Geneve Flow Infrastructure on vSRX Virtual Firewall 3.0
This topic provides overview and configuration of Geneve flow infrastructure on vSRX Virtual Firewall 3.0.
Overview
Generic Network Virtualization Encapsulation (Geneve) is a network encapsulation protocol developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF).
The Geneve protocol supports network virtualization use cases for data center environments. In such environments, the Geneve tunnels act as a backplane for the virtual network function (VNF) that runs on a cloud deployment—for example, an Amazon Web Services (AWS) or a VMware deployment.
Starting in Junos OS Release 23.1R1, vSRX Virtual Firewall 3.0—the current version of Juniper Networks® vSRX Virtual Firewall Virtual Firewall— supports Geneve flow infrastructure for Geneve tunnel packet processing. With this support, you can use vSRX Virtual Firewall 3.0 to:
With the Geneve flow infrastructure support, vSRX Virtual Firewall 3.0 can:
-
Perform the functions of a transit router or a tunnel endpoint device in various cloud deployments.
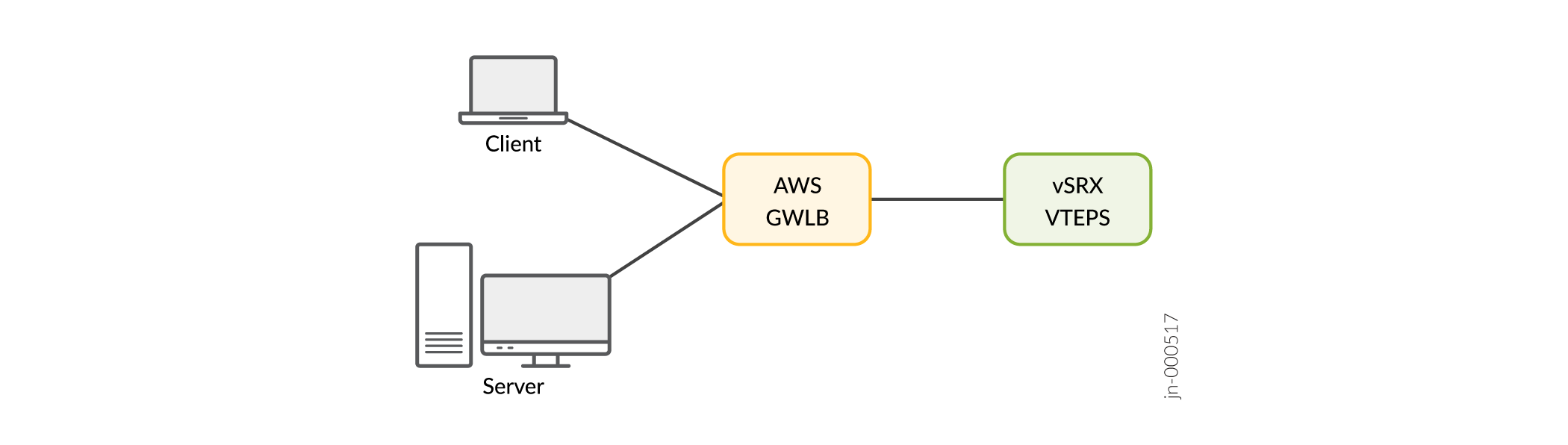
For example, you can deploy vSRX Virtual Firewall 3.0 with the AWS Gateway Load Balancer (GWLB) service that uses the Geneve protocol encapsulation for transparent load balancing and packet routing.
-
Encapsulate and de-encapsulate the received Geneve tunnel packets.
-
Apply Layer 4 (L4) and Layer 7 (L7) services on the inner traffic.
vSRX Virtual Firewall 3.0 as a tunnel endpoint in any cloud deployment receives Geneve packets on its Layer 3 (L3) interface and forwards the packet (after inspection) to the same destination endpoint.
You must attach a policy with an inspection profile that determines the:
-
Type of Geneve traffic that vSRX Virtual Firewall 3.0 processes.
-
Policies that vSRX Virtual Firewall 3.0 applies on the inner traffic.
You can configure the regular security policy on vSRX Virtual Firewall 3.0 to apply L4 and L7 services on the inner traffic.
After receiving the L3 encapsulated traffic without any changes, vSRX Virtual Firewall 3.0:
- De-encapsulates the received Geneve tunnel packets.
- Analyzes the tunnel header.
- Performs L4 and L7 inspection against the inner IP packet.
- Encapsulates the traffic.
- Forwards the traffic to the destination tunnel endpoint.
Benefits of Geneve Flow Infrastructure Support
-
Data encapsulation—Provides a framework to support tunneling for network virtualization.
-
Multitenant Support—Provides a framework to support tunneling for network virtualization. Multitenant cloud providers such as AWS can perform transparent load balancing by using the Geneve protocol.
-
Performs transparent routing of packets—GWLB and vSRX Virtual Firewall 3.0 exchange application traffic with each other using Geneve encapsulation, which allows GWLB to preserve the content of the original traffic.
-
Health check—Vendors (for example AWS) can perform health probe over the Geneve tunnel to determine the status of virtual machines (VMs).
Enable Security Policies for Geneve Packet Flow Tunnel Inspection
Use this configuration to enable security policies on vSRX Virtual Firewall 3.0 for Geneve packet flow tunnel inspection.
With Geneve support on vSRX Virtual Firewall 3.0 instances, you can use vSRX3.0 to:
-
Connect end points in a campus, data center, and public cloud environments and their banches.
-
Secure these environments with embedded security.
- Requirements
- Overview
- Configuration (vSRX Virtual Firewall 3.0 as Tunnel Endpoint)
- Configuration (vSRX Virtual Firewall 3.0 as Transit Router)
Requirements
This example uses the following hardware and software components:
-
vSRX Virtual Firewall 3.0
-
Junos OS Release 23.1R1
Before you begin:
-
Make sure you understand how the Geneve protocol works.
Overview
Using this configuration you can:
-
Enable the security policies to process the Geneve tunnel encapsulated L3 packets.
-
Create distinct profiles for Geneve traffic based on VNI and vendor TLV attributes-Policy once attached with an inspection profile dictates the type of Geneve traffic to be processed and policies to be applied to the inner traffic.
-
Configure the regular security policy on vSRX Virtual Firewall 3.0 to apply L4 and L7 services on the inner traffic.
Configuration (vSRX Virtual Firewall 3.0 as Tunnel Endpoint)
- Simplified Geneve Traffic Flow Topology with AWS GWLB and vSRX Virtual Firewall 3.0 as Tunnel End-point
- CLI Quick Configuration
- Procedure
- Results
- Verify Tunnel Inspection Profile and VNI
- Verify Tunnel Inspection Profile and VNI
Simplified Geneve Traffic Flow Topology with AWS GWLB and vSRX Virtual Firewall 3.0 as Tunnel End-point
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the following commands, paste them into a
text file, remove any line breaks, change any details necessary to match your
network configuration, copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the
[edit] hierarchy level, and then enter
commit from configuration mode.
Define a trust and untrust zone to permit all host traffic.
set security tunnel-inspection inspection-profile ti-vendor geneve g-rule policy-set ps-vendorset security tunnel-inspection inspection-profile ti-vendor geneve g-rule vni vni-vendorset security tunnel-inspection vni vni-vendor vni-id 0set security policies from-zone vtepc to-zone junos-host policy self match application junos-geneveset security policies from-zone vtepc to-zone junos-host policy self match source-address anyset security policies from-zone vtepc to-zone junos-host policy self match destination-address anyset security policies from-zone vtepc to-zone junos-host policy self then permit tunnel-inspection ti-vendorset security policies default-policy deny-allset security policies policy-set ps-vendor policy self match source-address anyset security policies policy-set ps-vendor policy self match destination-address anyset security policies policy-set ps-vendor policy self match application anyset security policies policy-set ps-vendor policy self then permitset interfaces ge-0/0/1 mtu 9000set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address anyset interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet6 address any
Procedure
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following example requires you to navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For instructions on how to do that, see Using the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode in the Junos OS CLI User Guide.
To configure Geneve flow support for tunnel inspection on vSRX Virtual Firewall 3.0:
-
Define a trust and untrust zone to permit all host traffic under the [edit security zones] hierarchy.
-
Define the
tunnel-inspectionprofile.[edit security tunnel-inspection] user@host# set security tunnel-inspection inspection-profile ti-vendor geneve g-rule policy-set ps-vendor user@host# set security tunnel-inspection inspection-profile ti-vendor geneve g-rule vni vni-vendor user@host# set security tunnel-inspection vni vni-vendor vni-id 0
-
Define outer session policies to the outer packets and attach the referenced tunnel inspection profile
Note:In the policy configuration, the
to-zonefor the outer policy in case of vSRX Virtual Firewall 3.0 as tunnel endpoint must bejunos-host, which is an inbuilt (reserved identifier) zone to process traffic.[edit security policies] user@host# set security policies from-zone vtepc to-zone junos-host policy self match source-address any user@host# set security policies from-zone vtepc to-zone junos-host policy self match destination-address any user@host# set security policies from-zone vtepc to-zone junos-host policy self match application junos-geneve user@host# set security policies from-zone vtepc to-zone junos-host policy self then permit tunnel-inspection ti-vendor user@host# set security policies default-policy deny-all
-
Define an inner policy under
policy-setto process the decapsulated packet.[edit security policies] user@host# set security policies policy-set ps-vendor policy self match source-address any user@host# set security policies policy-set ps-vendor policy self match destination-address any user@host# set security policies policy-set ps-vendor policy self match application any user@host# set security policies policy-set ps-vendor policy self then permit
-
Configure the interface associated with
from-zoneof the virtual tunnel endpoint client (VTEPC) to receive the Geneve-encapsulated packets and the health-check packets.[edit] user@host# set interfaces ge-0/0/1 mtu 9000 user@host# set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address any user@host# set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet6 address any
Results
From the configuration mode, confirm your configuration by entering the
show security policies command. If the output does not
display the intended configuration, repeat the instructions in this example to
correct the configuration.
user@host# show security policies
from-zone trust to-zone untrust {
policy p1 {
match {
source-address any;
destination-address any;
application any;
}
then {
permit {
application-services {
application-traffic-control {
rule-set ftp-test1;
}
}
}
}
}
policy internet-access {
match {
source-address any;
destination-address any;
application any;
}
then {
permit;
}
}
}
from-zone untrust to-zone trust {
policy dst-nat-pool-access {
match {
source-address any;
destination-address 233.252.0.1/21;
application any;
}
then {
permit;
}
}
}
from-zone vtepc to-zone junos-host {
policy self {
match {
source-address any;
destination-address any;
application junos-geneve;
}
then {
permit {
tunnel-inspection {
ti-vendor;
}
}
}
}
}
policy-set ps-vendor {
policy self {
match {
source-address any;
destination-address any;
application any;
}
then {
permit;
}
}
}
default-policy {
deny-all;
}user@host# show security tunnel-inspection
inspection-profile ti-vendor {
geneve g-rule {
policy-set ps-vendor;
vni vni-vendor;
}
}
vni v1 {
vni-id 0;
}
vni vni-vendor {
vni-id 0;
}After you complete configuring the feature on your device, enter
commit from the configuration mode.
Verify Tunnel Inspection Profile and VNI
Purpose
Verify that you have configured the tunnel-inspection
profile and the VXLAN network identifier (VNI).
Action
From operational mode, enter the show security tunnel-inspection
profiles ti-vendor and show security tunnel-inspection
vnis commands.
user@host> show security tunnel-inspection profiles ti-vendor
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
Logical system: root-logical-system
Profile count: 1
Profile: ti-vendor
Type: Geneve
geneve count: 1
geneve name: g-rule
VNI count: 1
VNI: vni-vendor
Policy set: ps-vendor
Inspection level: 1user@host> show security tunnel-inspection vnis
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
Logical system: root-logical-system
VNI count: 1
VNI name: vni-vendor
VNI id count: 0Meaning
The output displays that the Geneve tunnel-inspection profile is enabled and the VXLAN network identifier (VNI) is configured.
Verify Tunnel Inspection Profile and VNI
Purpose
Verify that you have configured the tunnel-inspection
profile and the VXLAN network identifier (VNI).
Action
From operational mode, enter the show security tunnel-inspection
profiles ti-vendor and show security tunnel-inspection
vnis commands.
user@host> show security tunnel-inspection profiles ti-vendor
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
Logical system: root-logical-system
Profile count: 1
Profile: ti-vendor
Type: Geneve
geneve count: 1
geneve name: g-rule
VNI count: 1
VNI: vni-vendor
Policy set: ps-vendor
Inspection level: 1user@host> show security tunnel-inspection vnis
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
Logical system: root-logical-system
VNI count: 1
VNI name: vni-vendor
VNI id count: 0Meaning
The output displays that the Geneve tunnel-inspection profile is enabled and the VXLAN network identifier (VNI) is configured.
Configuration (vSRX Virtual Firewall 3.0 as Transit Router)
- Simplified Geneve Traffic Flow Topology vSRX Virtual Firewall 3.0 as Transit Router
- CLI Quick Configuration
- Procedure
- Results
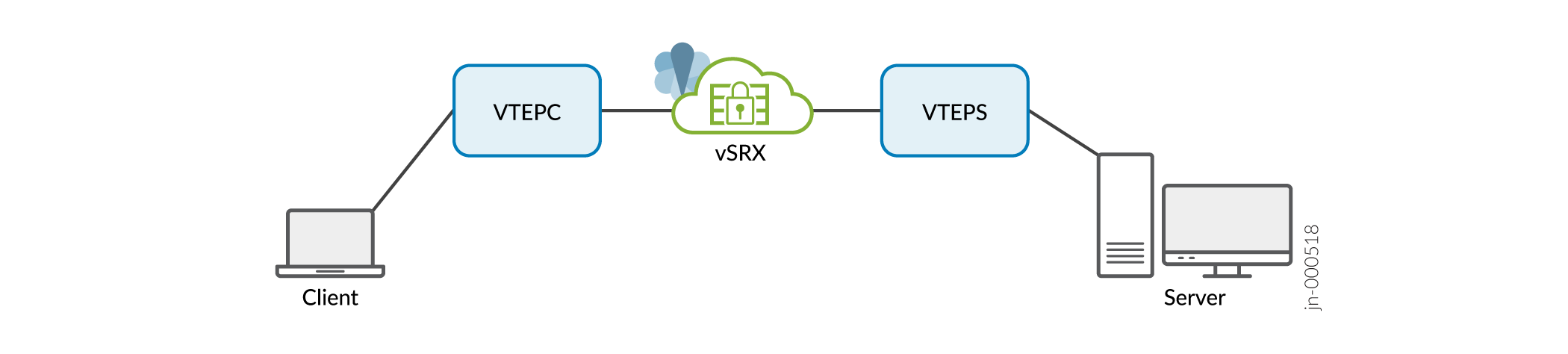
Simplified Geneve Traffic Flow Topology vSRX Virtual Firewall 3.0 as Transit Router
In this deployment mode the virtual tunnel endpoint client (vtepc) (Geneve tunnel endpoint) must ensure that packets destined to both the client and the server pass through virtual tunnel endpoint server (vteps) (vSRX Virtual Firewall 3.0). The source port is selected by the virtual tunnel endpoint (vtep).
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the following commands, paste them into a
text file, remove any line breaks, change any details necessary to match your
network configuration, copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the
[edit] hierarchy level, and then enter
commit from configuration mode.
set security tunnel-inspection vni r1 vni-range 1 to 100set security tunnel-inspection vni r1 vni-id 500set security tunnel-inspection profile inspection-profile ti-vendor geneve geneve1 vni r1set security tunnel-inspection profile inspection-profile ti-vendor geneve geneve1 policy-set pset1set security tunnel-inspection vni r2 vni-range 200 to 400set security tunnel-inspection vni r2 vni-id 500set security tunnel-inspection profile inspection-profile ti-vendor geneve geneve2 vni r2set security tunnel-inspection profile inspection-profile ti-vendor geneve geneve2 policy-set pset2set security policies from-zone vtepc to-zone vteps policy p1 match application junos-geneveset security policies from-zone vtepc to-zone vteps policy p1 match source-address anyset security policies from-zone vtepc to-zone vteps policy p1 match destination-address anyset security policies from-zone vtepc to-zone vteps policy p1 then permit tunnel-inspection ti-vendorset security policies from-zone vteps to-zone vtepc policy p1 match application junos-geneveset security policies from-zone vteps to-zone vtepc policy p1 match source-address anyset security policies from-zone vteps to-zone vtepc policy p1 match destination-address anyset security policies from-zone vteps to-zone vtepc policy p1 then permit tunnel-inspection ti-vendorset security policies default-policy deny-allset security policies policy-set pset1 policy pset_p1 match source-address anyset security policies policy-set pset1 policy pset_p1 match destination-address anyset security policies policy-set pset1 policy pset_p1 match application anyset security policies policy-set pset1 policy pset_p1 then permitset interfaces ge-0/0/1 mtu 9000set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address anyset interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet6 address any
Procedure
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following example requires you to navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For instructions on how to do that, see Using the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode in the Junos OS CLI User Guide.
To configure Geneve flow support for tunnel inspection on vSRX Virtual Firewall 3.0 (vSRX Virtual Firewall 3.0 as transit router) :
-
Define a trust and untrust zone to permit all host traffic under the [edit security zones] hierarchy.
-
Define the
tunnel-inspectionprofile.[edit security tunnel-inspection] user@host# set security tunnel-inspection vni r1 vni-range 1 to 100 user@host# set security tunnel-inspection vni r1 vni-id 500 user@host# set security tunnel-inspection profile inspection-profile ti-vendor geneve geneve1 vni r1 user@host# set security tunnel-inspection profile inspection-profile ti-vendor geneve geneve1 policy-set pset1 user@host# set security tunnel-inspection vni r2 vni-range 200 to 400 user@host# set security tunnel-inspection vni r2 vni-id 500 user@host# set security tunnel-inspection profile inspection-profile ti-vendor geneve geneve2 vni r2 user@host# set security tunnel-inspection profile inspection-profile ti-vendor geneve geneve2 policy-set pset2
-
Define outer session policies.
Note:For vSRX Virtual Firewall 3.0 as transit router, you need two policies in each direction. The
from-zoneandto-zoneare the respective zones that must be defined under the interfaces.[edit security policies] user@host# set security policies from-zone vtepc to-zone vteps policy p1 match source-address any user@host# set security policies from-zone vtepc to-zone vteps policy p1 match destination-address any user@host# set security policies from-zone vtepc to-zone vteps policy p1 match application junos-geneve user@host# set security policies from-zone vtepc to-zone vteps policy p1 then permit tunnel-inspection ti-vendor user@host# set security policies from-zone vteps to-zone vtepc policy p1 match application junos-geneve user@host# set security policies from-zone vteps to-zone vtepc policy p1 match source-address any user@host# set security policies from-zone vteps to-zone vtepc policy p1 match destination-address any user@host# set security policies from-zone vteps to-zone vtepc policy p1 then permit tunnel-inspection ti-vendor user@host#set security policies default-policy deny-all
-
Define an inner policy under
policy-setto process the decapsulated packet.[edit security policies] user@host# set security policies policy-set pset1 policy pset_p1 match source-address any user@host# set security policies policy-set pset1 policy pset_p1 match destination-address any user@host# set security policies policy-set pset1 policy pset_p1 match application any user@host# set security policies policy-set pset1 policy pset_p1 then permit
-
Configure the interface associated with
from-zoneof the virtual tunnel endpoint client (VTEPC) to receive the Geneve-encapsulated packets and the health-check packets.Note:In case of transit mode, vSRX Virtual Firewall 3.0 must be configured with two L3 interfaces for ingress and egress.
[edit] user@host# set interfaces ge-0/0/1 mtu 9000 user@host# set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address any user@host# set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet6 address any
Results
From the configuration mode, confirm your configuration by entering the
show security policies command. If the output does not
display the intended configuration, repeat the instructions in this example to
correct the configuration.
user@host# show security policies
from-zone trust to-zone untrust {
policy p1 {
match {
source-address any;
destination-address any;
application any;
}
then {
permit {
application-services {
application-traffic-control {
rule-set ftp-test1;
}
}
}
}
}
}
from-zone vtepc to-zone vteps {
policy p1 {
match {
source-address any;
destination-address any;
application junos-geneve;
}
then {
permit {
tunnel-inspection {
ti-vendor;
}
}
}
}
}
from-zone vteps to-zone vtepc {
policy p1 {
match {
source-address any;
destination-address any;
application junos-geneve;
}
then {
permit {
tunnel-inspection {
ti-vendor;
}
}
}
}
}
policy-set pset1 {
policy pset_p1 {
match {
source-address any;
destination-address any;
application any;
}
then {
permit;
}
}
}
default-policy {
deny-all;
}}user@host# show security tunnel-inspection
inspection-profile ti-vendor {
geneve g-rule {
policy-set ps-vendor;
vni vni-vendor;
}
}
inspection-profile pro1;
vni r1 {
vni-id 500;
}
vni r2 {
vni-id 500;
}
}After you complete configuring the feature on your device, enter
commit from the configuration mode.
