Example: Basic DS-Lite Configuration
DS-Lite employs IPv4-over-IPv6 tunnels to cross an IPv6 access network to reach a carrier-grade IPv4-IPv4 NAT. This facilitates the phased introduction of IPv6 on the Internet by providing backward compatibility with IPv4. See Understanding IPv6 Dual-Stack Lite.
Requirements
The following hardware components can perform DS-Lite:
M Series Multiservice Edge routers with Multiservices PICs.
T Series Core routers with Multiservices PICs.
MX Series 5G Universal Routing Platforms with Multiservices DPCs. Starting in Junos OS release 17.4R1, DS-Lite is supported on MX Series routers with MS-MPCs and MS-MICs.Starting in Junos OS release 19.2R1, DS-Lite is supported on MX Virtual Chassis and MX Broadband Network Gateway (BNG) routers.
Note:This example is based on a MS-DPC style IP services. As a result a sp-x/x/x interface is used to direct traffic into the service engine. When using a MS-MPC or MS-MIC the services interface takes the form of ms-x/x/x. Be sure to adapt this example as needed for the specifics of your hardware.
Configuration Overview and Topology
This example describes how configure an MX Series router with an MS-DPC as an AFTR to facilitate the flow shown in Figure 1.
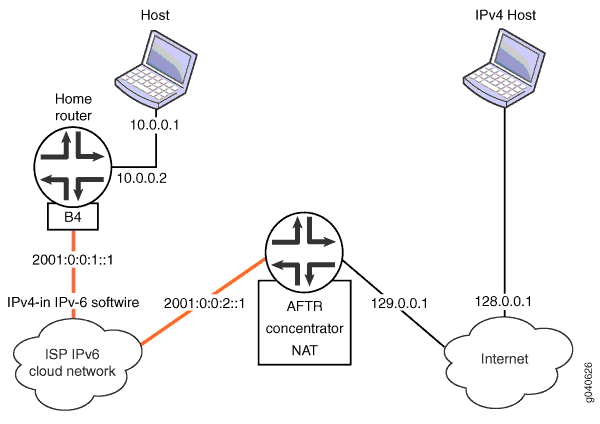
In this example, the DS-Lite softwire concentrator, or AFTR, is an MX Series router with two Gigabit interfaces and a Services DPC. The interface facing the B4 element is ge-3/1/5 and the interface facing the Internet is ge-3/1/0.
Configuration
- Chassis Configuration
- Interfaces Configuration
- Network Address and Port Translation Configuration
- Softwire Configuration
- Service Set Configuration
Chassis Configuration
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure the service PIC (FPC 0 Slot 0) with the Layer 3 service package:
Enter the edit chassis hierarchy level.
user@host# edit chassisConfigure the Layer 3 service package.
[edit chassis]user@host# set fpc 0 pic 0 adaptive-services service-package layer-3
Interfaces Configuration
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure interfaces facing the B4 (softwire initiator) and facing the Internet:
Go the
[edit interfaces]edit hierachy level for ge-3/1/0, which faces the Internet.host# edit interfaces ge-3/1/0Define the interface.
[edit interfaces ge-3/1/0]user@host# set description AFTR-Internet user@host# set unit 0 family inet address 128.0.0.2/24Go to the
[edit interfaces]hierachy level for ge-3/1/5, which faces the B4.user@host# up 1
[edit]user@host# edit interfaces ge-3/1/5Define the interface.
[edit interfaces ge-3/1/5]user@host# set description AFTR-B4 user@host# set unit 0 family inet user@host# edit unit 0 family inet6[edit unit 0 family inet6]user@host# set service input service-set sset user@host# set service output service-set sset user@host# set address 2001:0:0:2::1/48Go to the
[edit interfaces]hierarchy level for sp-0/0/0, used to host the DS-Lite AFTR.Note:The services interface is used to enable a number of routing services such as stateful firewall filters, IPSec, and Network Address Translation (NAT). Within a Services Router, packets are routed to this internal interface for encapsulation or processing, depending on the service that is configured. The services interface is an internal interface and is not associated with a physical medium. You must configure the service interface in order to use it for a service set.
[edit]user@host# edit interfaces sp-0/0/0Configure the services interface.
[edit interfaces sp-0/0/0]user@host# set description AFTR-B4 user@host# set unit 0 family inet user@host# set unit 0 family inet6
Results
user@host# show interfaces ge-3/1/0 description AFTR-Internet; unit 0 { family inet { address 128.0.0.2/24; } } user@host# show interfaces ge-3/1/5 description AFTR-B4; unit 0 { family inet; family inet6 { service { input { service-set sset; } output { service-set sset; } } address 2001:0:0:2::1/48; } } user@host# show interfaces sp-o/o/o unit 0 { family inet; family inet6; }
Network Address and Port Translation Configuration
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure NAPT:
Go to the
[edit services nat]hierarchy level.user@host# edit services nat
[edit services nat]Define a NAT pool p1.
user@host# set pool p1 address 129.0.0.1/32 port automaticDefine a NAT rule, beginning with the match direction.
[edit services nat]user@host# set rule r1 match-direction inputDefine a term for the rule, beginning with a from clause.
[edit services nat]user@host# set rule r1 term t1 from source-address 10.0.0.0/16Define the desired translation in a then clause. In this case, use dynamic source translation.
[edit services nat]user@host# set rule r1 term t1 then translated source-pool p1 translation-type napt-44(Optional) Configure logging of translation information for the rule.
[edit services nat]user@host# set rule r1 term t1 then syslog
Results
user@host# show services nat
pool p1 {
address 129.0.0.1/32;
port {
automatic;
}
}
rule r1 {
match-direction input;
term t1 {
from {
source-address {
10.0.0.0/16;
}
}
then {
translated {
source-pool p1;
translation-type {
napt-44;
}
}
syslog;
}
}Softwire Configuration
Step-by-Step Procedure
To configure the DS-Lite softwire concentrator, static route, and associated rules:
Go to the
[edit services softwire]hierarchy level.user@host# edit services softwireDefine the DS-Lite softwire concentrator. This includes the softwire IPv6 address. This address is used to support an IPv4 over IPv6 tunnel with the B4 router. A corresponding IP over IP tunnel is defined on the B4 router. Typically a static route is used at both ends to direct traffic destined for the remote end of the tunnel over the IPv6 link connecting the B4 and AFTR routers.
[edit services softwire]user@host# set softwire-concentrator ds-lite ds-1 softwire-address 1001::1 mtu-v6 1460Define the softwire rule.
[edit services softwire]user@host# set rule r1 match-direction input term t1 then ds-lite ds1.Define the static route to the B4 end of the IP over IP tunnel. In this example the B4 router uses the IPv6 address 5002::1/128 address to source traffic sent over the IP tunnel to the AFTR node. This address is assigned to a loopback interface so it can be used as the tunnel source address.
[edit routing-options]user@host# set rib inet6.0 static route 5002::1/128 next-hop 2001:0:0:1::1
Results
user@host# show services softwire
softwire-concentrator {
ds-lite ds1 {
softwire-address 1001::1;
mtu-v6 1460;
}
}
rule r1 {
match-direction input;
term t1 {
then {
ds-lite ds1;
}
}
}user@host# show routing-options rib inet6.0
static {
route 5002::1/128 next-hop 2001:0:0:1::1;
}Service Set Configuration
Step-by-Step Procedure
Configure a service set that includes softwire and NAT rules and specifies either interface-service or next-hop service. This example uses a next-hop service.
Go to the
[edit services service-set]hierarchy level, naming the service set.user@host# edit services service-set ssetDefine the NAT rule to be used for IPv4-to-IPv4 translation.
[edit services service-set sset]user@host# set nat-rules r1Define the softwire rule to define the softwire tunnel.
[edit services service-set sset]user@host# set softwire-rules r1Define the interface service,
[edit services service-set sset]user@host# set interface-service service-interface sp-0/0/0.0Tip:In order to avoid or minimize IPv6 fragmentation, you can configure a TCP maximum segment size (MSS) for your service set.
(Optional) Define a TCP MSS.
[edit services service-set sset]user@host# set tcp-mss 1024
Results
user@host# show services service-set
syslog {
host local {
services any;
}
}
softwire-rules r1;
nat-rules r1;
interface-service {
service-interface sp-0/0/0;
}
}