-switching-options {
nonstop-bridging;
}
Configuring RSTP and Nonstop Bridging on Switch 4
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure RSTP and nonstop bridging on Switch 4, copy the following commands and paste them into the switch terminal window:
[edit]
set vlans voice-vlan description “Voice VLAN”
set vlans voice-vlan vlan–id 10
set vlans employee-vlan description “Employee VLAN”
set vlans employee-vlan vlan-id 20
set vlans guest-vlan description “Guest VLAN”
set vlans guest-vlan vlan-id 30
set vlans camera-vlan description “Camera VLAN”
set vlans camera-vlan vlan-id 40
set interfaces ge-0/0/23 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40]
set interfaces ge-0/0/19 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40]
set interfaces ge-0/0/23 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode trunk
set interfaces ge-0/0/19 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode trunk
set protocols rstp bridge-priority 16k
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/23.0 cost 1000
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/23.0 mode point-to-point
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/19.0 cost 1000
set protocols rstp interface ge-0/0/19.0 mode point-to-point If Switch 4 includes dual Routing Engines, configure NSB. To quickly configure nonstop bridging on Switch 4, copy the following commands and paste them into the switch terminal window:
set chassis redundancy graceful-switchover set system commit synchronize set ethernet-switching-options nonstop-bridging
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure RSTP and nonstop bridging on Switch 4:
Configure the VLANs voice-vlan, employee-vlan, guest-vlan, and camera-vlan:
[edit vlans] user@switch4# set voice-vlan description “Voice VLAN” user@switch4# set voice-vlan vlan-id 10 user@switch4# set employee-vlan description “Employee VLAN” user@switch4# set employee-vlan vlan-id 20 user@switch4# set guest-vlan description “Guest VLAN” user@switch4# set guest-vlan vlan-id 30 user@switch4# set camera-vlan description “Camera VLAN” user@switch4# set camera-vlan vlan-id 40Configure the VLANs on the interfaces, including support for the Ethernet switching protocol:
[edit interfaces] user@switch4# set ge-0/0/23 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40] user@switch4# set ge-0/0/19 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members [10 20 30 40]Configure the port mode for the interfaces:
[edit interfaces] user@switch4# set ge-0/0/23 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode trunk user@switch4# set ge-0/0/19 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode trunk
Configure RSTP on the switch:
[edit protocols] user@switch4# rstp bridge-priority 16k user@switch4# rstp interface all cost 1000 user@switch4# rstp interface ge-0/0/23.0 cost 1000 user@switch4# rstp interface ge-0/0/23.0 mode point-to-point user@switch4# rstp interface ge-0/0/19.0 cost 1000 user@switch4# rstp interface ge-0/0/19.0 mode point-to-point
Step-by-Step Procedure
If Switch 4 includes dual Routing Engines, configure nonstop bridging. To configure NSB on Switch 4:
Enable graceful Routing Engine switchover (GRES):
[edit chassis redundancy] user@switch4# set graceful-switchover
Configure the switch to always synchronize configuration changes between the Routing Engines:
[edit system] user@switch4# set commit synchronize
If you try to commit a configuration in which nonstop bridging is configured but synchronization of configuration changes is not configured, the configuration is not committed.
Enable nonstop bridging:
[edit ethernet-switching-options] user@switch4# set nonstop-bridging
Note:This process enables NSB for all NSB-supported Layer 2 protocols on the switch, including RSTP.
Results
Check the results of the configuration:
user@switch4> show configuration
interfaces {
ge-0/0/23 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
port-mode trunk;
vlan {
members [10 20 30 40];
}
}
}
}
ge-0/0/19 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
port-mode trunk;
vlan {
members [10 20 30 40];
}
}
}
}
}
protocols {
rstp {
bridge-priority 16k;
interface ge-0/0/23.0 {
cost 1000;
mode point-to-point;
}
interface ge-0/0/19.0 {
cost 1000;
mode point-to-point;
}
}
}
}
vlans {
voice-vlan {
vlan-id 10;
}
employee-vlan {
vlan-id 20;
}
guest-vlan {
vlan-id 30;
}
camera-vlan {
vlan-id 40;
}
}
system {
commit synchronize;
}
chassis {
redundancy {
graceful-switchover;
}
ethernet-switching-options {
nonstop-bridging;
}
Verification
To confirm that the configuration is working properly, perform these tasks on both Routing Engines:
- Verifying RSTP Configuration on Switch 1
- Verifying RSTP Configuration on Switch 2
- Verifying RSTP Configuration on Switch 3
- Verifying RSTP Configuration on Switch 4
Verifying RSTP Configuration on Switch 1
Purpose
Verify the RSTP configuration on Switch 1.
Action
Use the operational mode command:
user@switch1> show spanning-tree interface
Spanning tree interface parameters for instance 0
Interface Port ID Designated Designated Port State Role
port ID bridge ID Cost
ge-0/0/13.0 128:526 128:526 16384.0019e25040e0 1000 BLK ALT
ge-0/0/9.0 128:522 128:522 32768.0019e2503d20 1000 BLK ALT
ge-0/0/11.0 128:524 128:524 8192.0019e25051e0 1000 FWD ROOT
Meaning
The operational mode command show spanning-tree
interface shows that ge-0/0/13.0 is in a forwarding
state. The other interfaces on Switch 1 are blocking.
Verifying RSTP Configuration on Switch 2
Purpose
Use this procedure to verify the RSTP configuration on both Switch 2 Routing Engines.
Action
Use the operational mode command:
user@switch2> show spanning-tree interface
Spanning tree interface parameters for instance 0
Interface Port ID Designated Designated Port State Role
port ID bridge ID Cost
ge-0/0/14.0 128:527 128:527 32768.0019e2503d20 1000 FWD DESG
ge-0/0/18.0 128:529 128:529 8192.0019e25051e0 1000 FWD ROOT
Meaning
The operational mode command show spanning-tree
interface shows that ge-0/0/18.0 is in a forwarding
state and is the root port.
Verifying RSTP Configuration on Switch 3
Purpose
Use this procedure to verify the RSTP configuration on both Switch 3 Routing Engines.
Action
Use the operational mode commands:
user@switch3> show spanning-tree interface
Spanning tree interface parameters for instance 0
Interface Port ID Designated Designated Port State Role
port ID bridge ID Cost
ge-0/0/26.0 128:539 128:539 8192.0019e25051e0 1000 FWD DESG
ge-0/0/28.0 128:541 128:541 8192.0019e25051e0 1000 FWD DESG
ge-0/0/24.0 128:537 128:537 8192.0019e25051e0 1000 FWD DESG
Meaning
The operational mode command show spanning-tree
interface shows that no interface is the root interface.
Verifying RSTP Configuration on Switch 4
Purpose
Use this procedure to verify the RSTP configuration on both Switch 4 Routing Engines.
Action
Use the operational mode commands:
user@switch4> show spanning-tree interface
Spanning tree interface parameters for instance 0
Interface Port ID Designated Designated Port State Role
port ID bridge ID Cost
ge-0/0/23.0 128:536 128:536 8192.0019e25051e0 1000 FWD ROOT
ge-0/0/19.0 128:532 128:532 16384.0019e25040e0 1000 FWD DESG
Meaning
The operational mode command show spanning-tree
interface shows that interface ge-0/0/23.0 is the root
interface and forwarding.
Forcing RSTP or VSTP to Run as IEEE 802.1D STP (CLI Procedure)
This procedure uses Junos OS for EX Series switches with support for the Enhanced Layer 2 Software (ELS) configuration style. For ELS details, see Using the Enhanced Layer 2 Software CLI.
On EX Series switches running Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) (the default) or VLAN Spanning Tree Protocol (VSTP), you can force the original IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) version to run in place of RSTP or VSTP. Configure the force-version stp statement for compatibility with older bridges that do not support RSTP or VSTP.
To force the spanning-tree protocol version to be the original IEEE 802.1D STP:
[edit protocols] user@switch# set (rstp | vstp) force-version stp
After using the force-version statement to enable xSTP globally, apply the force-version statement for specific Layer 2 ports.
Change History Table
Feature support is determined by the platform and release you are using. Use Feature Explorer to determine if a feature is supported on your platform.
