Network Interface Traffic Engineering
Network interface traffic engineering allows you to impose traffic limitations on all traffic egressing a specific network-interface. This configuration also applies to all associated adjacencies of the network-interface, but does not impact other traffic that is egressing the same device-interface but belongs to different network-interfaces.
How It Works
For network-interface traffic-engineering to make a scheduling decision, the egress VLAN ID of a packet is queried to determine whether that packet has scheduling enabled. If so, the packet is enqueued into a scheduler specific for that network-interface. If not, the packet continues with normal packet processing.
Configuration
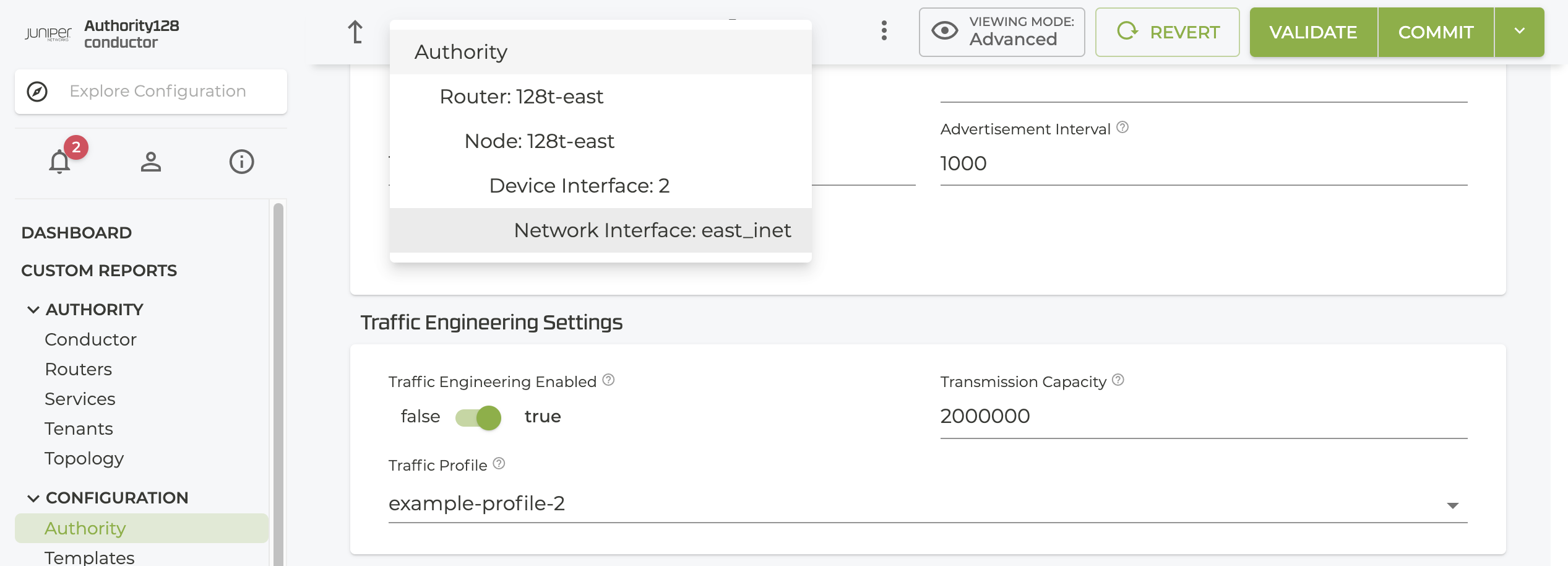
Network interface traffic engineering is configured as part of the network-interface, under the device-interface. It does not have any impact on other device interfaces, or to other network interfaces belonging to the same device interface, but it does impact associated adjacencies.
device-interface 2
network-interface east-inet
vlan 30
traffic-engineering
enabled true
transmit-cap 2000000
traffic-profile example-profile-2
exit
exit
exit
enabled: Creates the scheduler to be used on egress for the interfacetransmit-cap: The effective port rate of the interface in bits per second. This value is matched internally to the link speed of the device.traffic-profile: Identifies the traffic-profile to be used when determining the traffic class distributions.
In the GUI, configuration specific to network-interface traffic engineering is located in the network-interface section under Traffic Engineering Settings.
Limitations
Enabling traffic engineering will introduce a performance impact to the packet-per-second processing rate as the QoS engine works to ensure fairness of packet distribution under congestion scenarios. When used in conjunction with other traffic engineering settings (e.g., adjacency traffic engineering configured alongside device interface traffic engineering), performance may be further impacted.
Troubleshooting and Statistics
Given the packet performance nature of the scheduler, no logs exist at the per-packet level to monitor traffic-engineering performance. The statistics described below are the best source of information about performance. The success-bandwidth and failure-bandwidth meters are good indicators of how well the scheduler is handling packets. For failure-bandwidth, additional statistics can be used to determine the reason for loss. Some examples are a queue full scenario resulting from an unhandled burst, or packets being dropped due to excessive time spent within the scheduler.
Statistics for network-interface traffic engineering can be viewed from the show stats traffic-eng network-interface command. Use the following statistics to help analyze network-interface behavior when traffic-engineering is configured.
The general statistics apply to the scheduler as a whole. Per-traffic-class statistics are maintained for all the available traffic-classes (high, medium, low, best-effort).
Network-Interface Traffic Engineering Stats
show stats traffic-eng network-interface
==================================================== ============== =========== =================
Metric Node Netintf Value
==================================================== ============== =========== =================
dequeue-cycle-count combo-east-a intf10.10 91841637
enqueue-cycle-count combo-east-a intf10.10 91841637
packets-queued combo-east-a intf10.10 0
per-traffic-class buffer-capacity-exceeded-bytes combo-east-a intf10.10 0
per-traffic-class buffer-capacity-exceeded-packets combo-east-a intf10.10 0
per-traffic-class dequeue-aqm-drop-bytes combo-east-a intf10.10 0
per-traffic-class dequeue-aqm-drop-packets combo-east-a intf10.10 0
Network-Interface Traffic Engineering Statistics per Traffic Class
show stats traffic-eng network-interface per-traffic-class
================================== ============== =========== =============== ============
Metric Node Netintf Traffic-class Value
================================== ============== =========== =============== ============
buffer-capacity-exceeded-bytes combo-east-a intf10.10 best-effort 0
combo-east-a intf10.10 high 0
combo-east-a intf10.10 low 0
combo-east-a intf10.10 medium 0
buffer-capacity-exceeded-packets combo-east-a intf10.10 best-effort 0
Statistics Descriptions
To gather information about network interface traffic engineering, query the following statistics using the show stats traffic-eng network-interface command. These statistics are specific to the network interface and provide insight into how the schedulers are operating.
enqueue-cycle-count: The current enqueue cycle count in traffic engineering for this interface. This statistic refers to the last time (in cycles) that a packet was enqueued into the scheduler. This value is helpful when debugging.dequeue-cycle-count: The current dequeue cycle count in traffic engineering for this interface. This statistic refers to the last time (in cycles) that the scheduler attempted to dequeue a packet. This value is helpful when debugging.packets-queued: The current number of packets queued in traffic engineering for this interface.scheduler-reset: The number of times the scheduler was reset due to encountering an processing error.per-traffic-class schedule-success-bytes: The number of bytes successfully scheduled for transmission for this interface.per-traffic-class schedule-success-packets: The number of packets successfully scheduled for transmission for this interface.per-traffic-class schedule-failure-bytes: The number of bytes failed to be scheduled for transmission due to bandwidth oversubscription for this interface.per-traffic-class schedule-failure-packets: The number of packets failed to be scheduled for transmission due to bandwidth oversubscription for this interface.per-traffic-class dequeue-success-bytes: The number of bytes successfully dequeued from the scheduler for transmission for this interface.per-traffic-class dequeue-success-packets: The number of packets successfully dequeued from the scheduler for transmission for this interface.per-traffic-class dequeue-max-latency-drop-bytes: The number of bytes scheduled for transmission that were dropped due to excessive latency for this interface.per-traffic-class dequeue-max-latency-drop-packets: The number of packets scheduled for transmission that were dropped due to excessive latency for this interface.per-traffic-class dequeue-aqm-drop-bytes: The number of bytes scheduled for transmission that were dropped due to Active Queue Management for this interface.per-traffic-class dequeue-aqm-drop-packets: The number of packets scheduled for transmission that were dropped due to Active Queue Management for this interface.per-traffic-class buffer-capacity-exceeded-bytes: The number of bytes failed to be scheduled for transmission due to exceeded buffer capacity for this interface.per-traffic-class buffer-capacity-exceeded-packets: The number of packets failed to be scheduled for transmission due to exceeded buffer capacity for this interface.per-traffic-class schedule-success-bandwidth: Traffic bandwidth in bytes per second successfully scheduled for transmission for this interface.per-traffic-class schedule-failure-bandwidth: Traffic bandwidth in bytes per second that failed to be scheduled or was dropped due to active queue managment for this interface.