ON THIS PAGE
Example: Configuring Redundancy and Load Balancing Using a Single AFTR and Multiple Services PICs
This example shows how to configure redundancy and load balancing using a single DS-Lite Address Family Transition Router (AFTR).
Requirements
This example uses the following hardware and software components:
Juniper Networks MX Series 3D Universal Edge Routers with Multiservices Dense Port Concentrators (DPCs)
Juniper Networks® Junos® operating system (Junos OS) 10.4 or later running on the AFTR
This configuration example has been tested using the software release listed and is assumed to work on all later releases.
Overview
You can provide redundancy and load balancing using multiple Services PICs on the same AFTR and a single anycast address where the two Services PICs actively load-balance traffic. In Figure 1, three Basic Bridging BroadBand Elements (B4s or softwire initiators) are connected to the AFTR’s softwire (ID 1001::1) using different tunnels. The AFTR has two services for load balancing and redundancy. When HTTP clients connect to the server, traffic is load-balanced between the Services PICs. In addition, when one of the Services PICs is down, traffic from all three B4s is channelized through the other Services PIC.
Topology
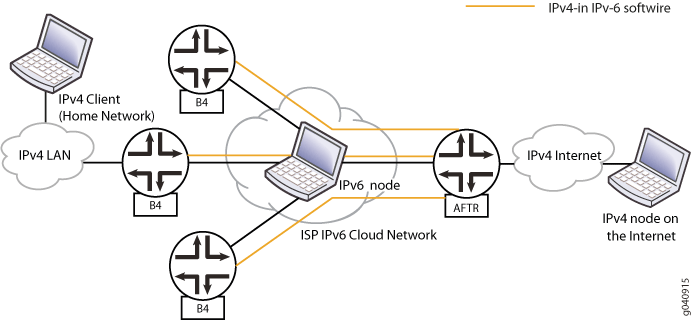
The IPv4 client or host in the home network is configured with an IPv4 interface to the ISP and a static route to the IPv4 server on the Internet.
The multiple B4s or softwire initiators are configured with an IPv4 interface, an IPv6 interface, and an IPv4-in-IPv6 tunnel to an anycast address.
The pure IPv6 node in the IPv6 cloud is configured with interfaces to the IPv6 interfaces.
The address range of the NAT pool between the AFTR and the Internet is 33.33.33.1 through 33.33.33.32 corresponding to NAT rule
dslite-nat-rule1, and 44.44.44.1 through 44.44.44.32 corresponding to NAT ruledslite-nat-rule2.NAT rule
dslite-nat-rule1corresponds to Services PICsp-0/1/0, and NAT ruledslite-nat-rule2corresponds to Services PICsp-1/3/0.The AFTR is configured with anycast address 2001::1/16 for the interface toward the three B4s. Address 200.200.200.1/24 is configured for the interface from the AFTR toward the Internet. The two Services PICs are
sp-0/1/0andsp-1/3/0.The IPv4 node on the Internet is configured with an IPv4 interface and routes for reverse traffic.
Configuration
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks,
change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
and then copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
AFTR
set chassis fpc 1 pic 1 adaptive-services service-package layer-3 set services nat pool dslite-pool1 address-range low 33.33.33.1 high 33.33.33.32 set services nat pool dslite-pool1 port automatic set services nat pool dslite-pool2 address-range low 44.44.44.1 high 44.44.44.32 set services nat pool dslite-pool2 port automatic set services nat rule dslite-nat-rule1 match-direction input set services nat rule dslite-nat-rule1 term t1 from source-address 20.20.0.0/16 set services nat rule dslite-nat-rule1 term t1 then translated source-pool dslite-pool1 set services nat rule dslite-nat-rule1 term t1 then translated translation-type napt-44 set services nat rule dslite-nat-rule2 match-direction input set services nat rule dslite-nat-rule2 term t1 from source-address 20.20.0.0/16 set services nat rule dslite-nat-rule2 term t1 then translated source-pool dslite-pool2 set services nat rule dslite-nat-rule2 term t1 then translated translation-type napt-44 set services softwire softwire-concentrator ds-lite ds1 softwire-address 1001::1 set services softwire softwire-concentrator ds-lite ds1 mtu-v6 9192 set services softwire rule dslite-rule match-direction input set services softwire rule dslite-rule term t1 then ds-lite ds1 set services service-set dslite-svc-set1 syslog host local services any set services service-set dslite-svc-set1 softwire-rules dslite-rule set services service-set dslite-svc-set1 stateful-firewall-rules sfw-r1 set services service-set dslite-svc-set1 nat-rules dslite-nat-rule1 set services service-set dslite-svc-set1 next-hop-service inside-service-interface sp-0/1/0.1 set services service-set dslite-svc-set1 next-hop-service outside-service-interface sp-0/1/0.2 set services service-set dslite-svc-set2 syslog host local services any set services service-set dslite-svc-set2 softwire-rules dslite-rule set services service-set dslite-svc-set2 stateful-firewall-rules sfw-r1 set services service-set dslite-svc-set2 nat-rules dslite-nat-rule2 set services service-set dslite-svc-set2 next-hop-service inside-service-interface sp-1/3/0.1 set services service-set dslite-svc-set2 next-hop-service outside-service-interface sp-1/3/0.2 set services stateful-firewall rule sfw-r1 match-direction input set services stateful-firewall rule sfw-r1 term t1 from applications junos-http set services stateful-firewall rule sfw-r1 term t1 from applications junos-ftp set services stateful-firewall rule sfw-r1 term t1 from applications junos-rtsp set services stateful-firewall rule sfw-r1 term t1 from applications junos-icmp-all set services stateful-firewall rule sfw-r1 term t1 then accept set services stateful-firewall rule sfw-r1 term t1 then syslog set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001::1/16 set interfaces ge-0/0/3 unit 0 family inet address 200.200.200.1/24 set interfaces sp-0/1/0 services-options syslog host local services any set interfaces sp-0/1/0 unit 0 family inet set interfaces sp-0/1/0 unit 0 family inet6 set interfaces sp-0/1/0 unit 1 family inet6 set interfaces sp-0/1/0 unit 1 service-domain inside set interfaces sp-0/1/0 unit 2 family inet6 set interfaces sp-0/1/0 unit 2 service-domain outside set interfaces sp-1/3/0 services-options syslog host local services any set interfaces sp-1/3/0 unit 0 family inet set interfaces sp-1/3/0 unit 0 family inet6 set interfaces sp-1/3/0 unit 1 family inet6 set interfaces sp-1/3/0 unit 1 service-domain inside set interfaces sp-1/3/0 unit 2 family inet6 set interfaces sp-1/3/0 unit 2 service-domain outside set routing-options forwarding-table export load-balancing-policy set policy-options policy-statement load-balancing-policy then load-balance per-packet set routing-options rib inet6.0 static route 1001::1/128 next-hop sp-1/3/0.1 set routing-options rib inet6.0 static route 1001::1/128 next-hop sp-0/1/0.1 set forwarding-options hash-key family inet6 layer-3 destination-address set forwarding-options hash-key family inet6 layer-3 source-address
Configuring the AFTR
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following example requires you to navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For information about navigating the CLI, see the CLI User Guide for Junos OS.
Configure the Layer 3 service package. This example assumes that the PIC is in FPC 1, slot 1.
[edit chassis] user@AFTR1# set fpc 1 pic 1 adaptive-services service-package layer-3
The service package with its associated
sp-interface is for manipulating traffic before it is delivered to its destination. For details about configuring service packages, see the Junos OS Services Interfaces Configuration Guide.Configure two different NAT pools and NAPT for the two Services PICs.
[edit services nat] user@AFTR1# set pool dslite-pool1 address-range low 33.33.33.1 high 33.33.33.32 user@AFTR1# set pool dslite-pool1 port automatic user@AFTR1# set pool dslite-pool2 address-range low 44.44.44.1 high 44.44.44.32 user@AFTR1# set pool dslite-pool2 port automatic user@AFTR1# set rule dslite-nat-rule1 match-direction input user@AFTR1# set rule dslite-nat-rule1 term t1 from source-address 20.20.0.0/16 user@AFTR1# set rule dslite-nat-rule1 term t1 then translated source-pool dslite-pool1 user@AFTR1# set rule dslite-nat-rule1 term t1 then translated translation-type napt-44 user@AFTR1# set rule dslite-nat-rule2 match-direction input user@AFTR1# set rule dslite-nat-rule2 term t1 from source-address 20.20.0.0/16 user@AFTR1# set rule dslite-nat-rule2 term t1 then translated source-pool dslite-pool2 user@AFTR1# set rule dslite-nat-rule2 term t1 then translated translation-type napt-44
Configure the softwire concentrator and create the softwire rule.
[edit services softwire] user@AFTR1# set softwire-concentrator ds-lite ds1 softwire-address 1001::1 user@AFTR1# set softwire-concentrator ds-lite ds1 mtu-v6 9192 user@AFTR1# set rule dslite-rule match-direction input user@AFTR1# set rule dslite-rule term t1 then ds-lite ds1
Configure next-hop-style service sets
dslite-svc-set1anddslite-svc-set2for Services PICssp-0/1/0andsp-1/3/0, respectively.[edit services] user@AFTR1# set service-set dslite-svc-set1 syslog host local services any user@AFTR1# set service-set dslite-svc-set1 softwire-rules dslite-rule user@AFTR1# set service-set dslite-svc-set1 stateful-firewall-rules sfw-r1 user@AFTR1# set service-set dslite-svc-set1 nat-rules dslite-nat-rule1 user@AFTR1# set service-set dslite-svc-set1 next-hop-service inside-service-interface sp-0/1/0.1 user@AFTR1# set service-set dslite-svc-set1 next-hop-service outside-service-interface sp-0/1/0.2 user@AFTR1# set service-set dslite-svc-set2 syslog host local services any user@AFTR1# set service-set dslite-svc-set2 softwire-rules dslite-rule user@AFTR1# set service-set dslite-svc-set2 stateful-firewall-rules sfw-r1 user@AFTR1# set service-set dslite-svc-set2 nat-rules dslite-nat-rule2 user@AFTR1# set service-set dslite-svc-set2 next-hop-service inside-service-interface sp-1/3/0.1 user@AFTR1# set service-set dslite-svc-set2 next-hop-service outside-service-interface sp-1/3/0.2
Configure stateful firewall and softwire rules.
[edit services] user@AFTR1# set stateful-firewall rule sfw-r1 match-direction input user@AFTR1# set stateful-firewall rule sfw-r1 term t1 from applications junos-http user@AFTR1# set stateful-firewall rule sfw-r1 term t1 from applications junos-ftp user@AFTR1# set stateful-firewall rule sfw-r1 term t1 from applications junos-rtsp user@AFTR1# set stateful-firewall rule sfw-r1 term t1 from applications junos-icmp-all user@AFTR1# set stateful-firewall rule sfw-r1 term t1 then accept user@AFTR1# set stateful-firewall rule sfw-r1 term t1 then syslog
Configure the services interfaces.
[edit interfaces] user@AFTR1# set sp-0/1/0 services-options syslog host local services any user@AFTR1# set sp-0/1/0 unit 0 family inet user@AFTR1# set sp-0/1/0 unit 0 family inet6 user@AFTR1# set sp-0/1/0 unit 1 family inet6 user@AFTR1# set sp-0/1/0 unit 1 service-domain inside user@AFTR1# set sp-0/1/0 unit 2 family inet6 user@AFTR1# set sp-0/1/0 unit 2 service-domain outside user@AFTR1# set sp-1/3/0 services-options syslog host local services any user@AFTR1# set sp-1/3/0 unit 0 family inet user@AFTR1# set sp-1/3/0 unit 0 family inet6 user@AFTR1# set sp-1/3/0 unit 1 family inet6 user@AFTR1# set sp-1/3/0 unit 1 service-domain inside user@AFTR1# set sp-1/3/0 unit 2 family inet6 user@AFTR1# set sp-1/3/0 unit 2 service-domain outside
Configure the interface between the home router running the B4 and the AFTR.
[edit interfaces] user@AFTR1# set ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet user@AFTR1# set ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001::1/16
Configure the interface between the AFTR and the Internet.
[edit interfaces] user@AFTR1# set ge-0/0/3 unit 0 family inet address 200.200.200.1/24
Configure load-balancing options for the Packet Forwarding Engine to determine how the traffic is load-balanced between the two Services PICs.
[edit] user@AFTR1# set policy-options policy-statement load-balancing-policy then load-balance per-packet user@AFTR1# set routing-options forwarding-table export load-balancing-policy
Configure routing options to install a route with high priority to the anycast address for both Services PICs.
Configure the static route destination address.
Configure the next hops to the destination address. Include the Services PICs (
sp-1/3/0.1sp-0/1/0.1) in the list of next hops.
[edit routing-options]user@AFTR1# set rib inet6.0 static route 1001::1/128 next-hop sp-1/3/0.1 user@AFTR1# set rib inet6.0 static route 1001::1/128 next-hop sp-0/1/0.1Configure load-balancing options for the Packet Forwarding Engine.
[edit forwarding-options] user@AFTR1# set hash-key family inet6 layer-3 destination-address user@AFTR1# set hash-key family inet6 layer-3 source-address
Results
In configuration mode, confirm your configuration by
entering the show chassis, show services, show interfaces, show routing-options, show
policy-options, and show forwarding-options commands.
If the output does not display the intended configuration, repeat
the instructions in this example to correct the configuration.
user@AFTR1# show chassis
fpc 1 {
pic 1 {
adaptive-services {
service-package layer-3;
}
}
}
user@AFTR1# show services
service-set dslite-svc-set1 {
syslog {
host local {
services any;
}
}
softwire-rules dslite-rule;
stateful-firewall-rules sfw-r1;
nat-rules dslite-nat-rule1;
next-hop-service {
inside-service-interface sp-0/1/0.1;
outside-service-interface sp-0/1/0.2;
}
}
service-set dslite-svc-set2 {
syslog {
host local {
services any;
}
}
softwire-rules dslite-rule;
stateful-firewall-rules sfw-r1;
nat-rules dslite-nat-rule2;
next-hop-service {
inside-service-interface sp-1/3/0.1;
outside-service-interface sp-1/3/0.2;
}
}
stateful-firewall {
rule sfw-r1 {
match-direction input;
term t1 {
from {
applications [ junos-http junos-ftp junos-rtsp junos-icmp-all ];
}
then {
accept;
syslog;
}
}
}
}
softwire {
softwire-concentrator {
ds-lite ds1 {
softwire-address 1001::1;
mtu-v6 9192;
}
}
rule dslite-rule {
match-direction input;
term t1 {
then {
ds-lite ds1;
}
}
}
}
nat {
pool dslite-pool1 {
address-range low 33.33.33.1 high 33.33.33.32;
port {
automatic;
}
}
pool dslite-pool2 {
address-range low 44.44.44.1 high 44.44.44.32;
port {
automatic;
}
}
rule dslite-nat-rule1 {
match-direction input;
term t1 {
from {
source-address {
20.20.0.0/16;
}
}
then {
translated {
source-pool dslite-pool1;
translation-type {
napt-44;
}
}
}
}
}
rule dslite-nat-rule2 {
match-direction input;
term t1 {
from {
source-address {
20.20.0.0/16;
}
}
then {
translated {
source-pool dslite-pool2;
translation-type {
napt-44;
}
}
}
}
}
}
user@AFTR1# show interfaces
ge-0/0/2 {
unit 0 {
family inet;
family inet6 {
address 2001::1/16;
}
}
}
ge-0/0/3 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 200.200.200.1/24;
}
}
}
sp-0/1/0 {
services-options {
syslog {
host local {
services any;
}
}
}
unit 0 {
family inet;
family inet6;
}
unit 1 {
family inet6;
service-domain inside;
}
unit 2 {
family inet6;
service-domain outside;
}
}
sp-1/3/0 {
services-options {
syslog {
host local {
services any;
}
}
}
unit 0 {
family inet;
family inet6;
}
unit 1 {
family inet6;
service-domain inside;
}
unit 2 {
family inet6;
service-domain outside;
}
}
user@AFTR1# show routing-options
rib inet6.0 {
static {
route 1001::1/128 next-hop [ sp-1/3/0.1 sp-0/1/0.1 ];
}
}
forwarding-table {
export load-balancing-policy;
}
user@AFTR1# show policy-options
policy-statement load-balancing-policy {
then {
load-balance per-packet;
}
}
user@AFTR1# show forwarding-options
hash-key {
family inet6 {
layer-3 {
destination-address;
source-address;
}
}
}
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Verification
Confirm that the configuration is working properly.
- Verifying Load Balancing Between the Two Services PICs
- Verifying Redundancy Between the Two Services PICs
Verifying Load Balancing Between the Two Services PICs
Purpose
Verify that traffic is load-balanced between the two Services PICs.
Action
Verify traffic flow between the IPv4 host on the home network and the IPv4 node on the Internet by using the
show services stateful-firewall flowscommand.user@AFTR> show services stateful-firewall flows Interface: sp-0/1/0, Service set: dslite-svc-set1 Flow State Dir Frm count ICMP 10.0.10.1 -> 45.45.45.2 Watch I 3 NAT source 10.0.10.1 -> 129.0.0.1 Softwire 5002::12 -> 1001::1 DS-LITE 5002::12 -> 1001::1 Forward I 6 ICMP 45.45.45.2 -> 129.0.0.1 Watch O 3 NAT dest 129.0.0.1 -> 10.0.10.1 Softwire 5002::12 -> 1001::1The output shows ICMP statistics indicating the traffic flow between the IPv4 host on the home network to the IPv4 node on the Internet.
Issue the
show services softwire,show services stateful-firewall conversations,show services stateful-firewall flows count, andshow services stateful-firewall statisticscommands to check the traffic flows.user@AFTR> show services softwire Interface: sp-0/1/0, Service set: dslite-svc-set2 Softwire Direction Flow count 2001::3 -> 1001::1 I 3 Interface: sp-1/3/0, Service set: dslite-svc-set1 Softwire Direction Flow count 2001::2 -> 1001::1 I 3
The output shows statistics for service set
dslite-svc-set2associated with the services interfacesp-0/1/0and service setdslite-svc-set1associated with the services interfacesp-1/3/0.user@AFTR> show services stateful-firewall conversations Interface: sp-0/1/0, Service set: dslite-svc-set2 Conversation: ALG protocol: tcp Number of initiators: 1, Number of responders: 1 Flow State Dir Frm count TCP 20.20.1.2:1025 -> 200.200.200.2:80 Forward I 189280 NAT source 20.20.1.2:1025 -> 44.44.44.1:1024 Softwire 2001::3 -> 1001::1 TCP 200.200.200.2:80 -> 44.44.44.1:1024 Forward O 363675 NAT dest 44.44.44.1:1024 -> 20.20.1.2:1025 Softwire 2001::3 -> 1001::1 Interface: sp-1/3/0, Service set: dslite-svc-set1 Conversation: ALG protocol: tcp Number of initiators: 1, Number of responders: 1 Flow State Dir Frm count TCP 20.20.1.2:1025 -> 200.200.200.2:80 Forward I 195847 NAT source 20.20.1.2:1025 -> 33.33.33.1:1025 Softwire 2001::2 -> 1001::1 TCP 200.200.200.2:80 -> 33.33.33.1:1025 Forward O 391972 NAT dest 33.33.33.1:1025 -> 20.20.1.2:1025 Softwire 2001::2 -> 1001::1 Conversation: ALG protocol: tcp Number of initiators: 1, Number of responders: 1 Flow State Dir Frm count TCP 20.20.1.2:1025 -> 200.200.200.2:80 Forward I 219333 NAT source 20.20.1.2:1025 -> 33.33.33.1:1024 Softwire 2001::4 -> 1001::1 TCP 200.200.200.2:80 -> 33.33.33.1:1024 Forward O 438848 NAT dest 33.33.33.1:1024 -> 20.20.1.2:1025 Softwire 2001::4 -> 1001::1The output shows traffic flows for both services interfaces,
sp-0/1/0andsp-1/3/0, indicating that both of the Services PICs are active.user@AFTR> show services stateful-firewall flows count Interface Service set Flow count sp-0/1/0 dslite-svc-set2 3 sp-1/3/0 dslite-svc-set1 6
The output shows flow counts for both services interfaces,
sp-0/1/0andsp-1/3/0, indicating that both of the Services PICs are active.user@AFTR> show services stateful-firewall statistics Interface Service set Accept Discard Reject Errors sp-0/1/0 dslite-svc-set2 118991296 0 0 0 sp-1/3/0 dslite-svc-set1 237615050 0 0 0
Meaning
The output shows traffic flows for both Services PICs, sp-0/1/0 and sp-1/3/0. This indicates that the traffic
is load-balanced between both of the Services PICs.
Verifying Redundancy Between the Two Services PICs
Purpose
Verify redundancy between the two Services PICs.
Action
Bring services PIC
sp-0/1/0offline by issuing therequest chassis pic fpc-slot slot-number pic-slot pic-number offlinecommand.user@host> request chassis pic fpc-slot 0 pic-slot 1 offline fpc 0 pic 1 offline initiated, use “show chassis fpc pic-status” to verify
Issue the
show services stateful-firewall conversationscommand again to check traffic flows through the redundant Services PICsp-1/3/0.Check the interface name and service-set name in the output.
user@host> show services stateful-firewall conversations Interface: sp-1/3/0, Service set: dslite-svc-set1 Conversation: ALG protocol: tcp Number of initiators: 1, Number of responders: 1 Flow State Dir Frm count TCP 20.20.1.2:1025 -> 200.200.200.2:80 Forward I 195847 NAT source 20.20.1.2:1025 -> 33.33.33.1:1025 Softwire 2001::2 -> 1001::1 TCP 200.200.200.2:80 -> 33.33.33.1:1025 Forward O 391972 NAT dest 33.33.33.1:1025 -> 20.20.1.2:1025 Softwire 2001::2 -> 1001::1 Conversation: ALG protocol: tcp Number of initiators: 1, Number of responders: 1 Flow State Dir Frm count TCP 20.20.1.2:1025 -> 200.200.200.2:80 Forward I 219333 NAT source 20.20.1.2:1025 -> 33.33.33.1:1024 Softwire 2001::4 -> 1001::1 TCP 200.200.200.2:80 -> 33.33.33.1:1024 Forward O 438848 NAT dest 33.33.33.1:1024 -> 20.20.1.2:1025 Softwire 2001::4 -> 1001::1
Meaning
The output indicates that all traffic is now routed
through Services PIC sp-1/3/0 when sp-0/1/0 is
deactivated. This indicates that redundancy is operational between
the two Services PICs.
